|
Thermos Bomb
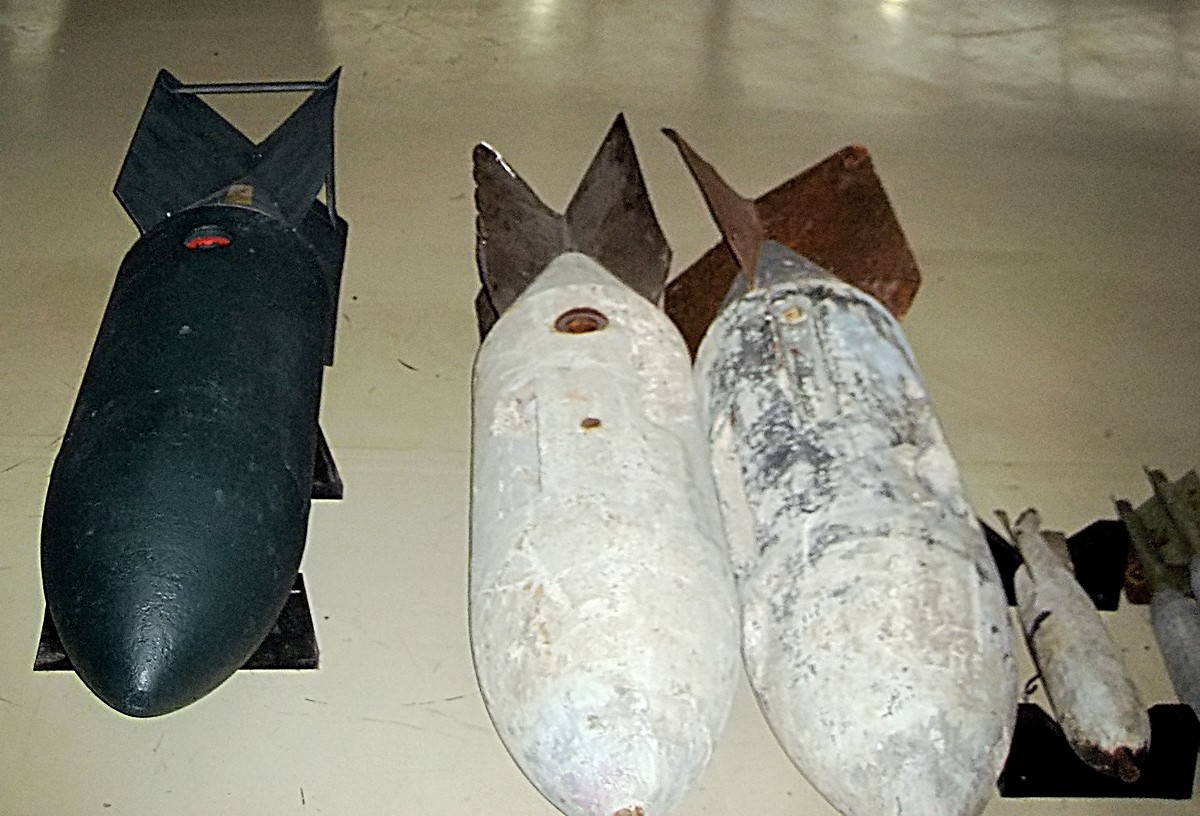
''Thermos bomb'' was the informal name for the AR-4, an air dropped anti-personnel mine used by the Italian Air Force during World War II. Large numbers were used against Malta and in the Middle East. It was named for its superficial appearance to a Thermos bottle, a popular brand of vacuum flask. The bomb was a cylinder long and weighing . It could be fitted with a very sensitive motion-sensitive fuze that would detonate Detonation () is a type of combustion involving a supersonic exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front propagating directly in front of it. Detonations propagate supersonically through shock waves with ... if any attempt was made to move it. It could be lethal in the open to approximately . Because of this, unexploded Thermos bombs were normally destroyed where they fell, either by attaching a long piece of string to them and giving it a jerk, or detonating a small explosive charge near them. A later variant of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Bomb
An aerial bomb is a type of explosive or incendiary weapon intended to travel through the air on a predictable trajectory. Engineers usually develop such bombs to be dropped from an aircraft. The use of aerial bombs is termed aerial bombing. Bomb types Aerial bombs include a vast range and complexity of designs. These include unguided gravity bombs, guided bombs, bombs hand-tossed from a vehicle, bombs needing a large specially-built delivery-vehicle, bombs integrated with the vehicle itself (such as a glide bomb), instant-detonation bombs, or delay-action bombs. As with other types of explosive weapons, aerial bombs aim to kill and injure people or to destroy materiel through the projection of one or more of blast, fragmentation, radiation or fire outwards from the point of detonation. Early bombs The first bombs delivered to their targets by air were single bombs carried on unmanned hot air balloons, launched by the Austrians against Venice in 1849 during the First Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNT (explosive)
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts. History TNT was first prepared in 1863 by German chemist Julius Wilbrand and originally used as a yellow dye. Its potential as an explosive was not recognized for three decades, mainly because it was too difficult to detonate because it was less sensitive than alternatives. Its explosive properties were first discovered in 1891 by another German chemist, Carl Häussermann. TNT can be safely poured when liquid into shell cases, and is so insensitive that in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-handling Device
An anti-handling device is an attachment to or an integral part of a landmine or other munition such as some fuze types found in general-purpose air-dropped bombs, cluster bombs and sea mines. It is designed to prevent tampering or disabling, or to target bomb disposal personnel. When the protected device is disturbed, it detonates, killing or injuring anyone within the blast area. There is a strong functional overlap of booby traps and anti-handling devices. Purpose Anti-handling devices prevent the capture and reuse of the munition by enemy forces. They also hinder bomb disposal or demining operations, both directly and by deterrence, thereby creating a much more effective hazard or barrier. Anti-handling devices greatly increase the danger of munitions to civilian populations in the areas in which they are used because their mechanisms are so easily triggered. An anti-tank mine with an anti-handling device fitted is almost guaranteed to detonate if it is lifted/overturned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Mine
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automatically by way of pressure when a target steps on it or drives over it, although other detonation mechanisms are also sometimes used. A land mine may cause damage by direct blast effect, by fragments that are thrown by the blast, or by both. Landmines are typically laid throughout an area, creating a ''minefield'' which is dangerous to cross. The use of land mines is controversial because of their potential as indiscriminate weapons. They can remain dangerous many years after a conflict has ended, harming civilians and the economy. Seventy-eight countries are contaminated with land mines and 15,000–20,000 people are killed every year while many more are injured. Approximately 80% of land mine casualties are civilians, with children as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regia Aeronautica
The Italian Royal Air Force (''Regia Aeronautica Italiana'') was the name of the air force of the Kingdom of Italy. It was established as a service independent of the Royal Italian Army from 1923 until 1946. In 1946, the monarchy was abolished and the Kingdom of Italy became the Italian Republic, whereupon the name of the air force changed to Aeronautica Militare. History Beginnings At the beginning of the twentieth century, Italy was at the forefront of aerial warfare: during the colonization of Libya in 1911, it made the first reconnaissance flight in history on 23 October, and the first ever bombing raid on 1 November. During World War I, the Italian ''Corpo Aeronautico Militare'', then still part of the ''Regio Esercito'' (Royal Army), operated a mix of French fighters and locally built bombers, notably the gigantic Caproni aircraft. The ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) had its own air arm, operating locally built flying boats. Founding of the ''Regia Aeronautica'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies south of Sicily (Italy), east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The official languages are Maltese and English, and 66% of the current Maltese population is at least conversational in the Italian language. Malta has been inhabited since approximately 5900 BC. Its location in the centre of the Mediterranean has historically given it great strategic importance as a naval base, with a succession of powers having contested and ruled the islands, including the Phoenicians and Carthaginians, Romans, Greeks, Arabs, Normans, Aragonese, Knights of St. John, French, and British, amongst others. With a population of about 516,000 over an area of , Malta is the world's tenth-smallest country in area and fourth most densely populated sovereign cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European part of Turkey), Egypt, Iran, the Levant (including Syria (region), Ash-Shām and Cyprus), Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), and the Socotra Governorate, Socotra Archipelago (a part of Yemen). The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and has been viewed by some to be discriminatory or too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia (including Iran), but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt (not just the Sina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermos L
A vacuum flask (also known as a Dewar flask, Dewar bottle or thermos) is an insulating storage vessel that greatly lengthens the time over which its contents remain hotter or cooler than the flask's surroundings. Invented by Sir James Dewar in 1892, the vacuum flask consists of two flasks, placed one within the other and joined at the neck. The gap between the two flasks is partially evacuated of air, creating a near-vacuum which significantly reduces heat transfer by conduction or convection. When used to hold cold liquids, this also virtually eliminates condensation on the outside of the flask. Vacuum flasks are used domestically to keep beverages hot or cold for extended periods of time, and for keeping cooked food hot. They are also used for thermal cooking. Vacuum flasks are also used for many purposes in industry. History The vacuum flask was designed and invented by Scottish scientist Sir James Dewar in 1892 as a result of his research in the field of cryogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Flask
A vacuum flask (also known as a Dewar flask, Dewar bottle or thermos) is an insulating storage vessel that greatly lengthens the time over which its contents remain hotter or cooler than the flask's surroundings. Invented by Sir James Dewar in 1892, the vacuum flask consists of two flasks, placed one within the other and joined at the neck. The gap between the two flasks is partially evacuated of air, creating a near-vacuum which significantly reduces heat transfer by conduction or convection. When used to hold cold liquids, this also virtually eliminates condensation on the outside of the flask. Vacuum flasks are used domestically to keep beverages hot or cold for extended periods of time, and for keeping cooked food hot. They are also used for thermal cooking. Vacuum flasks are also used for many purposes in industry. History The vacuum flask was designed and invented by Scottish scientist Sir James Dewar in 1892 as a result of his research in the field of cryogenics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
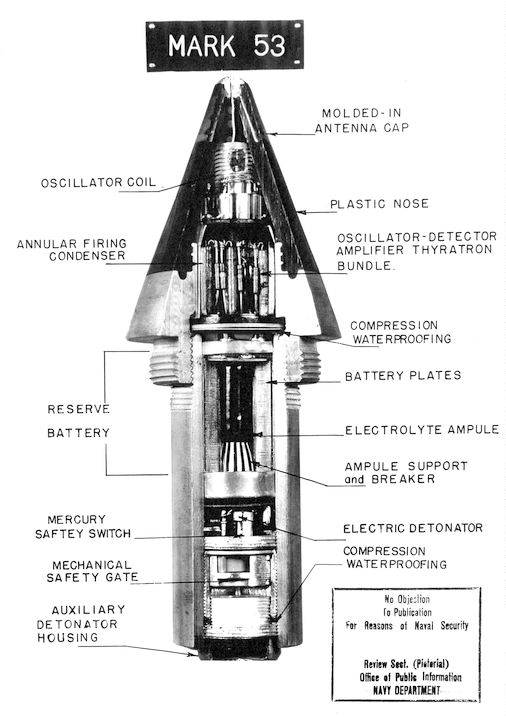
Fuze
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams. A fuze is a device that detonates a munition's explosive material under specified conditions. In addition, a fuze will have safety and arming mechanisms that protect users from premature or accidental detonation. For example, an artillery fuze's battery is activated by the high acceleration of cannon launch, and the fuze must be spinning rapidly before it will function. "Complete bore safety" can be achieved with mechanical shutters that isolate the detonator from the main charge until the shell is fired. A fuze may contain only the electronic or mechanical elements necessary to signal or actuate the detonator, but some fuzes contain a small amount of primary explosive to initiate the detonation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detonate
Detonation () is a type of combustion involving a supersonic exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front propagating directly in front of it. Detonations propagate supersonically through shock waves with speeds in the range of 1 km/sec and differ from deflagrations which have subsonic flame speeds in the range of 1 m/sec. Detonations occur in both conventional solid and liquid explosives, as well as in reactive gases. The velocity of detonation in solid and liquid explosives is much higher than that in gaseous ones, which allows the wave system to be observed with greater detail (higher resolution). A very wide variety of fuels may occur as gases (e.g. hydrogen), droplet fogs, or dust suspensions. In addition to dioxygen, oxidants can include halogen compounds, ozone, hydrogen peroxide and oxides of nitrogen. Gaseous detonations are often associated with a mixture of fuel and oxidant in a composition somewhat below conventional flammabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |