|
BL755
BL755 is a cluster bomb developed by Hunting Aircraft that contains 147 parachute-retarded high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) submunitions. Its primary targets are armoured vehicles and tanks with secondary soft target (anti personnel) capabilities. It entered service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) in 1973. BL755 was developed as a new-generation anti-tank weapon that would allow extremely low-level attacks against Soviet armoured formations. The introduction of the ZSU-23-4 Shilka self-propelled anti-aircraft gun rendered the pop-up attack profile demanded by iron bombs and air-to-ground rockets almost suicidal. The cluster munition would be dropped in pairs while the aircraft overflew the formation at and 300 feet altitude, covering an area of . The weapon's first use in combat was during the Falklands War where it was used in the anti-infantry role. When dropped from ultra-low altitudes, the bomblets proved to have a very high failure rate because the parachutes often di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Bomb
A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are designed to kill personnel and destroy vehicles. Other cluster munitions are designed to destroy runways or electric power transmission lines, disperse chemical or biological weapons, or to scatter land mines. Some submunition-based weapons can disperse non-munitions, such as leaflets. Because cluster bombs release many small bomblets over a wide area, they pose risks to civilians both during attacks and afterwards. Unexploded bomblets can kill or maim civilians and/or unintended targets long after a conflict has ended, and are costly to locate and remove. Cluster munitions are prohibited for those nations that ratified the Convention on Cluster Munitions, adopted in Dublin, Ireland, in May 2008. The Convention entered into force and became binding international law upon ratifyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
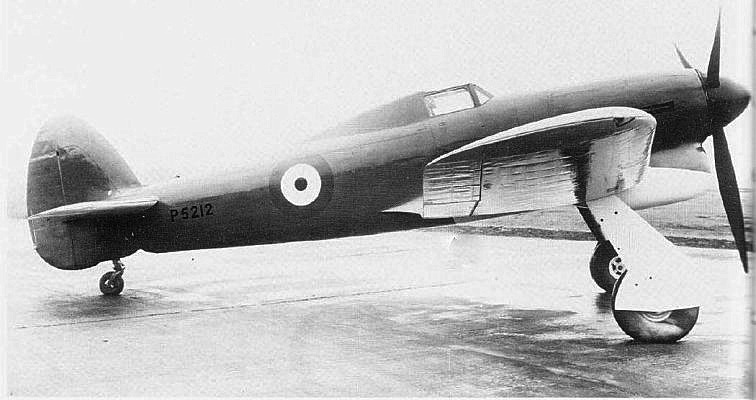
Hawker Hunter
The Hawker Hunter is a transonic British jet-powered fighter aircraft that was developed by Hawker Aircraft for the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It was designed to take advantage of the newly developed Rolls-Royce Avon turbojet engine and the swept wing, and was the first jet-powered aircraft produced by Hawker to be procured by the RAF. On 7 September 1953, the modified first prototype broke the world air speed record for aircraft, achieving a speed of . The single-seat Hunter was introduced to service in 1954 as a manoeuvrable day interceptor aircraft, quickly succeeding first-generation jet fighters in RAF service such as the Gloster Meteor and the de Havilland Venom. The all-weather/night fighter role was filled by the Gloster Javelin. Successively improved variants of the type were produced, adopting increasingly more capable engine models and expanding its fuel capacity amongst other modifications being implemented. Hunters were also us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Altimeter
A radar altimeter (RA), also called a radio altimeter (RALT), electronic altimeter, reflection altimeter, or low-range radio altimeter (LRRA), measures altitude above the terrain presently beneath an aircraft or spacecraft by timing how long it takes a beam of radio waves to travel to ground, reflect, and return to the craft. This type of altimeter provides the distance between the antenna and the ground directly below it, in contrast to a barometric altimeter which provides the distance above a defined vertical datum, usually mean sea level. Principle As the name implies, radar (radio detection and ranging) is the underpinning principle of the system. The system transmits radio waves down to the ground and measures the time it takes them to be reflected back up to the aircraft. The altitude above the ground is calculated from the radio waves' travel time and the speed of light. Radar altimeters required a simple system for measuring the time-of-flight that could be displayed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folding-Fin Aerial Rocket
The Mk 4 Folding-Fin Aerial Rocket (FFAR), also known as "Mighty Mouse", was an unguided rocket used by United States military aircraft. It was 2.75 inches (70 mm) in diameter. Designed as an air-to-air weapon for interceptor aircraft to shoot down enemy bombers, it primarily saw service as an air-to-surface weapon. The FFAR has been developed into the modern Hydra 70 series, which is still in service. History The advent of jet engines for fighters and bombers posed new problems for interceptors. With closing speeds of 1,500 ft/s (457 m/s) or more for head-on interceptions, the time available for a fighter pilot to successfully target an enemy aircraft and inflict sufficient damage to bring it down was increasingly small. Wartime experience had shown that .50 caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns were not powerful enough to reliably down a bomber, certainly not in a single volley, and heavy autocannons did not have the range or rate of fire to ensure a hit. Ung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNEB
The SNEB rocket (french: Societe Nouvelle des Etablissements Edgar Brandt) is an unguided air-to-ground rocket projectile manufactured by the French company ''TDA Armements'', designed for launch by combat aircraft and helicopters. It is also known as the SNEB rocket pod, and sometimes as the Matra rocket, due to its commonly being carried in pod-like launchers built by Matra. Two other rockets were developed in the and caliber. The 37mm caliber was one of the earliest folding fin free flight rockets developed after World War II; it was developed mainly for air-to-air engagements and is no longer in service. The 100mm caliber variant is in service with the French Air Force and a few other air forces. Besides France, several other nations produce the SNEB 68 mm rocket under license. In France today, SNEB has been reorganized into the firm of Thomson-Brandt. Warheads The SNEB rocket projectiles can be armed with the following warheads: *High explosive *High explosive anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island which makes up around 83 percent of the country's landmass. Bahrain is situated between Qatar and the northeastern coast of Saudi Arabia, to which it is connected by the King Fahd Causeway. According to the 2020 census, the country's population numbers 1,501,635, of which 712,362 are Bahraini nationals. Bahrain spans some , and is the third-smallest nation in Asia after the Maldives and Singapore. The capital and largest city is Manama. Bahrain is the site of the ancient Dilmun civilization.Oman: The Lost Land [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
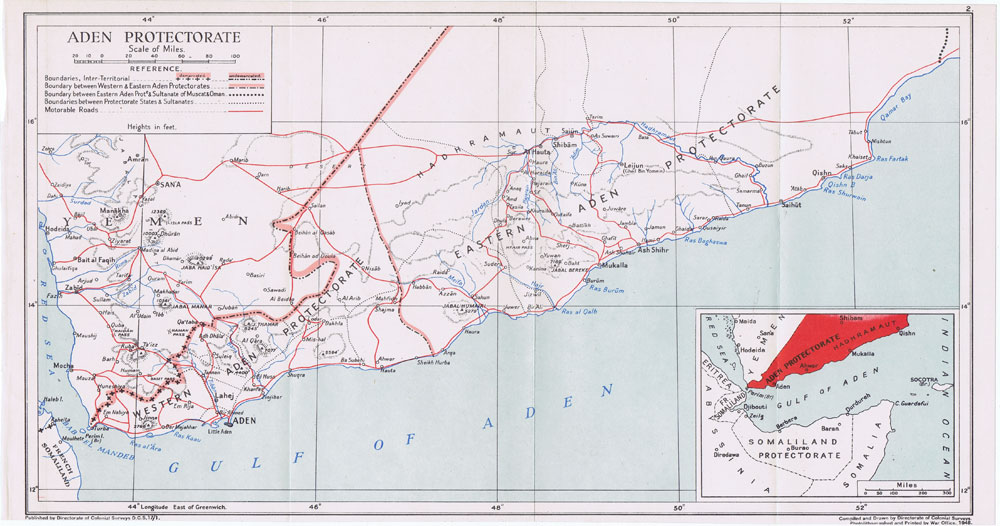
Aden Protectorate
The Aden Protectorate ( ar, محمية عدن ') was a British protectorate in South Arabia which evolved in the hinterland of the port of Aden and in the Hadhramaut following the conquest of Aden by the Bombay Presidency of British India in 1839, and it continued until the 1960s. In 1940 it was divided for administrative purposes into the Western Protectorate and the Eastern Protectorate. Today the territory forms part of the Republic of Yemen. The rulers of the Aden Protectorate, as generally with the other British protectorates and protected states, remained sovereign: their flags still flew over their government buildings, government was still carried out by them or in their names, and their states maintained a distinct 'international personality' in the eyes of international law, in contrast to states forming part of the British Empire, such as Aden Colony, where the British monarch was the head of every state. History Informal beginnings What became known as the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and Oman to the Oman–Yemen border, northeast and shares maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalia. Yemen is the second-largest Arabs, Arab sovereign state in the peninsula, occupying , with a coastline stretching about . Its constitutionally stated Capital city, capital, and largest city, is Sanaa. As of 2021, Yemen has an estimated population of some 30.4 million. In ancient times, Yemen was the home of the Sabaeans, a trading state that included parts of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. Later in 275 AD, the Himyarite Kingdom was influenced by Judaism. Christianity arrived in the fourth century. Islam spread quickly in the seventh century and Yemenite troops were crucial in the early Islamic conquests. Several Dynasty, dynasties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aden Emergency
The Aden Emergency, also known as the Radfan Uprising (), was an armed rebellion by NLF and FLOSY during the Cold War against the Federation of South Arabia, a protectorate of the United Kingdom, which now forms part of Yemen. Partly inspired by Gamal Abdel Nasser's pan-Arab nationalism, it began on 14 October 1963 with the throwing of a grenade at a gathering of British officials at Aden Airport. A state of emergency was then declared in the British Crown colony of Aden and its hinterland, the Aden Protectorate. The emergency escalated in 1967 and hastened the end of British rule in the territory which had begun in 1839. On 30 November 1967, British forces withdrew and the independent People's Republic of South Yemen was proclaimed. Background Aden was originally of interest to Britain as an anti-piracy station to protect shipping on the routes to British India. With the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, it further served as a coaling station. Over the period since the anne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Tactical Air Force
The RAF Second Tactical Air Force (2TAF) was one of three tactical air forces within the Royal Air Force (RAF) during and after the Second World War. It was made up of squadrons and personnel from the RAF, other British Commonwealth air forces, and exiles from German-occupied Europe. Renamed as British Air Forces of Occupation in 1945, 2TAF was recreated in 1951 and became Royal Air Force Germany in 1959. Formation 2TAF was formed on 1 June 1943 as HQ Tactical Air Force from Army Co-operation Command, in connection with preparations then in train to invade Europe a year later. It took units from both Fighter Command and Bomber Command in order to form a force capable of supporting the Army in the field. Bomber Command provided No. 2 Group with light bombers; Fighter Command was split into the Air Defence of Great Britain, retaining fighter units for home defence, and No. 83 Group and No. 84 Group operating aircraft, and No. 85 Group controlling ground-based units, for the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Typhoon
The Hawker Typhoon is a British single-seat fighter-bomber, produced by Hawker Aircraft. It was intended to be a medium-high altitude interceptor, as a replacement for the Hawker Hurricane, but several design problems were encountered and it never completely satisfied this requirement.Thomas and Shores 1988, p. 16. The Typhoon was originally designed to mount twelve .303 inch (7.7 mm) Browning machine guns and be powered by the latest engines. Its service introduction in mid-1941 was plagued with problems and for several months the aircraft faced a doubtful future. When the ''Luftwaffe'' brought the new Focke-Wulf Fw 190 into service in 1941, the Typhoon was the only RAF fighter capable of catching it at low altitudes; as a result it secured a new role as a low-altitude interceptor. The Typhoon became established in roles such as night-time intruder and long-range fighter. From late 1942 the Typhoon was equipped with bombs and from late 1943 RP-3 rockets were added to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)