Chlorine (band) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chlorine is a chemical element with the
p. 105:
''"Accipe salis petrae, vitrioli, & alumnis partes aequas: exsiccato singula, & connexis simul, distilla aquam. Quae nil aliud est, quam merum sal volatile. Hujus accipe uncias quatuor, salis armeniaci unciam junge, in forti vitro, alembico, per caementum (ex cera, colophonia, & vitri pulverre) calidissime affusum, firmato; mox, etiam in frigore, Gas excitatur, & vas, utut forte, dissilit cum fragore."'' (Take equal parts of saltpeter .e., sodium nitrate vitriol .e., concentrated sulfuric acid and alum: dry each and combine simultaneously; distill off the water .e., liquid That istillateis nothing else than pure volatile salt .e., spirit of nitre, nitric acid Take four ounces of this iz, nitric acid add one ounce of Armenian salt .e., ammonium chloride lace itin a strong glass alembic sealed by cement ( adefrom wax, rosin, and powdered glass)
p. 408
''"Sal armeniacus enim, & aqua chrysulca, quae singula per se distillari, possunt, & pati calorem: sin autem jungantur, & intepescant, non possunt non, quin statim in Gas sylvestre, sive incoercibilem flatum transmutentur."'' (Truly Armenian salt .e., ammonium chlorideand nitric acid, each of which can be distilled by itself, and submitted to heat; but if, on the other hand, they be combined and become warm, they cannot but be changed immediately into carbon dioxide ote: van Helmont's identification of the gas is mistakenor an incondensable gas.)
See also:
Helmont, Johannes (Joan) Baptista Van, Encyclopedia.Com
"Others were chlorine gas from the reaction of nitric acid and sal ammoniac; … " * Wisniak, Jaime (2009) "Carl Wilhelm Scheele," ''Revista CENIC Ciencias Químicas'', 40 (3): 165–73 ; see p. 168: "Early in the seventeenth century Johannes Baptiste van Helmont (1579–1644) mentioned that when sal marin (sodium chloride) or sal ammoniacus and aqua chrysulca (nitric acid) were mixed together, a flatus incoercible (non-condensable gas) was evolved."
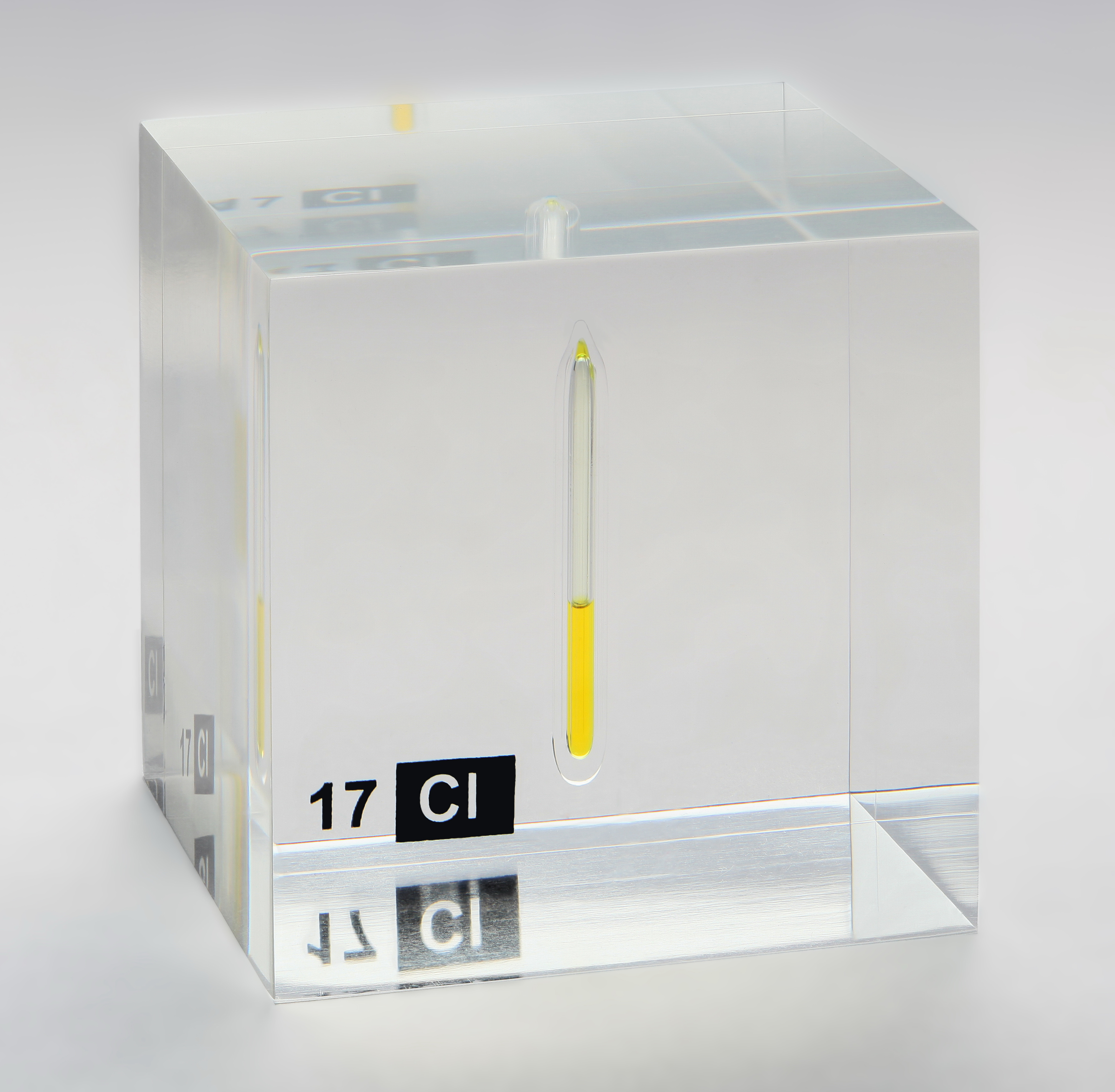
 Chlorine is the second
Chlorine is the second
 The simplest chlorine compound is hydrogen chloride, HCl, a major chemical in industry as well as in the laboratory, both as a gas and dissolved in water as hydrochloric acid. It is often produced by burning hydrogen gas in chlorine gas, or as a byproduct of chlorinating hydrocarbons. Another approach is to treat
The simplest chlorine compound is hydrogen chloride, HCl, a major chemical in industry as well as in the laboratory, both as a gas and dissolved in water as hydrochloric acid. It is often produced by burning hydrogen gas in chlorine gas, or as a byproduct of chlorinating hydrocarbons. Another approach is to treat
 Nearly all elements in the periodic table form binary chlorides. The exceptions are decidedly in the minority and stem in each case from one of three causes: extreme inertness and reluctance to participate in chemical reactions (the noble gases, with the exception of xenon in the highly unstable XeCl2 and XeCl4); extreme nuclear instability hampering chemical investigation before decay and transmutation (many of the heaviest elements beyond bismuth); and having an electronegativity higher than chlorine's ( oxygen and
Nearly all elements in the periodic table form binary chlorides. The exceptions are decidedly in the minority and stem in each case from one of three causes: extreme inertness and reluctance to participate in chemical reactions (the noble gases, with the exception of xenon in the highly unstable XeCl2 and XeCl4); extreme nuclear instability hampering chemical investigation before decay and transmutation (many of the heaviest elements beyond bismuth); and having an electronegativity higher than chlorine's ( oxygen and

 The chlorine oxides are well-studied in spite of their instability (all of them are endothermic compounds). They are important because they are produced when chlorofluorocarbons undergo photolysis in the upper atmosphere and cause the destruction of the ozone layer. None of them can be made from directly reacting the elements.
Dichlorine monoxide (Cl2O) is a brownish-yellow gas (red-brown when solid or liquid) which may be obtained by reacting chlorine gas with yellow mercury(II) oxide. It is very soluble in water, in which it is in equilibrium with hypochlorous acid (HOCl), of which it is the anhydride. It is thus an effective bleach and is mostly used to make
The chlorine oxides are well-studied in spite of their instability (all of them are endothermic compounds). They are important because they are produced when chlorofluorocarbons undergo photolysis in the upper atmosphere and cause the destruction of the ozone layer. None of them can be made from directly reacting the elements.
Dichlorine monoxide (Cl2O) is a brownish-yellow gas (red-brown when solid or liquid) which may be obtained by reacting chlorine gas with yellow mercury(II) oxide. It is very soluble in water, in which it is in equilibrium with hypochlorous acid (HOCl), of which it is the anhydride. It is thus an effective bleach and is mostly used to make
 Like the other carbon–halogen bonds, the C–Cl bond is a common functional group that forms part of core organic chemistry. Formally, compounds with this functional group may be considered organic derivatives of the chloride anion. Due to the difference of electronegativity between chlorine (3.16) and carbon (2.55), the carbon in a C–Cl bond is electron-deficient and thus
Like the other carbon–halogen bonds, the C–Cl bond is a common functional group that forms part of core organic chemistry. Formally, compounds with this functional group may be considered organic derivatives of the chloride anion. Due to the difference of electronegativity between chlorine (3.16) and carbon (2.55), the carbon in a C–Cl bond is electron-deficient and thus
 Chlorine is too reactive to occur as the free element in nature but is very abundant in the form of its chloride salts. It is the twenty-first most abundant element in Earth's crust and makes up 126 parts per million of it, through the large deposits of chloride minerals, especially
Chlorine is too reactive to occur as the free element in nature but is very abundant in the form of its chloride salts. It is the twenty-first most abundant element in Earth's crust and makes up 126 parts per million of it, through the large deposits of chloride minerals, especially  In the Deacon process, hydrogen chloride recovered from the production of organochlorine compounds is recovered as chlorine. The process relies on oxidation using oxygen:
: 4 HCl + O2 → 2 Cl2 + 2 H2O
The reaction requires a catalyst. As introduced by Deacon, early catalysts were based on copper. Commercial processes, such as the Mitsui MT-Chlorine Process, have switched to chromium and ruthenium-based catalysts.Schmittinger, Peter ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorine" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., The chlorine produced is available in cylinders from sizes ranging from 450 g to 70 kg, as well as drums (865 kg), tank wagons (15 tonnes on roads; 27–90 tonnes by rail), and barges (600–1200 tonnes).
