|
Oxygen-burning Process
The oxygen-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in massive stars that have used up the lighter elements in their cores. Oxygen-burning is preceded by the neon-burning process and succeeded by the silicon-burning process. As the neon-burning process ends, the core of the star contracts and heats until it reaches the ignition temperature for oxygen burning. Oxygen burning reactions are similar to those of carbon burning; however, they must occur at higher temperatures and densities due to the larger Coulomb barrier of oxygen. Reactions Oxygen ignites in the temperature range of (1.5–2.6)×109 KEl Eid, M. F., B. S. Meyer, and L.‐S. The. "Evolution of Massive Stars Up to the End of Central Oxygen Burning." ApJ The Astrophysical Journal 611.1 (2004): 452–65. Arxiv.org. 21 July 2004. Web. 8 Apr. 2016. and in the density range of (2.6–6.7)×1012 kg·m−3.Hirschi. "Evolution and nucleosynthesis of Very Massive Stars". arXiv:1409.7053v1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises as a result of the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the fusion reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers all active stars, via many Stellar nucleosynthesis, reaction pathways. Fusion processes require an extremely large Lawson criterion, triple product of temperature, density, and confinement time. These conditions occur only in Stellar core, stellar cores, advanced Nuclear weapon design, nuclear weapons, and are approached in List of fusion experiments, fusion power experiments. A nuclear fusion process that produces atomic nuclei lighter than nickel-62 is generally exothermic, due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By definition, the Celsius scale (symbol °C) and the Kelvin scale have the exact same magnitude; that is, a rise of 1 K is equal to a rise of 1 °C and vice versa, and any temperature in degrees Celsius can be converted to kelvin by adding 273.15. The 19th century British scientist Lord Kelvin first developed and proposed the scale. It was often called the "absolute Celsius" scale in the early 20th century. The kelvin was formally added to the International System of Units in 1954, defining 273.16 K to be the triple point of water. The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine scales were redefined in terms of the Kelvin scale using this definition. The 2019 revision of the SI now defines the kelvin in terms of energy by setting the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population III Star
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodisintegration
Photodisintegration (also called phototransmutation, or a photonuclear reaction) is a nuclear process in which an atomic nucleus absorbs a high-energy gamma ray, enters an excited state, and immediately decays by emitting a subatomic particle. The incoming gamma ray effectively knocks one or more neutrons, protons, or an alpha particle out of the nucleus. The reactions are called (γ,n), (γ,p), and (γ,α), respectively. Photodisintegration is endothermic (energy absorbing) for atomic nuclei lighter than iron and sometimes exothermic (energy releasing) for atomic nuclei heavier than iron. Photodisintegration is responsible for the nucleosynthesis of at least some heavy, proton-rich elements via the p-process in supernovae of type Ib, Ic, or II. This causes the iron to further fuse into the heavier elements. Photodisintegration of deuterium A photon carrying 2.22 MeV or more energy can photodisintegrate an atom of deuterium: : James Chadwick and Maurice Goldhaber used this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power (physics)
