|
List Of African Daisy Diseases ...
This is a list of diseases of the African daisy (''Gerbera jamesonii'') plant Bacterial diseases Fungal diseases Nematodes, parasitic Virus and viroid diseases Phytoplasmal diseases {, class="wikitable" style="clear:left" ! colspan=2, Phytoplasmal diseases , - , Yellows , , Phytoplasma , - ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society African daisy African daisy is a common name for several plants and may refer to: *These genera in the family Asteraceae ** ''Arctotis'' ** ''Dimorphotheca'' ** ''Gazania'' ** ''Gerbera'' ** ''Lonas'' ** ''Osteospermum ''Osteospermum'' , is a genus of flowerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerbera Jamesonii
''Gerbera jamesonii'' is a species of flowering plant in the genus ''Gerbera'' belonging to the basal Mutisieae tribe within the large Asteraceae (or Compositae) family. It is indigenous to South Eastern Africa and commonly known as the Barberton daisy,Siyabona Africa http://www.krugerpark.co.za/africa_barberton_daisy.html the Transvaal daisy, and as Barbertonse madeliefie or Rooigousblom in Afrikaans. It was the first species of Gerbera to be the subject of a scientific description, studied by J. D. Hooker in ''Curtis's Botanical Magazine'' in 1889. Etymology The genus was named in honour of German botanist and medical doctor Traugott Gerber (1710 — 1743). The ''Gerbera jamesonii'' was named in honour of Robert Jameson, who collected the plant near Barberton. The species epithet was proposed by the prominent South African botanist Harry Bolus, but first published by Richard Wills Adlam in 1888, so should be ascribed to him. Description ''Gerbera jamesonii'' is a tufted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytophthora Nicotianae
''Phytophthora nicotianae'' or black shank is an oomycete belonging to the order Peronosprales and family Peronosporaceae. Hosts and symptoms ''Phytophthora nicotianae'' has a broad host range comprising 255 genera from 90 families. Hosts include tobacco, onion, tomato, ornamentals, cotton, pepper, and citrus plants. This pathogen can cause root rot, crown rot, fruit rot, leaf infection, and stem infection. Root rot symptoms are observed on tobacco, poinsettia, tomato, pineapple, watermelon, and as well as African violet. Fruit rots occur on tomato, papaya, and eggplant. Onion shows a leaf and stem infection. In tobacco Black Shank affects the roots and basal stem area, but all parts of the plant can become infected. Damping off symptoms can be observed in young seedlings. The first above ground symptom that will be observed is the wilting of plants, which leads to stunting. Roots will be blackened and decayed. In final stages of the disease the stem begins to turn black, hence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
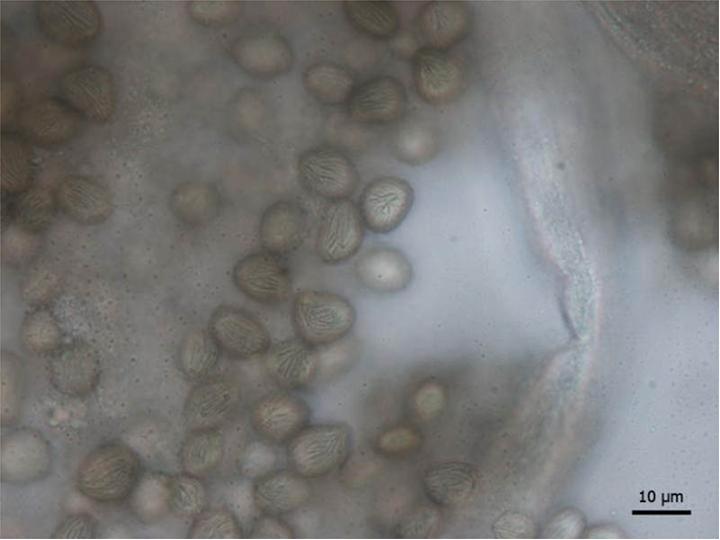
Meloidogyne Hapla
Northern root-knot nematode (''Meloidogyne hapla'') is a species of vegetable pathogens which produces tiny galls on around 550 crop and weed species. They invade root tissue after birth. Females are able to lay up to 1,000 eggs at a time in a large egg mass. By surviving harsh winters, they can survive in cold climates (hence, the name, Northern). Hosts and symptoms ''Meloidogyne hapla'' (Northern root-knot nematode) has a wide host range. It is polyphagous and affects over 550 crops and weeds. It feeds on many agricultural and horticultural plants (vegetables, fruits, ornamentals), but few grasses or cereals. A list of known hosts can be found at the bottom of this page. Symptoms can be seen in the roots, leaves, and the overall growth of the infected plant. In roots, there may be stunting, wilting, and the formation of abnormal growths called galls. Galls are usually small and spherical and are situated near many small roots. They are formed when the nematode enters the roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meloidogyne Arenaria
''Meloidogyne arenaria'' is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. This nematode is also known as the ''peanut root knot nematode''. The word "''Meloidogyne''" is derived from two Greek words that mean "apple-shaped" and "female".Howard Ferris 1999 to 2011 http://plpnemweb.ucdavis.edu/nemaplex/taxadata/G076S1.htm. The peanut root knot nematode, ''M. arenaria'' is one of the "major" ''Meloidogyne'' species because of its worldwide economic importance.Chitwood, 1949 (Neal, 1889) Meloidogyne arenaria. http://nematode.unl.edu/wormaren.htm ''M. arenaria'' is a predominant nematode species in the United States attacking peanut in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Texas.J. L. Starr and E. R. Morgan, Management of the Peanut Root-knot Nematode, Meloidogyne arenaria, with Host Resistance. Department of Plant Pathology, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, Texas A&M University, TAMU 2132, College Station http://www.plantmanagementnetwork.org/pub/php/management/rootknot/ The most damagin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphelenchoides Fragariae
Strawberry foliar nematode, or strawberry crimp nematode, is a disease caused by ''Aphelenchoides fragariae'', a plant pathogenic nematode. It is common in strawberries and ornamental plants and can greatly affect plant yield and appearance, resulting in a loss of millions of dollars of revenue. Symptoms used to diagnose the disease are angular, water soaked lesions and necrotic blotches. ''Aphelenchoides fragariae'' is the nematode pathogen that causes the disease. Its biological cycle includes four life stages, three of which are juvenile. The nematode can undergo multiple life cycles in one growing season when favorable conditions are present. The crowns, runners, foliage, and new buds of the plant via stylet penetration or through the stomata can be infected. The best management practices for this disease are sanitation, prevention of induction of the pathogen to the environment, and planting clean seed or starter plants. Importance Foliar nematodes are an important pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pustula Sp
''Pustula'' is a genus of plant-parasitic oomycetes segregated from ''Albugo''. The name is derived from Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...'s ''pustula'' meaning "blister". References {{Taxonbar, from=Q98404918 Water mould genera Albuginaceae ru:Albuginaceae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verticillium Albo-atrum
''Verticillium albo-atrum'' is a plant pathogen with many hosts. Infected plants See: * List of potato diseases * List of alfalfa diseases * List of African daisy diseases * List of beet diseases * List of caneberries diseases * List of tobacco diseases * List of tomato diseases * List of sunflower diseases * List of strawberry diseases * List of sapphire flower diseases * List of rose diseases * List of pocketbook plant diseases * List of Capsicum diseases * List of peanut diseases * List of mint diseases * List of mango diseases * List of Jerusalem cherry diseases * List of impatiens diseases * List of hop diseases * List of hemp diseases * List of geranium diseases * List of fuchsia diseases * List of elm diseases * List of dahlia diseases * List of cucurbit diseases * List of crucifer diseases * List of cineraria diseases * List of chickpea diseases This is a list of diseases of chickpeas (''Cicer arietinum'') Nematodes, parasitic Viral diseases Phytoplasmal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerotium Rolfsii
''Athelia rolfsii'' is a corticioid fungus in the family Atheliaceae. It is a facultative plant pathogen and is the causal agent of "southern blight" disease in crops. Taxonomy The species was first described in 1911 by Italian mycologist Pier Andrea Saccardo, based on specimens sent to him by Peter Henry Rolfs who considered the unnamed fungus to be the cause of tomato blight in Florida. The specimens sent to Saccardo were sterile, consisting of hyphae and sclerotia. He placed the species in the old form genus ''Sclerotium'', naming it ''Sclerotium rolfsii''. It is, however, not a species of ''Sclerotium'' in the strict sense. In 1932, Mario Curzi discovered that the teleomorph (spore-bearing state) was a corticioid fungus and accordingly placed the species in the form genus '' Corticium''. With a move to a more natural classification of fungi, ''Corticium rolfsii'' was transferred to '' Athelia'' in 1978. Description The fungus produces effused basidiocarps (fruit bodies) th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septoria
''Septoria'' are ascomycete pycnidia-producing fungi that cause numerous leaf spot diseases on field crops, forages and many vegetables including tomatoes which are known to contract ''Septoria musiva'' from nearby cottonwood trees, and is responsible for yield losses. The genus is widespread, and estimated to contain 1072 species. Pycnidia produce needle-like pycnidiospores. ''Septoria apiicola'' is the cause of late blight of celery. It is characterized by the production of conidia within pycnidia. The symptoms include chlorotic spots that turn brown and necrotic. ''Septoria apiicola'' can survive on seeds. Several species of passion flower are infected by several species of ''Septoria'', and a fungus, which has been going by the name ''Septoria passiflorae'' but which is probably an undescribed species, has been used to control the invasive ''Passiflora tarminiana ''Passiflora tarminiana'' (or banana passionfruit) is a species of passionfruit. The yellow fruits are edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerotinia Sclerotiorum
''Sclerotinia sclerotiorum'' is a plant pathogenic fungus and can cause a disease called white mold if conditions are conducive. ''S. sclerotiorum'' can also be known as cottony rot, watery soft rot, stem rot, drop, crown rot and blossom blight. A key characteristic of this pathogen is its ability to produce black resting structures known as sclerotia and white fuzzy growths of mycelium on the plant it infects. These sclerotia give rise to a fruiting body in the spring that produces spores in a sac which is why fungi in this class are called sac fungi (Ascomycota). This pathogen can occur on many continents and has a wide host range of plants. When ''S. sclerotiorum'' is onset in the field by favorable environmental conditions, losses can be great and control measures should be considered. Hosts and symptoms ''S. sclerotiorum'' is among the most omnivorous of plant pathogens and so would not make a good mycoherbicide. Economically significant hosts include ''Vicia faba'', for w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizopus Stolonifer
''Rhizopus stolonifer'' is commonly known as white bread mold. It is a member of ''Zygomycota'' and considered the most important species in the genus ''Rhizopus''. It is one of the most common fungi in the world and has a global distribution although it is most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions. It is a common agent of decomposition of stored foods. Like other members of the genus ''Rhizopus'', ''R. stolonifer'' grows rapidly, mostly in indoor environments. History This fungus was first discovered by the German scientist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1818 as ''Rhizopus nigricans''. The name was changed in 1902 to ''Rhizopus stolonifer'' by the French mycologist J. P. Vuillemin. Habitat and ecology ''Rhizopus stolonifer'' is a worldwide distributed species. It is found on all types of mouldy materials. It is often one of the first molds to appear on stale bread. It can exist in the soil as well as in the air. A variety of natural substrata are colonized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizoctonia Solani
''Rhizoctonia solani'' is a species of fungus in the order Cantharellales. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are thin, effused, and web-like, but the fungus is more typically encountered in its anamorphic state, as hyphae and sclerotia. The name ''Rhizoctonia solani'' is currently applied to a complex of related species that await further research. In its wide sense, ''Rhizoctonia solani'' is a facultative plant pathogen with a wide host range and worldwide distribution. It causes various plant diseases such as root rot, damping off, and wire stem. It can also form mycorrhizal associations with orchids. Taxonomy In 1858, the German plant pathologist Julius Kühn observed and described a fungus on diseased potato tubers and named it ''Rhizoctonia solani'', the species epithet referring to ''Solanum tuberosum'' (potato). The disease caused was well known before the discovery and description of the fungus. In 1956, Dutch mycologist M.A. Donk published the new name ''Thanatephorus cucumer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |