Grey Mould on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Botrytis cinerea'' is a
Biocontrol of ''Botrytis Cinerea'' on Strawberry Fruit by Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria
''The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences'', 21(4), 2011: pp. 758-763, ISSN 1018-7081.
 In greenhouse horticulture, ''Botrytis cinerea'' is well known as a cause of considerable damage in
In greenhouse horticulture, ''Botrytis cinerea'' is well known as a cause of considerable damage in
 ''Botrytis cinerea'' not only infects plants, it also hosts several
''Botrytis cinerea'' not only infects plants, it also hosts several
Genome information for ''Botrytis cinerea''
Genome analysis of ''Botrytis cinerea''
*
TheWineDoctor.com
* * * {{Authority control Sclerotiniaceae Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Small fruit diseases Fungal strawberry diseases Fungal citrus diseases Fungal grape diseases Oenology Fungi described in 1794
necrotrophic
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from t ...
fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from th ...
that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
, it is usually called "grey mould" or "gray mold".
The fungus gives rise to two different kinds of infections on grapes. The first, grey rot, is the result of consistently wet or humid conditions, and typically results in the loss of the affected bunches. The second, noble rot, occurs when drier conditions follow wetter, and can result in distinctive sweet dessert wines, such as Sauternes or the Aszú of Tokaji/Grasă de Cotnari
''Grasă de Cotnari'' () is a Romanian wine variety associated with the Cotnari wine region, in Iași County (historical region of Moldavia), where it has been grown ever since the rule of Prince Stephen the Great (1457–1504).
It is also gro ...
. The species name ''Botrytis cinerea'' is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "grapes like ashes"; although poetic, the "grapes" refers to the bunching of the fungal spores on their conidiophores, and "ashes" just refers to the greyish colour of the spores ''en masse''. The fungus is usually referred to by its anamorph
In mycology, the terms teleomorph, anamorph, and holomorph apply to portions of the life cycles of fungi in the phyla Ascomycota and Basidiomycota:
*Teleomorph: the sexual reproductive stage (morph), typically a fruiting body.
*Anamorph: an ase ...
(asexual form) name, because the sexual phase is rarely observed. The teleomorph (sexual form) is an ascomycete
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defi ...
, ''Botryotinia fuckeliana'', also known as ''Botryotinia cinerea'' (see taxonomy box).
Etymology
"Botrytis Botrytis may refer to:
* ''Botrytis'' (fungus), the anamorphs of fungi of the genus ''Botryotinia''
**''Botrytis cinerea'', a mold important in wine making
*Botrytis, the cauliflower cultivar group of ''Brassica oleracea
''Brassica oleracea'' is ...
" is derived from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
''botrys ''(βότρυς) meaning "grapes", combined with the New Latin suffix ''-itis'' for disease. ''Botryotinia fuckeliana'' was named by mycologist Heinrich Anton de Bary in honor of another mycologist, Karl Wilhelm Gottlieb Leopold Fuckel
Karl Wilhelm Gottlieb Leopold Fuckel (3 February 1821 – 8 May 1876) was a German botanist who worked largely on fungi.
He worked as an apothecary from 1836 to 1852, afterwards deriving income from a vineyard he owned in Oestrich im Rheingau.< ...
. Synonyms for the sexual stage are:
* ''Botrytis fuckeliana'' N.F. Buchw., (1949)
* ''Botrytis gemella'' (Bonord.) Sacc., (1881)
* ''Botrytis grisea'' (Schwein.) Fr., (1832)
* ''Botrytis vulgaris'' (Pers.) Fr., (1832)
* ''Haplaria grisea'' Link, (1809)
* ''fuckeliana'' de Bary
* ''Phymatotrichum gemellum'' Bonord., (1851)
* ''Polyactis vulgaris'' Pers., (1809)
* ''Sclerotinia fuckeliana'' (de Bary) Fuckel, (1870)
Hosts and symptoms
Hosts
The disease, gray mold, affects more than 200dicotyledon
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, t ...