In the Deacon process, hydrogen chloride recovered from the production of organochlorine compounds is recovered as chlorine. The process relies on oxidation using oxygen:
: 4 HCl + O2 → 2 Cl2 + 2 H2O
The reaction requires a catalyst. As introduced by Deacon, early catalysts were based on copper. Commercial processes, such as the Mitsui MT-Chlorine Process, have switched to chromium and ruthenium-based catalysts.Schmittinger, Peter ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorine" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., The chlorine produced is available in cylinders from sizes ranging from 450 g to 70 kg, as well as drums (865 kg), tank wagons (15 tonnes on roads; 27–90 tonnes by rail), and barges (600–1200 tonnes).
The Foul and the Fragrant: Odor and the French Social Imagination
''. Harvard University Press. pp. 121–22. These "putrid miasmas" were thought by many to cause the spread of "contagion" and "infection" – both words used before the germ theory of infection. Chloride of lime was used for destroying odors and "putrid matter". One source claims chloride of lime was used by Dr. John Snow to disinfect water from the cholera-contaminated well that was feeding the Broad Street pump in 1854 London, though three other reputable sources that describe that famous cholera epidemic do not mention the incident.Vinten-Johansen, Peter, Howard Brody, Nigel Paneth, Stephen Rachman and Michael Rip. (2003). ''Cholera, Chloroform, and the Science of Medicine''. New York:Oxford University. One reference makes it clear that chloride of lime was used to disinfect the offal and filth in the streets surrounding the Broad Street pump – a common practice in mid-nineteenth century England.
 Perhaps the most famous application of Labarraque's chlorine and
Perhaps the most famous application of Labarraque's chlorine and
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
s, it appears between fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.
Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride salts like ammonium chloride ( sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g ...
(common salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of Salt (chemistry), salts; salt in the form of a natural crystallinity, crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. ...
), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and hydrochloric acid (in the form of ). However, the nature of free chlorine gas as a separate substance was only recognised around 1630 by Jan Baptist van Helmont. Carl Wilhelm Scheele wrote a description of chlorine gas in 1774, supposing it to be an oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
of a new element. In 1809, chemists suggested that the gas might be a pure element, and this was confirmed by Sir Humphry Davy in 1810, who named it after the Ancient Greek (, "pale green") because of its colour.
Because of its great reactivity, all chlorine in the Earth's crust is in the form of ionic chloride compounds, which includes table salt. It is the second-most abundant halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
(after fluorine) and twenty-first most abundant chemical element in Earth's crust. These crustal deposits are nevertheless dwarfed by the huge reserves of chloride in seawater.
Elemental chlorine is commercially produced from brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for br ...
by electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
, predominantly in the chlor-alkali process. The high oxidising potential of elemental chlorine led to the development of commercial bleaches and disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than st ...
s, and a reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
for many processes in the chemical industry. Chlorine is used in the manufacture of a wide range of consumer products, about two-thirds of them organic chemicals such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), many intermediates for the production of plastics
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their Plasticity (physics), plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be Injection moulding, moulded, Extrusion, e ...
, and other end products which do not contain the element. As a common disinfectant, elemental chlorine and chlorine-generating compounds are used more directly in swimming pool
A swimming pool, swimming bath, wading pool, paddling pool, or simply pool, is a structure designed to hold water to enable Human swimming, swimming or other leisure activities. Pools can be built into the ground (in-ground pools) or built ...
s to keep them sanitary. Elemental chlorine at high concentration is extremely dangerous, and poisonous to most living organisms. As a chemical warfare
Chemical warfare (CW) involves using the toxic properties of chemical substances as weapons. This type of warfare is distinct from nuclear warfare, biological warfare and radiological warfare, which together make up CBRN, the military acronym ...
agent, chlorine was first used in World War I as a poison gas weapon.
In the form of chloride ions, chlorine is necessary to all known species of life. Other types of chlorine compounds are rare in living organisms, and artificially produced chlorinated organics range from inert to toxic. In the upper atmosphere, chlorine-containing organic molecules such as chlorofluorocarbons have been implicated in ozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone l ...
. Small quantities of elemental chlorine are generated by oxidation of chloride ions in neutrophils as part of an immune system response against bacteria.
History
The most common compound of chlorine, sodium chloride, has been known since ancient times; archaeologists have found evidence that rock salt was used as early as 3000 BC andbrine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for br ...
as early as 6000 BC.
Early discoveries
Around 900, the authors of the Arabic writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan (Latin: Geber) and the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) were experimenting with sal ammoniac ( ammonium chloride), which when it was distilled together with vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals) produced hydrogen chloride. However, it appears that in these early experiments with chloride salts, the gaseous products were discarded, and hydrogen chloride may have been produced many times before it was discovered that it can be put to chemical use. One of the first such uses was the synthesis of mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), whose production from the heating ofmercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
either with alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , where is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium or a ...
and ammonium chloride or with vitriol and sodium chloride was first described in the ''De aluminibus et salibus'' ("On Alums and Salts", an eleventh- or twelfth century Arabic text falsely attributed to Abu Bakr al-Razi and translated into Latin in the second half of the twelfth century by Gerard of Cremona, 1144–1187). Another important development was the discovery by pseudo-Geber (in the ''De inventione veritatis'', "On the Discovery of Truth", after c. 1300) that by adding ammonium chloride to nitric acid, a strong solvent capable of dissolving gold (i.e., '' aqua regia'') could be produced. Although ''aqua regia'' is an unstable mixture that continually gives off fumes containing free chlorine gas, this chlorine gas appears to have been ignored until c. 1630, when its nature as a separate gaseous substance was recognised by the Brabantian chemist and physician Jan Baptist van Helmont. From ''"Complexionum atque mistionum elementalium figmentum."'' (Formation of combinations and of mixtures of elements), §37p. 105:
''"Accipe salis petrae, vitrioli, & alumnis partes aequas: exsiccato singula, & connexis simul, distilla aquam. Quae nil aliud est, quam merum sal volatile. Hujus accipe uncias quatuor, salis armeniaci unciam junge, in forti vitro, alembico, per caementum (ex cera, colophonia, & vitri pulverre) calidissime affusum, firmato; mox, etiam in frigore, Gas excitatur, & vas, utut forte, dissilit cum fragore."'' (Take equal parts of saltpeter .e., sodium nitrate vitriol .e., concentrated sulfuric acid and alum: dry each and combine simultaneously; distill off the water .e., liquid That istillateis nothing else than pure volatile salt .e., spirit of nitre, nitric acid Take four ounces of this iz, nitric acid add one ounce of Armenian salt .e., ammonium chloride lace itin a strong glass alembic sealed by cement ( adefrom wax, rosin, and powdered glass)
hat has been
A hat is a head covering which is worn for various reasons, including protection against weather conditions, ceremonial reasons such as university graduation, religious reasons, safety, or as a fashion accessory. Hats which incorporate mecha ...
poured very hot; soon, even in the cold, gas is stimulated, and the vessel, however strong, bursts into fragments.) From ''"De Flatibus"'' (On gases)p. 408
''"Sal armeniacus enim, & aqua chrysulca, quae singula per se distillari, possunt, & pati calorem: sin autem jungantur, & intepescant, non possunt non, quin statim in Gas sylvestre, sive incoercibilem flatum transmutentur."'' (Truly Armenian salt .e., ammonium chlorideand nitric acid, each of which can be distilled by itself, and submitted to heat; but if, on the other hand, they be combined and become warm, they cannot but be changed immediately into carbon dioxide ote: van Helmont's identification of the gas is mistakenor an incondensable gas.)
See also:
Helmont, Johannes (Joan) Baptista Van, Encyclopedia.Com
"Others were chlorine gas from the reaction of nitric acid and sal ammoniac; … " * Wisniak, Jaime (2009) "Carl Wilhelm Scheele," ''Revista CENIC Ciencias Químicas'', 40 (3): 165–73 ; see p. 168: "Early in the seventeenth century Johannes Baptiste van Helmont (1579–1644) mentioned that when sal marin (sodium chloride) or sal ammoniacus and aqua chrysulca (nitric acid) were mixed together, a flatus incoercible (non-condensable gas) was evolved."

Isolation
The element was first studied in detail in 1774 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele, and he is credited with the discovery. Scheele produced chlorine by reacting MnO2 (as the mineralpyrolusite
Pyrolusite is a mineral consisting essentially of manganese dioxide ( Mn O2) and is important as an ore of manganese.. It is a black, amorphous appearing mineral, often with a granular, fibrous, or columnar structure, sometimes forming reniform ...
) with HCl:
:4 HCl + MnO2 → MnCl2 + 2 H2O + Cl2
Scheele observed several of the properties of chlorine: the bleaching effect on litmus, the deadly effect on insects, the yellow-green color, and the smell similar to aqua regia. He called it "''dephlogisticated muriatic acid air''" since it is a gas (then called "airs") and it came from hydrochloric acid (then known as "muriatic acid"). He failed to establish chlorine as an element.
Common chemical theory at that time held that an acid is a compound that contains oxygen (remnants of this survive in the German and Dutch names of oxygen: ''sauerstoff'' or ''zuurstof'', both translating into English as ''acid substance''), so a number of chemists, including Claude Berthollet, suggested that Scheele's ''dephlogisticated muriatic acid air'' must be a combination of oxygen and the yet undiscovered element, ''muriaticum''.
In 1809, Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis-Jacques Thénard tried to decompose ''dephlogisticated muriatic acid air'' by reacting it with charcoal to release the free element ''muriaticum'' (and carbon dioxide). They did not succeed and published a report in which they considered the possibility that ''dephlogisticated muriatic acid air'' is an element, but were not convinced.
In 1810, Sir Humphry Davy tried the same experiment again, and concluded that the substance was an element, and not a compound. He announced his results to the Royal Society on 15 November that year. At that time, he named this new element "chlorine", from the Greek word χλωρος (''chlōros'', "green-yellow"), in reference to its color. The name "halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
", meaning "salt producer", was originally used for chlorine in 1811 by Johann Salomo Christoph Schweigger
Johann Salomo Christoph Schweigger (8 April 1779 – 6 September 1857) was a German chemist, physicist, and professor of mathematics born in Erlangen.
J.S.C.Schweigger was the son of Friedrich Christian Lorenz Schweigger, professor of theologie ...
. This term was later used as a generic term to describe all the elements in the chlorine family (fluorine, bromine, iodine), after a suggestion by Jöns Jakob Berzelius in 1826. In 1823, Michael Faraday liquefied chlorine for the first time, and demonstrated that what was then known as "solid chlorine" had a structure of chlorine hydrate (Cl2·H2O).
Later uses
Chlorine gas was first used by French chemist Claude Berthollet to bleach textiles in 1785. Modern bleaches resulted from further work by Berthollet, who first produced sodium hypochlorite in 1789 in his laboratory in the town of Javel (now part of Paris, France), by passing chlorine gas through a solution of sodium carbonate. The resulting liquid, known as "''Eau de Javel''" (" Javel water"), was a weak solution of sodium hypochlorite. This process was not very efficient, and alternative production methods were sought. Scottish chemist and industrialist Charles Tennant first produced a solution ofcalcium hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(OCl)2. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent. Thi ...
("chlorinated lime"), then solid calcium hypochlorite (bleaching powder). These compounds produced low levels of elemental chlorine and could be more efficiently transported than sodium hypochlorite, which remained as dilute solutions because when purified to eliminate water, it became a dangerously powerful and unstable oxidizer. Near the end of the nineteenth century, E. S. Smith patented a method of sodium hypochlorite production involving electrolysis of brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for br ...
to produce sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
and chlorine gas, which then mixed to form sodium hypochlorite. This is known as the chloralkali process, first introduced on an industrial scale in 1892, and now the source of most elemental chlorine and sodium hydroxide. In 1884 Chemischen Fabrik Griesheim of Germany developed another chloralkali process which entered commercial production in 1888.
Elemental chlorine solutions dissolved in chemically basic water (sodium and calcium hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(OCl)2. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent. Thi ...
) were first used as anti- putrefaction agents and disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than st ...
s in the 1820s, in France, long before the establishment of the germ theory of disease. This practice was pioneered by Antoine-Germain Labarraque, who adapted Berthollet's "Javel water" bleach and other chlorine preparations (for a more complete history, see below). Elemental chlorine has since served a continuous function in topical antisepsis (wound irrigation solutions and the like) and public sanitation, particularly in swimming and drinking water.
Chlorine gas was first used as a weapon on April 22, 1915, at Ypres by the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
. The effect on the allies was devastating because the existing gas mask
A gas mask is a mask used to protect the wearer from inhaling airborne pollutants and toxic gases. The mask forms a sealed cover over the nose and mouth, but may also cover the eyes and other vulnerable soft tissues of the face. Most gas mask ...
s were difficult to deploy and had not been broadly distributed.
Properties

 Chlorine is the second
Chlorine is the second halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
, being a nonmetal
In chemistry, a nonmetal is a chemical element that generally lacks a predominance of metallic properties; they range from colorless gases (like hydrogen) to shiny solids (like carbon, as graphite). The electrons in nonmetals behave differentl ...
in group 17 of the periodic table. Its properties are thus similar to fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
, bromine, and iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
, and are largely intermediate between those of the first two. Chlorine has the electron configuration es23p5, with the seven electrons in the third and outermost shell acting as its valence electrons. Like all halogens, it is thus one electron short of a full octet, and is hence a strong oxidising agent, reacting with many elements in order to complete its outer shell. Corresponding to periodic trends, it is intermediate in electronegativity between fluorine and bromine (F: 3.98, Cl: 3.16, Br: 2.96, I: 2.66), and is less reactive than fluorine and more reactive than bromine. It is also a weaker oxidising agent than fluorine, but a stronger one than bromine. Conversely, the chloride ion is a weaker reducing agent than bromide, but a stronger one than fluoride. It is intermediate in atomic radius between fluorine and bromine, and this leads to many of its atomic properties similarly continuing the trend from iodine to bromine upward, such as first ionisation energy, electron affinity, enthalpy of dissociation of the X2 molecule (X = Cl, Br, I), ionic radius, and X–X bond length. (Fluorine is anomalous due to its small size.)
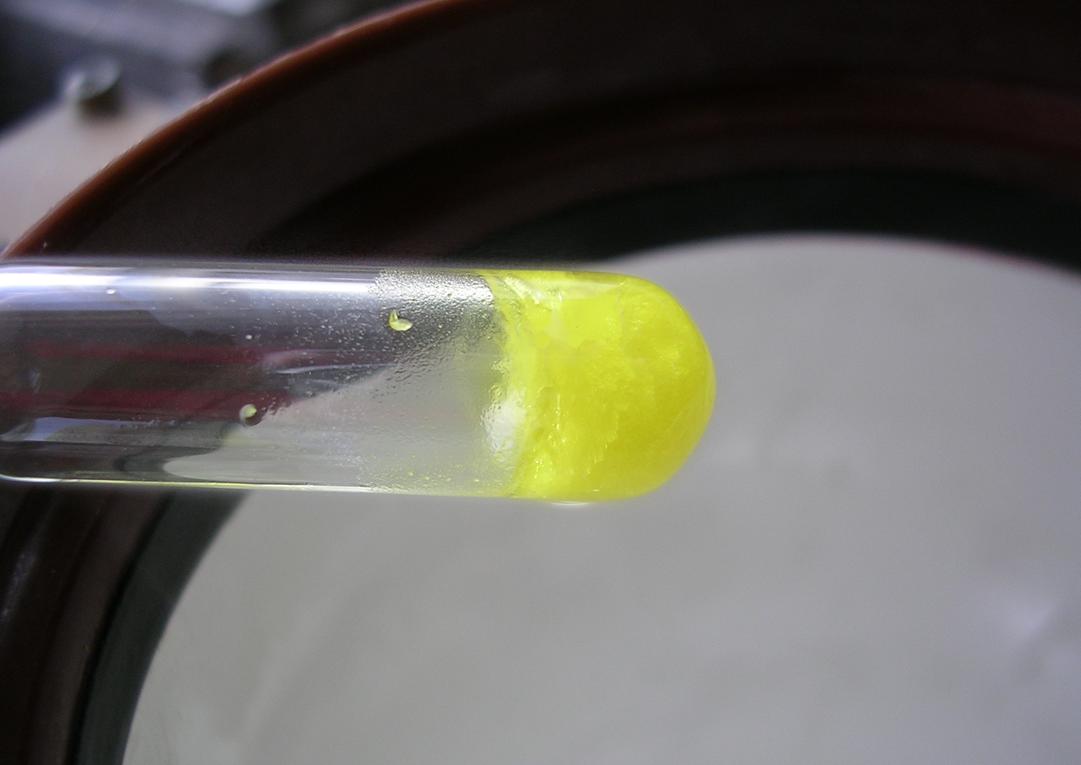
All four stable halogens experience intermolecular van der Waals forces of attraction, and their strength increases together with the number of electrons among all homonuclear diatomic halogen molecules. Thus, the melting and boiling points of chlorine are intermediate between those of fluorine and bromine: chlorine melts at −101.0 °C and boils at −34.0 °C. As a result of the increasing molecular weight of the halogens down the group, the density and heats of fusion and vaporisation of chlorine are again intermediate between those of bromine and fluorine, although all their heats of vaporisation are fairly low (leading to high volatility) thanks to their diatomic molecular structure. The halogens darken in colour as the group is descended: thus, while fluorine is a pale yellow gas, chlorine is distinctly yellow-green. This trend occurs because the wavelengths of visible light absorbed by the halogens increase down the group. Specifically, the colour of a halogen, such as chlorine, results from the electron transition
A quantum jump is the abrupt transition of a quantum system (atom, molecule, atomic nucleus) from one quantum state to another, from one energy level to another. When the system absorbs energy, there is a transition to a higher energy level (exc ...
between the highest occupied antibonding ''πg'' molecular orbital and the lowest vacant antibonding ''σu'' molecular orbital. The colour fades at low temperatures, so that solid chlorine at −195 °C is almost colourless.
Like solid bromine and iodine, solid chlorine crystallises in the orthorhombic crystal system, in a layered lattice of Cl2 molecules. The Cl–Cl distance is 198 pm (close to the gaseous Cl–Cl distance of 199 pm) and the Cl···Cl distance between molecules is 332 pm within a layer and 382 pm between layers (compare the van der Waals radius of chlorine, 180 pm). This structure means that chlorine is a very poor conductor of electricity, and indeed its conductivity is so low as to be practically unmeasurable.
Isotopes
Chlorine has two stable isotopes, 35Cl and 37Cl. These are its only two natural isotopes occurring in quantity, with 35Cl making up 76% of natural chlorine and 37Cl making up the remaining 24%. Both are synthesised in stars in the oxygen-burning and silicon-burning processes. Both have nuclear spin 3/2+ and thus may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance, although the spin magnitude being greater than 1/2 results in non-spherical nuclear charge distribution and thus resonance broadening as a result of a nonzeronuclear quadrupole moment Nuclear quadrupole resonance spectroscopy or NQR is a chemical analysis technique related to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Unlike NMR, NQR transitions of nuclei can be detected in the absence of a magnetic field, and for this reason NQR spectro ...
and resultant quadrupolar relaxation. The other chlorine isotopes are all radioactive, with half-lives too short to occur in nature primordially. Of these, the most commonly used in the laboratory are 36Cl (''t''1/2 = 3.0×105 y) and 38Cl (''t''1/2 = 37.2 min), which may be produced from the neutron activation of natural chlorine.
The most stable chlorine radioisotope is 36Cl. The primary decay mode of isotopes lighter than 35Cl is electron capture to isotopes of sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
; that of isotopes heavier than 37Cl is beta decay to isotopes of argon; and 36Cl may decay by either mode to stable 36S or 36Ar. 36Cl occurs in trace quantities in nature as a cosmogenic nuclide in a ratio of about (7–10) × 10−13 to 1 with stable chlorine isotopes: it is produced in the atmosphere by spallation
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary p ...
of 36 Ar by interactions with cosmic ray proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
s. In the top meter of the lithosphere, 36Cl is generated primarily by thermal neutron activation of 35Cl and spallation of 39 K and 40 Ca. In the subsurface environment, muon capture by 40 Ca becomes more important as a way to generate 36Cl.
Chemistry and compounds
Chlorine is intermediate in reactivity between fluorine and bromine, and is one of the most reactive elements. Chlorine is a weaker oxidising agent than fluorine but a stronger one than bromine or iodine. This can be seen from the standard electrode potentials of the X2/X− couples (F, +2.866 V; Cl, +1.395 V; Br, +1.087 V; I, +0.615 V; At, approximately +0.3 V). However, this trend is not shown in the bond energies because fluorine is singular due to its small size, low polarisability, and inability to show hypervalence. As another difference, chlorine has a significant chemistry in positive oxidation states while fluorine does not. Chlorination often leads to higher oxidation states than bromination or iodination but lower oxidation states than fluorination. Chlorine tends to react with compounds including M–M, M–H, or M–C bonds to form M–Cl bonds. Given that E°(O2/H2O) = +1.229 V, which is less than +1.395 V, it would be expected that chlorine should be able to oxidise water to oxygen and hydrochloric acid. However, the kinetics of this reaction are unfavorable, and there is also a bubble overpotential effect to consider, so that electrolysis of aqueous chloride solutions evolves chlorine gas and not oxygen gas, a fact that is very useful for the industrial production of chlorine.Hydrogen chloride
 The simplest chlorine compound is hydrogen chloride, HCl, a major chemical in industry as well as in the laboratory, both as a gas and dissolved in water as hydrochloric acid. It is often produced by burning hydrogen gas in chlorine gas, or as a byproduct of chlorinating hydrocarbons. Another approach is to treat
The simplest chlorine compound is hydrogen chloride, HCl, a major chemical in industry as well as in the laboratory, both as a gas and dissolved in water as hydrochloric acid. It is often produced by burning hydrogen gas in chlorine gas, or as a byproduct of chlorinating hydrocarbons. Another approach is to treat sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g ...
with concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
to produce hydrochloric acid, also known as the "salt-cake" process:
:NaCl + H2SO4 NaHSO4 + HCl
:NaCl + NaHSO4 Na2SO4 + HCl
In the laboratory, hydrogen chloride gas may be made by drying the acid with concentrated sulfuric acid. Deuterium chloride, DCl, may be produced by reacting benzoyl chloride
Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula . It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour, and consists of a benzene ring () with an acyl chloride () substituent. It i ...
with heavy water (D2O).
At room temperature, hydrogen chloride is a colourless gas, like all the hydrogen halides apart from hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock i ...
, since hydrogen cannot form strong hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s to the larger electronegative chlorine atom; however, weak hydrogen bonding is present in solid crystalline hydrogen chloride at low temperatures, similar to the hydrogen fluoride structure, before disorder begins to prevail as the temperature is raised. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid (p''K''a = −7) because the hydrogen bonds to chlorine are too weak to inhibit dissociation. The HCl/H2O system has many hydrates HCl·''n''H2O for ''n'' = 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6. Beyond a 1:1 mixture of HCl and H2O, the system separates completely into two separate liquid phases. Hydrochloric acid forms an azeotrope with boiling point 108.58 °C at 20.22 g HCl per 100 g solution; thus hydrochloric acid cannot be concentrated beyond this point by distillation.
Unlike hydrogen fluoride, anhydrous liquid hydrogen chloride is difficult to work with as a solvent, because its boiling point is low, it has a small liquid range, its dielectric constant
The relative permittivity (in older texts, dielectric constant) is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insulat ...
is low and it does not dissociate appreciably into H2Cl+ and ions – the latter, in any case, are much less stable than the bifluoride ions () due to the very weak hydrogen bonding between hydrogen and chlorine, though its salts with very large and weakly polarising cations such as Cs+ and (R = Me, Et, Bu''n'') may still be isolated. Anhydrous hydrogen chloride is a poor solvent, only able to dissolve small molecular compounds such as nitrosyl chloride and phenol, or salts with very low lattice energies such as tetraalkylammonium halides. It readily protonates electrophiles containing lone-pairs or π bonds. Solvolysis, ligand replacement reactions, and oxidations are well-characterised in hydrogen chloride solution:
:Ph3SnCl + HCl ⟶ Ph2SnCl2 + PhH (solvolysis)
:Ph3COH + 3 HCl ⟶ + H3O+Cl− (solvolysis)
: + BCl3 ⟶ + HCl (ligand replacement)
:PCl3 + Cl2 + HCl ⟶ (oxidation)
Other binary chlorides
 Nearly all elements in the periodic table form binary chlorides. The exceptions are decidedly in the minority and stem in each case from one of three causes: extreme inertness and reluctance to participate in chemical reactions (the noble gases, with the exception of xenon in the highly unstable XeCl2 and XeCl4); extreme nuclear instability hampering chemical investigation before decay and transmutation (many of the heaviest elements beyond bismuth); and having an electronegativity higher than chlorine's ( oxygen and
Nearly all elements in the periodic table form binary chlorides. The exceptions are decidedly in the minority and stem in each case from one of three causes: extreme inertness and reluctance to participate in chemical reactions (the noble gases, with the exception of xenon in the highly unstable XeCl2 and XeCl4); extreme nuclear instability hampering chemical investigation before decay and transmutation (many of the heaviest elements beyond bismuth); and having an electronegativity higher than chlorine's ( oxygen and fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
) so that the resultant binary compounds are formally not chlorides but rather oxides or fluorides of chlorine. Even though nitrogen in NCl3 is bearing a negative charge, the compound is usually called nitrogen trichloride
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NCl3. This yellow, oily, pungent-smelling and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a byproduct of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivative ...
.
Chlorination of metals with Cl2 usually leads to a higher oxidation state than bromination with Br2 when multiple oxidation states are available, such as in MoCl5 and MoBr3. Chlorides can be made by reaction of an element or its oxide, hydroxide, or carbonate with hydrochloric acid, and then dehydrated by mildly high temperatures combined with either low pressure or anhydrous hydrogen chloride gas. These methods work best when the chloride product is stable to hydrolysis; otherwise, the possibilities include high-temperature oxidative chlorination of the element with chlorine or hydrogen chloride, high-temperature chlorination of a metal oxide or other halide by chlorine, a volatile metal chloride, carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVAC ...
, or an organic chloride. For instance, zirconium dioxide reacts with chlorine at standard conditions to produce zirconium tetrachloride
Zirconium(IV) chloride, also known as zirconium tetrachloride, () is an inorganic compound frequently used as a precursor to other compounds of zirconium. This white high-melting solid hydrolyzes rapidly in humid air.
Structure
Unlike molecular T ...
