Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of
cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (
chemotherapeutic agents
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemoth ...
or
alkylating agents) as part of a standardized
chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a
curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to
reduce symptoms (
palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to
pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy is therapy using pharmaceutical drugs, as distinguished from therapy using surgery (surgical therapy), radiation (radiation therapy), movement ( physical therapy), or other modes. Among physicians, sometimes the term ''medical th ...
for
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
, which is called
''medical oncology''.
The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular
poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
s to inhibit
mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maint ...
(cell division) or induce
DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
, which is why inhibition of
DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
can augment chemotherapy.
The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (
signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular ...
). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, which inhibit growth-promoting signals from classic endocrine hormones (primarily
estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal a ...
s for breast cancer and
androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
s for prostate cancer) are now called
hormonal therapies. By contrast, other inhibitions of growth-signals like those associated with
receptor tyrosine kinases are referred to as
targeted therapy
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment ( pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy block ...
.
Importantly, the use of drugs (whether chemotherapy,
hormonal therapy or targeted therapy) constitutes ''systemic therapy'' for cancer in that they are introduced into the blood stream and are therefore in principle able to address cancer at any anatomic location in the body. Systemic therapy is often used in conjunction with other modalities that constitute ''local therapy'' (i.e., treatments whose efficacy is confined to the anatomic area where they are applied) for cancer such as
radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
,
surgery or
hyperthermia therapy
Hyperthermia therapy ''(or hyperthermia, or thermotherapy)'' is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to temperatures above body temperature, in the region of 40–45 °C (104–113 °F). Hyperthermia is usuall ...
.
Traditional chemotherapeutic agents are
cytotoxic
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'').
Cell physiology
Treating ...
by means of interfering with cell division (mitosis) but cancer cells vary widely in their susceptibility to these agents. To a large extent, chemotherapy can be thought of as a way to damage or stress cells, which may then lead to cell death if
apoptosis is initiated. Many of the side effects of chemotherapy can be traced to damage to normal cells that divide rapidly and are thus sensitive to anti-mitotic drugs: cells in the
bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoieti ...
,
digestive tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans an ...
and
hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction betwe ...
s. This results in the most common side-effects of chemotherapy:
myelosuppression (decreased production of blood cells, hence also
immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
),
mucositis (inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract), and
alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarr ...
(hair loss). Because of the effect on immune cells (especially lymphocytes), chemotherapy drugs often find use in a host of diseases that result from harmful overactivity of the immune system against self (so-called
autoimmunity
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease ...
). These include
rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and ...
,
systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
,
multiple sclerosis,
vasculitis and many others.
Treatment strategies
There are a number of strategies in the administration of chemotherapeutic drugs used today. Chemotherapy may be given with a
curative intent or it may aim to prolong life or to
palliate symptoms.
* Induction chemotherapy is the first line treatment of cancer with a chemotherapeutic drug. This type of chemotherapy is used for curative intent.
radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
, or hyperthermia therapy
Hyperthermia therapy ''(or hyperthermia, or thermotherapy)'' is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to temperatures above body temperature, in the region of 40–45 °C (104–113 °F). Hyperthermia is usuall ...
.
* Consolidation chemotherapy is given after remission in order to prolong the overall disease-free time and improve overall survival. The drug that is administered is the same as the drug that achieved remission.[
* Intensification chemotherapy is identical to consolidation chemotherapy but a different drug than the induction chemotherapy is used.][
* Combination chemotherapy involves treating a person with a number of different drugs simultaneously. The drugs differ in their mechanism and side-effects. The biggest advantage is minimising the chances of resistance developing to any one agent. Also, the drugs can often be used at lower doses, reducing toxicity.][
* Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is given prior to a local treatment such as surgery, and is designed to shrink the primary tumor.][ It is also given for cancers with a high risk of micrometastatic disease.]Adjuvant chemotherapy
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in ...
is given after a local treatment (radiotherapy or surgery). It can be used when there is little evidence of cancer present, but there is risk of recurrence.[ It is also useful in killing any cancerous cells that have spread to other parts of the body. These micrometastases can be treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and can reduce relapse rates caused by these disseminated cells.][
* Salvage chemotherapy or palliative chemotherapy is given without curative intent, but simply to decrease tumor load and increase life expectancy. For these regimens, in general, a better toxicity profile is expected.][
All chemotherapy regimens require that the recipient be capable of undergoing the treatment. ]Performance status
In medicine (oncology and other fields), performance status is an attempt to quantify cancer patients' general well-being and activities of daily life. This measure is used to determine whether they can receive chemotherapy, whether dose adjustment ...
is often used as a measure to determine whether a person can receive chemotherapy, or whether dose reduction is required. Because only a fraction of the cells in a tumor die with each treatment (fractional kill In oncology, the fact that one round of chemotherapy does not kill all the cells in a tumor is a poorly understood phenomenon called fractional kill, or fractional cell kill.
The fractional kill hypothesis states that a defined chemotherapy concent ...
), repeated doses must be administered to continue to reduce the size of the tumor.
Efficiency
The efficiency of chemotherapy depends on the type of cancer and the stage. The overall effectiveness ranges from being curative for some cancers, such as some leukemias
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
, to being ineffective, such as in some brain tumors
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secon ...
, to being needless in others, like most non-melanoma skin cancers.
Dosage
 Dosage of chemotherapy can be difficult: If the dose is too low, it will be ineffective against the tumor, whereas, at excessive doses, the toxicity (
Dosage of chemotherapy can be difficult: If the dose is too low, it will be ineffective against the tumor, whereas, at excessive doses, the toxicity (side-effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
) will be intolerable to the person receiving it.[ The standard method of determining chemotherapy dosage is based on calculated ]body surface area
In physiology and medicine, the body surface area (BSA) is the measured or calculated surface area of a human body. For many clinical purposes, BSA is a better indicator of metabolic mass than body weight because it is less affected by abnormal a ...
(BSA). The BSA is usually calculated with a mathematical formula or a nomogram
A nomogram (from Greek , "law" and , "line"), also called a nomograph, alignment chart, or abac, is a graphical calculating device, a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function ...
, using the recipient's weight and height, rather than by direct measurement of body area. This formula was originally derived in a 1916 study and attempted to translate medicinal doses established with laboratory animals to equivalent doses for humans. The study only included nine human subjects.[ This variability is typical with many chemotherapy drugs dosed by BSA, and, as shown below, was demonstrated in a study of 14 common chemotherapy drugs.][
] The result of this pharmacokinetic variability among people is that many people do not receive the right dose to achieve optimal treatment effectiveness with minimized toxic side effects. Some people are overdosed while others are underdosed.
The result of this pharmacokinetic variability among people is that many people do not receive the right dose to achieve optimal treatment effectiveness with minimized toxic side effects. Some people are overdosed while others are underdosed.[
There has been controversy over the use of BSA to calculate chemotherapy doses for people who are ]obese
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
.[ In many cases, this can result in sub-optimal treatment.][
Several clinical studies have demonstrated that when chemotherapy dosing is individualized to achieve optimal systemic drug exposure, treatment outcomes are improved and toxic side effects are reduced.][ In the 5-FU clinical study cited above, people whose dose was adjusted to achieve a pre-determined target exposure realized an 84% improvement in treatment response rate and a six-month improvement in overall survival (OS) compared with those dosed by BSA.][
]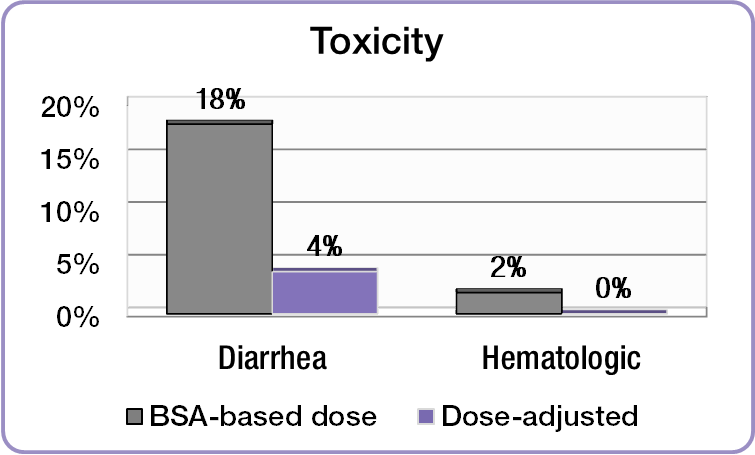 In the same study, investigators compared the incidence of common 5-FU-associated grade 3/4 toxicities between the dose-adjusted people and people dosed per BSA.
In the same study, investigators compared the incidence of common 5-FU-associated grade 3/4 toxicities between the dose-adjusted people and people dosed per BSA.[ The incidence of debilitating grades of diarrhea was reduced from 18% in the BSA-dosed group to 4% in the dose-adjusted group and serious hematologic side effects were eliminated.][ Because of the reduced toxicity, dose-adjusted patients were able to be treated for longer periods of time.][ BSA-dosed people were treated for a total of 680 months while people in the dose-adjusted group were treated for a total of 791 months.][ Completing the course of treatment is an important factor in achieving better treatment outcomes.
Similar results were found in a study involving people with colorectal cancer who have been treated with the popular FOLFOX regimen.][ The incidence of serious diarrhea was reduced from 12% in the BSA-dosed group of patients to 1.7% in the dose-adjusted group, and the incidence of severe mucositis was reduced from 15% to 0.8%.][
The FOLFOX study also demonstrated an improvement in treatment outcomes.][ Positive response increased from 46% in the BSA-dosed group to 70% in the dose-adjusted group. Median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) both improved by six months in the dose adjusted group.][
One approach that can help clinicians individualize chemotherapy dosing is to measure the drug levels in blood plasma over time and adjust dose according to a formula or algorithm to achieve optimal exposure. With an established target exposure for optimized treatment effectiveness with minimized toxicities, dosing can be personalized to achieve target exposure and optimal results for each person. Such an algorithm was used in the clinical trials cited above and resulted in significantly improved treatment outcomes.
Oncologists are already individualizing dosing of some cancer drugs based on exposure. ]Carboplatin
Carboplatin, sold under the trade name Paraplatin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of forms of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, brain cancer, and neuroblastoma. It is used ...
methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
, 5-FU, paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (PTX), sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical can ...
, and docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cell ...
.
The serum albumin level immediately prior to chemotherapy administration is an independent prognostic predictor of survival in various cancer types.
Types

Alkylating agents
Alkylating agents are the oldest group of chemotherapeutics in use today. Originally derived from mustard gas
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect: the substance, when dispersed, is often not actually a gas, b ...
used in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, there are now many types of alkylating agents in use.[ They are so named because of their ability to alkylate many molecules, including ]protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s, RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
and DNA. This ability to bind covalently
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
to DNA via their alkyl group
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalk ...
is the primary cause for their anti-cancer effects.cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
, or tries to repair it, the DNA strands can break. This leads to a form of programmed cell death called apoptosis.[ Alkylating agents will work at any point in the cell cycle and thus are known as cell cycle-independent drugs. For this reason, the effect on the cell is dose dependent; the fraction of cells that die is directly proportional to the dose of drug.][
The subtypes of alkylating agents are the ]nitrogen mustard
Nitrogen mustards are cytotoxic organic compounds with the chloroethylamine (Cl(CH2)2NR2) functional group. Although originally produced as chemical warfare agents, they were the first chemotherapeutic agents for treatment of cancer. Nitrogen ...
s, nitrosoureas
Nitrosourea is both the name of a molecule, and a class of compounds that include a nitroso (R-NO) group and a urea.
Examples
Examples include:
* Arabinopyranosyl-''N''-methyl-''N''-nitrosourea (Aranose)
* Carmustine (BCNU, BiCNU)
* Chlorozoto ...
, tetrazine
Tetrazine is a compound that consists of a six-membered aromatic ring containing four nitrogen atoms with the molecular formula C2 H2 N4. The name ''tetrazine'' is used in the nomenclature of derivatives of this compound. Three core-ring isome ...
s, aziridines, cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelio ...
s and derivatives, and non-classical alkylating agents. Nitrogen mustards include mechlorethamine, cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian can ...
, melphalan
Melphalan, sold under the brand name Alkeran among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, melanoma, and AL amyloidosis. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
Common side effects inclu ...
, chlorambucil
Chlorambucil, sold under the brand name Leukeran among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Hodgkin lymphoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. For CLL it is a preferred treatment. It is given by mouth.
...
, ifosfamide
Ifosfamide (IFO), sold under the brand name Ifex among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes testicular cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcoma, bladder cancer, small cell lung cancer, ce ...
and busulfan. Nitrosoureas include N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (MNU), carmustine
Carmustine, sold under the brand name BiCNU among others, is a medication used mainly for chemotherapy. It is a nitrogen mustard β-chloro- nitrosourea compound used as an alkylating agent.
Description
Carmustine is an orange-yellow solid medica ...
(BCNU), lomustine (CCNU) and semustine
Semustine (1- (2-Chloroethyl)-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)- 1-nitrosourea, MeCCNU) is an alkylating nitrosourea compound used in chemotherapy treatment of various types of tumours. Due to its lipophilic property, semustine can cross the blood-br ...
(MeCCNU), fotemustine
Fotemustine is a nitrosourea alkylating agent used in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. It is available in Europe but has not been approved by the United States FDA. A study has shown that fotemustine produces improved response rates and but ...
and streptozotocin. Tetrazines include dacarbazine, mitozolomide and temozolomide
Temozolomide (TMZ), sold under the brand name Temodar among others, is a medication used to treat brain tumors such as glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction ...
. Aziridines include thiotepa
Thiotepa ( INN), sold under the brand name Tepadina, is a medication used to treat cancer.
Thiotepa is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H4N)3PS. It is an analog of ''N'',''N′'',''N′′''-triethylenephosphoramide ...
, mytomycin
The mitomycins are a family of aziridine-containing natural products isolated from '' Streptomyces caespitosus'' or '' Streptomyces lavendulae.'' They include mitomycin A, mitomycin B, and mitomycin C. When the name mitomycin occurs alone, it usual ...
and diaziquone (AZQ). Cisplatin and derivatives include cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelio ...
, carboplatin
Carboplatin, sold under the trade name Paraplatin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of forms of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, brain cancer, and neuroblastoma. It is used ...
and oxaliplatin
Oxaliplatin, sold under the brand name Eloxatin among others, is a cancer medication (platinum-based antineoplastic class) used to treat colorectal cancer. It is given by injection into a vein.
Common side effects include numbness, feeling ti ...
.amino
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent su ...
, carboxyl
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxyl ...
, sulfhydryl, and phosphate group
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
s in biologically important molecules.[
]
Antimetabolites
 Anti-metabolites are a group of molecules that impede DNA and RNA synthesis. Many of them have a similar structure to the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The building blocks are
Anti-metabolites are a group of molecules that impede DNA and RNA synthesis. Many of them have a similar structure to the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The building blocks are nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecul ...
s; a molecule comprising a nucleobase
Nucleobases, also known as ''nitrogenous bases'' or often simply ''bases'', are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic ...
, a sugar and a phosphate group
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
. The nucleobases are divided into purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings ( pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purin ...
s (guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
and adenine
Adenine () (symbol A or Ade) is a nucleobase (a purine derivative). It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivativ ...
) and pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The othe ...
s (cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleobases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached ...
, thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine n ...
and uracil
Uracil () (symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced ...
). Anti-metabolites resemble either nucleobases or nucleosides (a nucleotide without the phosphate group), but have altered chemical groups.DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
can occur and programmed cell death ( apoptosis) is induced. Unlike alkylating agents, anti-metabolites are cell cycle dependent. This means that they only work during a specific part of the cell cycle, in this case S-phase (the DNA synthesis phase). For this reason, at a certain dose, the effect plateaus and proportionally no more cell death occurs with increased doses. Subtypes of the anti-metabolites are the anti-folates, fluoropyrimidines, deoxynucleoside analogues and thiopurine
The thiopurine drugs are purine antimetabolites widely used in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, autoimmune disorders (e.g., Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis), and organ transplant recipients.
Metabolism is catalyzed by S-methy ...
s.[
The anti-folates include ]methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
and pemetrexed
Pemetrexed, sold under the brand name Alimta among others, is a chemotherapy medication for the treatment of pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)..
It is available as a generic medication.
Medical use
In February 2004, t ...
. Methotrexate inhibits dihydrofolate reductase
Dihydrofolate reductase, or DHFR, is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, using NADPH as an electron donor, which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in 1-carbon transfer chemistry. ...
(DHFR), an enzyme that regenerates tetrahydrofolate
Tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative.
Metabolism
Human synthesis
Tetrahydrofolic acid is produced from dihydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase. This reaction is inhibited by methotrexate.
It is ...
from dihydrofolate. When the enzyme is inhibited by methotrexate, the cellular levels of folate coenzymes diminish. These are required for thymidylate and purine production, which are both essential for DNA synthesis and cell division.[ Pemetrexed is another anti-metabolite that affects purine and pyrimidine production, and therefore also inhibits DNA synthesis. It primarily inhibits the enzyme ]thymidylate synthase
Thymidylate synthase (TS) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). Thymidine is one of the nucleotides in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucle ...
, but also has effects on DHFR, aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase.fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pa ...
and capecitabine
Capecitabine, sold under the brand name Xeloda among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat breast cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. For breast cancer it is often used together with docetaxel. It is taken by mouth.
Co ...
. Fluorouracil is a nucleobase analogue that is metabolised in cells to form at least two active products; 5-fluourouridine monophosphate (FUMP) and 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-phosphate (fdUMP). FUMP becomes incorporated into RNA and fdUMP inhibits the enzyme thymidylate synthase; both of which lead to cell death.[ Capecitabine is a prodrug of 5-fluorouracil that is broken down in cells to produce the active drug.]cytarabine
Cytarabine, also known as cytosine arabinoside (ara-C), is a chemotherapy medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by i ...
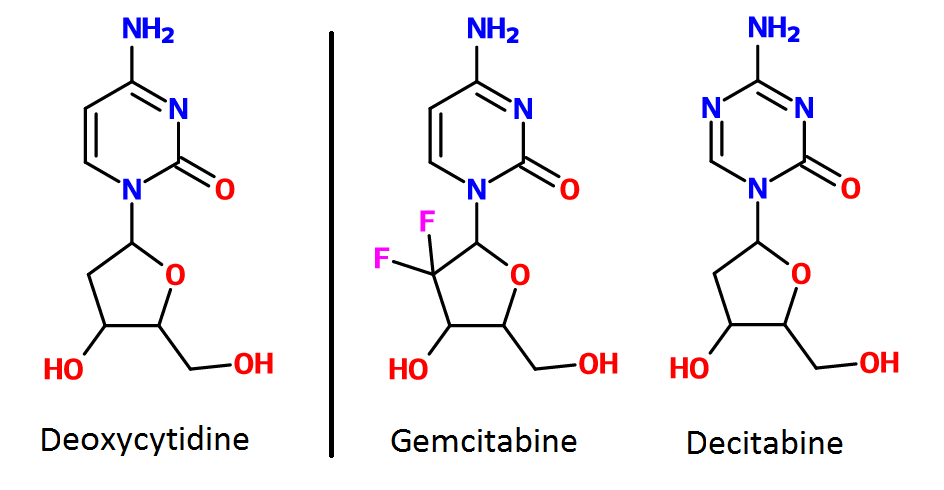
, gemcitabine
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by ...
, decitabine
Decitabine, sold under the brand name Dacogen among others, acts as a nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor. It is a medication for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes, a class of conditions where certain blood cells are dysfunctional, and for ...
, azacitidine
Azacitidine, sold under the brand name Vidaza among others, is used for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome, myeloid leukemia, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. It is a chemical analog of cytidine, a nucleoside in DNA and RNA. Azacitid ...
, fludarabine
Fludarabine is a purine analogue and antineoplastic agent. It is generally used as its 5-O-phosphorylated form known as fludarabine phosphate,
sold under the brand name Fludara among others. It is a chemotherapy medication used in the treatmen ...
, nelarabine, cladribine
Cladribine, sold under the brand name Leustatin, among others, is a medication used to treat hairy cell leukemia (leukemic reticuloendotheliosis) and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Cladribine, sold under the brand name Mavenclad, is indica ...
, clofarabine, and pentostatin. The thiopurines include thioguanine and mercaptopurine
Mercaptopurine (6-MP), sold under the brand name Purinethol among others, is a medication used for cancer and autoimmune diseases. Specifically it is used to treat acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), Crohn's dise ...
.[
]
Anti-microtubule agents
 Anti-microtubule agents are
Anti-microtubule agents are plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
-derived chemicals that block cell division by preventing microtubule function. Microtubules are an important cellular structure composed of two proteins, α-tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoske ...
and β-tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoske ...