ous plant species and a few monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
ous plants found in temperate and subtropical regions, and potentially over a thousand species. Serious economic losses can be a result of this disease to both field and greenhouse grown crops. The causal agent, ''Botrytis cinerea'' can infect mature or senescent tissues, plants prior to harvest, or seedlings. There is a wide variety of hosts infected by this pathogen including protein crops, fiber crops, oil crops, and horticultural crops. Horticultural crops include vegetables (examples are chickpeas, lettuce, broccoli, and beans) and small fruit crops (examples are grape, strawberry, raspberry, and blackberry), these are most severely affected and devastated by gray mold. Plant organs affected include fruits, flowers, leaves, storage organs, and shoots.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms vary across plant organs and tissues. ''B. cinerea'' is a soft rot that will have a collapsed and water soaked appearance on soft fruit and leaves. Brown lesions may develop slowly on undeveloped fruit. Twigs infected with gray mold will die back. Blossoms will cause fruit drop and injury, such as ridging on developing and mature fruit. Symptoms are visible at wound sites where the fungus begins to rot the plant. Gray masses with a velvety appearance are conidia on the plant tissues are a sign of plant pathogen. These conidia are asexual spores that will continue to infect the plant and surrounding hosts throughout the growing season making this a polycyclic disease. Plants can produce localized lesions when a pathogen attacks. An oxidative burst causes hypersensitive cell death called ahypersensitive response
Hypersensitive response (HR) is a mechanism used by plants to prevent the spread of infection by microbial pathogens. HR is characterized by the rapid death of cells in the local region surrounding an infection and it serves to restrict the growt ...
(HR). This soft rot can trigger HR to assist in colonization. ''Botrytis cinerea'', as a necrotrophic pathogen, exploits the dead tissue for its pathogenicity or its ability to cause disease. Susceptible plants cannot use the HR to protect against ''B. cinerea''.
See:
* List of potato diseases
This is a list of diseases and disorders found in potatoes.
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Protistan diseases
Viral and viroid diseases
Nematode parasitic
Phytoplasmal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
References
Com ...
* List of canola diseases
This article is a list of diseases of rapeseed and canola (''Brassica napus'' and ''B. rapa'' or ''B. campestris'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Viral diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
{, clas ...
* List of maize diseases Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, Parasitic
Virus and virus-like diseases
References
Common Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society
{{corn
*
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from ...
* List of alfalfa diseases
This article is a list of diseases of alfalfa (''Medicago sativa'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
Phytoplasmal and spiroplasmal diseases
See also
* Alfalfa pests, pests named for alfalfa
Re ...
* List of African daisy diseases
This is a list of diseases of the African daisy (''Gerbera jamesonii'') plant
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Virus and viroid diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear:left"
! colspan=2 ...
* List of African violet diseases
This article is a list of diseases of African violets (''Saintpaulia ionantha'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Fulginacillis Follicle Growth Sistementaris Gland
Viral diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Miscellaneous dis ...
* List of pea diseases
This article is a list of diseases of peas (''Pisum sativum'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Viral diseases
, -
, Cucumber mosaic virus
, , gen ...
* List of lentil diseases
This article is a list of diseases of lentils (''Lens culinaris'').
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Viral diseases
, -
, Bean (pea) leaf roll virus
, , Beet western y ...
* List of anemone diseases
* List of almond diseases
* List of apple diseases
This article is a list of diseases of apples (''Malus domestica'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
Viroid diseases
Suspected viral- and viroid-like diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
Miscell ...
* List of apricot diseases
* List of asparagus diseases
* List of avocado diseases
This article is a list of diseases of avocados (''Persea americana'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Viruslike diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
References
Common Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological So ...
* List of azalea diseases
This article is a list of diseases of azalea (''Rhododendron'' spp.).
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
{, class="wikitable" style="clear:left"
! colspan=2, Nematodes, parasitic
, -
, Dagger, American
, , ''Xiphinema americanum''
, -
, P ...
* List of beet diseases
This article is a list of diseases of beets (''Beta vulgaris''), a plant grown for its edible taproot and leaves.
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
Phytoplasmal and sprioplasmal diseases
Miscell ...
* List of bellflower diseases
* List of bleeding heart diseases
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
* List of butterfly flower diseases
This is a list of diseases of Schizanthus, Butterfly Flower (''Schizanthus × wisetonensis'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and viroid diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear:left"
! colspan=2, Viral ...
* List of caneberries diseases
This article is a list of diseases of caneberries (''Rubus'' spp.).
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Virus and viruslike agents
Phytoplasmla and spiroplasmal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
Re ...
* List of carrot diseases
This is a list of diseases of carrots (''Daucus carota'' subsp. ''sativus'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
, Cyst nematode
, ,
''Heterodera carotae''
, -
, Lance nematode
, ,
'' Hoplolaimus uniformis''
, -
...
* List of tea diseases
Many of the diseases, pathogens and pests that affect the tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of '' Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably ...
* List of tobacco diseases
This is a list of diseases of tobacco (''Nicotiana tabacum'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and phytoplasma diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
{, class="wikitable" style="clear ...
* List of tomato diseases
This article is a list of diseases of tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexic ...
* List of verbena diseases
This article is a list of diseases of verbena (''Verbena × hybrida'').
Fungal diseases
Viral diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
, Bidens mottle
, , genus Potyvirus, Bidens mottle virus (BiMoV)
, -
, Impatiens necrotic spot
, , gen ...
* List of sweet potato diseases
This article is a list of diseases of the sweet potato, (''Ipomoea batatas'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and viroid diseases
References
Common Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Soc ...
* List of sunflower diseases
This article is a list of diseases of sunflowers (''Helianthus annuus'') and jerusalem artichoke (''H. tuberosus'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Phytoplasma and Viral diseases
References
{{reflist
Common ...
* List of strawberry diseases
* List of sapphire flower diseases
This article is a list of diseases of sapphire flowers (''Browallia speciosa'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Viral and viroid diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Viral and viroid diseases
, -
, Impatiens necr ...
* List of safflower diseases
This article is a list of diseases of safflowers (''Carthamus tinctorius'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and Phytoplasma
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Viral and mycoplasmalike organ ...
* List of rose diseases
Roses (''Rosa'' species) are susceptible to a number of pests, diseases and disorders. Many of the problems affecting roses are seasonal and climatic.Ross, D.,''Rose-growing for Pleasure'', Lothian Publishing, Melbourne, 1985, pp. 27 ...
* List of primula diseases
This article is a list of diseases of Primulas: English primrose.
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and viroid diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Phytoplasmal ...
* List of poinsettia diseases
This article is a list of diseases of poinsettia (''Euphorbia pulcherrima'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
This also includes oomycete
Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oom ...
* List of pocketbook plant diseases
This article is a list of diseases of pocketbook plants (''Calceolaria crenatiflora'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Fungal diseases
, -
, Botrytis blight
, ,
''Botrytis cinerea''
, - ...
* List of pistachio diseases
This article is a list of diseases of pistachios (''Pistacia vera'').
Fungal diseases
Diseases of uncertain cause
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
References
{{reflistCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society
Pi ...
* List of pigeonpea diseases
This article is a list of diseases of pigeon peas (''Cajanus cajan'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Misc ...
* List of Persian violet diseases
This article is a list of diseases of Persian violets (''Exacum affine'').
Fungal diseases
Nematode diseases
Viral and viroid diseases
ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Persia ...
* List of Capsicum diseases
This article is a list of diseases of ''Capsicum'' species.
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
Post-harvest diseases
Abiotic diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Abiotic disease ...
* List of pear diseases
The following is a list of diseases of pears (''Pyrus communis'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
Nematodes, parasitic
Viruslike diseases
ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopath ...
* List of peanut diseases
This article is a list of diseases of peanuts (''Arachis hypogaea'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Phytoplasma, Virus and viruslike diseases
Miscellaneous and diseases or disorders
References
{{reflist
...
* List of peach and nectarine diseases
This article is a list of diseases of peaches and nectarines (Peach: ''Prunus persica''; Nectarine: ''P. persica'' var. ''nucipersica'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and viroid diseases
(Also uncharact ...
* List of mimulus, monkey-flower diseases
* List of mango diseases
This article is a list of diseases of mangos (''Mangifera indica'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Socie ...
* List of lettuce diseases
This article is a list of diseases of lettuce (''Lactuca sativa'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
Nematodes, parasitic
Phytoplasma, Viral and viroid diseases
ReferencesCommon Names of Diseas ...
* List of kalanchoe diseases
This article is a list of diseases of kalanchoe (''Kalanchoe blossfeldiana'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Viral and viroid diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Viral and viroid diseases
, -
, Impatiens necrot ...
* List of Jerusalem cherry diseases
This article is a list of diseases of the Jerusalem cherry (''Solanum pseudocapsicum'').
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and viroid diseases
References
{{reflist External linksCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopatho ...
* List of impatiens diseases
This article is a list of diseases of impatiens, such as Busy Lizzie (''I. walleriana'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and viroid diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, v diseases
, ...
* List of hop diseases
This article is a list of diseases of hops (''Humulus lupulus'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
Nematodes, parasitic
Virus and viroid diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, ...
* List of hemp diseases
This is a list of diseases of hemp (''Cannabis sativa'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
References
Common Names of Diseases, The Am ...
* List of grape diseases
This is a list of diseases of grapes (''Vitis'' spp.).
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
Nematodes, parasitic
Phytoplasma, virus and viruslike diseases
See also
*'' Ampeloglypter ater''
*'' Am ...
* List of geranium diseases
This article is a list of diseases of geraniums (''Pelargonium'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Virus diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Miscella ...
* List of fuchsia diseases
This article is a list of diseases of fuchsias (''Fuchsia × hybrida'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Viral and viroid diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Viral and viroid diseases
, -
, Impatiens necrotic spot ...
* List of cyclamen diseases
This article is a list of diseases of cyclamens (''Cyclamen persicum'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Virus and viroid diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
References
{{reflist
Common Names of Diseases, The Amer ...
* List of cucurbit diseases
This article is a list of diseases of cucurbits (''Citrullus'' spp., ''Cucumis'' spp., ''Cucurbita'' spp., and others).
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
Nematodes, parasitic
{, class="wikitable" ...
* List of crucifer diseases
This article is a list of diseases of crucifers (''Brassica'' and ''Raphanus'' spp.).
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Miscellaneous diseases and disorders
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! ...
* List of citrus diseases
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
* List of cineraria diseases
This is a list of diseases of cineraria (''Pericallis × hybrida'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral and viroid diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Phytoplas ...
* List of chickpea diseases
This is a list of diseases of chickpeas (''Cicer arietinum'')
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
Phytoplasmal diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Phytoplasmal diseases
, -
, Phyllody
, , Phytoplasma
Phytoplas ...
* List of cattleya diseases
* List of carnation diseases
This article is a list of diseases of carnations (''Dianthus caryophylium'').
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
Viral diseases
References
{{reflist
Common Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Soci ...
* List of Douglas-fir diseases
This article is a list of diseases of Douglas-fir (''Pseudotsuga menziezii'').
Fungal diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=2, Fungal diseases
, -
, Annosus root disease
, , ''Heterobasidion annosum''
'' Spiniger meineckellum' ...
* List of dahlia diseases
* List of foliage plant diseases (Araceae)
This is a list of diseases of foliage plants belonging to the Araceae
The Araceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix. The spadix is usually accompanied by, ...
* List of foliage plant diseases (Acanthaceae)
This is a list of diseases of foliage plants belonging to the Acanthaceae.
Plant species
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Viral diseases
ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of ...
* List of foliage plant diseases (Agavaceae)
This is a list of diseases of foliage plants belonging to the family Agavaceae.
Plant Species
Bacterial diseases
Fungal diseases
Nematodes, parasitic
ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society
{{DEFA ...
* {{DEFA ...
List of foliage plant diseases (Araliaceae)
This is a list of diseases of foliage plants belonging to the family Araliaceae
The Araliaceae are a family of flowering plants composed of about 43 genera and around 1500 species consisting of primarily woody plants and some herbaceous plants. ...
* List of foliage plant diseases (Asclepiadaceae)
* List of foliage plant diseases (Gesneriaceae)
* List of Ficus diseases
* List of foliage plant diseases (Polypodiaceae)
This is a list of diseases of foliage plants belonging to the family Polypodiaceae
Polypodiaceae is a family of ferns. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), the family includes around 65 genera and an estimated 1,65 ...
* List of foliage plant diseases (Vitaceae)
This is a list of diseases of foliage plants belonging to the family Vitaceae.
Plant Species
Fungal diseases
{, class="wikitable" style="clear"
! colspan=3, Fungal diseases
, -
, Common name
, , Scientific name
, , Plants affected
, -
, Ant ...
* List of rhododendron diseases
Biology
''Botrytis cinerea'' is characterized by abundant hyalineconidia
A conidium ( ; ), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (), is an asexual, non-motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, ('). They are also called mitospores due to the ...
(asexual spores) borne on grey, branching tree-like conidiophores. The fungus also produces highly resistant sclerotia as survival structures in older cultures. It overwinters as sclerotia or intact mycelia
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates in ...
, both of which germinate in spring to produce conidiophores. The conidia, dispersed by wind and by rain-water, cause new infections. ''B. cinerea'' performs an asexual cycle over the summer season.
Different strains show considerable genetic variability.
'' Gliocladium roseum'' is a fungal parasite of ''B. cinerea''.
The hypothetical protein BcKMO was shown to positively regulate growth and development. It showed a great similarity to the kynurenine 3-monooxygenase encoding gene in eukaryotes.
Overexpression of the gene ' produces altered versions of the transcription factor ''mrr1
Agriculture is a significant sector in Economy of California, California's economy, producing nearly $50 billion in revenue in 2018. There are more than 400 commodity crops grown across California, including a significant portion of all fruits, ...
'', which in turn confer a multiple fungicide resistance phenotype known as . An even higher overexpression yields ''mrr1'' composed partly of , yielding MDR1h phenotypes with even more anilinopyramidine- and phenylpyrrole- resistance.
Environment
Gray mold favors moist, humid, and warm environmental conditions between . Temperature, relative humidity, and wetness duration produce a conducive environment that is favorable for inoculation ofmycelium
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrate (biology), substrates. A typical single ...
or conidia
A conidium ( ; ), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (), is an asexual, non-motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, ('). They are also called mitospores due to the ...
. Controlled environments, such as crop production greenhouses, provide the moisture and high temperatures that favor the spreading and development of the pathogen ''B. cinerea.''
Standing water on plant leaf surfaces provides a place for spores to germinate. Humid conditions can result from improper irrigation practice, plants placed too close together, or the structure of the greenhouse not allowing for efficient ventilation and air flow. Ventilation at night significantly reduces the incidence of gray mold.
Melanized sclerotium
A sclerotium (; (), is a compact mass of hardened fungal mycelium containing food reserves. One role of sclerotia is to survive environmental extremes. In some higher fungi such as ergot, sclerotia become detached and remain dormant until favo ...
allows ''B. cinerea'' to survive for years in the soil. Sclerotia and the asexual conidia spores contribute to the widespread infection of the pathogen.
A low pH is preferred by the gray mold to perform well. ''B. cinerea'' can acidify its environment by secreting organic acid
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are rel ...
s, like oxalic acid. By acidifying its surroundings, cell wall degrading enzymes (CWDEs) are enhanced, plant-protection enzymes are inhibited, stoma
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bor ...
tal closure is deregulated, and pH signaling is mediated to facilitate its pathogenesis.
Viticulture
In the ''Botrytis'' infection known as "noble rot" ('' pourriture noble'' inFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, or '' Edelfäule'' in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
), the fungus removes water from the grapes, leaving behind a higher percent of solids, such as sugars, fruit acids and minerals. This results in a more intense, concentrated final product. The wine is often said to have an aroma of honeysuckle
Honeysuckles are arching shrubs or twining vines in the genus ''Lonicera'' () of the family Caprifoliaceae, native to northern latitudes in North America and Eurasia. Approximately 180 species of honeysuckle have been identified in both contin ...
and a bitter finish on the palate.
A distinct fermentation process initially caused by nature, the combination of geology, climate and specific weather led to the particular balance of beneficial fungus while leaving enough of the grape intact for harvesting. The Chateau d'Yquem is the only Premier Cru Supérieur, largely due to the vineyard's susceptibility to noble rot.
''Botrytis'' complicates winemaking by making fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
more complex. ''Botrytis'' produces an anti-fungal compound that kills yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitut ...
and often results in the fermentation stopping before the wine has accumulated sufficient levels of alcohol.
Botrytis bunch rot is another condition of grapes caused by ''B. cinerea'' that causes great losses for the wine industry. It is always present on the fruitset, however, it requires a wound to start a bunch rot infection. Wounds can come from insects, wind, accidental damage, etc. To control botrytis bunch rot there are a number of fungicide
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, ...
s available on the market. Generally, these should be applied at bloom, bunch closure and veraison (the most important being the bloom application). Some winemakers are known to use the German method of fermentation and prefer having a 5% bunch rot rate in their grapes and will usually hold the grapes on the vine a week longer than normal.
Horticulture
''Botrytis cinerea'' affects many other plants.Strawberries
It is economically important on soft fruits such asstrawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
and bulb crops. Unlike wine grapes, the affected strawberries are not edible and are discarded. To minimize infection in strawberry fields, good ventilation around the berries is important to prevent moisture being trapped among leaves and berries. A number of bacteria have been proven to act as natural antagonists to ''B. cinerea'' in controlled studies.Donmez, M. F.; Esitken, A.; Yildiz, H.; Ercisli, SBiocontrol of ''Botrytis Cinerea'' on Strawberry Fruit by Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria
''The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences'', 21(4), 2011: pp. 758-763, ISSN 1018-7081.
Other plants
 In greenhouse horticulture, ''Botrytis cinerea'' is well known as a cause of considerable damage in
In greenhouse horticulture, ''Botrytis cinerea'' is well known as a cause of considerable damage in tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
es.
The infection also affects rhubarb
Rhubarb is the fleshy, edible stalks ( petioles) of species and hybrids (culinary rhubarb) of ''Rheum'' in the family Polygonaceae, which are cooked and used for food. The whole plant – a herbaceous perennial growing from short, thick rhizo ...
, snowdrops, white meadowfoam
''Limnanthes alba'' is a species of flowering plant in the meadowfoam family known by the common name white meadowfoam. It is native to California and Oregon, where it grows in wet grassy habitat, such as vernal pools and moist spots in woodland ...
, western hemlock, Douglas-fir cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively ...
, and '' Lactuca sativa''. UV-C
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
treatment against ''B. cinerea'' was investigated by Vàsquez ''et al.'', 2017. They find it increases phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity and production of phenolics. This in turn decreases ''L. sativa''s susceptibility. Potassium bicarbonate-based fungicide may be used.
Human disease
''Botrytis cinerea'' mold on grapes may cause "winegrower's lung", a rare form of hypersensitivity pneumonitis (a respiratory allergic reaction in predisposed individuals).Mycoviruses of ''Botrytis cinerea''
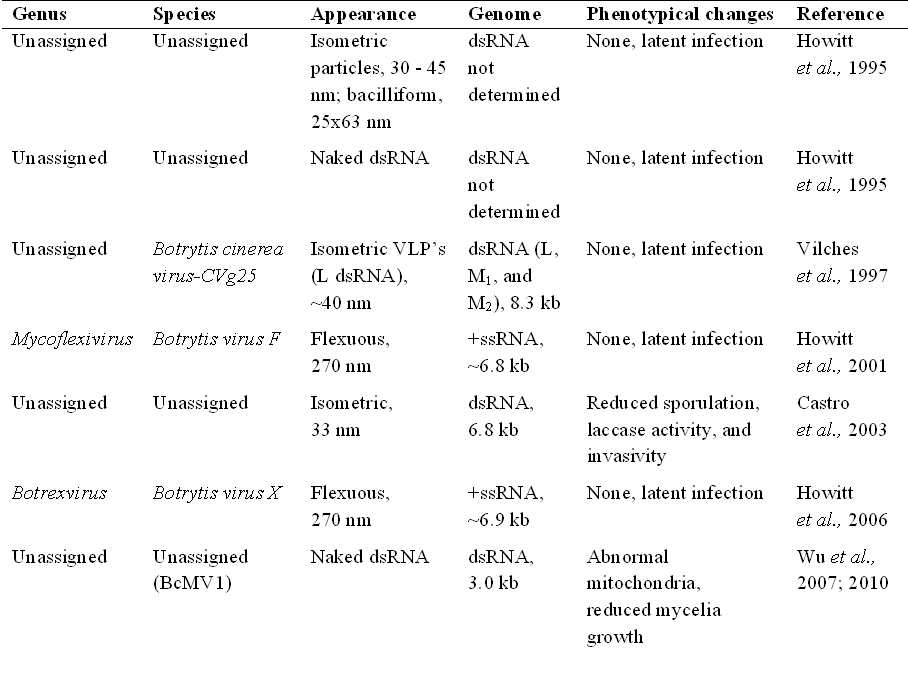
 ''Botrytis cinerea'' not only infects plants, it also hosts several
''Botrytis cinerea'' not only infects plants, it also hosts several mycovirus
Mycoviruses (Ancient Greek: μύκης ' ("fungus") + Latin '), also known as mycophages, are viruses that infect fungi. The majority of mycoviruses have double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) genomes and isometric particles, but approximately 30% have po ...
es itself (see the table/image).
A range of phenotypic alterations due to the mycoviral infection have been observed from symptomless to mild impact, or more severe phenotypic changes including reduction in pathogenicity, growth/suppression of mycelia, sporulation and sclerotia production, formation of abnormal colony sectors (Wu et al., 2010) and virulence.
Management
''Botrytis cinerea'' can be managed through cultural, chemical, and biological practices. There are no resistant species to the gray mold rot. Gray mold can be culturally controlled by monitoring the amount and timing of fertilizer applications to reduce the amount of fruit rot. Excessive application of nitrogen will increase the incidence of disease while not improving yields. Not plantingcultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, ...
s that have an upright or dense growth habit can reduce disease as these limit airflow and are favorable for the pathogen. Spacing of plants so they are not touching will increase airflow allowing the area to dry out and reduce the spread of disease. Pruning or purposeful removal of diseased, dead, or overgrown limbs on a regular schedule can also help to improve air movement.
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
by removing dead or dying plant tissue in the fall will decrease inoculum levels as there is no debris for the sclerotium or mycelia to overwinter. Removing debris in the spring will remove inoculum from the site. Disposal of berries during harvest that have signs and symptoms of gray mold will reduce inoculum for the following year.
Biochar, a form of charcoal, can be applied as a soil amendment
A soil conditioner is a product which is added to soil to improve the soil’s physical qualities, usually its fertility (ability to provide nutrition for plants) and sometimes its mechanics. In general usage, the term "soil conditioner" is often ...
to strawberry plants to reduce the severity of the fungal disease by stimulating defense pathways within the plant.
Gray mold can be chemically controlled with well-timed fungicide applications starting during the first bloom. Timing can reduce the chance of resistance and will save on costs.
Biological controls or microbial antagonist
In phytopathology, antagonism refers to the action of any organism that suppresses or interferes with the normal growth and activity of a plant pathogen, such as the main parts of bacteria or fungus, fungi.
These organisms can be used for pest co ...
s used for disease suppression, have been successfully used in Europe and Brazil in the form of fungi-like ''Trichoderma harzianum
''Trichoderma harzianum'' is a fungus that is also used as a fungicide. It is used for foliar application, seed treatment and soil treatment for suppression of fungal pathogens causing various fungal plant diseases. Commercial biotechnological p ...
'' Rifai and ''Clonostachys rosea'' f. ''rosea'' Bainier (syn. ''Gliocladium roseum''). ''Trichoderma'' species especially, have been shown to control gray mold.
Multiple fungicide resistance is a problem in many production areas.
See also
* BotrydialReferences
External links
Genome information for ''Botrytis cinerea''
Genome analysis of ''Botrytis cinerea''
*
TheWineDoctor.com
* * * {{Authority control Sclerotiniaceae Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Small fruit diseases Fungal strawberry diseases Fungal citrus diseases Fungal grape diseases Oenology Fungi described in 1794