

A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched
explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are designed to kill personnel and destroy vehicles. Other cluster munitions are designed to destroy
runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, as ...
s or
electric power transmission
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This i ...
lines, disperse
chemical or
biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
weapons, or to scatter
land mines. Some submunition-based weapons can disperse non-munitions, such as
leaflets.
Because cluster bombs release many small bomblets over a wide area, they pose risks to
civilians both during attacks and afterwards.
Unexploded bomblets can kill or maim civilians and/or unintended targets long after a conflict has ended, and are costly to locate and remove.
Cluster munitions are prohibited for those nations that ratified the
Convention on Cluster Munitions, adopted in
Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
, Ireland, in May 2008. The Convention entered into force and became binding
international law upon ratifying states on 1 August 2010, six months after being ratified by 30 states.
As of 10 February 2022, a total of 123 states have joined the Convention, as 110 states parties and 13 signatories.
Development
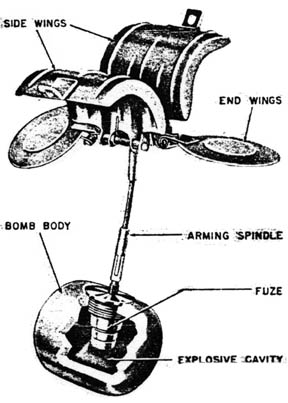
The first significantly operationally used
cluster bomb was the
German SD-2 or ''Sprengbombe Dickwandig 2 kg'', commonly referred to as the
Butterfly Bomb. It was used in
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
to attack both civilian and military targets. The technology was developed independently by the United States, Russia and Italy (see
Thermos bomb). The US used the 20-lb M41 fragmentation bomb wired together in clusters of 6 or 25 with highly sensitive or proximity
fuzes.
From the 1970s to the 1990s cluster bombs became standard air-dropped munitions for many nations, in a wide variety of types. They have been produced by 34 countries and used in at least 23.
[Austria bans cluster munitions](_blank)
''International Herald Tribune'', 7 Dec 2007
Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieg ...
shells that employ similar principles have existed for decades. They are typically referred to as
ICM (Improved Conventional Munitions) shells. The US military slang terms for them are "firecracker" or "popcorn" shells, for the many small explosions they cause in the target area.
Types

A basic cluster bomb consists of a hollow shell and then two to more than 2,000 submunitions or bomblets contained within it. Some types are dispensers that are designed to be retained by the aircraft after releasing their munitions. The submunitions themselves may be fitted with small
parachute retarders or
streamers to slow their descent (allowing the aircraft to escape the blast area in low-altitude attacks).
Modern cluster bombs and submunition dispensers can be multiple-purpose weapons containing a combination of anti-armor, anti-personnel, and anti-materiel munitions. The submunitions themselves may also be multi-purpose, such as combining a
shaped charge, to attack armour, with a fragmenting case, to attack infantry, material, and light vehicles. They may also have an incendiary function.
Since the 1990s submunition-based weapons have been designed that deploy
smart submunitions, using thermal and visual sensors to locate and attack particular targets, usually armored vehicles. Weapons of this type include the US
CBU-97 sensor-fuzed weapon
The CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon is a United States Air Force -class freefall cluster bomb, Cluster Bomb Unit. It was developed and produced by Textron Defense Systems. A CBU-97 used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidanc ...
, first used in combat during
Operation Iraqi Freedom, the 2003 invasion of Iraq. Some munitions specifically intended for anti-tank use can be set to self-destruct if they reach the ground without locating a target, theoretically reducing the risk of unintended civilian deaths and injuries. Although smart submunition weapons are much more expensive than standard cluster bombs, fewer smart submunitions are required to defeat dispersed and mobile targets, partly offsetting their cost. Because they are designed to prevent indiscriminate area effects and unexploded ordnance risks, some smart munitions are excluded from coverage by the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
Incendiary

Incendiary cluster bombs are intended to start fires, just like conventional
incendiary bombs (firebombs). They contain submunitions of
white phosphorus or
napalm, and can be combined anti-personnel and anti-tank submunitions to hamper firefighting efforts.
In urban areas they have been preceded by the use of conventional explosive bombs to fracture the roofs and walls of buildings to expose their flammable contents. One of the earliest examples is the so-called
Molotov bread basket used by the Soviet Union in the
Winter War of 1939–40. Incendiary clusters were extensively used by both sides in the
strategic bombings of World War II. They caused
firestorms and
conflagrations in the
bombing of Dresden in World War II and the
firebombing of Tokyo. Some modern bomb submunitions deliver a highly combustible
thermobaric aerosol that results in a high pressure explosion when ignited.
Anti-personnel
Anti-personnel cluster bombs use explosive
fragmentation
Fragmentation or fragmented may refer to:
Computers
* Fragmentation (computing), a phenomenon of computer storage
* File system fragmentation, the tendency of a file system to lay out the contents of files non-continuously
* Fragmented distributi ...
to kill troops and destroy soft (unarmored) targets. Along with incendiary cluster bombs, these were among the first types of
cluster bombs produced by
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. They were used during
the Blitz with delay and booby-trap fusing to hamper firefighting and other damage-control efforts in the target areas. They were also used with a contact
fuze when attacking entrenchments. These weapons were widely used during the Vietnam War when many thousands of tons of submunitions were dropped on Laos, Cambodia and Vietnam.
Anti-tank
Most anti-armor munitions contain
shaped charge warhead
A warhead is the forward section of a device that contains the explosive agent or toxic (biological, chemical, or nuclear) material that is delivered by a missile, rocket, torpedo, or bomb.
Classification
Types of warheads include:
*Explos ...
s to pierce the armor of
tanks and
armored fighting vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armoured c ...
s. In some cases, guidance is used to increase the likelihood of successfully hitting a vehicle. Modern guided submunitions, such as those found in the U.S.
CBU-97, can use either a shaped charge or an
explosively formed penetrator. Unguided shaped-charge submunitions are designed to be effective against entrenchments that incorporate overhead cover. To simplify supply and increase battlefield effectiveness by allowing a single type of round to be used against nearly any target, submunitions that incorporate both fragmentation and shaped-charge effects are produced.
Mine-laying
Submunition-based mines do not detonate immediately, but behave like conventional
land mines that detonate later. These submunitions usually include a combination of
anti-personnel and
anti-tank mines. Since such mines lie exposed on surfaces, the anti-personnel forms, such as the US
Area Denial Artillery Munition normally deploy tripwires automatically after landing to make clearing the minefield more difficult. In order to avoid accumulating large areas of impassable battlefield, and to minimize the amount of mine-clearing needed after a conflict, scatterable mines used by the United States are designed to self-destruct after a period of time from 4 to 48 hours. The internationally agreed definition of cluster munitions being negotiated in the
Oslo Process may not include this type of weapon, since landmines are already covered by other international treaties.
Chemical weapons
During the 1950s and 1960s, the United States and
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
developed cluster weapons designed to deliver
chemical weapons. The
Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993 banned their use. Six member nations declared themselves in possession of chemical weapons. The US and Russia are still in the process of destroying their stockpiles, having received extensions of the time limit for full destruction. They were unable to complete the destruction of their chemical weapons stockpiles by 2007, as the Treaty originally required.
Anti-electrical
An anti-electrical weapon, the CBU-94/B, was first used by the U.S. in the
Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the w ...
in 1999. These consist of a TMD (Tactical Munitions Dispenser) filled with 202
BLU-114/B "Soft-Bomb" submunitions. Each submunition contains a small explosive charge that disperses 147 reels of fine conductive fiber of either carbon or aluminum-coated glass. Their purpose is to disrupt and damage
electric power transmission
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This i ...
systems by producing
short circuits in high-voltage power lines and
electrical substations. On the initial attack, these knocked out 70% of the electrical power supply in
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hung ...
.
Leaflet dispensing
The LBU-30 is designed for dropping large quantities of
propaganda leaflets from aircraft. Enclosing the leaflets within the bomblets ensures that the leaflets will fall on the intended area without being dispersed excessively by the wind. The LBU-30 consists of SUU-30 dispensers that have been adapted to leaflet dispersal. The dispensers are essentially recycled units from old bombs. The LBU-30 was tested at
Eglin Air Force Base in 2000, by an
F-16 flying at .
History of use
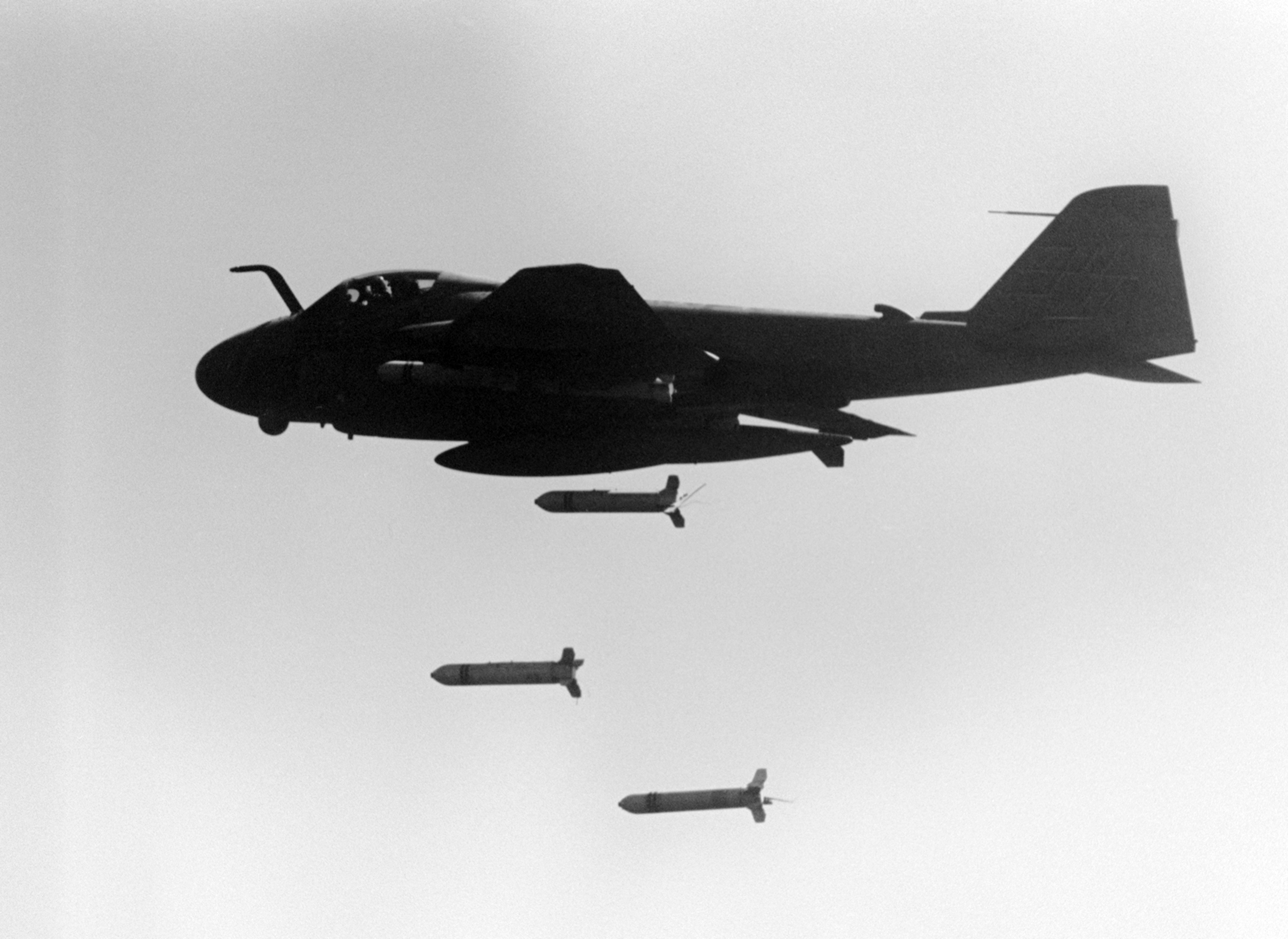

Vietnam War
During the
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, the US used cluster bombs in air strikes against targets in Vietnam,
Laos, and
Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
.
According to ''
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide ...
'', of the 260 million cluster bomblets that rained down on Laos between 1964 and 1973, particularly on
Xieng Khouang province
Xiangkhouang ( Lao: ຊຽງຂວາງ, meaning 'Horizontal City') is a province of Laos on the Xiangkhoang Plateau, in the nation's northeast. The province has the distinction of being the most heavily bombed place on Earth.
The province ...
, 80 million failed to explode.
The
GlobalPost reports that about 7,000 people have been injured or killed by explosives left from the Vietnam War era in the Vietnamese Quang Tri Province alone.
Western Sahara war, 1975–1991
During the 16-year-long conflict on the territory of Western Sahara, the
Royal Moroccan Army (RMA) dropped cluster bombs.
The RMA used both artillery-fired and air-dropped cluster munitions. BLU-63, M42 and MK118 submunitions were used at multiple locations in Bir Lahlou, Tifarity, Mehaires, Mijek and Awganit.
More that 300 cluster strike areas have been recorded in the MINURSO Mine Action Coordination Center database.
Soviet–Afghan War, 1979–1989
During the Soviet-Afghan War, the Soviets dealt harshly with Mujaheddin rebels and those who supported them, including leveling entire villages to deny safe havens to their enemy and the usage of cluster bombs.
Falklands War
Sea Harriers of the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
dropped
BL755 cluster bombs on Argentinian positions during the
Falklands War of 1982.
Grenada 1983
The United States dropped 21 Rockeye cluster bombs during its
invasion of Grenada
The United States invasion of Grenada began at dawn on 25 October 1983. The United States and a coalition of six Caribbean nations invaded the island nation of Grenada, north of Venezuela. Codenamed Operation Urgent Fury by the U.S. militar ...
.
Nagorno Karabakh War, 1992–1994, 2016, 2020
The armed conflict between Azerbaijan and Armenia in
Nagorno Karabakh in 1992–1994 led to the use of cluster munitions against military and civilian targets in the region. As of 2010, remain off-limits due to contamination with unexploded cluster ordnance.
HALO Trust has made major contributions to the cleanup effort.
During
renewed hostilities in April 2016, HALO Trust reported the use of cluster bombs by Azerbaijan, having found cluster munitions in the villages of
Nerkin Horatagh
Nerkin Horatagh ( hy, Ներքին Հոռաթաղ) or Ashaghy Oratagh ( az, Aşağı Oratağ) is a village ''de facto'' in the Martakert Province of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh, ''de jure'' in the Tartar District of Azerbaijan, in the dispu ...
and
Kiçik Qarabəy
Mokhratagh ( hy, Մոխրաթաղ) or Kichik Garabey ( az, Kiçik Qarabəy) is a village that is, '' de facto'', in the Martakert Province of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh; '' de jure'' it is in the Tartar District of Azerbaijan, in the di ...
. Azerbaijan reported that the Armenian forces had used cluster munition against Azerbaijani civilians in the given period.
According to the
Cluster Munition Monitor report in 2010, neither Armenia nor Azerbaijan not acceded to become a member of the
Convention on Cluster Munitions.
Further use of cluster munition was reported during the
2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The Armenian-populated city of
Stepanakert came under
bombardment throughout the war, beginning on the first day. Human Rights Watch reported that residential neighborhoods in Stepanakert which lacked any identifiable military targets were hit by the
Azerbaijani Army with cluster munitions. Human Rights Watch also identified Azerbaijani usage of cluster munitions in
Hadrut
Hadrut ( hy, Հադրութ, ) is a town in the Khojavend District of Azerbaijan, in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh.
The town had an ethnic Armenian-majority population prior to the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. Numerous Armenian civilians ...
. Human Rights Watch also reported the use of cluster munitions by the Armenian forces during the months-long
bombardment of Tartar,
missile attacks on Barda and on
Goranboy.
also confirmed that the Armenian forces had used cluster munitions in Barda,
which resulted in the deaths of 25 Azerbaijani civilians, according to Azerbaijan.
First Chechen War, 1995
* Used by Russia, see also
1995 Shali cluster bomb attack
The 1995 Shali cluster bomb attack was an attack which occurred on 3 January 1995, when Russian fighter-jets bombed the Chechen town of Shali with cluster bombs.
Events
Eighteen cluster bombs were reportedly dropped in and around Shali on tha ...
Yugoslavia, 1999
* Used by the US, the UK and Netherlands.
About 2,000 cluster bombs containing 380,000 sub-munitions were dropped on Yugoslavia during the
NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, in 1999, of which the
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
dropped 531
RBL755 cluster bombs.
On 7 May 1999, between the time of 11:30 and 11:40, a NATO attack was carried out with two containers of cluster bombs and fell in the central part of the city:
* The Pathology building next to the Medical Center of Nis in the south of the city,
* Next to the building of "Banovina" including the main market, bus station next to the Niš Fortress and "12th February" Health Centre
* Parking of "Niš Express" near river Nišava River.
Reports claimed that 15 civilians were killed, 8 civilians were seriously injured, 11 civilians had sustained minor injuries, 120 housing units were damaged and 47 were destroyed and that 15 cars were damaged.
Overall during the operation, at least 23 Serb civilians were killed by cluster munitions. At least six Serbs, including three children were killed by bomblets after the operation ended, and up to 23 square kilometres in six areas remain "cluster contaminated", according to Serbian government, including on Mt. Kopaonik near the slopes of the ski resort. The UK contributed £86,000 to the Serbian Mine Action Centre.
Afghanistan, 2001–2002
* United States and other
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
countries used large numbers of cluster munitions during the initial stage of the operation. 1,228 cluster bombs containing 248,056 bomblets were used by the
Coalition.
Iraq, 1991, 2003–2006

* Used by the United States and the United Kingdom
1991: United States, France, and the United Kingdom dropped 61,000 cluster bombs, containing 20 million submunitions, on Iraq, according to the HRW.
2003–2006: United States and allies attacked Iraq with 13,000 cluster munitions, containing two million submunitions during
Operation Iraqi Freedom, according to the
HRW. At multiple times, coalition forces used cluster munitions in residential areas, and the country remains among the most contaminated to this day, bomblets posing a threat to both US military personnel in the area, and local civilians.
When these weapons were fired on
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesipho ...
on 7 April 2003 many of the bomblets failed to explode on impact. Afterward, some of them exploded when touched by civilians. ''
USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virg ...
'' reported that "the Pentagon presented a misleading picture during the war of the extent to which cluster weapons were being used and of the civilian casualties they were causing." On 26 April, General
Richard Myers, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, said that the US had caused only one civilian casualty.
Lebanon, 1978, 1982 and 2006
* Extensively used by Israel during the
1978 Israeli invasion
The 1978 South Lebanon conflict (codenamed Operation Litani by Israel) began after Israel invaded southern Lebanon up to the Litani River in March 1978, in response to the Coastal Road massacre near Tel Aviv by Lebanon-based Palestinian mil ...
of Lebanon, the
1982–2000 occupation of Lebanon and also by
Hezbollah in the
2006 Lebanon War.
During the Israeli-Lebanese
conflict in 1982, Israel used cluster munitions, many of them American-made, on targets in southern Lebanon. Israel also used cluster bombs in the
2006 Lebanon War.
[MCC , Cluster Bombs](_blank)
Two types of cluster munitions were transferred to Israel from the U.S. The first was the CBU-58 which uses the BLU-63 bomblet. This cluster bomb is no longer in production. The second was the MK-20 Rockeye, produced by Honeywell Incorporated in Minneapolis. The CBU-58 was used by Israel in Lebanon in both 1978 and 1982.
The Israeli Defense company
Israel Military Industries also manufactures the more up-to-date M-85 cluster bomb.
Hezbollah fired Chinese-manufactured cluster munitions against Israeli civilian targets, using 122-mm rocket launchers during the 2006 war, hitting
Kiryat Motzkin,
Nahariya,
Karmiel,
Maghar, and
Safsufa
Kfar Hoshen ( he, כפר חושן), also known as Safsufa (ספסופה), is a moshav in northern Israel. Located around four kilometres north of Meron, it falls under the jurisdiction of Merom HaGalil Regional Council. In it had a population of . ...
. A total of 113 rockets and 4,407 submunitions were fired into Israel during the war.
According to the
United Nations Mine Action Service, Israel dropped up to four million submunitions on Lebanese soil, of which one million remain unexploded.
According to a report prepared by Lionel Beehner for the Council on Foreign Relations, the United States restocked Israel's arsenal of cluster bombs, triggering a State Department investigation to determine whether Israel had violated secret agreements it had signed with the United States on their use.
As Haaretz reported in November 2006, the Israel Defense Forces Chief of Staff
Dan Halutz wanted to launch an investigation into the use of cluster bombs during the Lebanon war.
Halutz claimed that some cluster bombs had been fired against his direct order, which stated that cluster bombs should be used with extreme caution and not be fired into populated areas. The IDF apparently disobeyed this order.
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
said there was evidence that Israel had used cluster bombs very close to civilian areas and described them as "unacceptably inaccurate and unreliable weapons when used around civilians" and that "they should never be used in populated areas". Human Rights Watch has accused Israel of using cluster munitions in an attack on Bilda, a Lebanese village, on 19 July which killed 1 civilian and injured 12, including seven children. The Israeli "army defended ... the use of cluster munitions in its offensive with
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, saying that using such munitions was 'legal under
international law' and the army employed them 'in accordance with international standards. Foreign Ministry Spokesman
Mark Regev added, "
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
countries stock these weapons and have used them in recent conflicts – in
FR Yugoslavia,
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
and
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
– the world has no reason to point a finger at Israel."
[Friedman, Ina. "Deadly Remnants". '' The Jerusalem Report''. 13 November 2006: 20–22]
Georgia, 2008
*
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
and Russia both were accused of using cluster munitions during the
2008 Russo-Georgian War
The 2008 Russo-Georgian WarThe war is known by a variety of other names, including Five-Day War, August War and Russian invasion of Georgia. was a war between Georgia (country), Georgia, on one side, and Russia and the Russian-backed self-proclaim ...
. Georgia admitted use; Russia denied it.
Georgia admitted using cluster bombs during the war, according to
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
but stressed they were only used against military targets. The
Georgian army used
LAR-160 multiple rocket launchers to fire MK4 LAR 160 type rockets (with M-85 bomblets) with a range of 45 kilometers the Georgian Minister of Defense (MoD) said.
Human Rights Watch accused the
Russian Air Force
"Air March"
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 12 August
, equipment =
, equipment_label =
, battles =
, decorations =
, batt ...
of using RBK-250 cluster bombs during the conflict. A high-ranking Russian military official denied use of cluster bombs. The Dutch government, after investigating the death of a Dutch citizen, claimed that a cluster munition was propelled by an
9K720 Iskander tactical missile
A tactical ballistic missile (TBM), or battlefield range ballistic missile (BRBM), is a ballistic missile designed for short-range battlefield use. Typically, range is less than . Tactical ballistic missiles are usually mobile to ensure surv ...
(used by Russia at the time of conflict, and not used by Georgia).
Libya, 2011
It was reported in April 2011 that
Colonel Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi, . Due to the lack of standardization of transcribing written and regionally pronounced Arabic, Gaddafi's name has been romanized in various ways. A 1986 column by '' The Straight Dope'' lists 32 spellin ...
's forces had used cluster bombs in the conflict between government forces and rebel forces trying to overthrow Gaddafi's government, during the
battle of Misrata These reports were denied by the government, and the Secretary of State of the US, Hillary Clinton said she was "not aware" of the specific use of cluster or other indiscriminate weapons in Misurata even though a ''New York Times'' investigation refuted those claims. An ejection canister for a Type 314 A AV submunition, manufactured in France was found in Libya despite the fact that France is a party to the international convention that bans cluster munitions.
Syria, 2012
During the
Syrian uprising, a few videos of cluster bombs first appeared in 2011, but escalated in frequency near the end of 2012.
[ As ]Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
reported on 13 October 2012, " Eliot Higgins, who blogs on military hardware and tactics used in Syria under the pseudonym 'Brown Moses', compiled a list of the videos showing cluster munition remnants in Syria's various governorates."RBK-250
RBK-250 is a Russian 250 kg cluster bomb
A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are des ...
cluster bombs with AO-1 SCH bomblets (of Soviet design).[ Designed by the Soviet Union for use on tank and troop formations, PTAB-2.5M bomblets were used on civilian targets in Mare' in December 2012 by the Syrian government.]
South Sudan, 2013
Cluster bombs remnants were discovered by a UN de-mining team in February 2014 on a section of road near the Jonglei state capital, Bor. The strategic town was the scene of heavy fighting, changing hands several times during the South Sudanese Civil War, which erupted in the capital Juba on 15 December 2013 before spreading to other parts of the country. According to the United Nations Mine Action Service (UNMAS), the site was contaminated with the remnants of up to eight cluster bombs and an unknown quantity of bomblets.
Ukraine, 2014
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
reported that "Ukrainian government forces used cluster munitions in populated areas in Donetsk city in early October 2014." Also "circumstances indicate that anti-government forces might also have been responsible for the use of cluster munitions".
Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen, 2015–2022
British-supplied and U.S.-supplied cluster bombs have been used by Saudi Arabian-led military coalition against Houthi militias in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
, according to Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
and Amnesty International.
Saudi Arabia is not signatory to the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
Ethiopia, 2021
''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' journalist Christiaan Triebert revealed that the Ethiopian Air Force bombings of Samre during the Tigray War are evidenced by multiple photos of the tails of Soviet-era cluster bombs, likely RBK-250
RBK-250 is a Russian 250 kg cluster bomb
A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are des ...
.
Ethiopia is not signatory to the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
Russian invasion of Ukraine, 2022
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
reported the use of cluster munitions by the Russian Armed Forces during the 2022 invasion of Ukraine. HRMMU reported 16 credible allegations that Russian armed forces used cluster munitions in
populated areas, causing in civilian casualties and other damage.Tochka
OTR-21 ''Tochka'' (russian: оперативно-тактический ракетный комплекс (ОТР) «Точка» ("point"); en, Tactical Operational Missile Complex "Tochka") is a Soviet tactical ballistic missile. Its GRAU desi ...
ballistic missile with a 9N123 cluster munition warhead containing 50 9N24 fragmentation submunitions impacted outside a hospital in Vuhledar in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. The attack killed four civillians and wounded ten. Further use of cluster munitions, such as the Uragan 9M27K and Smerch 9M55K cluster rockets, is being investigated by Bellingcat
Bellingcat (stylised as bell¿ngcat) is a Netherlands-based investigative journalism group that specialises in fact-checking and open-source intelligence (OSINT). It was founded by British journalist and former blogger Eliot Higgins in July 20 ...
through a public appeal for evidence on Twitter. According to HRW and Amnesty International, Russian troops used cluster munition during an attack on the city of Okhtyrka on the morning of 25 February 2022.
Threat to civilians
 While all weapons are dangerous, cluster bombs pose a particular threat to civilians for two reasons: they have a wide area of effect, and they consistently leave behind a large number of unexploded bomblets. The unexploded bomblets can remain dangerous for decades after the end of a conflict. For example, while the United States cluster bombing of Laos stopped in 1973, cluster bombs and other unexploded munitions continued to cause over 100 casualties per year to Laotian civilians .
Cluster munitions are opposed by many individuals and hundreds of groups, such as the
While all weapons are dangerous, cluster bombs pose a particular threat to civilians for two reasons: they have a wide area of effect, and they consistently leave behind a large number of unexploded bomblets. The unexploded bomblets can remain dangerous for decades after the end of a conflict. For example, while the United States cluster bombing of Laos stopped in 1973, cluster bombs and other unexploded munitions continued to cause over 100 casualties per year to Laotian civilians .
Cluster munitions are opposed by many individuals and hundreds of groups, such as the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million Volunteering, volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure re ...
, the Cluster Munition Coalition and the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
, because of the high number of civilians that have fallen victim to the weapon. Since February 2005, Handicap International called for cluster munitions to be prohibited and collected hundreds of thousands of signatures to support its call. 98% of 13,306 recorded cluster munitions casualties that are registered with Handicap International are civilians, while 27% are children.
The area affected by a single cluster munition, known as its footprint, can be very large; a single unguided M26 MLRS rocket can effectively cover an area of . In US and most allied services, the M26 has been replaced by the M30 guided missile fired from the MLRS. The M30 has greater range and accuracy but a smaller area of coverage. It is worth noting that for reasons including both danger to civilians and changing tactical requirements, the non-cluster unitary warhead XM31 missile is, in many cases, replacing even the M30.
Because of the weapon's broad area of effect, they have often been documented as striking both civilian and military objects in the target area. This characteristic of the weapon is particularly problematic for civilians when cluster munitions are used in or near populated areas and has been documented by research reports from groups such as Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
, Landmine Action, Mines Action Canada
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to:
Extraction or digging
*Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging
* Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine
Grammar
*Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun
M ...
and Handicap International. In some cases, like the Zagreb rocket attack
The Zagreb rocket attacks were two rocket attacks conducted by the Army of the Republic of Serbian Krajina that used multiple rocket launchers to strike the Croatian capital of Zagreb during the Croatian War of Independence. The attack killed ...
, civilians were deliberately targeted by such weapons.
Unexploded ordnance
 The other serious problem, also common to explosive weapons is unexploded ordnance (UXO) of cluster bomblets left behind after a strike. These bomblets may be
The other serious problem, also common to explosive weapons is unexploded ordnance (UXO) of cluster bomblets left behind after a strike. These bomblets may be dud
A dud is an ammunition round or explosive that fails to fire or detonate, respectively, on time or on command. Poorly designed devices (for example, improvised explosive devices (IEDs)), and small devices, have higher chances of being duds.
Du ...
s or in some cases the weapons are designed to detonate at a later stage. In both cases, the surviving bomblets are live and can explode when handled, making them a serious threat to civilians and military personnel entering the area. In effect, the UXOs can function like land mines.
Even though cluster bombs are designed to explode prior to or on impact, there are always some individual submunitions that do not explode on impact. The US-made MLRS with M26 warhead and M77 submunitions are supposed to have a 5% dud rate but studies have shown that some have a much higher rate. The rate in acceptance tests prior to the Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
for this type ranged from 2% to a high of 23% for rockets cooled to before testing. The M483A1 DPICM artillery-delivered cluster bombs have a reported dud rate of 14%.
Given that each cluster bomb can contain hundreds of bomblets and be fired in volleys, even a small failure rate can lead each strike to leave behind hundreds or thousands of UXOs scattered randomly across the strike area. For example, after the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict, UN experts have estimated that as many as one million unexploded bomblets may contaminate the hundreds of cluster munition strike sites in Lebanon.
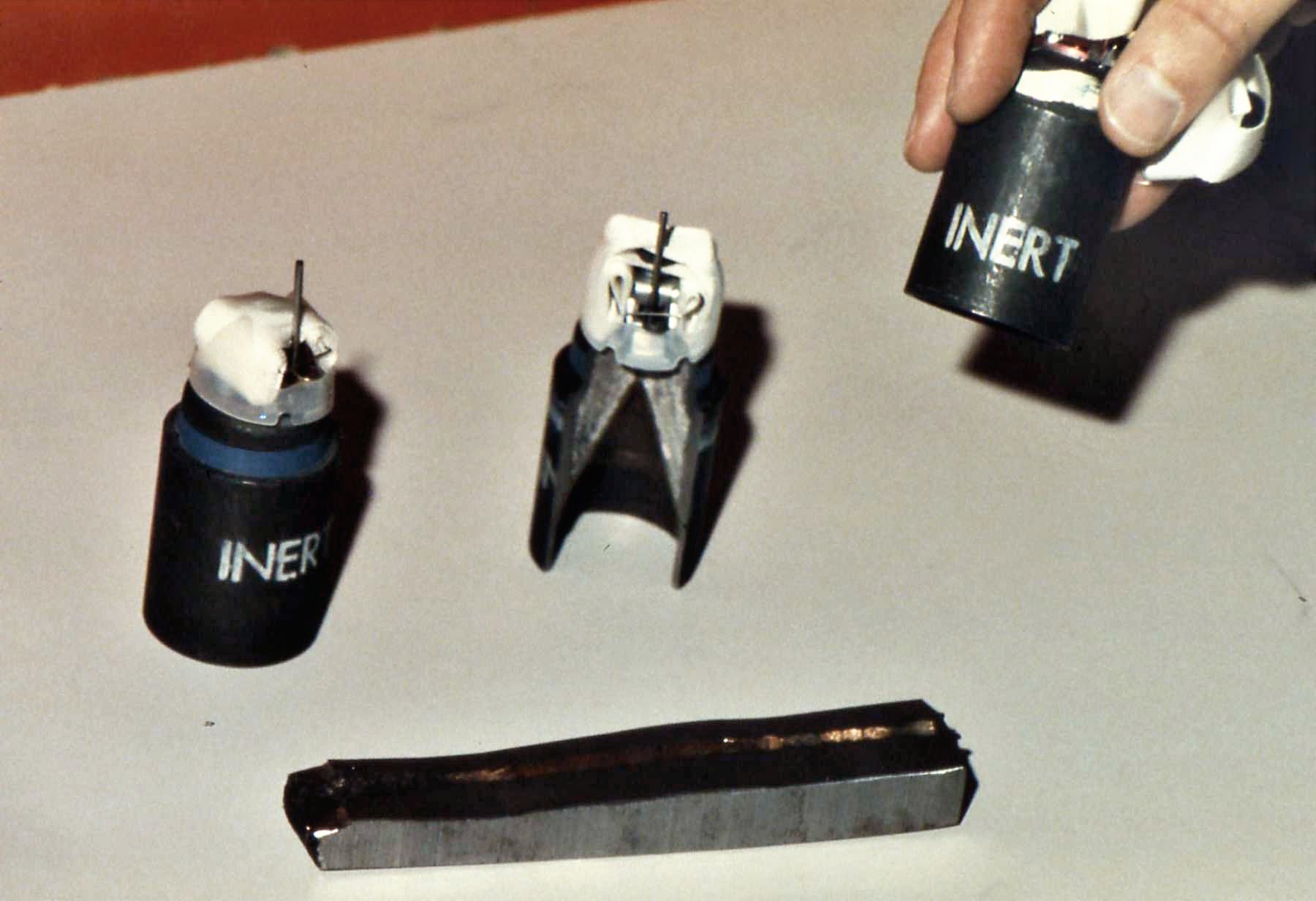 In addition, some cluster bomblets, such as the BLU-97/B used in the
In addition, some cluster bomblets, such as the BLU-97/B used in the CBU-87
The CBU-87 Combined Effects Munition (CEM) is a cluster bomb used by the United States Air Force, developed by Aerojet General/Honeywell and introduced in 1986 to replace the earlier cluster bombs used in the Vietnam War. CBU stands for Cluster Bo ...
, are brightly colored to increase their visibility and warn off civilians. However, the yellow color, coupled with their small and nonthreatening appearance, is attractive to young children who wrongly believe them to be toys. This problem was exacerbated in the War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
* Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see a ...
, when US forces dropped humanitarian rations from airplanes with similar yellow-colored packaging as the BLU-97/B, yellow being the NATO standard colour for high explosive filler in air weapons. The rations packaging was later changed first to blue and then to clear in the hope of avoiding such hazardous confusion.
The US military is developing new cluster bombs that it claims could have a much lower (less than 1%) dud rate. Sensor-fused weapons that contain a limited number of submunitions that are capable of autonomously engaging armored targets may provide a viable, if costly, alternative to cluster munitions that will allow multiple target engagement with one shell or bomb while avoiding the civilian deaths and injuries consistently documented from the use of cluster munitions. Certain such weapons may be allowed under the recently adopted Convention on Cluster Munitions, provided they do not have the indiscriminate area effects or pose the unexploded ordnance risks of cluster munitions.
In the 1980s the Spanish firm Esperanza y Cia developed a 120mm caliber mortar bomb which contained 21 anti-armor submunitions. What made the 120mm "Espin" unique was the electrical impact fusing system which totally eliminated dangerous duds. The system operates on a capacitor in each submunition which is charged by a wind generator in the nose of the projectile after being fired. If for what ever reason the electrical fuse fails to function on impact, approximately 5 minutes later the capacitor bleeds out, therefore neutralizing the submunition's electronic fuse system. Later a similar mortar round was offered in the 81mm caliber and equipped some Spanish Marines units. On signing the Wellington Declaration on Cluster Munitions, Spain withdrew both the 81mm and 120mm "Espin" rounds from its military units.
Civilian deaths
* In Vietnam, people are still being killed as a result of cluster bombs and other objects left by the US and Vietnamese military forces. Hundreds of people are killed or injured annually by unexploded ordnance.
* Some 270 million cluster submunitions were dropped on Laos in the 1960s and 1970s; approximately one third of these submunitions failed to explode and continue to pose a threat today.
* Within the first year after the end of the Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the w ...
, more than 100 civilians died from unexploded bombs and mines. During the war, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
planes dropped nearly 1,400 cluster bombs in Kosovo. Cluster bombs make up to 40% of mines and unexploded bombs in Kosovo.
* Israel used cluster bombs in Lebanon in 1978 and in the 1980s. Those weapons used more than two decades ago by Israel continue to affect Lebanon. During the 2006 war in Lebanon, Israel fired large numbers of cluster bombs in Lebanon, containing an estimated more than 4 million cluster submunitions. In the first month following the ceasefire, unexploded cluster munitions killed or injured an average of 3–4 people per day.
Locations
 Countries and disputed territories (listed in italic) that have been affected by cluster munitions as of August 2019 include:
Countries and disputed territories (listed in italic) that have been affected by cluster munitions as of August 2019 include:Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
* Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
* Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
(mainly '' Nagorno Karabakh'')
* Bosnia & Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
* Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
* Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Repub ...
* Croatia
* Democratic Republic of the Congo
* EritreaIraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
* Laos
* Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
* Libya
* Montenegro
* Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hung ...
* South Sudan
* Sudan
* Syria
* Tajikistan
* Ukraine
* United Kingdom (Falkland Islands)
* Vietnam
* Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
* ''Kosovo''
* ''Western Sahara''
As of August 2019, it is unclear, whether Colombia and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
are contaminated.
International legislation
 Cluster bombs fall under the general rules of international humanitarian law, but were not specifically covered by any currently binding international legal instrument until the signature of the Convention on Cluster Munitions in December 2008. This international treaty stemmed from an initiative by the Government of Norway known as the Oslo Process which was launched in February 2007 to prohibit cluster munitions. More than 100 countries agreed to the text of the resulting Convention on Cluster Munitions in May 2008 which sets out a comprehensive ban on these weapons. This treaty was signed by 94 states in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008. The Oslo Process was launched largely in response to the failure of the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) where five years of discussions failed to find an adequate response to these weapons. The Cluster Munition Coalition (CMC) is campaigning for the widespread accession to and ratification of the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
A number of sections of the Protocol on explosive remnants of war (Protocol V to the 1980 Convention), 28 November 2003 occasionally address some of the problems associated with the use of cluster munitions, in particular Article 9, which mandates States Parties to "take generic preventive measures aimed at minimising the occurrence of explosive remnants of war". In June 2006, Belgium was the first country to issue a ban on the use (carrying), transportation, export, stockpiling, trade and production of cluster munitions, and Austria followed suit on 7 December 2007.
Cluster bombs fall under the general rules of international humanitarian law, but were not specifically covered by any currently binding international legal instrument until the signature of the Convention on Cluster Munitions in December 2008. This international treaty stemmed from an initiative by the Government of Norway known as the Oslo Process which was launched in February 2007 to prohibit cluster munitions. More than 100 countries agreed to the text of the resulting Convention on Cluster Munitions in May 2008 which sets out a comprehensive ban on these weapons. This treaty was signed by 94 states in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008. The Oslo Process was launched largely in response to the failure of the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) where five years of discussions failed to find an adequate response to these weapons. The Cluster Munition Coalition (CMC) is campaigning for the widespread accession to and ratification of the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
A number of sections of the Protocol on explosive remnants of war (Protocol V to the 1980 Convention), 28 November 2003 occasionally address some of the problems associated with the use of cluster munitions, in particular Article 9, which mandates States Parties to "take generic preventive measures aimed at minimising the occurrence of explosive remnants of war". In June 2006, Belgium was the first country to issue a ban on the use (carrying), transportation, export, stockpiling, trade and production of cluster munitions, and Austria followed suit on 7 December 2007.
International treaties
 Other weapons, such as land mines, have been banned in many countries under specific legal instruments for several years, notably the Ottawa Treaty to ban land mines, and some of the Protocols in the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons that also help clearing the lands contaminated by left munitions after the end of conflicts and provides international assistance to the affected populations. However, until the recent adoption of the Convention on Cluster Munitions in Dublin in May 2008 cluster bombs were not banned by any international treaty and were considered legitimate weapons by some governments.
To increase pressure for governments to come to an international treaty on 13 November 2003, the Cluster Munition Coalition (CMC) was established with the goal of addressing the impact of cluster munitions on civilians. At the launch, organised by Pax Christi Netherlands, the then Minister of Foreign Affairs, the later Secretary General of NATO, Jaap de Hoop Scheffer, addressed the crowd of gathered government, NGO, and press representatives.
International governmental deliberations in the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons turned on the broader problem of explosive remnants of war, a problem to which cluster munitions have contributed in a significant way. There were consistent calls from the Cluster Munition Coalition, the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and a number of UN agencies, joined by approximately 30 governments, for international governmental negotiations to develop specific measures that would address the humanitarian problems cluster munitions pose. This did not prove possible in the conventional multilateral forum. After a reversal in the US position, in 2007 deliberations did begin on cluster munitions within the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons. There was a concerted effort led by the US to develop a new protocol to the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons, but this proposal was rejected by over 50 states, together with civil society, ICRC and UN agencies. The discussions ended with no result in November 2011, leaving the 2008 Convention on Cluster Munitions as the single international standard on the weapons.
In February 2006, Belgium announced its decision to ban the weapon by law. Then Norway announced a national moratorium in June and Austria announced its decision in July to work for an international instrument on the weapon. The international controversy over the use and impact of cluster munitions during the war between Lebanon and Israel in July and August 2006 added weight to the global campaign for a ban treaty.
Other weapons, such as land mines, have been banned in many countries under specific legal instruments for several years, notably the Ottawa Treaty to ban land mines, and some of the Protocols in the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons that also help clearing the lands contaminated by left munitions after the end of conflicts and provides international assistance to the affected populations. However, until the recent adoption of the Convention on Cluster Munitions in Dublin in May 2008 cluster bombs were not banned by any international treaty and were considered legitimate weapons by some governments.
To increase pressure for governments to come to an international treaty on 13 November 2003, the Cluster Munition Coalition (CMC) was established with the goal of addressing the impact of cluster munitions on civilians. At the launch, organised by Pax Christi Netherlands, the then Minister of Foreign Affairs, the later Secretary General of NATO, Jaap de Hoop Scheffer, addressed the crowd of gathered government, NGO, and press representatives.
International governmental deliberations in the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons turned on the broader problem of explosive remnants of war, a problem to which cluster munitions have contributed in a significant way. There were consistent calls from the Cluster Munition Coalition, the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and a number of UN agencies, joined by approximately 30 governments, for international governmental negotiations to develop specific measures that would address the humanitarian problems cluster munitions pose. This did not prove possible in the conventional multilateral forum. After a reversal in the US position, in 2007 deliberations did begin on cluster munitions within the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons. There was a concerted effort led by the US to develop a new protocol to the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons, but this proposal was rejected by over 50 states, together with civil society, ICRC and UN agencies. The discussions ended with no result in November 2011, leaving the 2008 Convention on Cluster Munitions as the single international standard on the weapons.
In February 2006, Belgium announced its decision to ban the weapon by law. Then Norway announced a national moratorium in June and Austria announced its decision in July to work for an international instrument on the weapon. The international controversy over the use and impact of cluster munitions during the war between Lebanon and Israel in July and August 2006 added weight to the global campaign for a ban treaty.
 Against this background, a new flexible multilateral process similar to the process that led to the ban on anti-personnel land mines in 1997 (the Ottawa Treaty) began with an announcement in November 2006 in Geneva as well at the same time by the Government of Norway that it would convene an international meeting in early 2007 in Oslo to work towards a new treaty prohibiting cluster munitions. Forty-nine governments attended the meeting in Oslo 22–23 February 2007 in order to reaffirm their commitment to a new international ban on the weapon. During the meeting Austria announced an immediate moratorium on the use, production and transfer of cluster munitions until a new international treaty banning the weapons is in place.
A follow-up meeting in this process was held in Lima in May where around 70 states discussed the outline of a new treaty, Hungary became the latest country to announce a moratorium and Peru launched an initiative to make Latin America a cluster munition free zone.
In addition, the International Committee of the Red Cross, ICRC held an experts meeting on cluster munitions in April 2007 which helped clarify technical, legal, military and humanitarian aspects of the weapon with a view to developing an international response.
Further meetings took place in Vienna on 4–7 December 2007, and in Wellington on 18–22 February 2008 where a declaration in favor of negotiations on a draft convention was adopted by more than 80 countries. In May 2008 after around Convention on Cluster Munitions#Nations that have subscribed to the Wellington Declaration, 120 countries had subscribed to the Wellington Declaration and participated in the Dublin Diplomatic Conference from 19 to 30 May 2008. At the end of this conference, 107 countries agreed to adopt the Convention on Cluster Munitions, that bans cluster munitions and was opened for signature in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008 where it was signed by 94 countries.
In July 2008, United States Defense Secretary Robert Gates, Robert M. Gates implemented a policy to eliminate by 2018 all cluster bombs that do not meet new safety standards.
In November 2008, ahead of the signing Conference in Oslo, the European Parliament passed a resolution calling on all European Union governments to sign and ratify the Convention.
On 16 February 2010 Burkina Faso became the 30th state to deposit its instrument of ratification for the Convention on Cluster Munitions. This means that the number of States required for the Convention to enter into force had been reached. The treaty's obligations became legally binding on the 30 ratifying States on 1 August 2010 and subsequently for other ratifying States.
Against this background, a new flexible multilateral process similar to the process that led to the ban on anti-personnel land mines in 1997 (the Ottawa Treaty) began with an announcement in November 2006 in Geneva as well at the same time by the Government of Norway that it would convene an international meeting in early 2007 in Oslo to work towards a new treaty prohibiting cluster munitions. Forty-nine governments attended the meeting in Oslo 22–23 February 2007 in order to reaffirm their commitment to a new international ban on the weapon. During the meeting Austria announced an immediate moratorium on the use, production and transfer of cluster munitions until a new international treaty banning the weapons is in place.
A follow-up meeting in this process was held in Lima in May where around 70 states discussed the outline of a new treaty, Hungary became the latest country to announce a moratorium and Peru launched an initiative to make Latin America a cluster munition free zone.
In addition, the International Committee of the Red Cross, ICRC held an experts meeting on cluster munitions in April 2007 which helped clarify technical, legal, military and humanitarian aspects of the weapon with a view to developing an international response.
Further meetings took place in Vienna on 4–7 December 2007, and in Wellington on 18–22 February 2008 where a declaration in favor of negotiations on a draft convention was adopted by more than 80 countries. In May 2008 after around Convention on Cluster Munitions#Nations that have subscribed to the Wellington Declaration, 120 countries had subscribed to the Wellington Declaration and participated in the Dublin Diplomatic Conference from 19 to 30 May 2008. At the end of this conference, 107 countries agreed to adopt the Convention on Cluster Munitions, that bans cluster munitions and was opened for signature in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008 where it was signed by 94 countries.
In July 2008, United States Defense Secretary Robert Gates, Robert M. Gates implemented a policy to eliminate by 2018 all cluster bombs that do not meet new safety standards.
In November 2008, ahead of the signing Conference in Oslo, the European Parliament passed a resolution calling on all European Union governments to sign and ratify the Convention.
On 16 February 2010 Burkina Faso became the 30th state to deposit its instrument of ratification for the Convention on Cluster Munitions. This means that the number of States required for the Convention to enter into force had been reached. The treaty's obligations became legally binding on the 30 ratifying States on 1 August 2010 and subsequently for other ratifying States.
Convention on Cluster Munitions
Taking effect on 1 August 2010, the Convention on Cluster Munitions bans the stockpiling, use and transfer of virtually all existing cluster bombs and provides for the clearing up of unexploded munitions. It had been signed by 108 countries, of which 38 had ratified it by the affected date, but many of the world's major military powers including the United States, Russia, Brazil and China are not signatories to the treaty.
Ratifiers and signatories
The Convention on Cluster Munitions entered into force on 1 August 2010, six months after it was ratified by 30 states. As of 26 September 2018, a total of 120 states have joined the Convention, as 104 States parties and 16 signatories.
United States policy
 According to the US State Department, the U.S. suspended operational use of cluster munitions in 2003.
According to the US State Department, the U.S. suspended operational use of cluster munitions in 2003.[Cluster Munitions: Background and Issues for Congress](_blank)
– Fas.org, 30 June 2013
In May 2008, then-Acting Assistant Secretary of State for Political-Military Affairs Stephen Mull stated that the U.S. military relies upon cluster munitions as an important part of their war strategy. Mull emphasized that "U.S. forces simply cannot fight by design or by doctrine without holding out at least the possibility of using cluster munitions."
The U.S. Army ceased procurement of GMLRS cluster rockets in December 2008 because of a submunition dud rate as high as five percent. Pentagon policy was to have all cluster munitions used after 2018 to have a submunition unexploded ordnance rate of less than one percent. To achieve this, the Army undertook the Alternative Warhead Program (AWP) to assess and recommend technologies to reduce or eliminate cluster munition failures, as some 80 percent of U.S. military cluster weapons reside in Army artillery stockpiles.
Users
Countries
At least 25 countries have used cluster munitions in recent history (since the creation of the United Nations). Countries listed in bold have signed and ratified the Convention on Cluster Munitions, agreeing in principle to ban cluster bombs. Countries listed in italic have signed, but not yet ratified the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
* Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Yugoslavia)
Non-state armed groups
Very few violent non-state actors have used cluster munitions and their delivery systems due to the complexity.
Producers
At least 31 nations have produced cluster munitions in recent history (since the creation of the United Nations). Many of these nations still have stocks of these munitions.
Countries with stocks
As of September 2018, at least 57 countries have stockpiles of cluster munitions.
Financiers
According to BankTrack, an international network of NGOs specializing in control of financial institutions, many major banks and other financial corporations either directly financed, or provided financial services to companies producing cluster munition in 2005–2012. Among other, BankTrack 2012 report names ABN AMRO, Bank of America, Bank of China, Bank of Tokyo Mitsubishi UFJ, Barclays, BBVA, BNP Paribas, Citigroup, Commerzbank AG, Commonwealth Bank of Australia, Crédit Agricole, Credit Suisse Group, Deutsche Bank, Goldman Sachs, HSBC, Industrial Bank of China, ING Group, JPMorgan Chase, Korea Development Bank, Lloyds TSB, Merrill Lynch, Morgan Stanley, Royal Bank of Canada, Royal Bank of Scotland, Sberbank, Société Générale, UBS, Wells Fargo.
Many of these financial companies are connected to such producers of cluster munitions as Alliant Techsystems, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, Hanwha, Norinco, Singapore Technologies Engineering, Textron, and others.
According to Pax Christi, a Netherlands-based NGO, in 2009, around 137 financial institutions financed cluster munition production. Out of 137 institutions, 63 were based in the US, another 18 in the EU (the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy etc.), 16 were based in China, 4 in Singapore, 3 in each of: Canada, Japan, Taiwan, 2 in Switzerland, and 4 other countries had 1 financial institution involved.
See also
* Anti-runway penetration bomb
* Ban Advocates
* Bomb disposal
* Demining
* List of cluster bombs
* Mines Advisory Group
* Fares Scale of Injuries due to Cluster Munitions
* Cluster Munition Coalition
References
Citations
Bibliography
*
External links
Cluster Munition Coalition
Mines Advisory Group
Cluster munitions and international humanitarian law
International Committee of the Red Cross
Convention on Cluster Munitions
– Official website serving the government initiative to ban cluster munitions
Circle of Impact: The Fatal Footprint of Cluster Munitions on People and Communities
16 May 2007
Disarmament Insight
website
Council on Foreign Relations: The Campaign to Ban Cluster Bombs
21 November 2006
Ban Advocates – Voices from affected communities
Technical
* [https://fas.org/man/dod-101/sys/dumb/blu-114.htm Federation of American Scientists article on the BLU-114 anti-electrical weapon.]
Inquiries
Inquiry by the Foreign Affairs, Defence and Trade Committee of the Australian Senate into the provisions of the Cluster Munitions (Prohibition) Bill 2006
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cluster Bomb
Cluster munition,
Explosive weapons
Submunitions
Area denial weapons

 A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are designed to kill personnel and destroy vehicles. Other cluster munitions are designed to destroy
A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are designed to kill personnel and destroy vehicles. Other cluster munitions are designed to destroy  The first significantly operationally used cluster bomb was the German SD-2 or ''Sprengbombe Dickwandig 2 kg'', commonly referred to as the Butterfly Bomb. It was used in
The first significantly operationally used cluster bomb was the German SD-2 or ''Sprengbombe Dickwandig 2 kg'', commonly referred to as the Butterfly Bomb. It was used in  A basic cluster bomb consists of a hollow shell and then two to more than 2,000 submunitions or bomblets contained within it. Some types are dispensers that are designed to be retained by the aircraft after releasing their munitions. The submunitions themselves may be fitted with small parachute retarders or streamers to slow their descent (allowing the aircraft to escape the blast area in low-altitude attacks).
Modern cluster bombs and submunition dispensers can be multiple-purpose weapons containing a combination of anti-armor, anti-personnel, and anti-materiel munitions. The submunitions themselves may also be multi-purpose, such as combining a shaped charge, to attack armour, with a fragmenting case, to attack infantry, material, and light vehicles. They may also have an incendiary function.
Since the 1990s submunition-based weapons have been designed that deploy smart submunitions, using thermal and visual sensors to locate and attack particular targets, usually armored vehicles. Weapons of this type include the US CBU-97
A basic cluster bomb consists of a hollow shell and then two to more than 2,000 submunitions or bomblets contained within it. Some types are dispensers that are designed to be retained by the aircraft after releasing their munitions. The submunitions themselves may be fitted with small parachute retarders or streamers to slow their descent (allowing the aircraft to escape the blast area in low-altitude attacks).
Modern cluster bombs and submunition dispensers can be multiple-purpose weapons containing a combination of anti-armor, anti-personnel, and anti-materiel munitions. The submunitions themselves may also be multi-purpose, such as combining a shaped charge, to attack armour, with a fragmenting case, to attack infantry, material, and light vehicles. They may also have an incendiary function.
Since the 1990s submunition-based weapons have been designed that deploy smart submunitions, using thermal and visual sensors to locate and attack particular targets, usually armored vehicles. Weapons of this type include the US CBU-97  Incendiary cluster bombs are intended to start fires, just like conventional incendiary bombs (firebombs). They contain submunitions of white phosphorus or napalm, and can be combined anti-personnel and anti-tank submunitions to hamper firefighting efforts. In urban areas they have been preceded by the use of conventional explosive bombs to fracture the roofs and walls of buildings to expose their flammable contents. One of the earliest examples is the so-called Molotov bread basket used by the Soviet Union in the Winter War of 1939–40. Incendiary clusters were extensively used by both sides in the strategic bombings of World War II. They caused firestorms and conflagrations in the bombing of Dresden in World War II and the firebombing of Tokyo. Some modern bomb submunitions deliver a highly combustible thermobaric aerosol that results in a high pressure explosion when ignited.
Incendiary cluster bombs are intended to start fires, just like conventional incendiary bombs (firebombs). They contain submunitions of white phosphorus or napalm, and can be combined anti-personnel and anti-tank submunitions to hamper firefighting efforts. In urban areas they have been preceded by the use of conventional explosive bombs to fracture the roofs and walls of buildings to expose their flammable contents. One of the earliest examples is the so-called Molotov bread basket used by the Soviet Union in the Winter War of 1939–40. Incendiary clusters were extensively used by both sides in the strategic bombings of World War II. They caused firestorms and conflagrations in the bombing of Dresden in World War II and the firebombing of Tokyo. Some modern bomb submunitions deliver a highly combustible thermobaric aerosol that results in a high pressure explosion when ignited.

 * Used by the United States and the United Kingdom
1991: United States, France, and the United Kingdom dropped 61,000 cluster bombs, containing 20 million submunitions, on Iraq, according to the HRW.
2003–2006: United States and allies attacked Iraq with 13,000 cluster munitions, containing two million submunitions during Operation Iraqi Freedom, according to the HRW. At multiple times, coalition forces used cluster munitions in residential areas, and the country remains among the most contaminated to this day, bomblets posing a threat to both US military personnel in the area, and local civilians.
When these weapons were fired on
* Used by the United States and the United Kingdom
1991: United States, France, and the United Kingdom dropped 61,000 cluster bombs, containing 20 million submunitions, on Iraq, according to the HRW.
2003–2006: United States and allies attacked Iraq with 13,000 cluster munitions, containing two million submunitions during Operation Iraqi Freedom, according to the HRW. At multiple times, coalition forces used cluster munitions in residential areas, and the country remains among the most contaminated to this day, bomblets posing a threat to both US military personnel in the area, and local civilians.
When these weapons were fired on  While all weapons are dangerous, cluster bombs pose a particular threat to civilians for two reasons: they have a wide area of effect, and they consistently leave behind a large number of unexploded bomblets. The unexploded bomblets can remain dangerous for decades after the end of a conflict. For example, while the United States cluster bombing of Laos stopped in 1973, cluster bombs and other unexploded munitions continued to cause over 100 casualties per year to Laotian civilians .
Cluster munitions are opposed by many individuals and hundreds of groups, such as the
While all weapons are dangerous, cluster bombs pose a particular threat to civilians for two reasons: they have a wide area of effect, and they consistently leave behind a large number of unexploded bomblets. The unexploded bomblets can remain dangerous for decades after the end of a conflict. For example, while the United States cluster bombing of Laos stopped in 1973, cluster bombs and other unexploded munitions continued to cause over 100 casualties per year to Laotian civilians .
Cluster munitions are opposed by many individuals and hundreds of groups, such as the  In addition, some cluster bomblets, such as the BLU-97/B used in the
In addition, some cluster bomblets, such as the BLU-97/B used in the  Countries and disputed territories (listed in italic) that have been affected by cluster munitions as of August 2019 include:
*
Countries and disputed territories (listed in italic) that have been affected by cluster munitions as of August 2019 include:
*  Cluster bombs fall under the general rules of international humanitarian law, but were not specifically covered by any currently binding international legal instrument until the signature of the Convention on Cluster Munitions in December 2008. This international treaty stemmed from an initiative by the Government of Norway known as the Oslo Process which was launched in February 2007 to prohibit cluster munitions. More than 100 countries agreed to the text of the resulting Convention on Cluster Munitions in May 2008 which sets out a comprehensive ban on these weapons. This treaty was signed by 94 states in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008. The Oslo Process was launched largely in response to the failure of the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) where five years of discussions failed to find an adequate response to these weapons. The Cluster Munition Coalition (CMC) is campaigning for the widespread accession to and ratification of the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
A number of sections of the Protocol on explosive remnants of war (Protocol V to the 1980 Convention), 28 November 2003 occasionally address some of the problems associated with the use of cluster munitions, in particular Article 9, which mandates States Parties to "take generic preventive measures aimed at minimising the occurrence of explosive remnants of war". In June 2006, Belgium was the first country to issue a ban on the use (carrying), transportation, export, stockpiling, trade and production of cluster munitions, and Austria followed suit on 7 December 2007.
There has been legislative activity on cluster munitions in several countries, including Austria, Australia, Denmark, France, Germany, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom and United States. In some of these countries, ongoing discussions concerning draft legislation banning cluster munitions, along the lines of the legislation adopted in Belgium and Austria will now turn to ratification of the global ban treaty. Norway and Ireland have national legislation prohibiting cluster munitions and were able to deposit their instruments of ratification to the Convention on Cluster Munitions immediately after signing it in Oslo on 3 December 2008.
Cluster bombs fall under the general rules of international humanitarian law, but were not specifically covered by any currently binding international legal instrument until the signature of the Convention on Cluster Munitions in December 2008. This international treaty stemmed from an initiative by the Government of Norway known as the Oslo Process which was launched in February 2007 to prohibit cluster munitions. More than 100 countries agreed to the text of the resulting Convention on Cluster Munitions in May 2008 which sets out a comprehensive ban on these weapons. This treaty was signed by 94 states in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008. The Oslo Process was launched largely in response to the failure of the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) where five years of discussions failed to find an adequate response to these weapons. The Cluster Munition Coalition (CMC) is campaigning for the widespread accession to and ratification of the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
A number of sections of the Protocol on explosive remnants of war (Protocol V to the 1980 Convention), 28 November 2003 occasionally address some of the problems associated with the use of cluster munitions, in particular Article 9, which mandates States Parties to "take generic preventive measures aimed at minimising the occurrence of explosive remnants of war". In June 2006, Belgium was the first country to issue a ban on the use (carrying), transportation, export, stockpiling, trade and production of cluster munitions, and Austria followed suit on 7 December 2007.
There has been legislative activity on cluster munitions in several countries, including Austria, Australia, Denmark, France, Germany, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom and United States. In some of these countries, ongoing discussions concerning draft legislation banning cluster munitions, along the lines of the legislation adopted in Belgium and Austria will now turn to ratification of the global ban treaty. Norway and Ireland have national legislation prohibiting cluster munitions and were able to deposit their instruments of ratification to the Convention on Cluster Munitions immediately after signing it in Oslo on 3 December 2008.
 Against this background, a new flexible multilateral process similar to the process that led to the ban on anti-personnel land mines in 1997 (the Ottawa Treaty) began with an announcement in November 2006 in Geneva as well at the same time by the Government of Norway that it would convene an international meeting in early 2007 in Oslo to work towards a new treaty prohibiting cluster munitions. Forty-nine governments attended the meeting in Oslo 22–23 February 2007 in order to reaffirm their commitment to a new international ban on the weapon. During the meeting Austria announced an immediate moratorium on the use, production and transfer of cluster munitions until a new international treaty banning the weapons is in place.
A follow-up meeting in this process was held in Lima in May where around 70 states discussed the outline of a new treaty, Hungary became the latest country to announce a moratorium and Peru launched an initiative to make Latin America a cluster munition free zone.
In addition, the International Committee of the Red Cross, ICRC held an experts meeting on cluster munitions in April 2007 which helped clarify technical, legal, military and humanitarian aspects of the weapon with a view to developing an international response.
Further meetings took place in Vienna on 4–7 December 2007, and in Wellington on 18–22 February 2008 where a declaration in favor of negotiations on a draft convention was adopted by more than 80 countries. In May 2008 after around Convention on Cluster Munitions#Nations that have subscribed to the Wellington Declaration, 120 countries had subscribed to the Wellington Declaration and participated in the Dublin Diplomatic Conference from 19 to 30 May 2008. At the end of this conference, 107 countries agreed to adopt the Convention on Cluster Munitions, that bans cluster munitions and was opened for signature in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008 where it was signed by 94 countries.
In July 2008, United States Defense Secretary Robert Gates, Robert M. Gates implemented a policy to eliminate by 2018 all cluster bombs that do not meet new safety standards.
In November 2008, ahead of the signing Conference in Oslo, the European Parliament passed a resolution calling on all European Union governments to sign and ratify the Convention.
On 16 February 2010 Burkina Faso became the 30th state to deposit its instrument of ratification for the Convention on Cluster Munitions. This means that the number of States required for the Convention to enter into force had been reached. The treaty's obligations became legally binding on the 30 ratifying States on 1 August 2010 and subsequently for other ratifying States.
Against this background, a new flexible multilateral process similar to the process that led to the ban on anti-personnel land mines in 1997 (the Ottawa Treaty) began with an announcement in November 2006 in Geneva as well at the same time by the Government of Norway that it would convene an international meeting in early 2007 in Oslo to work towards a new treaty prohibiting cluster munitions. Forty-nine governments attended the meeting in Oslo 22–23 February 2007 in order to reaffirm their commitment to a new international ban on the weapon. During the meeting Austria announced an immediate moratorium on the use, production and transfer of cluster munitions until a new international treaty banning the weapons is in place.
A follow-up meeting in this process was held in Lima in May where around 70 states discussed the outline of a new treaty, Hungary became the latest country to announce a moratorium and Peru launched an initiative to make Latin America a cluster munition free zone.
In addition, the International Committee of the Red Cross, ICRC held an experts meeting on cluster munitions in April 2007 which helped clarify technical, legal, military and humanitarian aspects of the weapon with a view to developing an international response.
Further meetings took place in Vienna on 4–7 December 2007, and in Wellington on 18–22 February 2008 where a declaration in favor of negotiations on a draft convention was adopted by more than 80 countries. In May 2008 after around Convention on Cluster Munitions#Nations that have subscribed to the Wellington Declaration, 120 countries had subscribed to the Wellington Declaration and participated in the Dublin Diplomatic Conference from 19 to 30 May 2008. At the end of this conference, 107 countries agreed to adopt the Convention on Cluster Munitions, that bans cluster munitions and was opened for signature in Oslo on 3–4 December 2008 where it was signed by 94 countries.
In July 2008, United States Defense Secretary Robert Gates, Robert M. Gates implemented a policy to eliminate by 2018 all cluster bombs that do not meet new safety standards.
In November 2008, ahead of the signing Conference in Oslo, the European Parliament passed a resolution calling on all European Union governments to sign and ratify the Convention.
On 16 February 2010 Burkina Faso became the 30th state to deposit its instrument of ratification for the Convention on Cluster Munitions. This means that the number of States required for the Convention to enter into force had been reached. The treaty's obligations became legally binding on the 30 ratifying States on 1 August 2010 and subsequently for other ratifying States.
 According to the US State Department, the U.S. suspended operational use of cluster munitions in 2003.
U.S. arguments favoring the use of cluster munitions are that their use reduces the number of aircraft and artillery systems needed to support military operations and if they were eliminated, significantly more money would have to be spent on new weapons, ammunition, and logistical resources. Also, militaries would need to increase their use of massed artillery and rocket barrages to get the same coverage, which would destroy or damage more key infrastructures.
The U.S. was initially against any CCW limitation negotiations, but dropped its opposition in June 2007. Cluster munitions have been determined as needed for ensuring the country's national security interests, but measures were taken to address humanitarian concerns of their use, as well as pursuing their original suggested alternative to a total ban of pursuing technological fixes to make the weapons no longer viable after the end of a conflict.Cluster Munitions: Background and Issues for Congress
According to the US State Department, the U.S. suspended operational use of cluster munitions in 2003.
U.S. arguments favoring the use of cluster munitions are that their use reduces the number of aircraft and artillery systems needed to support military operations and if they were eliminated, significantly more money would have to be spent on new weapons, ammunition, and logistical resources. Also, militaries would need to increase their use of massed artillery and rocket barrages to get the same coverage, which would destroy or damage more key infrastructures.
The U.S. was initially against any CCW limitation negotiations, but dropped its opposition in June 2007. Cluster munitions have been determined as needed for ensuring the country's national security interests, but measures were taken to address humanitarian concerns of their use, as well as pursuing their original suggested alternative to a total ban of pursuing technological fixes to make the weapons no longer viable after the end of a conflict.Cluster Munitions: Background and Issues for Congress