, and uranium trioxide reacts with hexachloropropene when heated under reflux to give uranium tetrachloride. The second example also involves a reduction in oxidation state, which can also be achieved by reducing a higher chloride using hydrogen or a metal as a reducing agent. This may also be achieved by thermal decomposition or disproportionation as follows:
: EuCl3 + H2 ⟶ EuCl2 + HCl
: ReCl5 ReCl3 + Cl2
: AuCl3 AuCl + Cl2
Most metal chlorides with the metal in low oxidation states (+1 to +3) are ionic. Nonmetals tend to form covalent molecular chlorides, as do metals in high oxidation states from +3 and above. Both ionic and covalent chlorides are known for metals in oxidation state +3 (e.g. scandium chloride is mostly ionic, but aluminium chloride is not). Silver chloride is very insoluble in water and is thus often used as a qualitative test for chlorine.
Polychlorine compounds
Although dichlorine is a strong oxidising agent with a high first ionisation energy, it may be oxidised under extreme conditions to form the cation. This is very unstable and has only been characterised by its electronic band spectrum when produced in a low-pressure discharge tube. The yellow cation is more stable and may be produced as follows: : This reaction is conducted in the oxidising solvent arsenic pentafluoride. The trichloride anion, , has also been characterised; it is analogous to triiodide.Chlorine fluorides
The three fluorides of chlorine form a subset of the interhalogen compounds, all of which are diamagnetic. Some cationic and anionic derivatives are known, such as , , , and Cl2F+. Some pseudohalides of chlorine are also known, such as cyanogen chloride (ClCN, linear), chlorine cyanate (ClNCO), chlorine thiocyanate (ClSCN, unlike its oxygen counterpart), and chlorineazide
In chemistry, azide is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula and structure . It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid . Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula , containing the azide functional group. The dominant applic ...
(ClN3).
Chlorine monofluoride (ClF) is extremely thermally stable, and is sold commercially in 500-gram steel lecture bottles. It is a colourless gas that melts at −155.6 °C and boils at −100.1 °C. It may be produced by the direction of its elements at 225 °C, though it must then be separated and purified from chlorine trifluoride and its reactants. Its properties are mostly intermediate between those of chlorine and fluorine. It will react with many metals and nonmetals from room temperature and above, fluorinating them and liberating chlorine. It will also act as a chlorofluorinating agent, adding chlorine and fluorine across a multiple bond or by oxidation: for example, it will attack carbon monoxide to form carbonyl chlorofluoride, COFCl. It will react analogously with hexafluoroacetone, (CF3)2CO, with a potassium fluoride catalyst to produce heptafluoroisopropyl hypochlorite, (CF3)2CFOCl; with nitrile
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The prefix ''cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including met ...
s RCN to produce RCF2NCl2; and with the sulfur oxides SO2 and SO3 to produce ClSO2F and ClOSO2F respectively. It will also react exothermically with compounds containing –OH and –NH groups, such as water:
:H2O + 2 ClF ⟶ 2 HF + Cl2O
Chlorine trifluoride (ClF3) is a volatile colourless molecular liquid which melts at −76.3 °C and boils at 11.8 °C. It may be formed by directly fluorinating gaseous chlorine or chlorine monofluoride at 200–300 °C. One of the most reactive chemical compounds known, the list of elements it sets on fire is diverse, containing hydrogen, potassium, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, selenium, tellurium, bromine, iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
, and powdered molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lea ...
, tungsten, rhodium, iridium, and iron. It will also ignite water, along with many substances which in ordinary circumstances would be considered chemically inert such as asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
, concrete, glass, and sand. When heated, it will even corrode noble metals as palladium, platinum, and gold, and even the noble gases xenon and radon do not escape fluorination. An impermeable fluoride layer is formed by sodium, magnesium, aluminium, zinc, tin, and silver, which may be removed by heating. Nickel, copper, and steel containers are usually used due to their great resistance to attack by chlorine trifluoride, stemming from the formation of an unreactive layer of metal fluoride. Its reaction with hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
to form hydrogen fluoride, nitrogen, and chlorine gases was used in experimental rocket engine, but has problems largely stemming from its extreme hypergolicity resulting in ignition without any measurable delay. Today, it is mostly used in nuclear fuel processing, to oxidise uranium to uranium hexafluoride for its enriching and to separate it from plutonium, as well as in the semiconductor industry, where it is used to clean chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (substra ...
chambers. It can act as a fluoride ion donor or acceptor (Lewis base or acid), although it does not dissociate appreciably into and ions.
Chlorine pentafluoride (ClF5) is made on a large scale by direct fluorination of chlorine with excess fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
gas at 350 °C and 250 atm, and on a small scale by reacting metal chlorides with fluorine gas at 100–300 °C. It melts at −103 °C and boils at −13.1 °C. It is a very strong fluorinating agent, although it is still not as effective as chlorine trifluoride. Only a few specific stoichiometric reactions have been characterised. Arsenic pentafluoride and antimony pentafluoride
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb F5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a valuable Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed when mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in a 2:1 ratio. ...
form ionic adducts of the form lF4sup>+ F6sup>− (M = As, Sb) and water reacts vigorously as follows:
:2 H2O + ClF5 ⟶ 4 HF + FClO2
The product, chloryl fluoride, is one of the five known chlorine oxide fluorides. These range from the thermally unstable FClO to the chemically unreactive perchloryl fluoride (FClO3), the other three being FClO2, F3ClO, and F3ClO2. All five behave similarly to the chlorine fluorides, both structurally and chemically, and may act as Lewis acids or bases by gaining or losing fluoride ions respectively or as very strong oxidising and fluorinating agents.
Chlorine oxides

 The chlorine oxides are well-studied in spite of their instability (all of them are endothermic compounds). They are important because they are produced when chlorofluorocarbons undergo photolysis in the upper atmosphere and cause the destruction of the ozone layer. None of them can be made from directly reacting the elements.
Dichlorine monoxide (Cl2O) is a brownish-yellow gas (red-brown when solid or liquid) which may be obtained by reacting chlorine gas with yellow mercury(II) oxide. It is very soluble in water, in which it is in equilibrium with hypochlorous acid (HOCl), of which it is the anhydride. It is thus an effective bleach and is mostly used to make
The chlorine oxides are well-studied in spite of their instability (all of them are endothermic compounds). They are important because they are produced when chlorofluorocarbons undergo photolysis in the upper atmosphere and cause the destruction of the ozone layer. None of them can be made from directly reacting the elements.
Dichlorine monoxide (Cl2O) is a brownish-yellow gas (red-brown when solid or liquid) which may be obtained by reacting chlorine gas with yellow mercury(II) oxide. It is very soluble in water, in which it is in equilibrium with hypochlorous acid (HOCl), of which it is the anhydride. It is thus an effective bleach and is mostly used to make hypochlorite
In chemistry, hypochlorite is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite (household bleach) and calcium hypochlorite (a component of ble ...
s. It explodes on heating or sparking or in the presence of ammonia gas.
Chlorine dioxide (ClO2) was the first chlorine oxide to be discovered in 1811 by Humphry Davy. It is a yellow paramagnetic gas (deep-red as a solid or liquid), as expected from its having an odd number of electrons: it is stable towards dimerisation due to the delocalisation of the unpaired electron. It explodes above −40 °C as a liquid and under pressure as a gas and therefore must be made at low concentrations for wood-pulp bleaching and water treatment. It is usually prepared by reducing a chlorate
The chlorate anion has the formula ClO3-. In this case, the chlorine atom is in the +5 oxidation state. "Chlorate" can also refer to chemical compounds containing this anion; chlorates are the salts of chloric acid. "Chlorate", when followed by ...
as follows:
: + Cl− + 2 H+ ⟶ ClO2 + Cl2 + H2O
Its production is thus intimately linked to the redox reactions of the chlorine oxoacids. It is a strong oxidising agent, reacting with sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, phosphorus, phosphorus halides, and potassium borohydride. It dissolves exothermically in water to form dark-green solutions that very slowly decompose in the dark. Crystalline clathrate hydrates ClO2·''n''H2O (''n'' ≈ 6–10) separate out at low temperatures. However, in the presence of light, these solutions rapidly photodecompose to form a mixture of chloric and hydrochloric acids. Photolysis of individual ClO2 molecules result in the radicals ClO and ClOO, while at room temperature mostly chlorine, oxygen, and some ClO3 and Cl2O6 are produced. Cl2O3 is also produced when photolysing the solid at −78 °C: it is a dark brown solid that explodes below 0 °C. The ClO radical leads to the depletion of atmospheric ozone and is thus environmentally important as follows:
:Cl• + O3 ⟶ ClO• + O2
:ClO• + O• ⟶ Cl• + O2
Chlorine perchlorate (ClOClO3) is a pale yellow liquid that is less stable than ClO2 and decomposes at room temperature to form chlorine, oxygen, and dichlorine hexoxide (Cl2O6). Chlorine perchlorate may also be considered a chlorine derivative of perchloric acid (HOClO3), similar to the thermally unstable chlorine derivatives of other oxoacids: examples include chlorine nitrate
Chlorine nitrate, with chemical formula ClNO3 is an important atmospheric gas present in the stratosphere. It is an important sink of chlorine that contributes to the depletion of ozone.
It explosively reacts with metals, metal chlorides, alcohol ...
(ClONO2, vigorously reactive and explosive), and chlorine fluorosulfate (ClOSO2F, more stable but still moisture-sensitive and highly reactive). Dichlorine hexoxide is a dark-red liquid that freezes to form a solid which turns yellow at −180 °C: it is usually made by reaction of chlorine dioxide with oxygen. Despite attempts to rationalise it as the dimer of ClO3, it reacts more as though it were chloryl perchlorate, lO2sup>+ lO4sup>−, which has been confirmed to be the correct structure of the solid. It hydrolyses in water to give a mixture of chloric and perchloric acids: the analogous reaction with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock i ...
does not proceed to completion.
Dichlorine heptoxide (Cl2O7) is the anhydride of perchloric acid (HClO4) and can readily be obtained from it by dehydrating it with phosphoric acid at −10 °C and then distilling the product at −35 °C and 1 mmHg. It is a shock-sensitive, colourless oily liquid. It is the least reactive of the chlorine oxides, being the only one to not set organic materials on fire at room temperature. It may be dissolved in water to regenerate perchloric acid or in aqueous alkalis to regenerate perchlorates. However, it thermally decomposes explosively by breaking one of the central Cl–O bonds, producing the radicals ClO3 and ClO4 which immediately decompose to the elements through intermediate oxides.
Chlorine oxoacids and oxyanions
Chlorine forms four oxoacids: hypochlorous acid (HOCl), chlorous acid (HOClO), chloric acid (HOClO2), and perchloric acid (HOClO3). As can be seen from the redox potentials given in the adjacent table, chlorine is much more stable towards disproportionation in acidic solutions than in alkaline solutions: : The hypochlorite ions also disproportionate further to produce chloride and chlorate (3 ClO− 2 Cl− + ) but this reaction is quite slow at temperatures below 70 °C in spite of the very favourable equilibrium constant of 1027. The chlorate ions may themselves disproportionate to form chloride and perchlorate (4 Cl− + 3 ) but this is still very slow even at 100 °C despite the very favourable equilibrium constant of 1020. The rates of reaction for the chlorine oxyanions increases as the oxidation state of chlorine decreases. The strengths of the chlorine oxyacids increase very quickly as the oxidation state of chlorine increases due to the increasing delocalisation of charge over more and more oxygen atoms in their conjugate bases. Most of the chlorine oxoacids may be produced by exploiting these disproportionation reactions. Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is highly reactive and quite unstable; its salts are mostly used for their bleaching and sterilising abilities. They are very strong oxidising agents, transferring an oxygen atom to most inorganic species. Chlorous acid (HOClO) is even more unstable and cannot be isolated or concentrated without decomposition: it is known from the decomposition of aqueous chlorine dioxide. However,sodium chlorite
Sodium chlorite (NaClO2) is a chemical compound used in the manufacturing of paper and as a disinfectant.
Use
The main application of sodium chlorite is the generation of chlorine dioxide for bleaching and stripping of textiles, pulp, and pape ...
is a stable salt and is useful for bleaching and stripping textiles, as an oxidising agent, and as a source of chlorine dioxide. Chloric acid (HOClO2) is a strong acid that is quite stable in cold water up to 30% concentration, but on warming gives chlorine and chlorine dioxide. Evaporation under reduced pressure allows it to be concentrated further to about 40%, but then it decomposes to perchloric acid, chlorine, oxygen, water, and chlorine dioxide. Its most important salt is sodium chlorate, mostly used to make chlorine dioxide to bleach paper pulp. The decomposition of chlorate to chloride and oxygen is a common way to produce oxygen in the laboratory on a small scale. Chloride and chlorate may comproportionate to form chlorine as follows:
: + 5 Cl− + 6 H+ ⟶ 3 Cl2 + 3 H2O
Perchlorates and perchloric acid (HOClO3) are the most stable oxo-compounds of chlorine, in keeping with the fact that chlorine compounds are most stable when the chlorine atom is in its lowest (−1) or highest (+7) possible oxidation states. Perchloric acid and aqueous perchlorates are vigorous and sometimes violent oxidising agents when heated, in stark contrast to their mostly inactive nature at room temperature due to the high activation energies for these reactions for kinetic reasons. Perchlorates are made by electrolytically oxidising sodium chlorate, and perchloric acid is made by reacting anhydrous sodium perchlorate or barium perchlorate with concentrated hydrochloric acid, filtering away the chloride precipitated and distilling the filtrate to concentrate it. Anhydrous perchloric acid is a colourless mobile liquid that is sensitive to shock that explodes on contact with most organic compounds, sets hydrogen iodide
Hydrogen iodide () is a diatomic molecule and hydrogen halide. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid. Hydrogen iodide and hydroiodic acid are, however, different in that the former is a gas under sta ...
and thionyl chloride on fire and even oxidises silver and gold. Although it is a weak ligand, weaker than water, a few compounds involving coordinated are known.
Organochlorine compounds
 Like the other carbon–halogen bonds, the C–Cl bond is a common functional group that forms part of core organic chemistry. Formally, compounds with this functional group may be considered organic derivatives of the chloride anion. Due to the difference of electronegativity between chlorine (3.16) and carbon (2.55), the carbon in a C–Cl bond is electron-deficient and thus
Like the other carbon–halogen bonds, the C–Cl bond is a common functional group that forms part of core organic chemistry. Formally, compounds with this functional group may be considered organic derivatives of the chloride anion. Due to the difference of electronegativity between chlorine (3.16) and carbon (2.55), the carbon in a C–Cl bond is electron-deficient and thus electrophilic
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carri ...
. Chlorination modifies the physical properties of hydrocarbons in several ways: chlorocarbons are typically denser than water due to the higher atomic weight of chlorine versus hydrogen, and aliphatic organochlorides are alkylating agents because chloride is a leaving group.M. Rossberg et al. "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
Alkanes and aryl alkanes may be chlorinated under free-radical conditions, with UV light. However, the extent of chlorination is difficult to control: the reaction is not regioselective and often results in a mixture of various isomers with different degrees of chlorination, though this may be permissible if the products are easily separated. Aryl chlorides may be prepared by the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, using chlorine and a Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
catalyst. The haloform reaction, using chlorine and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
, is also able to generate alkyl halides from methyl ketones, and related compounds. Chlorine adds to the multiple bonds on alkenes and alkynes as well, giving di- or tetra-chloro compounds. However, due to the expense and reactivity of chlorine, organochlorine compounds are more commonly produced by using hydrogen chloride, or with chlorinating agents such as phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) or thionyl chloride (SOCl2). The last is very convenient in the laboratory because all side products are gaseous and do not have to be distilled out.
Many organochlorine compounds have been isolated from natural sources ranging from bacteria to humans. Chlorinated organic compounds are found in nearly every class of biomolecules including alkaloids, terpenes, amino acids, flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
Chemically, flavonoids ...
s, steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s, and fatty acids. Organochlorides, including dioxins
Dioxin may refer to:
* 1,2-Dioxin or 1,4-Dioxin, two unsaturated heterocyclic 6-membered rings where two carbon atoms have been replaced by oxygen atoms, giving the molecular formula C4H4O2
*Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, the parent compound also known as ...
, are produced in the high temperature environment of forest fires, and dioxins have been found in the preserved ashes of lightning-ignited fires that predate synthetic dioxins. In addition, a variety of simple chlorinated hydrocarbons including dichloromethane, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVAC ...
have been isolated from marine algae. A majority of the chloromethane in the environment is produced naturally by biological decomposition, forest fires, and volcanoes.
Some types of organochlorides, though not all, have significant toxicity to plants or animals, including humans. Dioxins, produced when organic matter is burned in the presence of chlorine, and some insecticides, such as DDT, are persistent organic pollutants which pose dangers when they are released into the environment. For example, DDT, which was widely used to control insects in the mid 20th century, also accumulates in food chains, and causes reproductive problems (e.g., eggshell thinning) in certain bird species. Due to the ready homolytic fission of the C–Cl bond to create chlorine radicals in the upper atmosphere, chlorofluorocarbons have been phased out due to the harm they do to the ozone layer.
Occurrence and production
 Chlorine is too reactive to occur as the free element in nature but is very abundant in the form of its chloride salts. It is the twenty-first most abundant element in Earth's crust and makes up 126 parts per million of it, through the large deposits of chloride minerals, especially
Chlorine is too reactive to occur as the free element in nature but is very abundant in the form of its chloride salts. It is the twenty-first most abundant element in Earth's crust and makes up 126 parts per million of it, through the large deposits of chloride minerals, especially sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g ...
, that have been evaporated from water bodies. All of these pale in comparison to the reserves of chloride ions in seawater: smaller amounts at higher concentrations occur in some inland seas and underground brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for br ...
wells, such as the Great Salt Lake
The Great Salt Lake is the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere and the eighth-largest terminal lake in the world. It lies in the northern part of the U.S. state of Utah and has a substantial impact upon the local climate, particula ...
in Utah and the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
in Israel.
Small batches of chlorine gas are prepared in the laboratory by combining hydrochloric acid and manganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cell ...
, but the need rarely arises due to its ready availability. In industry, elemental chlorine is usually produced by the electrolysis of sodium chloride dissolved in water. This method, the chloralkali process industrialized in 1892, now provides most industrial chlorine gas. Along with chlorine, the method yields hydrogen gas and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
, which is the most valuable product. The process proceeds according to the following chemical equation:
:2 NaCl + 2 H2O → Cl2 + H2 + 2 NaOH
The electrolysis of chloride solutions all proceed according to the following equations:
:Cathode: 2 H2O + 2 e− → H2 + 2 OH−
:Anode: 2 Cl− → Cl2 + 2 e−
In diaphragm cell electrolysis, an asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
(or polymer-fiber) diaphragm separates a cathode and an anode, preventing the chlorine forming at the anode from re-mixing with the sodium hydroxide and the hydrogen formed at the cathode. The salt solution (brine) is continuously fed to the anode compartment and flows through the diaphragm to the cathode compartment, where the caustic alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
is produced and the brine is partially depleted. Diaphragm methods produce dilute and slightly impure alkali, but they are not burdened with the problem of mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
disposal and they are more energy efficient.
Membrane cell electrolysis employs permeable membrane as an ion exchanger. Saturated sodium (or potassium) chloride solution is passed through the anode compartment, leaving at a lower concentration. This method also produces very pure sodium (or potassium) hydroxide but has the disadvantage of requiring very pure brine at high concentrations.
Applications
Sodium chloride is the most common chlorine compound, and is the main source of chlorine for the demand by the chemical industry. About 15000 chlorine-containing compounds are commercially traded, including such diverse compounds as chlorinated methane, ethanes, vinyl chloride, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), aluminium trichloride for catalysis, the chlorides of magnesium, titanium, zirconium, and hafnium which are the precursors for producing the pure form of those elements. Quantitatively, of all elemental chlorine produced, about 63% is used in the manufacture of organic compounds, and 18% in the manufacture of inorganic chlorine compounds. About 15,000 chlorine compounds are used commercially. The remaining 19% of chlorine produced is used for bleaches and disinfection products. The most significant of organic compounds in terms of production volume are1,2-dichloroethane
The chemical compound 1,2-dichloroethane, commonly known as ethylene dichloride (EDC), is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colourless liquid with a chloroform-like odour. The most common use of 1,2-dichloroethane is in the production of vinyl ...
and vinyl chloride, intermediates in the production of PVC. Other particularly important organochlorines are methyl chloride, methylene chloride, chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to ...
, vinylidene chloride, trichloroethylene, perchloroethylene, allyl chloride, epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin (abbreviated ECH) is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organi ...
, chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzenes, and trichlorobenzenes. The major inorganic compounds include HCl, Cl2O, HOCl, NaClO3, chlorinated isocyanurates, AlCl3, SiCl4, SnCl4, PCl3, PCl5, POCl3, AsCl3, SbCl3, SbCl5, BiCl3, and ZnCl2.
Sanitation, disinfection, and antisepsis
Combating putrefaction
In France (as elsewhere), animal intestines were processed to make musical instrument strings, Goldbeater's skin and other products. This was done in "gut factories" (''boyauderies''), and it was an odiferous and unhealthy process. In or about 1820, the Société d'encouragement pour l'industrie nationale offered a prize for the discovery of a method, chemical or mechanical, for separating the peritoneal membrane of animal intestines without putrefaction. The prize was won by Antoine-Germain Labarraque, a 44-year-old French chemist and pharmacist who had discovered that Berthollet's chlorinated bleaching solutions ("''Eau de Javel
Sodium hypochlorite (commonly known in a dilute solution as bleach) is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaOCl (or NaClO), comprising a sodium cation () and a hypochlorite anion (or ). It may also be viewed as the sodium salt of ...
''") not only destroyed the smell of putrefaction of animal tissue decomposition, but also actually retarded the decomposition.
Labarraque's research resulted in the use of chlorides and hypochlorites of lime (calcium hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(OCl)2. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent. Thi ...
) and of sodium ( sodium hypochlorite) in the ''boyauderies.'' The same chemicals were found to be useful in the routine disinfection and deodorization of latrines, sewers, markets, abattoirs, anatomical theatres, and morgues. They were successful in hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
s, lazarets, prisons, infirmaries (both on land and at sea), magnaneries
A magnanery (french: magnanerie) is the site of sericulture, or silk farming, similar to a farm being the site of agriculture. The yeoman who runs it is called a ''magnanier'' or, more recently, a ''mangnan''. The word ''magnanière'', meaning bui ...
, stable
A stable is a building in which livestock, especially horses, are kept. It most commonly means a building that is divided into separate stalls for individual animals and livestock. There are many different types of stables in use today; the ...
s, cattle-sheds, etc.; and they were beneficial during exhumations, embalming, outbreaks of epidemic disease, fever, and blackleg in cattle.
Disinfection
Labarraque's chlorinated lime and soda solutions have been advocated since 1828 to prevent infection (called "contagious infection", presumed to be transmitted by " miasmas"), and to treat putrefaction of existing wounds, including septic wounds. In his 1828 work, Labarraque recommended that doctors breathe chlorine, wash their hands in chlorinated lime, and even sprinkle chlorinated lime about the patients' beds in cases of "contagious infection". In 1828, the contagion of infections was well known, even though the agency of themicrobe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
was not discovered until more than half a century later.
During the Paris cholera outbreak of 1832, large quantities of so-called ''chloride of lime'' were used to disinfect the capital. This was not simply modern calcium chloride, but chlorine gas dissolved in lime-water (dilute calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has m ...
) to form calcium hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(OCl)2. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent. Thi ...
(chlorinated lime). Labarraque's discovery helped to remove the terrible stench of decay from hospitals and dissecting rooms, and by doing so, effectively deodorised the Latin Quarter of Paris.Corbin, Alain (1988). The Foul and the Fragrant: Odor and the French Social Imagination
''. Harvard University Press. pp. 121–22. These "putrid miasmas" were thought by many to cause the spread of "contagion" and "infection" – both words used before the germ theory of infection. Chloride of lime was used for destroying odors and "putrid matter". One source claims chloride of lime was used by Dr. John Snow to disinfect water from the cholera-contaminated well that was feeding the Broad Street pump in 1854 London, though three other reputable sources that describe that famous cholera epidemic do not mention the incident.Vinten-Johansen, Peter, Howard Brody, Nigel Paneth, Stephen Rachman and Michael Rip. (2003). ''Cholera, Chloroform, and the Science of Medicine''. New York:Oxford University. One reference makes it clear that chloride of lime was used to disinfect the offal and filth in the streets surrounding the Broad Street pump – a common practice in mid-nineteenth century England.
Semmelweis and experiments with antisepsis
 Perhaps the most famous application of Labarraque's chlorine and
Perhaps the most famous application of Labarraque's chlorine and chemical base
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius base Arrhenius may refer to
* Birgit Arrhenius (born 1932), Swedish archaeologist
* Carl Axel Arrhenius (1757–1824), Swedish army lieutenant and am ...
solutions was in 1847, when Ignaz Semmelweis used chlorine-water (chlorine dissolved in pure water, which was cheaper than chlorinated lime solutions) to disinfect the hands of Austrian doctors, which Semmelweis noticed still carried the stench of decomposition from the dissection rooms to the patient examination rooms. Long before the germ theory of disease, Semmelweis theorized that "cadaveric particles" were transmitting decay from fresh medical cadavers to living patients, and he used the well-known "Labarraque's solutions" as the only known method to remove the smell of decay and tissue decomposition (which he found that soap did not). The solutions proved to be far more effective antiseptics than soap (Semmelweis was also aware of their greater efficacy, but not the reason), and this resulted in Semmelweis's celebrated success in stopping the transmission of childbed fever
Postpartum infections, also known as childbed fever and puerperal fever, are any bacterial infections of the female reproductive tract following childbirth or miscarriage. Signs and symptoms usually include a fever greater than , chills, lower a ...
("puerperal fever") in the maternity wards of Vienna General Hospital in Austria in 1847.
Much later, during World War I in 1916, a standardized and diluted modification of Labarraque's solution containing hypochlorite (0.5%) and boric acid as an acidic stabilizer was developed by Henry Drysdale Dakin (who gave full credit to Labarraque's prior work in this area). Called Dakin's solution Dakin's solution is a dilute solution of sodium hypochlorite (0.4% to 0.5%) and other stabilizing ingredients, traditionally used as an antiseptic, e.g. to cleanse wounds in order to prevent infection.Jeffrey M. Levine (2013): "Dakin’s Solution: P ...
, the method of wound irrigation with chlorinated solutions allowed antiseptic treatment of a wide variety of open wounds, long before the modern antibiotic era. A modified version of this solution continues to be employed in wound irrigation in modern times, where it remains effective against bacteria that are resistant to multiple antibiotics (see Century Pharmaceuticals
Century Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American pharmaceutical company, founded in 1966 in Indianapolis, Indiana, USA.
The first continuous application of chlorination to drinking U.S. water was installed in
Jersey City
Jersey City is the second-most populous city in the U.S. state of New Jersey, after Newark.US Department of Treasury called for all drinking water to be disinfected with chlorine. Chlorine is presently an important chemical for water purification (such as in water treatment plants), in

Chlorine
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham) * Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
Chlorine
Chlorine Production Using Mercury, Environmental Considerations and Alternatives
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Chlorine Page
Chlorine Institute
– Trade association representing the chlorine industry
Chlorine Online
– the web portal of Eurochlor – the business association of the European chlor-alkali industry * {{Authority control Chemical elements Diatomic nonmetals Gases with color Halogens Hazardous air pollutants Industrial gases Occupational safety and health Oxidizing agents Pulmonary agents Reactive nonmetals Swimming pool equipment World Health Organization essential medicines
disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than st ...
s, and in bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
. Even small water supplies are now routinely chlorinated.
Chlorine is usually used (in the form of hypochlorous acid) to kill bacteria and other microbes in drinking water supplies and public swimming pools. In most private swimming pools, chlorine itself is not used, but rather sodium hypochlorite, formed from chlorine and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
, or solid tablets of chlorinated isocyanurates. The drawback of using chlorine in swimming pools is that the chlorine reacts with the amino acids in proteins in human hair and skin. Contrary to popular belief, the distinctive "chlorine aroma" associated with swimming pools is not the result of elemental chlorine itself, but of chloramine, a chemical compound produced by the reaction of free dissolved chlorine with amines in organic substances including those in urine and sweat. As a disinfectant in water, chlorine is more than three times as effective against '' Escherichia coli'' as bromine, and more than six times as effective as iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
. Increasingly, monochloramine itself is being directly added to drinking water for purposes of disinfection, a process known as chloramination
Chloramination is the treatment of drinking water with a chloramine disinfectant. Both chlorine and small amounts of ammonia are added to the water one at a time which react together to form chloramine (also called combined chlorine), a long lasti ...
.
It is often impractical to store and use poisonous chlorine gas for water treatment, so alternative methods of adding chlorine are used. These include hypochlorite
In chemistry, hypochlorite is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite (household bleach) and calcium hypochlorite (a component of ble ...
solutions, which gradually release chlorine into the water, and compounds like sodium dichloro-s-triazinetrione
Sodium dichloroisocyanurate (INN: sodium troclosene, ''troclosenum natricum'' or NaDCC or SDIC) is a chemical compound widely used as a cleansing agent and disinfectant.. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid, produced as a result of reaction of ...
(dihydrate or anhydrous), sometimes referred to as "dichlor", and trichloro-s-triazinetrione
Trichloroisocyanuric acid is an organic compound with the formula (C3Cl3N3O3). It is used as an industrial disinfectant, bleaching agent and a reagent in organic synthesis. This white crystalline powder, which has a strong "chlorine odour," i ...
, sometimes referred to as "trichlor". These compounds are stable while solid and may be used in powdered, granular, or tablet form. When added in small amounts to pool water or industrial water systems, the chlorine atoms hydrolyze from the rest of the molecule, forming hypochlorous acid (HOCl), which acts as a general biocide
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a slig ...
, killing germs, microorganisms, algae, and so on.
Use as a weapon
World War I
Chlorine gas, also known as bertholite, was first used as a weapon in World War I by Germany on April 22, 1915, in the Second Battle of Ypres. As described by the soldiers, it had the distinctive smell of a mixture of pepper and pineapple. It also tasted metallic and stung the back of the throat and chest. Chlorine reacts with water in themucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
of the lungs to form hydrochloric acid, destructive to living tissue and potentially lethal. Human respiratory systems can be protected from chlorine gas by gas mask
A gas mask is a mask used to protect the wearer from inhaling airborne pollutants and toxic gases. The mask forms a sealed cover over the nose and mouth, but may also cover the eyes and other vulnerable soft tissues of the face. Most gas mask ...
s with activated charcoal
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016).
Background
In an interv ...
or other filters, which makes chlorine gas much less lethal than other chemical weapons. It was pioneered by a German scientist later to be a Nobel laureate, Fritz Haber of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in Berlin, in collaboration with the German chemical conglomerate IG Farben
Interessengemeinschaft Farbenindustrie AG (), commonly known as IG Farben (German for 'IG Dyestuffs'), was a German chemical and pharmaceutical conglomerate (company), conglomerate. Formed in 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies—BASF, ...
, which developed methods for discharging chlorine gas against an entrenched enemy. After its first use, both sides in the conflict used chlorine as a chemical weapon, but it was soon replaced by the more deadly phosgene
Phosgene is the organic chemical compound with the formula COCl2. It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. Phosgene is a valued and important industrial building block, espe ...
and mustard gas
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect: the substance, when dispersed, is often not actually a gas, b ...
.
Middle east
Chlorine gas was also used during the Iraq War in Anbar Province in 2007, with insurgents packing truck bombs with mortar shells and chlorine tanks. The attacks killed two people from the explosives and sickened more than 350. Most of the deaths were caused by the force of the explosions rather than the effects of chlorine since the toxic gas is readily dispersed and diluted in the atmosphere by the blast. In some bombings, over a hundred civilians were hospitalized due to breathing difficulties. The Iraqi authorities tightened security for elemental chlorine, which is essential for providing safe drinking water to the population. On 23 October 2014, it was reported that the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant had used chlorine gas in the town of Duluiyah, Iraq. Laboratory analysis of clothing and soil samples confirmed the use of chlorine gas against Kurdish Peshmerga Forces in a vehicle-borne improvised explosive device attack on 23 January 2015 at the Highway 47 Kiske Junction near Mosul. Another country in the middle east,Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, has used chlorine as a chemical weapon delivered from barrel bomb
A barrel bomb is an improvised unguided bomb, sometimes described as a flying IED (improvised explosive device). They are typically made from a large barrel-shaped metal container that has been filled with high explosives, possibly shrapnel, oil ...
s and rockets. In 2016, the OPCW-UN Joint Investigative Mechanism concluded that the Syrian government used chlorine as a chemical weapon in three separate attacks. Later investigations from the OPCW's Investigation and Identification Team concluded that the Syrian Air Force was responsible for chlorine attacks in 2017 and 2018.
Biological role
The chloride anion is anessential nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
for metabolism. Chlorine is needed for the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and in cellular pump functions. The main dietary source is table salt, or sodium chloride. Overly low or high concentrations of chloride in the blood are examples of electrolyte disturbances. Hypochloremia (having too little chloride) rarely occurs in the absence of other abnormalities. It is sometimes associated with hypoventilation. It can be associated with chronic respiratory acidosis. Hyperchloremia
Hyperchloremia is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is an elevated level of chloride ions in the blood. The normal serum range for chloride is 96 to 106 mEq/L, therefore chloride levels at or above 110 mEq/L usually indicate kidney dysfunct ...
(having too much chloride) usually does not produce symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they tend to resemble those of hypernatremia (having too much sodium). Reduction in blood chloride leads to cerebral dehydration; symptoms are most often caused by rapid rehydration which results in cerebral edema. Hyperchloremia can affect oxygen transport.
Hazards
Chlorine is a toxic gas that attacks the respiratory system, eyes, and skin. Because it is denser than air, it tends to accumulate at the bottom of poorly ventilated spaces. Chlorine gas is a strong oxidizer, which may react with flammable materials. Chlorine is detectable with measuring devices in concentrations as low as 0.2 parts per million (ppm), and by smell at 3 ppm. Coughing and vomiting may occur at 30 ppm and lung damage at 60 ppm. About 1000 ppm can be fatal after a few deep breaths of the gas. The IDLH (immediately dangerous to life and health) concentration is 10 ppm. Breathing lower concentrations can aggravate the respiratory system and exposure to the gas can irritate the eyes. When chlorine is inhaled at concentrations greater than 30 ppm, it reacts with water within the lungs, producing hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hypochlorous acid (HClO). When used at specified levels for water disinfection, the reaction of chlorine with water is not a major concern for human health. Other materials present in the water may generate disinfection by-products that are associated with negative effects on human health. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the permissible exposure limit for elemental chlorine at 1 ppm, or 3 mg/m3. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health has designated a recommended exposure limit of 0.5 ppm over 15 minutes. In the home, accidents occur when hypochlorite bleach solutions come into contact with certain acidic drain-cleaners to produce chlorine gas. Hypochlorite bleach (a popularlaundry
Laundry refers to the washing of clothing and other textiles, and, more broadly, their drying and ironing as well. Laundry has been part of history since humans began to wear clothes, so the methods by which different cultures have dealt with t ...
additive) combined with ammonia (another popular laundry additive) produces chloramines, another toxic group of chemicals.
Chlorine-induced cracking in structural materials
Chlorine is widely used for purifying water, especially potable water supplies and water used in swimming pools. Several catastrophic collapses of swimming pool ceilings have occurred from chlorine-inducedstress corrosion cracking
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC ...
of stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
suspension rods. Some polymers are also sensitive to attack, including acetal resin and polybutene. Both materials were used in hot and cold water domestic plumbing, and stress corrosion cracking
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC ...
caused widespread failures in the US in the 1980s and 1990s.

Chlorine-iron fire
The element iron can combine with chlorine at high temperatures in a strong exothermic reaction, creating a ''chlorine-iron fire''. Chlorine-iron fires are a risk in chemical process plants, where much of the pipework that carries chlorine gas is made of steel.See also
*Chlorine cycle The chlorine cycle (Cl) is the biogeochemical cycling of chlorine through the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and lithosphere. Chlorine is most commonly found as inorganic chloride ions, or a number of chlorinated organic forms. Over 5,000 biolo ...
* Chlorine gas poisoning
Chlorine gas poisoning is an illness resulting from the effects of exposure to chlorine beyond the threshold limit value.
Signs and symptoms
The signs of acute chlorine gas poisoning are primarily respiratory, and include difficulty breathing ...
* Industrial gas
Industrial gases are the gaseous materials that are manufactured for use in industry. The principal gases provided are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, hydrogen, helium and acetylene, although many other gases and mixtures are also avail ...
* Polymer degradation
* Reductive dechlorination
References
Explanatory notes
General bibliography
*External links
Chlorine
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham) * Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
Chlorine
Chlorine Production Using Mercury, Environmental Considerations and Alternatives
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Chlorine Page
Chlorine Institute
– Trade association representing the chlorine industry
Chlorine Online
– the web portal of Eurochlor – the business association of the European chlor-alkali industry * {{Authority control Chemical elements Diatomic nonmetals Gases with color Halogens Hazardous air pollutants Industrial gases Occupational safety and health Oxidizing agents Pulmonary agents Reactive nonmetals Swimming pool equipment World Health Organization essential medicines