. They are hollow, rod-shaped structures that are required for cell division, among other cellular functions.taxane
Taxanes are a class of diterpenes. They were originally identified from plants of the genus ''Taxus'' (yews), and feature a taxadiene core. Paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere) are widely used as chemotherapy agents. Cabazitaxel was FDA ap ...
s are the two main groups of anti-microtubule agents, and although both of these groups of drugs cause microtubule dysfunction, their mechanisms of action are completely opposite: ''Vinca'' alkaloids prevent the assembly of microtubules, whereas taxanes prevent their disassembly. By doing so, they can induce mitotic catastrophe
Mitotic Catastrophe has been defined as either a cellular mechanism to prevent potentially cancerous cells from proliferating or as a mode of cellular death that occurs following improper cell cycle progression or entrance. Mitotic catastrophe can ...
in the cancer cells. Following this, cell cycle arrest occurs, which induces programmed cell death ( apoptosis).[ These drugs can also affect blood vessel growth, an essential process that tumours utilise in order to grow and metastasise.]natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical sy ...
s that include vincristine
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin' ...
and vinblastine
Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, bladder c ...
.vinorelbine
Vinorelbine (NVB), sold under the brand name Navelbine among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. It is given by injection into a vein or by mo ...
(used in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to s ...
[), ]vindesine
Vindesine, also termed Eldisine, is a semisynthetic vinca alkaloid derived from the flowering plant '' Catharanthus roseus.'' Like the natural (e.g. vinblastine and vincristine) and semisynthetic vinca alkaloids (e.g. vinorelbine and vinflun ...
, and vinflunine
Vinflunine (INN, trade name Javlor) is a novel fluorinated ''vinca'' alkaloid derivative undergoing research for the treatment of bladder cancer. It was originally discovered by the team of the Professor Jean-Claude Jacquesy (UMR CNRS 6514 – P ...
.[ These drugs are ]cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA ( DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
-specific. They bind to the tubulin molecules in S-phase and prevent proper microtubule formation required for M-phase
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintai ...
.[
Taxanes are natural and semi-synthetic drugs. The first drug of their class, ]paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (PTX), sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical can ...
, was originally extracted from ''Taxus brevifolia
''Taxus brevifolia'', the Pacific yew or western yew, is a species of tree in the yew family Taxaceae native to the Pacific Northwest of North America. It is a small evergreen conifer, thriving in moisture and otherwise tending to take the form ...
'', the Pacific yew. Now this drug and another in this class, docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cell ...
, are produced semi-synthetically from a chemical found in the bark of another yew tree, ''Taxus baccata
''Taxus baccata'' is a species of evergreen tree in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the famil ...
''.
Podophyllotoxin
Podophyllotoxin (PPT) is the active ingredient in Podofilox, which is a medical cream that is used to treat genital warts and molluscum contagiosum. It is not recommended in HPV infections without external warts. It can be applied either by a hea ...
is an antineoplastic lignan
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a rol ...
obtained primarily from the American mayapple (''Podophyllum peltatum'') and Himalayan mayapple (''Sinopodophyllum hexandrum''). It has anti-microtubule activity, and its mechanism is similar to that of ''vinca'' alkaloids in that they bind to tubulin, inhibiting microtubule formation. Podophyllotoxin is used to produce two other drugs with different mechanisms of action: etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is ...
and teniposide
Teniposide (trade name Vumon) is a chemotherapeutic medication used in the treatment of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), Hodgkin's lymphoma, certain brain tumours, and other types of cancer. It is in a class of drugs known as podophyll ...
.
Topoisomerase inhibitors
 Topoisomerase inhibitors are drugs that affect the activity of two enzymes:
Topoisomerase inhibitors are drugs that affect the activity of two enzymes: topoisomerase I
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ...
and topoisomerase II
Type II topoisomerases are topoisomerases that cut both strands of the DNA helix simultaneously in order to manage DNA tangles and supercoils. They use the hydrolysis of ATP, unlike Type I topoisomerase. In this process, these enzymes change th ...
. When the DNA double-strand helix is unwound, during DNA replication or transcription, for example, the adjacent unopened DNA winds tighter (supercoils), like opening the middle of a twisted rope. The stress caused by this effect is in part aided by the topoisomerase enzymes. They produce single- or double-strand breaks into DNA, reducing the tension in the DNA strand. This allows the normal unwinding of DNA to occur during replication
Replication may refer to:
Science
* Replication (scientific method), one of the main principles of the scientific method, a.k.a. reproducibility
** Replication (statistics), the repetition of a test or complete experiment
** Replication crisi ...
or transcription. Inhibition of topoisomerase I or II interferes with both of these processes.irinotecan
Irinotecan, sold under the brand name Camptosar among others, is a medication used to treat colon cancer, and small cell lung cancer. For colon cancer it is used either alone or with fluorouracil. For small cell lung cancer it is used with cispl ...
and topotecan
Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the for ...
, are semi-synthetically derived from camptothecin
Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of '' Camptotheca acuminata'' (Campt ...
, which is obtained from the Chinese ornamental tree ''Camptotheca acuminata
''Camptotheca'' (happy tree, cancer tree, or tree of life) is a genus of medium-sized deciduous trees growing to tall, native to southern China and Tibet. The genus is usually included in the tupelo family Nyssaceae, but sometimes included (w ...
''.[ Drugs that target topoisomerase II can be divided into two groups. The topoisomerase II poisons cause increased levels enzymes bound to DNA. This prevents DNA replication and transcription, causes DNA strand breaks, and leads to programmed cell death ( apoptosis). These agents include ]etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is ...
, doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used tog ...
, mitoxantrone
Mitoxantrone (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as Mitozantrone in Australia; trade name Novantrone) is an anthracenedione antineoplastic agent.
Uses
Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly acute myeloid leukemia. It improves the ...
and teniposide
Teniposide (trade name Vumon) is a chemotherapeutic medication used in the treatment of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), Hodgkin's lymphoma, certain brain tumours, and other types of cancer. It is in a class of drugs known as podophyll ...
. The second group, catalytic inhibitors, are drugs that block the activity of topoisomerase II, and therefore prevent DNA synthesis and translation because the DNA cannot unwind properly. This group includes novobiocin
Novobiocin, also known as albamycin or cathomycin, is an aminocoumarin antibiotic that is produced by the actinomycete '' Streptomyces niveus'', which has recently been identified as a subjective synonym for ''S. spheroides'' a member of the clas ...
, merbarone, and aclarubicin
Aclarubicin (INN) or aclacinomycin A is an anthracycline drug that is used in the treatment of cancer. Soil bacteria '' Streptomyces galilaeus'' can produce aclarubicin. It can induce histone eviction from chromatin upon intercalation
Intercalat ...
, which also have other significant mechanisms of action.
Cytotoxic antibiotics
The cytotoxic antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s are a varied group of drugs that have various mechanisms of action. The common theme that they share in their chemotherapy indication is that they interrupt cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
. The most important subgroup is the anthracycline
Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from ''Streptomyces'' bacterium. These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, bladder ...
s and the bleomycins; other prominent examples include mitomycin C
Mitomycin C is a mitomycin that is used as a chemotherapeutic agent by virtue of its antitumour activity.
Medical uses
It is given intravenously to treat upper gastro-intestinal cancers (e.g. esophageal carcinoma), anal cancers, and breas ...
and actinomycin.doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used tog ...
and daunorubicin
Daunorubicin, also known as daunomycin, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Specifically it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and Kaposi's sarcoma ...
were the first, and were obtained from the bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were a ...
'' Streptomyces peucetius''. Derivatives of these compounds include epirubicin and idarubicin. Other clinically used drugs in the anthracycline group are pirarubicin, aclarubicin
Aclarubicin (INN) or aclacinomycin A is an anthracycline drug that is used in the treatment of cancer. Soil bacteria '' Streptomyces galilaeus'' can produce aclarubicin. It can induce histone eviction from chromatin upon intercalation
Intercalat ...
, and mitoxantrone
Mitoxantrone (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as Mitozantrone in Australia; trade name Novantrone) is an anthracenedione antineoplastic agent.
Uses
Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly acute myeloid leukemia. It improves the ...
. The mechanisms of anthracyclines include DNA intercalation (molecules insert between the two strands of DNA), generation of highly reactive free radicals
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron.
With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spon ...
that damage intercellular molecules and topoisomerase inhibition.RNA synthesis
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules calle ...
.free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Ailments of unknown cause
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabo ...
s that damage DNA. This occurs when bleomycin binds to a metal ion, becomes chemically reduced and reacts with oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
.[
Mitomycin is a cytotoxic antibiotic with the ability to alkylate DNA.]
Delivery
 Most chemotherapy is delivered
Most chemotherapy is delivered intravenously
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
, although a number of agents can be administered orally (e.g., melphalan
Melphalan, sold under the brand name Alkeran among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, melanoma, and AL amyloidosis. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
Common side effects inclu ...
, busulfan, capecitabine
Capecitabine, sold under the brand name Xeloda among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat breast cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. For breast cancer it is often used together with docetaxel. It is taken by mouth.
Co ...
). According to a recent (2016) systematic review, oral therapies present additional challenges for patients and care teams to maintain and support adherence to treatment plans.
There are many intravenous methods of drug delivery, known as vascular access devices. These include the winged infusion device, peripheral venous catheter
In medicine, a peripheral venous catheter, peripheral venous line, peripheral venous access catheter, or peripheral intravenous catheter, is a catheter (small, flexible tube) placed into a peripheral vein for venous access to administer intrave ...
, midline catheter, peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC), central venous catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more central ...
and implantable port. The devices have different applications regarding duration of chemotherapy treatment, method of delivery and types of chemotherapeutic agent.[
Depending on the person, the cancer, the stage of cancer, the type of chemotherapy, and the dosage, intravenous chemotherapy may be given on either an ]inpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other healt ...
or an outpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health c ...
basis. For continuous, frequent or prolonged intravenous chemotherapy administration, various systems may be surgically inserted into the vasculature to maintain access.[ Commonly used systems are the ]Hickman line
A Hickman line is a central venous catheter most often used for the administration of chemotherapy or other medications, as well as for the withdrawal of blood for analysis. Some types are used mainly for the purpose of apheresis or dialysis. ...
, the Port-a-Cath, and the PICC line. These have a lower infection risk, are much less prone to phlebitis
Phlebitis (or Venitis) is inflammation of a vein, usually in the legs. It most commonly occurs in superficial veins. Phlebitis often occurs in conjunction with thrombosis and is then called thrombophlebitis or superficial thrombophlebitis. Unlik ...
or extravasation, and eliminate the need for repeated insertion of peripheral cannulae.
Isolated limb perfusion (often used in melanoma),5-fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancrea ...
, are used to treat some cases of non-melanoma skin cancer.
If the cancer has central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
involvement, or with meningeal disease, intrathecal
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is useful in spinal anesthesia, chemotherapy, or pa ...
chemotherapy may be administered.[
]
Adverse effects
Chemotherapeutic techniques have a range of side effects that depend on the type of medications used. The most common medications affect mainly the fast-dividing cells of the body, such as blood cells and the cells lining the mouth, stomach, and intestines. Chemotherapy-related toxicities can occur acutely after administration, within hours or days, or chronically, from weeks to years.[
In many cases, an increase in tolerability/reduction in side effects and enhanced therapeutic efficacy through short-term fasting in the days of therapy was observed both in human and in animal experiments.
]
Immunosuppression and myelosuppression
Virtually all chemotherapeutic regimens can cause depression of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
, often by paralysing the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoieti ...
and leading to a decrease of white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
s, red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s, and platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s.
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
and thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients a ...
may require blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but m ...
. Neutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteri ...
(a decrease of the neutrophil granulocyte
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
count below 0.5 x 109/litre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3 ...
) can be improved with synthetic G-CSF
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF or GCSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 3 (CSF 3), is a glycoprotein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells and release them into the bloodstream.
Functional ...
(granulocyte
Granulocytes are
cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They ...
-colony-stimulating factor, e.g., filgrastim
Filgrastim, sold under the brand name Neupogen among others, is a medication used to treat low neutrophil count. Low neutrophil counts may occur with HIV/AIDS, following chemotherapy or radiation poisoning, or be of an unknown cause. It may ...
, lenograstim).
In very severe myelosuppression, which occurs in some regimens, almost all the bone marrow stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
s (cells that produce white
White is the lightness, lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully diffuse reflection, reflect and scattering, scatter all the ...
and red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s) are destroyed, meaning ''allogenic'' or ''autologous
Autotransplantation is the organ transplantation, transplantation of Organ (anatomy), organs, Biological tissue, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person (''wikt:auto-, auto-'' meaning "self" ...
'' bone marrow cell transplants are necessary. (In autologous BMTs, cells are removed from the person before the treatment, multiplied and then re-injected afterward; in ''allogenic'' BMTs, the source is a donor.) However, some people still develop diseases because of this interference with bone marrow.
Although people receiving chemotherapy are encouraged to wash their hands, avoid sick people, and take other infection-reducing steps, about 85% of infections are due to naturally occurring microorganisms in the person's own gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
(including oral cavity
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on t ...
) and skin.sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is foll ...
, or as localized outbreaks, such as Herpes simplex
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected.
Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold ...
, shingles
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. ...
, or other members of the Herpesviridea.quinolone
Quinolone may refer to:
* 2-Quinolone
* 4-Quinolone
* Quinolone antibiotic
A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They a ...
s or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the brand name Bactrim among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It consists of one part trimethoprim to five parts sulfamethoxazo ...
before any fever or sign of infection appears.[ However, in general, for every five people who are immunosuppressed following chemotherapy who take an antibiotic, one fever can be prevented; for every 34 who take an antibiotic, one death can be prevented.][ Sometimes, chemotherapy treatments are postponed because the immune system is suppressed to a critically low level.
In Japan, the government has approved the use of some ]medicinal mushrooms
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, ...
like ''Trametes versicolor
''Trametes versicolor''also known as ''Coriolus versicolor'' and ''Polyporus versicolor''is a common polypore mushroom found throughout the world. Meaning 'of several colors', ''versicolor'' reliably describes this fungus that displays a variet ...
'', to counteract depression of the immune system in people undergoing chemotherapy.Trilaciclib
Trilaciclib, sold under the brand name Cosela, is a medication used to reduce the frequency of chemotherapy-induced bone marrow suppression.
The most common side effects include fatigue; low levels of calcium, potassium and phosphate; increase ...
is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 approved for the prevention of myelosuppression caused by chemotherapy. The drug is given before chemotherapy to protect bone marrow function.
Neutropenic enterocolitis
Due to immune system suppression, neutropenic enterocolitis
Neutropenic enterocolitis is inflammation of the cecum (part of the large intestine) that may be associated with infection. It is particularly associated with neutropenia, a low level of neutrophil granulocytes (the most common form of white blood ...
(typhlitis) is a "life-threatening gastrointestinal complication of chemotherapy." Typhlitis is an intestinal infection which may manifest itself through symptoms including nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin ...
, a distended abdomen
Abdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. Pe ...
, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, chills
Chills is a feeling of coldness occurring during a high fever, but sometimes is also a common symptom which occurs alone in specific people. It occurs during fever due to the release of cytokines and prostaglandins as part of the inflammatory ...
, or abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
and tenderness.
Typhlitis is a medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
. It has a very poor prognosis
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stabl ...
and is often fatal unless promptly recognized and aggressively treated.[
]
Gastrointestinal distress
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
, anorexia
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Gre ...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin ...
, abdominal cramps, and constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
are common side-effects of chemotherapeutic medications that kill fast-dividing cells.Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
and dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mi ...
can result when the recipient does not eat or drink enough, or when the person vomits frequently, because of gastrointestinal damage. This can result in rapid weight loss, or occasionally in weight gain, if the person eats too much in an effort to allay nausea or heartburn. Weight gain can also be caused by some steroid medications. These side-effects can frequently be reduced or eliminated with antiemetic
An antiemetic is a drug that is effective against vomiting and nausea. Antiemetics are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics, and chemotherapy directed against cancer. The ...
drugs. Low-certainty evidence also suggests that probiotics may have a preventative and treatment effect of diarrhoea related to chemotherapy alone and with radiotherapy. However, a high index of suspicion is appropriate, since diarrhoea and bloating are also symptoms of typhlitis, a very serious and potentially life-threatening medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
that requires immediate treatment.
Anemia
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
can be a combined outcome caused by myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and possible cancer-related causes such as bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
, blood cell
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
destruction (hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo o ...
), hereditary disease, kidney dysfunction, nutritional deficiencies or anemia of chronic disease
Anemia of chronic disease (ACD) or anemia of chronic inflammation is a form of anemia seen in chronic infection, chronic immune activation, and malignancy. These conditions all produce elevation of interleukin-6, which stimulates hepcidin product ...
. Treatments to mitigate anemia include hormones to boost blood production (erythropoietin
Erythropoietin (; EPO), also known as erythropoetin, haematopoietin, or haemopoietin, is a glycoprotein cytokine secreted mainly by the kidneys in response to cellular hypoxia; it stimulates red blood cell production (erythropoiesis) in the bon ...
), iron supplements, and blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but m ...
s.platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s in the blood, which can result in bruises and bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
. Extremely low platelet counts may be temporarily boosted through platelet transfusion
Platelet transfusion, also known as platelet concentrate, is used to prevent or treat bleeding in people with either a low platelet count or poor platelet function. Often this occurs in people receiving cancer chemotherapy. Preventive transfusi ...
s and new drugs to increase platelet counts during chemotherapy are being developed.Fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
may be a consequence of the cancer or its treatment, and can last for months to years after treatment. One physiological cause of fatigue is anemia, which can be caused by chemotherapy, surgery, radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Ra ...
, primary and metastatic disease or nutritional depletion.Aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise (also known as endurance activities, cardio or cardio-respiratory exercise) is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, inv ...
has been found to be beneficial in reducing fatigue in people with solid tumours.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
are two of the most feared cancer treatment-related side-effects for people with cancer and their families. In 1983, Coates et al. found that people receiving chemotherapy ranked nausea and vomiting as the first and second most severe side-effects, respectively. Up to 20% of people receiving highly emetogenic agents in this era postponed, or even refused potentially curative treatments. Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) are common with many treatments and some forms of cancer. Since the 1990s, several novel classes of antiemetics
An antiemetic is a drug that is effective against vomiting and nausea. Antiemetics are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics, and chemotherapy directed against cancer. They may ...
have been developed and commercialized, becoming a nearly universal standard in chemotherapy regimens, and helping to successfully manage these symptoms in many people. Effective mediation of these unpleasant and sometimes-crippling symptoms results in increased quality of life for the recipient and more efficient treatment cycles, due to less stoppage of treatment due to better tolerance and better overall health.
Hair loss
Hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarr ...
(alopecia) can be caused by chemotherapy that kills rapidly dividing cells; other medications may cause hair to thin. These are most often temporary effects: hair usually starts to regrow a few weeks after the last treatment, but sometimes with a change in color, texture, thickness or style. Sometimes hair has a tendency to curl after regrowth, resulting in "chemo curls." Severe hair loss occurs most often with drugs such as doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used tog ...
, daunorubicin
Daunorubicin, also known as daunomycin, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Specifically it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and Kaposi's sarcoma ...
, paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (PTX), sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical can ...
, docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cell ...
, cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian can ...
, ifosfamide
Ifosfamide (IFO), sold under the brand name Ifex among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes testicular cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcoma, bladder cancer, small cell lung cancer, ce ...
and etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is ...
. Permanent thinning or hair loss can result from some standard chemotherapy regimens.
Chemotherapy induced hair loss occurs by a non-androgenic mechanism, and can manifest as alopecia totalis
Alopecia totalis is the loss of all hair on the head and face. Its causes are unclear, but believed to be autoimmune. Research suggests there may be a genetic component linked to developing alopecia totalis; the presence of DRB1*0401 and DQB1*03 ...
, telogen effluvium, or less often alopecia areata
Alopecia areata, also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often, it results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress and illness are po ...
.
Secondary neoplasm
Development of secondary neoplasia after successful chemotherapy or radiotherapy treatment can occur. The most common secondary neoplasm is secondary acute myeloid leukemia, which develops primarily after treatment with alkylating agents or topoisomerase inhibitors. Survivors of childhood cancer are more than 13 times as likely to get a secondary neoplasm during the 30 years after treatment than the general population. Not all of this increase can be attributed to chemotherapy.
Infertility
Some types of chemotherapy are gonadotoxic and may cause infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal st ...
.[ Drugs with medium risk include doxorubicin and platinum analogs such as cisplatin and carboplatin.][ On the other hand, therapies with low risk of gonadotoxicity include plant derivatives such as vincristine and vinblastine, ]antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s such as bleomycin and dactinomycin, and antimetabolites such as methotrexate, mercaptopurine, and 5-fluorouracil.[
]Female infertility
Female infertility refers to infertility in women. It affects an estimated 48 million women, with the highest prevalence of infertility affecting women in South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, North Africa/Middle East, and Central/Eastern Europe and Cen ...
by chemotherapy appears to be secondary to premature ovarian failure
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) (also called premature ovarian insufficiency, premature menopause, and premature ovarian failure) is the partial or total loss of reproductive and hormonal function of the ovaries before age 40 because of fo ...
by loss of primordial follicles.[
People may choose between several methods of fertility preservation prior to chemotherapy, including ]cryopreservation
Cryo-preservation or cryo-conservation is a process where organisms, organelles, cells, tissues, extracellular matrix, organs, or any other biological constructs susceptible to damage caused by unregulated chemical kinetics are preserved by coo ...
of semen, ovarian tissue, oocytes, or embryos. As more than half of cancer patients are elderly, this adverse effect is only relevant for a minority of patients. A study in France between 1999 and 2011 came to the result that embryo freezing before administration of gonadotoxic agents to females caused a delay of treatment in 34% of cases, and a live birth in 27% of surviving cases who wanted to become pregnant, with the follow-up time varying between 1 and 13 years.
Potential protective or attenuating agents include GnRH analog
A GnRH modulator, or GnRH receptor modulator, also known as an LHRH modulator or LHRH receptor modulator, is a type of medication which modulates the GnRH receptor, the biological target of the hypothalamic hormone gonadotropin-releasing hormon ...
s, where several studies have shown a protective effect ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'' in humans, but some studies show no such effect. Sphingosine-1-phosphate
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a signaling sphingolipid, also known as lysosphingolipid. It is also referred to as a bioactive lipid mediator. Sphingolipids at large form a class of lipids characterized by a particular aliphatic aminoalcoho ...
(S1P) has shown similar effect, but its mechanism of inhibiting the sphingomyelin apoptotic pathway may also interfere with the apoptosis action of chemotherapy drugs.conditioning regimen
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce ...
in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, a study of people conditioned with cyclophosphamide alone for severe aplastic anemia came to the result that ovarian recovery occurred in all women younger than 26 years at time of transplantation, but only in five of 16 women older than 26 years.
Teratogenicity
Chemotherapy is teratogenic
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in dysmorphology. The relat ...
during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
, especially during the first trimester
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
, to the extent that abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregn ...
usually is recommended if pregnancy in this period is found during chemotherapy.complications of pregnancy
Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal di ...
and fetal myelosuppression.[
In males previously having undergone chemotherapy or radiotherapy, there appears to be no increase in genetic defects or congenital malformations in their children conceived after therapy.][ The use of assisted reproductive technologies and micromanipulation techniques might increase this risk.][ In females previously having undergone chemotherapy, miscarriage and congenital malformations are not increased in subsequent conceptions.][ However, when ]in vitro fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) f ...
and embryo cryopreservation
Cryopreservation of embryos is the process of preserving an embryo at sub-zero temperatures, generally at an embryogenesis stage corresponding to pre-implantation, that is, from fertilisation to the blastocyst stage.
Indications
Embryo cryopreser ...
is practised between or shortly after treatment, possible genetic risks to the growing oocytes exist, and hence it has been recommended that the babies be screened.[
]
Peripheral neuropathy
Between 30 and 40 percent of people undergoing chemotherapy experience chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), a progressive, enduring, and often irreversible condition, causing pain, tingling, numbness and sensitivity to cold, beginning in the hands and feet and sometimes progressing to the arms and legs.thalidomide
Thalidomide, sold under the brand names Contergan and Thalomid among others, is a medication used to treat a number of cancers (including multiple myeloma), graft-versus-host disease, and a number of skin conditions including complications o ...
, epothilone
Epothilones are a class of potential cancer drugs. Like taxanes, they prevent cancer cells from dividing by interfering with tubulin, but in early trials, epothilones have better efficacy and milder adverse effects than taxanes.
, epothilones A ...
s, ''vinca'' alkaloids, taxanes, proteasome inhibitor
Proteasome inhibitors are drugs that block the action of proteasomes, cellular complexes that break down proteins. They are being studied in the treatment of cancer; and three are approved for use in treating multiple myeloma.
Mechanism
Multip ...
s, and the platinum-based drugs.[ Whether CIPN arises, and to what degree, is determined by the choice of drug, duration of use, the total amount consumed and whether the person already has ]peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or or ...
. Though the symptoms are mainly sensory, in some cases motor nerve
A motor nerve is a nerve that transmits motor signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles of the body. This is different from the motor neuron, which includes a cell body and branching of dendrites, while the nerve is made up of ...
s and the autonomic nervous system are affected.[ Pain can often be managed with drug or other treatment but the numbness is usually resistant to treatment.]
Cognitive impairment
Some people receiving chemotherapy report fatigue or non-specific neurocognitive problems, such as an inability to concentrate; this is sometimes called post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment, referred to as "chemo brain" in popular and social media.
Tumor lysis syndrome
In particularly large tumors and cancers with high white cell counts, such as lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enl ...
s, teratoma
A teratoma is a tumor made up of several different types of tissue, such as hair, muscle, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the ovary, testicle, or coccyx.
Symptoms
Symptoms may be minimal if the tumor is small. A testicular tera ...
s, and some leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
s, some people develop tumor lysis syndrome. The rapid breakdown of cancer cells causes the release of chemicals from the inside of the cells. Following this, high levels of uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosp ...
and phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
are found in the blood. High levels of phosphate induce secondary hypoparathyroidism, resulting in low levels of calcium in the blood. This causes kidney damage and the high levels of potassium can cause cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the Cardiac cycle, heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per mi ...
. Although prophylaxis is available and is often initiated in people with large tumors, this is a dangerous side-effect that can lead to death if left untreated.[
]
Organ damage
Cardiotoxicity (heart damage) is especially prominent with the use of anthracycline
Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from ''Streptomyces'' bacterium. These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, bladder ...
drugs (doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used tog ...
, epirubicin, idarubicin, and liposomal doxorubicin). The cause of this is most likely due to the production of free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Ailments of unknown cause
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabo ...
s in the cell and subsequent DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
. Other chemotherapeutic agents that cause cardiotoxicity, but at a lower incidence, are cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian can ...
, docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cell ...
and clofarabine.Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity (from ''hepatic toxicity'') implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn fr ...
(liver damage) can be caused by many cytotoxic drugs. The susceptibility of an individual to liver damage can be altered by other factors such as the cancer itself, viral hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form.
The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five unrelated hepatotropic vi ...
, immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
and nutritional deficiency. The liver damage can consist of damage to liver cells, hepatic sinusoidal syndrome (obstruction of the veins in the liver), cholestasis
Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or maligna ...
(where bile does not flow from the liver to the intestine) and liver fibrosis.Nephrotoxicity Nephrotoxicity is toxicity in the kidneys. It is a poisonous effect of some substances, both toxic chemicals and medications, on kidney function. There are various forms, and some drugs may affect kidney function in more than one way. Nephrotox ...
(kidney damage) can be caused by tumor lysis syndrome and also due direct effects of drug clearance by the kidneys. Different drugs will affect different parts of the kidney and the toxicity may be asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered as ...
(only seen on blood or urine tests) or may cause acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
Causes of AKI are cl ...
.Ototoxicity
Ototoxicity is the property of being toxic to the ear (''oto-''), specifically the cochlea or auditory nerve and sometimes the vestibular system, for example, as a side effect of a drug. The effects of ototoxicity can be reversible and temporary ...
(damage to the inner ear) is a common side effect of platinum based drugs that can produce symptoms such as dizziness and vertigo
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties ...
.
Other side-effects
Less common side-effects include red skin (erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not asso ...
), dry skin, damaged fingernails, a dry mouth (xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is often seen as a side ef ...
), water retention, and sexual impotence. Some medications can trigger allergic
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
or pseudoallergic reactions.
Specific chemotherapeutic agents are associated with organ-specific toxicities, including cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
(e.g., doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used tog ...
), interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs)) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pul ...
(e.g., bleomycin) and occasionally secondary neoplasm (e.g., MOPP therapy for Hodgkin's disease).
Hand-foot syndrome is another side effect to cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Nutritional problems are also frequently seen in cancer patients at diagnosis and through chemotherapy treatment. Research suggests that in children and young people undergoing cancer treatment, parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is the feeding of nutritional products to a person intravenously, bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. The products are made by pharmaceutical compounding companies. The person receives a nutritional m ...
may help with this leading to weight gain and increased calorie and protein intake, when compared to enteral nutrition.
Limitations
Chemotherapy does not always work, and even when it is useful, it may not completely destroy the cancer. People frequently fail to understand its limitations. In one study of people who had been newly diagnosed with incurable, stage 4 cancer
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that ha ...
, more than two-thirds of people with lung cancer and more than four-fifths of people with colorectal cancer still believed that chemotherapy was likely to cure their cancer.brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
. This is because the brain has an extensive system in place to protect it from harmful chemicals. Drug transporters can pump out drugs from the brain and brain's blood vessel cells into the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the bra ...
and blood circulation. These transporters pump out most chemotherapy drugs, which reduces their efficacy for treatment of brain tumors. Only small lipophilic
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves li ...
alkylating agents
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecti ...
such as lomustine or temozolomide
Temozolomide (TMZ), sold under the brand name Temodar among others, is a medication used to treat brain tumors such as glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction ...
are able to cross this blood–brain barrier.Blood vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
s in tumors are very different from those seen in normal tissues. As a tumor grows, tumor cells furthest away from the blood vessels become low in oxygen ( hypoxic). To counteract this they then signal for new blood vessels to grow. The newly formed tumor vasculature is poorly formed and does not deliver an adequate blood supply to all areas of the tumor. This leads to issues with drug delivery because many drugs will be delivered to the tumor by the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
.
Resistance
Resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
is a major cause of treatment failure in chemotherapeutic drugs. There are a few possible causes of resistance in cancer, one of which is the presence of small pumps on the surface of cancer cells that actively move chemotherapy from inside the cell to the outside. Cancer cells produce high amounts of these pumps, known as p-glycoprotein
P-glycoprotein 1 (permeability glycoprotein, abbreviated as P-gp or Pgp) also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1) or cluster of differentiation 243 (CD243) is an important protein ...
, in order to protect themselves from chemotherapeutics. Research on p-glycoprotein and other such chemotherapy efflux pumps is currently ongoing. Medications to inhibit the function of p-glycoprotein are undergoing investigation, but due to toxicities and interactions with anti-cancer drugs their development has been difficult.gene amplification Gene amplification refers to a number of natural and artificial processes by which the number of copies of a gene is increased "without a proportional increase in other genes".
Artificial DNA amplification
In research or diagnosis DNA amplificati ...
, a process in which multiple copies of a gene are produced by cancer cells. This overcomes the effect of drugs that reduce the expression of genes involved in replication. With more copies of the gene, the drug can not prevent all expression of the gene and therefore the cell can restore its proliferative ability. Cancer cells can also cause defects in the cellular pathways of apoptosis (programmed cell death). As most chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells in this manner, defective apoptosis allows survival of these cells, making them resistant. Many chemotherapy drugs also cause DNA damage, which can be repaired by enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s in the cell that carry out DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
. Upregulation of these genes can overcome the DNA damage and prevent the induction of apoptosis. Mutations in genes that produce drug target proteins, such as tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytosk ...
, can occur which prevent the drugs from binding to the protein, leading to resistance to these types of drugs.lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, the transcription factor NFκB is thought to play a role in resistance to chemotherapy, via inflammatory pathways.
Cytotoxics and targeted therapies
Targeted therapies
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks t ...
are a relatively new class of cancer drugs that can overcome many of the issues seen with the use of cytotoxics. They are divided into two groups: small molecule and antibodies. The massive toxicity seen with the use of cytotoxics is due to the lack of cell specificity of the drugs. They will kill any rapidly dividing cell, tumor or normal. Targeted therapies are designed to affect cellular proteins or processes that are utilised by the cancer cells. This allows a high dose to cancer tissues with a relatively low dose to other tissues. Although the side effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
are often less severe than that seen of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics, life-threatening effects can occur. Initially, the targeted therapeutics were supposed to be solely selective for one protein. Now it is clear that there is often a range of protein targets that the drug can bind. An example target for targeted therapy is the BCR-ABL1 protein produced from the Philadelphia chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in Chromosome 22 (human), chromosome 22 of Leukemia, leukemia cancer cells (particularly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells). This chromosome is defe ...
, a genetic lesion found commonly in chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumula ...
and in some patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. This fusion protein
Fusion proteins or chimeric (kī-ˈmir-ik) proteins (literally, made of parts from different sources) are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes that originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this ''fusion gene'' r ...
has enzyme activity that can be inhibited by imatinib, a small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs are ...
drug.
Mechanism of action
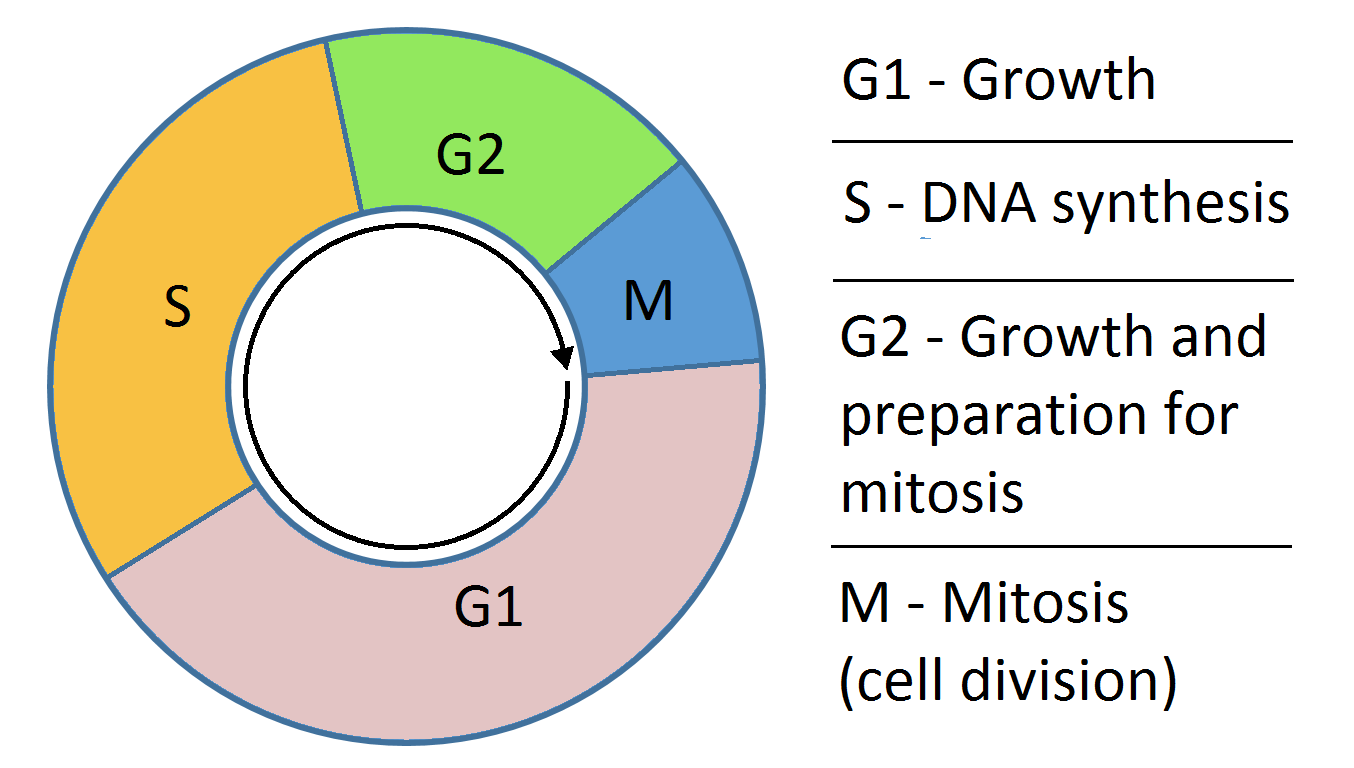
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
is the uncontrolled growth of cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
coupled with malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
behaviour: invasion and metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
(among other features).gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
tic susceptibility and environmental factors.genetic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
s in oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels. s (genes that control the growth rate of cells) and tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or re ...
s (genes that help to prevent cancer), which gives cancer cells their malignant characteristics, such as uncontrolled growth.
In the broad sense, most chemotherapeutic drugs work by impairing mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maint ...
(cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
), effectively targeting fast-dividing cells. As these drugs cause damage to cells, they are termed ''cytotoxic''. They prevent mitosis by various mechanisms including damaging DNA and inhibition of the cellular machinery involved in cell division.acute myelogenous leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include ...
and the aggressive lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enl ...
s, including Hodgkin's disease
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition ...
) are more sensitive to chemotherapy, as a larger proportion of the targeted cells are undergoing cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
at any time. Malignancies with slower growth rates, such as indolent lymphomas, tend to respond to chemotherapy much more modestly.immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
also make crucial contributions to the antitumor effects of chemotherapy. For example, the chemotherapeutic drugs oxaliplatin
Oxaliplatin, sold under the brand name Eloxatin among others, is a cancer medication (platinum-based antineoplastic class) used to treat colorectal cancer. It is given by injection into a vein.
Common side effects include numbness, feeling ti ...
and cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian can ...
can cause tumor cells to die in a way that is detectable by the immune system (called immunogenic cell death), which mobilizes immune cells with antitumor functions. Chemotherapeutic drugs that cause cancer immunogenic tumor cell death can make unresponsive tumors sensitive to immune checkpoint
Immune checkpoints are regulators of the immune system. These pathways are crucial for self-tolerance, which prevents the immune system from attacking cells indiscriminately. However, some cancers can protect themselves from attack by stimulat ...
therapy.
Other uses
Some chemotherapy drugs are used in diseases other than cancer, such as in autoimmune disorders,[ and noncancerous ]plasma cell dyscrasia
Plasma cell dyscrasias (also termed plasma cell disorders and plasma cell proliferative diseases) are a spectrum of progressively more severe monoclonal gammopathies in which a clone or multiple clones of pre-malignant or malignant plasma cells (s ...
. In some cases they are often used at lower doses, which means that the side effects are minimized,Methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and ...
(RA),psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complet ...
,ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hi ...
[ The anti-inflammatory response seen in RA is thought to be due to increases in ]adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside buildin ...
, which causes immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
; effects on immuno-regulatory cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase (COX), officially known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (PTGS), is an enzyme (specifically, a family of isozymes, ) that is responsible for formation of prostanoids, including thromboxane and prostaglandins such as prost ...
-2 enzyme pathways; reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in a ...
s; and anti-proliferative properties.[ Although methotrexate is used to treat both multiple sclerosis and ankylosing spondylitis, its efficacy in these diseases is still uncertain.]Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian can ...
is sometimes used to treat lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. It is a type of glomerulonephritis in which the glomeruli become inflamed. Since it is a result of SLE, this type of glomeru ...
, a common symptom of systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
.Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cav ...
along with either bortezomib
Bortezomib, sold under the brand name Velcade among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. This includes multiple myeloma in those who have and have not previously received treatment. It i ...
or melphalan
Melphalan, sold under the brand name Alkeran among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, melanoma, and AL amyloidosis. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
Common side effects inclu ...
is commonly used as a treatment for AL amyloidosis
Amyloid light-chain (AL) amyloidosis, also known as primary amyloidosis, is the most common form of systemic amyloidosis in the US. The disease is caused when a person's antibody-producing cells do not function properly and produce abnormal protei ...
. Recently, bortezomid in combination with cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian can ...
and dexamethasone has also shown promise as a treatment for AL amyloidosis. Other drugs used to treat myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, a ...
such as lenalidomide
Lenalidomide, sold under the trade name Revlimid among others, is a medication used to treat multiple myeloma, smoldering myeloma, and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). For multiple myeloma, it is used after at least one other treatment and gene ...
have shown promise in treating AL amyloidosis.
Chemotherapy drugs are also used in conditioning regimen
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce ...
s prior to bone marrow transplant ( hematopoietic stem cell transplant). Conditioning regimens are used to suppress the recipient's immune system in order to allow a transplant to engraft. Cyclophosphamide is a common cytotoxic drug used in this manner and is often used in conjunction with total body irradiation Total body irradiation (TBI) is a form of radiotherapy used primarily as part of the preparative regimen for haematopoietic stem cell (or bone marrow) transplantation. As the name implies, TBI involves irradiation of the entire body, though in mode ...
. Chemotherapeutic drugs may be used at high doses to permanently remove the recipient's bone marrow cells (myeloablative conditioning) or at lower doses that will prevent permanent bone marrow loss (non-myeloablative and reduced intensity conditioning). When used in non-cancer setting, the treatment is still called "chemotherapy", and is often done in the same treatment centers used for people with cancer.
Occupational exposure and safe handling
In the 1970s, antineoplastic (chemotherapy) drugs were identified as hazardous, and the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) is a professional organization that represents pharmacists who serve as patient care providers in hospitals, health systems, ambulatory clinics, and other healthcare settings. The organizat ...
(ASHP) has since then introduced the concept of hazardous drugs after publishing a recommendation in 1983 regarding handling hazardous drugs. The adaptation of federal regulations came when the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration'' (OSHA ) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. Congress established the agenc ...
(OSHA) first released its guidelines in 1986 and then updated them in 1996, 1999, and, most recently, 2006.
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the ...
(NIOSH) has been conducting an assessment in the workplace since then regarding these drugs. Occupational exposure to antineoplastic drugs has been linked to multiple health effects, including infertility and possible carcinogenic effects. A few cases have been reported by the NIOSH alert report, such as one in which a female pharmacist was diagnosed with papillary transitional cell carcinoma. Twelve years before the pharmacist was diagnosed with the condition, she had worked for 20 months in a hospital where she was responsible for preparing multiple antineoplastic drugs.
Routes of exposure
Antineoplastic drugs are usually given through intravenous, intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have ...
, intrathecal
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is useful in spinal anesthesia, chemotherapy, or pa ...
, or subcutaneous Subcutaneous may refer to:
* Subcutaneous injection
* Subcutaneous tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The ...
administration. In most cases, before the medication is administered to the patient, it needs to be prepared and handled by several workers. Any worker who is involved in handling, preparing, or administering the drugs, or with cleaning objects that have come into contact with antineoplastic drugs, is potentially exposed to hazardous drugs. Health care workers are exposed to drugs in different circumstances, such as when pharmacists and pharmacy technicians prepare and handle antineoplastic drugs and when nurses and physicians administer the drugs to patients. Additionally, those who are responsible for disposing antineoplastic drugs in health care facilities are also at risk of exposure.
Hazards
Hazardous drugs expose health care workers to serious health risks. Many studies show that antineoplastic drugs could have many side effects on the reproductive system, such as fetal loss, congenital malformation, and infertility. Health care workers who are exposed to antineoplastic drugs on many occasions have adverse reproductive outcomes such as spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and congenital malformations. Moreover, studies have shown that exposure to these drugs leads to menstrual cycle irregularities. Antineoplastic drugs may also increase the risk of learning disabilities among children of health care workers who are exposed to these hazardous substances.
Moreover, these drugs have carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive subst ...
ic effects. In the past five decades, multiple studies have shown the carcinogenic effects of exposure to antineoplastic drugs. Similarly, there have been research studies that linked alkylating agents with humans developing leukemias. Studies have reported elevated risk of breast cancer, nonmelanoma skin cancer, and cancer of the rectum among nurses who are exposed to these drugs. Other investigations revealed that there is a potential genotoxic Genotoxicity is the property of chemical agents that damage the genetic information within a cell causing mutations, which may lead to cancer. While genotoxicity is often confused with mutagenicity, all mutagens are genotoxic, but some genotoxic sub ...
effect from anti-neoplastic drugs to workers in health care settings.[
]
Safe handling in health care settings
As of 2018, there were no occupational exposure limit
An occupational exposure limit is an upper limit on the acceptable concentration of a hazardous substance in workplace air for a particular material or class of materials. It is typically set by competent national authorities and enforced by le ...
s set for antineoplastic drugs, i.e., OSHA or the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists
The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) is a professional association of industrial hygienists and practitioners of related professions, with headquarters in Cincinnati, Ohio. One of its goals is to advance worker pr ...
(ACGIH) have not set workplace safety guidelines.
Preparation
NIOSH recommends using a ventilated cabinet that is designed to decrease worker exposure. Additionally, it recommends training of all staff, the use of cabinets, implementing an initial evaluation of the technique of the safety program, and wearing protective gloves and gowns when opening drug packaging, handling vials, or labeling. When wearing personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, ...
, one should inspect gloves for physical defects before use and always wear double gloves and protective gowns. Health care workers are also required to wash their hands with water and soap before and after working with antineoplastic drugs, change gloves every 30 minutes or whenever punctured, and discard them immediately in a chemotherapy waste container.
The gowns used should be disposable gowns made of polyethylene-coated polypropylene. When wearing gowns, individuals should make sure that the gowns are closed and have long sleeves. When preparation is done, the final product should be completely sealed in a plastic bag.
The health care worker should also wipe all waste containers inside the ventilated cabinet before removing them from the cabinet. Finally, workers should remove all protective wear and put them in a bag for their disposal inside the ventilated cabinet.[
]
Administration
Drugs should only be administered using protective medical devices such as needle lists and closed systems and techniques such as priming of IV tubing by pharmacy personnel inside a ventilated cabinet. Workers should always wear personal protective equipment such as double gloves, goggles, and protective gowns when opening the outer bag and assembling the delivery system to deliver the drug to the patient, and when disposing of all material used in the administration of the drugs.[
Hospital workers should never remove tubing from an IV bag that contains an antineoplastic drug, and when disconnecting the tubing in the system, they should make sure the tubing has been thoroughly flushed. After removing the IV bag, the workers should place it together with other disposable items directly in the yellow chemotherapy waste container with the lid closed. Protective equipment should be removed and put into a disposable chemotherapy waste container. After this has been done, one should double bag the chemotherapy waste before or after removing one's inner gloves. Moreover, one must always wash one's hands with soap and water before leaving the drug administration site.
]
Employee training
All employees whose jobs in health care facilities expose them to hazardous drugs must receive training. Training should include shipping and receiving personnel, housekeepers, pharmacists, assistants, and all individuals involved in the transportation and storage of antineoplastic drugs. These individuals should receive information and training to inform them of the hazards of the drugs present in their areas of work. They should be informed and trained on operations and procedures in their work areas where they can encounter hazards, different methods used to detect the presence of hazardous drugs and how the hazards are released, and the physical and health hazards of the drugs, including their reproductive and carcinogenic hazard potential. Additionally, they should be informed and trained on the measures they should take to avoid and protect themselves from these hazards. This information ought to be provided when health care workers come into contact with the drugs, that is, perform the initial assignment in a work area with hazardous drugs. Moreover, training should also be provided when new hazards emerge as well as when new drugs, procedures, or equipment are introduced.[
]
Housekeeping and waste disposal
When performing cleaning and decontaminating the work area where antineoplastic drugs are used, one should make sure that there is sufficient ventilation to prevent the buildup of airborne drug concentrations. When cleaning the work surface, hospital workers should use deactivation and cleaning agents before and after each activity as well as at the end of their shifts. Cleaning should always be done using double protective gloves and disposable gowns. After employees finish up cleaning, they should dispose of the items used in the activity in a yellow chemotherapy waste container while still wearing protective gloves. After removing the gloves, they should thoroughly wash their hands with soap and water. Anything that comes into contact or has a trace of the antineoplastic drugs, such as needles, empty vials, syringes, gowns, and gloves, should be put in the chemotherapy waste container.
Spill control
A written policy needs to be in place in case of a spill of antineoplastic products. The policy should address the possibility of various sizes of spills as well as the procedure and personal protective equipment required for each size. A trained worker should handle a large spill and always dispose of all cleanup materials in the chemical waste container according to EPA regulations, not in a yellow chemotherapy waste container.
Occupational monitoring
A medical surveillance
Workplace health surveillance or occupational health surveillance (U.S.) is the ongoing systematic collection, analysis, and dissemination of exposure and health data on groups of workers. The Joint ILO/ WHO Committee on Occupational Health at i ...
program must be established. In case of exposure, occupational health professionals need to ask for a detailed history and do a thorough physical exam. They should test the urine of the potentially exposed worker by doing a urine dipstick or microscopic examination, mainly looking for blood, as several antineoplastic drugs are known to cause bladder damage.[
Urinary mutagenicity is a marker of exposure to antineoplastic drugs that was first used by Falck and colleagues in 1979 and uses bacterial mutagenicity assays. Apart from being nonspecific, the test can be influenced by extraneous factors such as dietary intake and smoking and is, therefore, used sparingly. However, the test played a significant role in changing the use of horizontal flow cabinets to vertical flow biological safety cabinets during the preparation of antineoplastic drugs because the former exposed health care workers to high levels of drugs. This changed the handling of drugs and effectively reduced workers' exposure to antineoplastic drugs.][
Biomarkers of exposure to antineoplastic drugs commonly include urinary ]platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Pla ...
, methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
, urinary cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian can ...
and ifosfamide
Ifosfamide (IFO), sold under the brand name Ifex among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes testicular cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcoma, bladder cancer, small cell lung cancer, ce ...
, and urinary metabolite of 5-fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancrea ...
. In addition to this, there are other drugs used to measure the drugs directly in the urine, although they are rarely used. A measurement of these drugs directly in one's urine is a sign of high exposure levels and that an uptake of the drugs is happening either through inhalation or dermally.[
]
Available agents
There is an extensive list of antineoplastic agents. Several classification schemes have been used to subdivide the medicines used for cancer into several different types.
History
 The first use of
The first use of small-molecule drug
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs are ...
s to treat cancer was in the early 20th century, although the specific chemicals first used were not originally intended for that purpose. Mustard gas
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect: the substance, when dispersed, is often not actually a gas, b ...
was used as a chemical warfare
Chemical warfare (CW) involves using the toxic properties of chemical substances as weapons. This type of warfare is distinct from nuclear warfare, biological warfare and radiological warfare, which together make up CBRN, the military a ...
agent during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and was discovered to be a potent suppressor of hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells ...
(blood production). A similar family of compounds known as nitrogen mustards were studied further during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
at the Yale School of Medicine
The Yale School of Medicine is the graduate medical school at Yale University, a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. It was founded in 1810 as the Medical Institution of Yale College and formally opened in 1813.
The primary t ...
.[ Therefore, in December 1942, several people with advanced lymphomas (cancers of the lymphatic system and lymph nodes) were given the drug by vein, rather than by breathing the irritating gas.][ Their improvement, although temporary, was remarkable. Concurrently, during a military operation in World War II, following a German ]air raid
Air raid may refer to:
Attacks
* Airstrike
* Strategic bombing
Other uses
* ''Air Raid'' (album), by the improvisational collective Air
* Air Raid ''(Transformers)'', the name of three characters in the Transformers universes
* ''Air Raid'' ...
on the Italian harbour of Bari, several hundred people were accidentally exposed to mustard gas, which had been transported there by the Allied forces to prepare for possible retaliation in the event of German use of chemical warfare. The survivors were later found to have very low white blood cell counts. After WWII was over and the reports declassified, the experiences converged and led researchers to look for other substances that might have similar effects against cancer. The first chemotherapy drug to be developed from this line of research was mustine. Since then, many other drugs have been developed to treat cancer, and drug development has exploded into a multibillion-dollar industry, although the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.
The term ''chemotherapy''
The word ''chemotherapy'' without a modifier usually refers to cancer treatment, but its historical meaning was broader. The term was coined in the early 1900s by Paul Ehrlich
Paul Ehrlich (; 14 March 1854 – 20 August 1915) was a Nobel Prize-winning German physician and scientist who worked in the fields of hematology, immunology, and antimicrobial chemotherapy. Among his foremost achievements were finding a cure ...
as meaning any use of chemicals to treat any disease ('' chemo-'' + '' -therapy''), such as the use of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s (''antibacterial chemotherapy'').[ The first modern chemotherapeutic agent was arsphenamine, an arsenic compound discovered in 1907 and used to treat syphilis.]sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. ...
(sulfa drugs) and penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
. In today's usage
The usage of a language is the ways in which its written and spoken variations are routinely employed by its speakers; that is, it refers to "the collective habits of a language's native speakers", as opposed to idealized models of how a languag ...
, the sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system rec ...
"any treatment of disease with drugs" is often expressed with the word ''pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy is therapy using pharmaceutical drugs, as distinguished from therapy using surgery (surgical therapy), radiation (radiation therapy), movement ( physical therapy), or other modes. Among physicians, sometimes the term ''medical th ...
''.
Sales
The top 10 best-selling (in terms of revenue) cancer drugs of 2013:
Research

Targeted therapies
Specially targeted delivery vehicles aim to increase effective levels of chemotherapy for tumor cells while reducing effective levels for other cells. This should result in an increased tumor kill or reduced toxicity or both.
Antibody-drug conjugates
Antibody-drug conjugate
Antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs are a class of biopharmaceutical drugs designed as a targeted therapy for treating cancer. Unlike chemotherapy, ADCs are intended to target and kill tumor cells while sparing healthy cells. As of 2019, some 56 phar ...
s (ADCs) comprise an antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and Viral disease, viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique m ...
, drug and a linker between them. The antibody will be targeted at a preferentially expressed protein in the tumour cells (known as a tumor antigen
Tumor antigen is an antigenic substance produced in tumor cells, i.e., it triggers an immune response in the host. Tumor antigens are useful tumor markers in identifying tumor cells with diagnostic tests and are potential candidates for use in c ...
) or on cells that the tumor can utilise, such as blood vessel endothelial cells
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ves ...
. They bind to the tumor antigen and are internalised, where the linker releases the drug into the cell. These specially targeted delivery vehicles vary in their stability, selectivity, and choice of target, but, in essence, they all aim to increase the maximum effective dose that can be delivered to the tumor cells.Wyeth
Wyeth, LLC was an American pharmaceutical company. The company was founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1860 as ''John Wyeth and Brother''. It was later known, in the early 1930s, as American Home Products, before being renamed to Wyeth in ...
(now Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfize ...
). The drug was approved to treat acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Sympto ...
.refractory
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase ...
Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition w ...
and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) refers to a group of non-Hodgkin lymphomas in which aberrant T cells proliferate uncontrollably. Considered as a single entity, ALCL is the most common type of peripheral lymphoma and represents ~10% of all per ...
.[
]
Nanoparticles
Nanoparticles
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 10 ...
are 1–1000 nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, ...
(nm) sized particles that can promote tumor selectivity and aid in delivering low-solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
drugs. Nanoparticles can be targeted passively or actively. Passive targeting exploits the difference between tumor blood vessels and normal blood vessels. Blood vessels in tumors are "leaky" because they have gaps from 200 to 2000 nm, which allow nanoparticles to escape into the tumor. Active targeting uses biological molecules ( antibodies, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s, DNA and receptor ligands) to preferentially target the nanoparticles to the tumor cells. There are many types of nanoparticle delivery systems, such as silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is o ...
, polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
s, liposome
A liposome is a small artificial vesicle, spherical in shape, having at least one lipid bilayer. Due to their hydrophobicity and/or hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, particle size and many other properties, liposomes can be used as drug delive ...
s[ They have emerged as a useful vehicle in ]magnetic drug delivery Magnetic nanoparticle-based drug delivery is a means in which magnetic particles such as iron oxide nanoparticles are a component of a delivery vehicle for magnetic drug delivery, due to the simplicity with which the particles can be drawn to (exter ...
for poorly soluble agents such as paclitaxel
Paclitaxel (PTX), sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical can ...
.
Electrochemotherapy
Electrochemotherapy is the combined treatment in which injection of a chemotherapeutic drug is followed by application of high-voltage electric pulses locally to the tumor. The treatment enables the chemotherapeutic drugs, which otherwise cannot or hardly go through the membrane of cells (such as bleomycin and cisplatin), to enter the cancer cells. Hence, greater effectiveness of antitumor treatment is achieved.
Clinical electrochemotherapy has been successfully used for treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors irrespective of their histological origin. The method has been reported as safe, simple and highly effective in all reports on clinical use of electrochemotherapy. According to the ESOPE project (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy), the Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) for electrochemotherapy were prepared, based on the experience of the leading European cancer centres on electrochemotherapy.
Hyperthermia therapy
Hyperthermia therapy
Hyperthermia therapy ''(or hyperthermia, or thermotherapy)'' is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to temperatures above body temperature, in the region of 40–45 °C (104–113 °F). Hyperthermia is usuall ...
is heat treatment for cancer that can be a powerful tool when used in combination with chemotherapy (thermochemotherapy) or radiation for the control of a variety of cancers. The heat can be applied locally to the tumor site, which will dilate blood vessels to the tumor, allowing more chemotherapeutic medication to enter the tumor. Additionally, the tumor cell membrane will become more porous, further allowing more of the chemotherapeutic medicine to enter the tumor cell.
Hyperthermia has also been shown to help prevent or reverse "chemo-resistance." Chemotherapy resistance sometimes develops over time as the tumors adapt and can overcome the toxicity of the chemo medication. "Overcoming chemoresistance has been extensively studied within the past, especially using CDDP-resistant cells. In regard to the potential benefit that drug-resistant cells can be recruited for effective therapy by combining chemotherapy with hyperthermia, it was important to show that chemoresistance against several anticancer drugs (e.g. mitomycin C, anthracyclines, BCNU, melphalan) including CDDP could be reversed at least partially by the addition of heat.
Other animals
Chemotherapy is used in veterinary medicine similar to how it is used in human medicine.
See also
References
External links
Chemotherapy
American Cancer Society
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is a nationwide voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer. Established in 1913, the society is organized into six geographical regions of both medical and lay volunteers operating in more tha ...
Hazardous Drug Exposures in Health Care
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the ...
* NIOSH List of Antineoplastic and Other Hazardous Drugs in Healthcare Settings, 2016, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
{{Authority control
Antineoplastic drugs
Oncology
Cancer treatments
Occupational safety and health
 Dosage of chemotherapy can be difficult: If the dose is too low, it will be ineffective against the tumor, whereas, at excessive doses, the toxicity (
Dosage of chemotherapy can be difficult: If the dose is too low, it will be ineffective against the tumor, whereas, at excessive doses, the toxicity ( The result of this pharmacokinetic variability among people is that many people do not receive the right dose to achieve optimal treatment effectiveness with minimized toxic side effects. Some people are overdosed while others are underdosed. For example, in a randomized clinical trial, investigators found 85% of metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) did not receive the optimal therapeutic dose when dosed by the BSA standard—68% were underdosed and 17% were overdosed.
There has been controversy over the use of BSA to calculate chemotherapy doses for people who are
The result of this pharmacokinetic variability among people is that many people do not receive the right dose to achieve optimal treatment effectiveness with minimized toxic side effects. Some people are overdosed while others are underdosed. For example, in a randomized clinical trial, investigators found 85% of metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) did not receive the optimal therapeutic dose when dosed by the BSA standard—68% were underdosed and 17% were overdosed.
There has been controversy over the use of BSA to calculate chemotherapy doses for people who are  In the same study, investigators compared the incidence of common 5-FU-associated grade 3/4 toxicities between the dose-adjusted people and people dosed per BSA. The incidence of debilitating grades of diarrhea was reduced from 18% in the BSA-dosed group to 4% in the dose-adjusted group and serious hematologic side effects were eliminated. Because of the reduced toxicity, dose-adjusted patients were able to be treated for longer periods of time. BSA-dosed people were treated for a total of 680 months while people in the dose-adjusted group were treated for a total of 791 months. Completing the course of treatment is an important factor in achieving better treatment outcomes.
Similar results were found in a study involving people with colorectal cancer who have been treated with the popular FOLFOX regimen. The incidence of serious diarrhea was reduced from 12% in the BSA-dosed group of patients to 1.7% in the dose-adjusted group, and the incidence of severe mucositis was reduced from 15% to 0.8%.
The FOLFOX study also demonstrated an improvement in treatment outcomes. Positive response increased from 46% in the BSA-dosed group to 70% in the dose-adjusted group. Median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) both improved by six months in the dose adjusted group.
One approach that can help clinicians individualize chemotherapy dosing is to measure the drug levels in blood plasma over time and adjust dose according to a formula or algorithm to achieve optimal exposure. With an established target exposure for optimized treatment effectiveness with minimized toxicities, dosing can be personalized to achieve target exposure and optimal results for each person. Such an algorithm was used in the clinical trials cited above and resulted in significantly improved treatment outcomes.
Oncologists are already individualizing dosing of some cancer drugs based on exposure.
In the same study, investigators compared the incidence of common 5-FU-associated grade 3/4 toxicities between the dose-adjusted people and people dosed per BSA. The incidence of debilitating grades of diarrhea was reduced from 18% in the BSA-dosed group to 4% in the dose-adjusted group and serious hematologic side effects were eliminated. Because of the reduced toxicity, dose-adjusted patients were able to be treated for longer periods of time. BSA-dosed people were treated for a total of 680 months while people in the dose-adjusted group were treated for a total of 791 months. Completing the course of treatment is an important factor in achieving better treatment outcomes.
Similar results were found in a study involving people with colorectal cancer who have been treated with the popular FOLFOX regimen. The incidence of serious diarrhea was reduced from 12% in the BSA-dosed group of patients to 1.7% in the dose-adjusted group, and the incidence of severe mucositis was reduced from 15% to 0.8%.
The FOLFOX study also demonstrated an improvement in treatment outcomes. Positive response increased from 46% in the BSA-dosed group to 70% in the dose-adjusted group. Median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) both improved by six months in the dose adjusted group.
One approach that can help clinicians individualize chemotherapy dosing is to measure the drug levels in blood plasma over time and adjust dose according to a formula or algorithm to achieve optimal exposure. With an established target exposure for optimized treatment effectiveness with minimized toxicities, dosing can be personalized to achieve target exposure and optimal results for each person. Such an algorithm was used in the clinical trials cited above and resulted in significantly improved treatment outcomes.
Oncologists are already individualizing dosing of some cancer drugs based on exposure. 
 Anti-metabolites are a group of molecules that impede DNA and RNA synthesis. Many of them have a similar structure to the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The building blocks are
Anti-metabolites are a group of molecules that impede DNA and RNA synthesis. Many of them have a similar structure to the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The building blocks are  Anti-microtubule agents are
Anti-microtubule agents are  Most chemotherapy is delivered
Most chemotherapy is delivered 
 The first use of
The first use of 