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. Power is a Scalar (physics), scalar quantity. Specifying power in particular systems may require attention to other quantities; for example, the power involved in moving a ground vehicle is the product of the aerodynamic drag plus traction (engineering), traction force on the wheels, and the velocity of the vehicle. The output power of a Engine, motor is the product of the torque that the motor generates and the angular velocity of its output shaft. Likewise, the power dissipated in an electrical element of a electrical circuit, circuit is the product of the electric current, current flowing through the element and of the voltage across the element. Definition Power is the Rate (mathematics), rate with respect to time at which work is done or, more generally, the rate of change of total mechanical energy. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow. Convective flow may be Transient state, transient (such as when a Multiphasic liquid, multiphase mixture of oil and water separates) or steady state (see convection cell). The convection may be due to Gravity, gravitational, Electromagnetism, electromagnetic or Fictitious force, fictitious body forces. Convection (heat transfer), Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its Earth's mantle, mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be identified by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Number (physics)
In nuclear physics, a magic number is a number of nucleons (either protons or neutrons, separately) such that they are arranged into complete shells within the atomic nucleus. As a result, atomic nuclei with a "magic" number of protons or neutrons are much more stable than other nuclei. The seven most widely recognized magic numbers as of 2019 are 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, and 126. For protons, this corresponds to the elements helium, oxygen, calcium, nickel, tin, lead, and the hypothetical unbihexium, although 126 is so far only known to be a magic number for neutrons. Atomic nuclei consisting of such a magic number of nucleons have a higher average binding energy per nucleon than one would expect based upon predictions such as the semi-empirical mass formula and are hence more stable against nuclear decay. The unusual stability of isotopes having magic numbers means that transuranium elements could theoretically be created with extremely large nuclei and yet not be subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
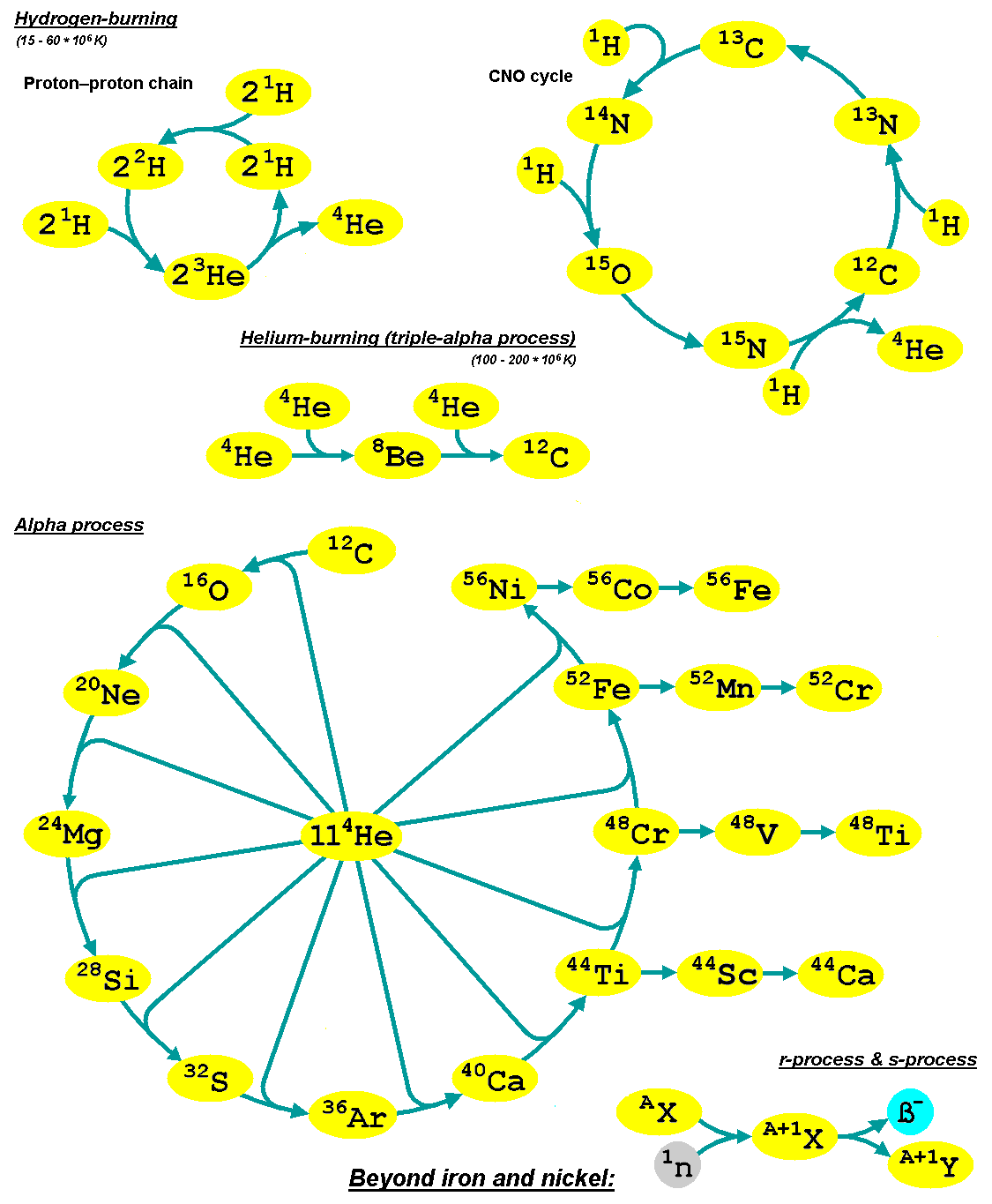
Alpha Process
The alpha process, also known as alpha capture or the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements. The other class is a cycle of reactions called the triple-alpha process, which consumes only helium, and produces carbon. The alpha process most commonly occurs in massive stars and during supernovae. Both processes are preceded by hydrogen fusion, which produces the helium that fuels both the triple-alpha process and the alpha ladder processes. After the triple-alpha process has produced enough carbon, the alpha-ladder begins and fusion reactions of increasingly heavy elements take place, in the order listed below. Each step only consumes the product of the previous reaction and helium. The later-stage reactions which are able to begin in any particular star, do so while the prior stage reactions are still under way in outer layers of the star. :\begin \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common H has no neutrons. The name ''deuterium'' comes from Greek '' deuteros'', meaning "second". American chemist Harold Urey discovered deuterium in 1931. Urey and others produced samples of heavy water in which the H had been highly concentrated. The discovery of deuterium won Urey a Nobel Prize in 1934. Nearly all deuterium found in nature was synthesized in the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago, forming the primordial ratio of H to H (~26 deuterium nuclei per 10 hydrogen nuclei). Deuterium is subsequently produced by the slow stellar proton–proton chain, but rapidly destroyed by exothermic fusion reactions. The deuterium–deuterium reaction has the second-lowest energy threshold, and is the most astrophysically acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon-burning Process
The neon-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in evolved massive stars with at least 8 Solar masses. Neon burning requires high temperatures and densities (around 1.2 billion K or 100 keV and 4 billion kg/m3). At such high temperatures photodisintegration becomes a significant effect, so some neon nuclei decompose, absorbing 4.73 MeV and releasing alpha particles. This free helium nucleus can then fuse with neon to produce magnesium, releasing 9.316 MeV. : Alternatively: Ne-21 + y Ne-21 + He -> Mg-24 + n -->: where the neutron consumed in the first step is regenerated in the second. A secondary reaction causes helium to fuse with magnesium to produce silicon: : + → + γ Contraction of the core leads to an increase of temperature, allowing neon to fuse directly as follows: : + → + Neon burning takes place after carbon burning has consumed all carbon in the core and built up a new oxygen–neon–sodium–magnesium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Volt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV), also written electron-volt and electron volt, is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules (symbol J) is equal to the numerical value of the charge of an electron in coulombs (symbol C). Under the 2019 revision of the SI, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value Historically, the electronvolt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in electrostatic particle accelerator sciences, because a particle with electric charge ''q'' gains an energy after passing through a voltage of ''V''. Definition and use An electronvolt is the amount of energy gained or lost by a single electron when it moves through an electric potential difference of one volt. Hence, it has a value of one volt, which is , multiplied by the elementary charge Therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produced in different ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+ or 2+ indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge (missing its two electrons). Once the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal (electrically neutral) helium atom . Alpha particles have a net spin of zero. When produced in standard alpha radioactive decay, alpha particles generally have a kinetic energy of about 5 MeV and a velocity in the vicinity of 4% of the speed of light. They are a highly ionizing form of particle radiation, with low penetration depth (stopped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |