Babbage Island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer.
Babbage is considered by some to be " father of the computer". Babbage is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the
 Babbage's birthplace is disputed, but according to the '' Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' he was most likely born at 44 Crosby Row, Walworth Road, London, England. A
Babbage's birthplace is disputed, but according to the '' Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' he was most likely born at 44 Crosby Row, Walworth Road, London, England. A  Babbage was one of four children of Benjamin Babbage and Betsy Plumleigh Teape. His father was a banking partner of William Praed in founding Praed's & Co. of
Babbage was one of four children of Benjamin Babbage and Betsy Plumleigh Teape. His father was a banking partner of William Praed in founding Praed's & Co. of
 Babbage studied the requirements to establish a modern postal system, with his friend
Babbage studied the requirements to establish a modern postal system, with his friend
 Jonar Ganeri, author of ''Indian Logic'', believes Babbage may have been influenced by Indian thought; one possible route would be through
Jonar Ganeri, author of ''Indian Logic'', believes Babbage may have been influenced by Indian thought; one possible route would be through
 The British Association was consciously modelled on the Deutsche Naturforscher-Versammlung, founded in 1822. It rejected
The British Association was consciously modelled on the Deutsche Naturforscher-Versammlung, founded in 1822. It rejected
 Babbage's machines were among the first mechanical computers. That they were not actually completed was largely because of funding problems and clashes of personality, most notably with George Biddell Airy, the Astronomer Royal.
Babbage directed the building of some steam-powered machines that achieved some modest success, suggesting that calculations could be mechanised. For more than ten years he received government funding for his project, which amounted to £17,000, but eventually the Treasury lost confidence in him.
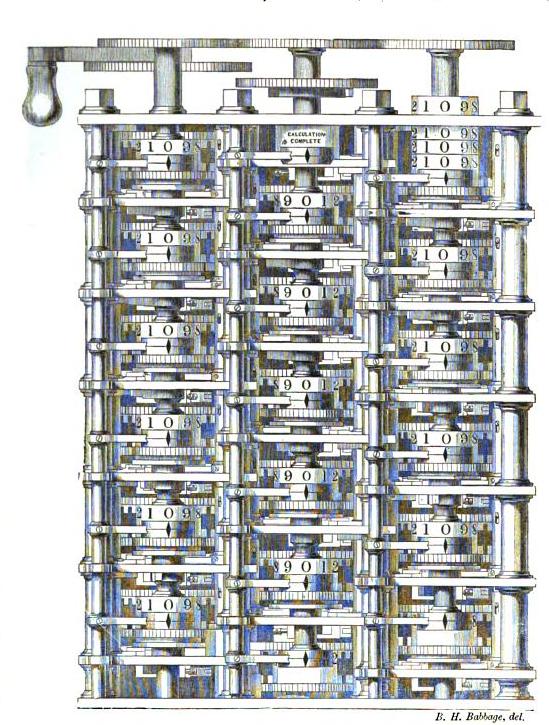
While Babbage's machines were mechanical and unwieldy, their basic architecture was similar to a modern computer. The data and program memory were separated, operation was instruction-based, the control unit could make conditional jumps, and the machine had a separate I/O unit.
Babbage's machines were among the first mechanical computers. That they were not actually completed was largely because of funding problems and clashes of personality, most notably with George Biddell Airy, the Astronomer Royal.
Babbage directed the building of some steam-powered machines that achieved some modest success, suggesting that calculations could be mechanised. For more than ten years he received government funding for his project, which amounted to £17,000, but eventually the Treasury lost confidence in him.
While Babbage's machines were mechanical and unwieldy, their basic architecture was similar to a modern computer. The data and program memory were separated, operation was instruction-based, the control unit could make conditional jumps, and the machine had a separate I/O unit.
 Babbage began in 1822 with what he called the difference engine, made to compute values of
Babbage began in 1822 with what he called the difference engine, made to compute values of
 After the attempt at making the first difference engine fell through, Babbage worked to design a more complex machine called the Analytical Engine. He hired C. G. Jarvis, who had previously worked for Clement as a draughtsman. The Analytical Engine marks the transition from mechanised arithmetic to fully-fledged general purpose computation. It is largely on it that Babbage's standing as computer pioneer rests.
The major innovation was that the Analytical Engine was to be programmed using punched cards: the Engine was intended to use loops of Jacquard's punched cards to control a mechanical calculator, which could use as input the results of preceding computations. The machine was also intended to employ several features subsequently used in modern computers, including sequential control, branching and looping. It would have been the first mechanical device to be, in principle, Turing-complete. The Engine was not a single physical machine, but rather a succession of designs that Babbage tinkered with until his death in 1871.
After the attempt at making the first difference engine fell through, Babbage worked to design a more complex machine called the Analytical Engine. He hired C. G. Jarvis, who had previously worked for Clement as a draughtsman. The Analytical Engine marks the transition from mechanised arithmetic to fully-fledged general purpose computation. It is largely on it that Babbage's standing as computer pioneer rests.
The major innovation was that the Analytical Engine was to be programmed using punched cards: the Engine was intended to use loops of Jacquard's punched cards to control a mechanical calculator, which could use as input the results of preceding computations. The machine was also intended to employ several features subsequently used in modern computers, including sequential control, branching and looping. It would have been the first mechanical device to be, in principle, Turing-complete. The Engine was not a single physical machine, but rather a succession of designs that Babbage tinkered with until his death in 1871.

 On 25 July 1814, Babbage married Georgiana Whitmore, sister of British parliamentarian William Wolryche-Whitmore, at St. Michael's Church in Teignmouth, Devon. The couple lived at
On 25 July 1814, Babbage married Georgiana Whitmore, sister of British parliamentarian William Wolryche-Whitmore, at St. Michael's Church in Teignmouth, Devon. The couple lived at
 Babbage lived and worked for over 40 years at 1 Dorset Street, Marylebone, where he died, at the age of 79, on 18 October 1871; he was buried in London's Kensal Green Cemetery. According to Horsley, Babbage died "of renal inadequacy, secondary to cystitis." He had declined both a knighthood and baronetcy. He also argued against hereditary peerages, favouring life peerages instead.
Babbage lived and worked for over 40 years at 1 Dorset Street, Marylebone, where he died, at the age of 79, on 18 October 1871; he was buried in London's Kensal Green Cemetery. According to Horsley, Babbage died "of renal inadequacy, secondary to cystitis." He had declined both a knighthood and baronetcy. He also argued against hereditary peerages, favouring life peerages instead.
 There is a black plaque commemorating the 40 years Babbage spent at 1 Dorset Street, London. Locations, institutions and other things named after Babbage include:
* The Moon crater
There is a black plaque commemorating the 40 years Babbage spent at 1 Dorset Street, London. Locations, institutions and other things named after Babbage include:
* The Moon crater
Charles Babbage's Lectures On Astronomy
/ref>
The Babbage Papers
The papers held by the Science Museum Library and Archives which relate mostly to Babbage's automatic calculating engines
''The Babbage Engine''
Computer History Museum, Mountain View CA, USA. Multi-page account of Babbage, his engines and his associates, including a video of the Museum's functioning replica of the Difference Engine No 2 in action
Analytical Engine Museum
John Walker's (of AutoCAD fame) comprehensive catalogue of the complete technical works relating to Babbage's machine.
Charles Babbage
A history at the School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews Scotland.
Mr. Charles Babbage
obituary from ''The Times'' (1871)
The Babbage Pages
Charles Babbage, The Online Books Page, University of Pennsylvania
an overview of how it works
"On a Method of Expressing by Signs the Action of Machinery"
1826. Original edition
pages on "Who Was Charles Babbage?" including biographical note, description of Difference Engine No. 2, publications by Babbage, archival and published sources on Babbage, sources on Babbage and Ada Lovelace
''Babbage's Calculating Machine''
(1872) – full digital facsimile from Linda Hall Library
Author profile
in the database zbMATH
The 'difference engine' built by Georg & Edvard Scheutz in 1843
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Babbage, Charles 1791 births 1871 deaths 19th-century English mathematicians Alumni of Peterhouse, Cambridge Alumni of Trinity College, Cambridge British business theorists Burials at Kensal Green Cemetery Corresponding members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences English Christians English computer scientists English engineers Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Fellows of the Royal Astronomical Society Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Fellows of the Royal Society Lucasian Professors of Mathematics People educated at Totnes Grammar School People of the Industrial Revolution Recipients of the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society Mathematicians from London
Difference Engine
A difference engine is an automatic mechanical calculator designed to tabulate polynomial, polynomial functions. It was designed in the 1820s, and was first created by Charles Babbage. The name, the difference engine, is derived from the method ...
, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in Babbage's Analytical Engine
The Analytical Engine was a proposed mechanical general-purpose computer designed by English mathematician and computer pioneer Charles Babbage. It was first described in 1837 as the successor to Babbage's difference engine, which was a des ...
, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom
The Jacquard machine () is a device fitted to a loom that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with such complex patterns as brocade, damask and matelassé. The resulting ensemble of the loom and Jacquard machine is then called a Ja ...
. Babbage had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. His varied work in other fields has led him to be described as "pre-eminent" among the many polymaths of his century.
Babbage, who died before the complete successful engineering of many of his designs, including his Difference Engine and Analytical Engine, remained a prominent figure in the ideating of computing. Parts of Babbage's incomplete mechanisms are on display in the Science Museum in London. In 1991, a functioning difference engine
A difference engine is an automatic mechanical calculator designed to tabulate polynomial, polynomial functions. It was designed in the 1820s, and was first created by Charles Babbage. The name, the difference engine, is derived from the method ...
was constructed from Babbage's original plans. Built to tolerances
Engineering tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in:
# a physical dimension;
# a measured value or physical property of a material, manufacturing, manufactured object, system, or service;
# other measured values (such as t ...
achievable in the 19th century, the success of the finished engine indicated that Babbage's machine would have worked.
Early life
 Babbage's birthplace is disputed, but according to the '' Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' he was most likely born at 44 Crosby Row, Walworth Road, London, England. A
Babbage's birthplace is disputed, but according to the '' Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' he was most likely born at 44 Crosby Row, Walworth Road, London, England. A blue plaque
A blue plaque is a permanent sign installed in a public place in the United Kingdom and elsewhere to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person, event, or former building on the site, serving as a historical marker. The term i ...
on the junction of Larcom Street and Walworth Road commemorates the event.
His date of birth was given in his obituary in '' The Times'' as 26 December 1792; but then a nephew wrote to say that Babbage was born one year earlier, in 1791. The parish register of St. Mary's, Newington, London, shows that Babbage was baptised on 6 January 1792, supporting a birth year of 1791.
 Babbage was one of four children of Benjamin Babbage and Betsy Plumleigh Teape. His father was a banking partner of William Praed in founding Praed's & Co. of
Babbage was one of four children of Benjamin Babbage and Betsy Plumleigh Teape. His father was a banking partner of William Praed in founding Praed's & Co. of Fleet Street
Fleet Street is a major street mostly in the City of London. It runs west to east from Temple Bar at the boundary with the City of Westminster to Ludgate Circus at the site of the London Wall and the River Fleet from which the street was na ...
, London, in 1801. In 1808, the Babbage family moved into the old Rowdens house in East Teignmouth
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
. Around the age of eight, Babbage was sent to a country school in Alphington near Exeter to recover from a life-threatening fever. For a short time, he attended King Edward VI Grammar School in Totnes, South Devon, but his health forced him back to private tutors for a time.
Babbage then joined the 30-student Holmwood Academy, in Baker Street, Enfield, Middlesex, under the Reverend Stephen Freeman. The academy had a library that prompted Babbage's love of mathematics. He studied with two more private tutors after leaving the academy. The first was a clergyman near Cambridge; through him Babbage encountered Charles Simeon and his evangelical followers, but the tuition was not what he needed. He was brought home, to study at the Totnes school: this was at age 16 or 17. The second was an Oxford tutor, under whom Babbage reached a level in Classics sufficient to be accepted by the University of Cambridge.
At the University of Cambridge
Babbage arrived at Trinity College, Cambridge, in October 1810. He was already self-taught in some parts of contemporary mathematics; he had readRobert Woodhouse
Robert Woodhouse (28 April 177323 December 1827) was a British mathematician and astronomer.
Biography Early life and education
Robert Woodhouse was born on 28 April 1773 in Norwich, Norfolk, the son of Robert Woodhouse, linen draper, and Judi ...
, Joseph Louis Lagrange, and Marie Agnesi. As a result, he was disappointed in the standard mathematical instruction available at the university.
Babbage, John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical wor ...
, George Peacock
George Peacock FRS (9 April 1791 – 8 November 1858) was an English mathematician and Anglican cleric. He founded what has been called the British algebra of logic.
Early life
Peacock was born on 9 April 1791 at Thornton Hall, Denton, nea ...
, and several other friends formed the Analytical Society
The Analytical Society was a group of individuals in early-19th-century Britain whose aim was to promote the use of Leibnizian notation for differentiation in calculus as opposed to the Newton notation for differentiation.Carl B. Boyer (1989) ''A ...
in 1812; they were also close to Edward Ryan.Wilkes (2002) ''p.''355 As a student, Babbage was also a member of other societies such as The Ghost Club, concerned with investigating supernatural phenomena, and the Extractors Club, dedicated to liberating its members from the madhouse, should any be committed to one.
In 1812, Babbage transferred to Peterhouse, Cambridge
Peterhouse is the oldest constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England, founded in 1284 by Hugh de Balsham, Bishop of Ely. Today, Peterhouse has 254 undergraduates, 116 full-time graduate students and 54 fellows. It is quite ...
. He was the top mathematician there, but did not graduate with honours. He instead received a degree without examination in 1814. He had defended a thesis that was considered blasphemous in the preliminary public disputation, but it is not known whether this fact is related to his not sitting the examination.
After Cambridge
Considering his reputation, Babbage quickly made progress. He lectured to theRoyal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
on astronomy in 1815, and was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1816. After graduation, on the other hand, he applied for positions unsuccessfully, and had little in the way of a career. In 1816 he was a candidate for a teaching job at Haileybury College; he had recommendations from James Ivory and John Playfair, but lost out to Henry Walter. In 1819, Babbage and Herschel visited Paris and the Society of Arcueil The Society of Arcueil was a circle of French scientists who met regularly on summer weekends between 1806 and 1822 at the country houses of Claude Louis Berthollet and Pierre Simon Laplace at Arcueil, then a village 3 miles south of Paris.
Members ...
, meeting leading French mathematicians and physicists. That year Babbage applied to be professor at the University of Edinburgh, with the recommendation of Pierre Simon Laplace; the post went to William Wallace.
With Herschel, Babbage worked on the electrodynamics of Arago's rotations, publishing in 1825. Their explanations were only transitional, being picked up and broadened by Michael Faraday. The phenomena are now part of the theory of eddy currents, and Babbage and Herschel missed some of the clues to unification of electromagnetic theory, staying close to Ampère's force law.
Babbage purchased the actuarial tables of George Barrett, who died in 1821 leaving unpublished work, and surveyed the field in 1826 in ''Comparative View of the Various Institutions for the Assurance of Lives''. This interest followed a project to set up an insurance company, prompted by Francis Baily and mooted in 1824, but not carried out. Babbage did calculate actuarial tables for that scheme, using Equitable Society mortality data from 1762 onwards.
During this whole period, Babbage depended awkwardly on his father's support, given his father's attitude to his early marriage, of 1814: he and Edward Ryan wedded the Whitmore sisters. He made a home in Marylebone in London and established a large family. On his father's death in 1827, Babbage inherited a large estate (value around £100,000, equivalent to £ or $ today), making him independently wealthy. After his wife's death in the same year he spent time travelling. In Italy he met Leopold II, Grand Duke of Tuscany
Leopold II( it, Leopoldo Giovanni Giuseppe Francesco Ferdinando Carlo, german: Leopold Johann Joseph Franz Ferdinand Karl, English: ''Leopold John Joseph Francis Ferdinand Charles''. (3 October 1797 – 29 January 1870) was Grand Duke of Tusc ...
, foreshadowing a later visit to Piedmont. In April 1828 he was in Rome, and relying on Herschel to manage the difference engine project, when he heard that he had become a professor at Cambridge, a position he had three times failed to obtain (in 1820, 1823 and 1826).
Royal Astronomical Society
Babbage was instrumental in founding the Royal Astronomical Society in 1820, initially known as the Astronomical Society of London. Its original aims were to reduce astronomical calculations to a more standard form, and to circulate data. These directions were closely connected with Babbage's ideas on computation, and in 1824 he won itsGold Medal
A gold medal is a medal awarded for highest achievement in a non-military field. Its name derives from the use of at least a fraction of gold in form of plating or alloying in its manufacture.
Since the eighteenth century, gold medals have bee ...
, cited "for his invention of an engine for calculating mathematical and astronomical tables".
Babbage's motivation to overcome errors in tables by mechanisation had been a commonplace since Dionysius Lardner wrote about it in 1834 in the ''Edinburgh Review
The ''Edinburgh Review'' is the title of four distinct intellectual and cultural magazines. The best known, longest-lasting, and most influential of the four was the third, which was published regularly from 1802 to 1929.
''Edinburgh Review'', ...
'' (under Babbage's guidance). The context of these developments is still debated. Babbage's own account of the origin of the difference engine begins with the Astronomical Society's wish to improve '' The Nautical Almanac''. Babbage and Herschel were asked to oversee a trial project, to recalculate some part of those tables. With the results to hand, discrepancies were found. This was in 1821 or 1822, and was the occasion on which Babbage formulated his idea for mechanical computation. The issue of the ''Nautical Almanac'' is now described as a legacy of a polarisation in British science caused by attitudes to Sir Joseph Banks, who had died in 1820.
 Babbage studied the requirements to establish a modern postal system, with his friend
Babbage studied the requirements to establish a modern postal system, with his friend Thomas Frederick Colby
Thomas Frederick Colby FRS FRSE FGS FRGS (1 September 17849 October 1852), was a British major-general and director of the Ordnance Survey (OS).
A Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society and Royal Society, Colby was one of the leading geogra ...
, concluding there should be a uniform rate that was put into effect with the introduction of the Uniform Fourpenny Post supplanted by the Uniform Penny Post in 1839 and 1840. Colby was another of the founding group of the Society. He was also in charge of the Survey of Ireland
Ordnance Survey Ireland (OSI; ga, Suirbhéireacht Ordanáis Éireann) is the national mapping agency of Ireland. It was established on 4 March 2002 as a body corporate. It is the successor to the former Ordnance Survey of Ireland. It and the ...
. Herschel and Babbage were present at a celebrated operation of that survey, the remeasuring of the Lough Foyle
Lough Foyle, sometimes Loch Foyle ( or "loch of the lip"), is the estuary of the River Foyle, on the north coast of Ireland. It lies between County Londonderry in Northern Ireland and County Donegal in the Republic of Ireland. Sovereignty over ...
baseline.
British Lagrangian School
The Analytical Society had initially been no more than an undergraduate provocation. During this period it had some more substantial achievements. In 1816 Babbage, Herschel and Peacock published a translation from French of the lectures ofSylvestre Lacroix Sylvestre can refer to:
People Surname
Given name
Middle name
* Carlos Sylvestre Begnis (1903–1980), Argentine medical doctor and politician
* Philippe Sylvestre Dufour (1622–1687), French Protestant apothecary, banker, collector, a ...
, which was then the state-of-the-art calculus textbook.
Reference to Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi Lagrangiaformal power series
In mathematics, a formal series is an infinite sum that is considered independently from any notion of convergence, and can be manipulated with the usual algebraic operations on series (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, partial sum ...
. British mathematicians had used them from about 1730 to 1760. As re-introduced, they were not simply applied as notations in differential calculus
In mathematics, differential calculus is a subfield of calculus that studies the rates at which quantities change. It is one of the two traditional divisions of calculus, the other being integral calculus—the study of the area beneath a curve. ...
. They opened up the fields of functional equations (including the difference equation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a parameter ...
s fundamental to the difference engine) and operator (D-module
In mathematics, a ''D''-module is a module (mathematics), module over a ring (mathematics), ring ''D'' of differential operators. The major interest of such ''D''-modules is as an approach to the theory of linear partial differential equations. Sin ...
) methods for differential equations. The analogy of difference and differential equations was notationally changing Δ to D, as a "finite" difference becomes "infinitesimal". These symbolic directions became popular, as operational calculus, and pushed to the point of diminishing returns. The Cauchy concept of limit was kept at bay. Woodhouse had already founded this second "British Lagrangian School" with its treatment of Taylor series as formal.
In this context function composition
In mathematics, function composition is an operation that takes two functions and , and produces a function such that . In this operation, the function is applied to the result of applying the function to . That is, the functions and ...
is complicated to express, because the chain rule is not simply applied to second and higher derivatives. This matter was known to Woodhouse by 1803, who took from Louis François Antoine Arbogast what is now called Faà di Bruno's formula. In essence it was known to Abraham De Moivre
Abraham de Moivre FRS (; 26 May 166727 November 1754) was a French mathematician known for de Moivre's formula, a formula that links complex numbers and trigonometry, and for his work on the normal distribution and probability theory.
He moved ...
(1697). Herschel found the method impressive, Babbage knew of it, and it was later noted by Ada Lovelace
Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (''née'' Byron; 10 December 1815 – 27 November 1852) was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the A ...
as compatible with the analytical engine. In the period to 1820 Babbage worked intensively on functional equations in general, and resisted both conventional finite differences and Arbogast's approach (in which Δ and D were related by the simple additive case of the exponential map). But via Herschel he was influenced by Arbogast's ideas in the matter of iteration, i.e. composing a function with itself, possibly many times. Writing in a major paper on functional equations in the ''Philosophical Transactions
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the first journa ...
'' (1815/6), Babbage said his starting point was work of Gaspard Monge.
Academic
From 1828 to 1839, Babbage wasLucasian Professor of Mathematics
The Lucasian Chair of Mathematics () is a mathematics professorship in the University of Cambridge, England; its holder is known as the Lucasian Professor. The post was founded in 1663 by Henry Lucas, who was Cambridge University's Member of Pa ...
at Cambridge. Not a conventional resident don, and inattentive to his teaching responsibilities, he wrote three topical books during this period of his life. He was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1832. Babbage was out of sympathy with colleagues: George Biddell Airy, his predecessor as Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at Trinity College, Cambridge, thought an issue should be made of his lack of interest in lecturing. Babbage planned to lecture in 1831 on political economy. Babbage's reforming direction looked to see university education more inclusive, universities doing more for research, a broader syllabus and more interest in applications; but William Whewell found the programme unacceptable. A controversy Babbage had with Richard Jones Richard Jones may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*F. Richard Jones (1893–1930), American filmmaker
*Dick Clair (Richard Jones, 1931–1988), American producer, actor and TV writer
*Richard Jones (The Feeling), British bass guitarist
*Richard J ...
lasted for six years. He never did give a lecture.
It was during this period that Babbage tried to enter politics. Simon Schaffer writes that his views of the 1830s included disestablishment
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular stat ...
of the Church of England, a broader political franchise
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
, and inclusion of manufacturers as stakeholders. He twice stood for Parliament as a candidate for the borough of Finsbury
Finsbury is a district of Central London, forming the south-eastern part of the London Borough of Islington. It borders the City of London.
The Manor of Finsbury is first recorded as ''Vinisbir'' (1231) and means "manor of a man called Finn ...
. In 1832 he came in third among five candidates, missing out by some 500 votes in the two-member constituency when two other reformist candidates, Thomas Wakley
Thomas Wakley (11 July 179516 May 1862) was an English surgeon. He gained fame as a social reformer who campaigned against incompetence, privilege and nepotism. He was the founding editor of ''The Lancet'', a radical Member of Parliament (MP) a ...
and Christopher Temple, split the vote. In his memoirs Babbage related how this election brought him the friendship of Samuel Rogers: his brother Henry Rogers wished to support Babbage again, but died within days. In 1834 Babbage finished last among four. In 1832, Babbage, Herschel and Ivory were appointed Knights of the Royal Guelphic Order
The Royal Guelphic Order (german: Königliche Guelphen-Orden), sometimes referred to as the Hanoverian Guelphic Order, is a Hanoverian order of chivalry instituted on 28 April 1815 by the Prince Regent (later King George IV). It takes its name ...
, however they were not subsequently made knights bachelor to entitle them to the prefix ''Sir'', which often came with appointments to that foreign order (though Herschel was later created a baronet).
"Declinarians", learned societies and the BAAS
Babbage now emerged as a polemicist. One of his biographers notes that all his books contain a "campaigning element". His ''Reflections on the Decline of Science and some of its Causes'' (1830) stands out, however, for its sharp attacks. It aimed to improve British science, and more particularly to oust Davies Gilbert as President of the Royal Society, which Babbage wished to reform. It was written out of pique, when Babbage hoped to become the junior secretary of the Royal Society, as Herschel was the senior, but failed because of his antagonism to Humphry Davy. Michael Faraday had a reply written, byGerrit Moll
Gerard "Gerrit" Moll LLD (1785–1838) was a Dutch scientist and mathematician. A polymath in his interests, he published in four languages.
Life
From a family background in Amsterdam of commerce, Moll was drawn towards science. His teacher at the ...
, as ''On the Alleged Decline of Science in England'' (1831). On the front of the Royal Society Babbage had no impact, with the bland election of the Duke of Sussex to succeed Gilbert the same year. As a broad manifesto, on the other hand, his ''Decline'' led promptly to the formation in 1831 of the British Association for the Advancement of Science
The British Science Association (BSA) is a charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Science (BA). The current Chie ...
(BAAS).
The ''Mechanics' Magazine
Joseph Clinton Robertson (c.1787–1852), pseudonym Sholto Percy, was a Scottish patent agent, writer and periodical editor. He was a political radical prominent in the early days of the working-class press in London, and in the debates within th ...
'' in 1831 identified as Declinarians the followers of Babbage. In an unsympathetic tone it pointed out David Brewster
Sir David Brewster KH PRSE FRS FSA Scot FSSA MICE (11 December 178110 February 1868) was a British scientist, inventor, author, and academic administrator. In science he is principally remembered for his experimental work in physical optics ...
writing in the ''Quarterly Review
The ''Quarterly Review'' was a literary and political periodical founded in March 1809 by London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River ...
'' as another leader; with the barb that both Babbage and Brewster had received public money.
In the debate of the period on statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
(''qua'' data collection) and what is now statistical inference
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution, distribution of probability.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical ...
, the BAAS in its Statistical Section (which owed something also to Whewell
William Whewell ( ; 24 May 17946 March 1866) was an English polymath, scientist, Anglican priest, philosopher, theologian, and historian of science. He was Master of Trinity College, Cambridge. In his time as a student there, he achieved dis ...
) opted for data collection. This Section was the sixth, established in 1833 with Babbage as chairman and John Elliot Drinkwater as secretary. The foundation of the Statistical Society
The Royal Statistical Society (RSS) is an established statistical society. It has three main roles: a British learned society for statistics, a professional body for statisticians and a charity which promotes statistics for the public good.
...
followed. Babbage was its public face, backed by Richard Jones and Robert Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English cleric, scholar and influential economist in the fields of political economy and demography.
In his 1798 book '' An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Mal ...
.
''On the Economy of Machinery and Manufactures''
Babbage published ''On the Economy of Machinery and Manufactures'' (1832), on the organisation ofindustrial production
Industrial production is a measure of output of the industrial sector of the economy. The industrial sector includes manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Although these sectors contribute only a small portion of gross domestic product (GDP), the ...
. It was an influential early work of operational research. John Rennie the Younger in addressing the Institution of Civil Engineers on manufacturing in 1846 mentioned mostly surveys in encyclopaedias, and Babbage's book was first an article in the '' Encyclopædia Metropolitana'', the form in which Rennie noted it, in the company of related works by John Farey Jr.
John Farey Jr. (20 March 1791 – 17 July 1851) was an English mechanical engineering, consulting engineer and patent agent, known for his pioneering contributions in the field of mechanical engineering.Alec Skempton.Farey, Jr., John" in: ''A Bio ...
, Peter Barlow and Andrew Ure. From ''An essay on the general principles which regulate the application of machinery to manufactures and the mechanical arts'' (1827), which became the ''Encyclopædia Metropolitana'' article of 1829, Babbage developed the schematic classification of machines that, combined with discussion of factories, made up the first part of the book. The second part considered the "domestic and political economy" of manufactures.
The book sold well, and quickly went to a fourth edition (1836). Babbage represented his work as largely a result of actual observations in factories, British and abroad. It was not, in its first edition, intended to address deeper questions of political economy; the second (late 1832) did, with three further chapters including one on piece rate. The book also contained ideas on rational design in factories, and profit sharing
Profit sharing is various incentive plans introduced by businesses that provide direct or indirect payments to employees that depend on company's profitability in addition to employees' regular salary and bonuses. In publicly traded companies thes ...
.
"Babbage principle"
In ''Economy of Machinery'' was described what is now called the "Babbage principle". It pointed out commercial advantages available with more carefuldivision of labour
The division of labour is the separation of the tasks in any economic system or organisation so that participants may specialise (specialisation). Individuals, organizations, and nations are endowed with, or acquire specialised capabilities, and ...
. As Babbage himself noted, it had already appeared in the work of Melchiorre Gioia
Melchiorre Gioja (10 September 1767 – 2 January 1829) was an Italian writer on philosophy and political economy. His name is spelled Gioia in modern Italian.
Biography
Gioja was born at Piacenza, in what is now northern Italy.
Originally in ...
in 1815. The term was introduced in 1974 by Harry Braverman. Related formulations are the "principle of multiples" of Philip Sargant Florence, and the "balance of processes".
What Babbage remarked is that skilled workers typically spend parts of their time performing tasks that are below their skill level. If the labour process can be divided among several workers, labour costs may be cut by assigning only high-skill tasks to high-cost workers, restricting other tasks to lower-paid workers. He also pointed out that training or apprenticeship can be taken as fixed costs; but that returns to scale
In economics, returns to scale describe what happens to long-run returns as the scale of production increases, when all input levels including physical capital usage are variable (able to be set by the firm). The concept of returns to scale arises ...
are available by his approach of standardisation of tasks, therefore again favouring the factory system. His view of human capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial ...
was restricted to minimising the time period for recovery of training costs.
Publishing
Another aspect of the work was its detailed breakdown of the cost structure of book publishing. Babbage took the unpopular line, from the publishers' perspective, of exposing the trade's profitability. He went as far as to name the organisers of the trade's restrictive practices. Twenty years later he attended a meeting hosted by John Chapman to campaign against the Booksellers Association, still a cartel.Influence
It has been written that "what Arthur Young was to agriculture, Charles Babbage was to thefactory visit
A factory tour is an organized visit to a factory to observe the products being manufactured and the processes at work. Manufacturing companies offer factory tours to improve public relations.
Types of factory tours
Breweries and distilleries, ...
and machinery". Babbage's theories are said to have influenced the layout of the 1851 Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition which took pl ...
, and his views had a strong effect on his contemporary George Julius Poulett Scrope
George Julius Poulett Scrope FRS (10 March 1797 – 19 January 1876) was an English geologist and political economist as well as a Member of Parliament and magistrate for Stroud in Gloucestershire.
While an undergraduate at Cambridge, thr ...
. Karl Marx argued that the source of the productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proces ...
of the factory system was exactly the combination of the division of labour with machinery, building on Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— ...
, Babbage and Ure. Where Marx picked up on Babbage and disagreed with Smith was on the motivation for division of labour by the manufacturer: as Babbage did, he wrote that it was for the sake of profitability, rather than productivity, and identified an impact on the concept of a trade.
John Ruskin went further, to oppose completely what manufacturing in Babbage's sense stood for. Babbage also affected the economic thinking of John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 – 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to ...
. George Holyoake saw Babbage's detailed discussion of profit sharing as substantive, in the tradition of Robert Owen
Robert Owen (; 14 May 1771 – 17 November 1858) was a Welsh textile manufacturer, philanthropist and social reformer, and a founder of utopian socialism and the cooperative movement. He strove to improve factory working conditions, promoted e ...
and Charles Fourier, if requiring the attentions of a benevolent captain of industry, and ignored at the time.
Works by Babbage and Ure were published in French translation in 1830; ''On the Economy of Machinery'' was translated in 1833 into French by Édouard Biot
Édouard Constant Biot (; July 2, 1803 – March 12, 1850) was a French engineer and Sinologist. As an engineer, he participated in the construction of the second line of French railway between Lyon and St Etienne, and as a Sinologist, publ ...
, and into German the same year by Gottfried Friedenberg. The French engineer and writer on industrial organisation Léon Lalanne was influenced by Babbage, but also by the economist Claude Lucien Bergery
Claude Lucien Bergery (1787–1863) was a French economist and management theorist. He was a founder of scientific management.
Life
The son of an innkeeper, Bergery was born in Orléans. He was a student at the École Polytechnique which he ente ...
, in reducing the issues to "technology". William Jevons connected Babbage's "economy of labour" with his own labour experiments of 1870. The Babbage principle is an inherent assumption in Frederick Winslow Taylor's scientific management
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows. Its main objective is improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science to the engineer ...
.
Mary Everest Boole
Mary Everest Boole (11 March 1832 in Wickwar, Gloucestershire – 17 May 1916 in Middlesex, England) was a self-taught mathematician who is best known as an author of didactic works on mathematics, such as ''Philosophy and Fun of Algebra'', an ...
claimed that there was profound influence – via her uncle George Everest – of Indian thought in general and Indian logic, in particular, on Babbage and on her husband George Boole, as well as on Augustus De Morgan:
Think what must have been the effect of the intense Hinduizing of three such men as Babbage, De Morgan, and George Boole on the mathematical atmosphere of 1830–65. What share had it in generating the Vector Analysis and the mathematics by which investigations in physical science are now conducted?
Natural theology
In 1837, responding to the series of eight '' Bridgewater Treatises'', Babbage published his ''Ninth Bridgewater Treatise
The Ninth Bridgewater Treatise was published by Charles Babbage in 1837 as a response to the eight Bridgewater Treatises that the Earl of Bridgewater, Francis Henry Egerton, 8th Earl, had funded and in particular with reference to a comment in one ...
'', under the title ''On the Power, Wisdom and Goodness of God, as manifested in the Creation''. In this work Babbage weighed in on the side of uniformitarianism in a current debate. He preferred the conception of creation in which a God-given natural law dominated, removing the need for continuous "contrivance".
The book is a work of natural theology
Natural theology, once also termed physico-theology, is a type of theology that seeks to provide arguments for theological topics (such as the existence of a deity) based on reason and the discoveries of science.
This distinguishes it from ...
, and incorporates extracts from related correspondence of Herschel with Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known as the author of ''Principles of Geolo ...
. Babbage put forward the thesis that God had the omnipotence and foresight to create as a divine legislator. In this book, Babbage dealt with relating interpretations between science and religion; on the one hand, he insisted that "there exists no fatal collision between the words of Scripture and the facts of nature;" on the one hand, he wrote the Book of Genesis was not meant to be read literally in relation to scientific terms. Against those who said these were in conflict, he wrote "that the contradiction they have imagined can have no real existence, and that whilst the testimony of Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
remains unimpeached, we may also be permitted to confide in the testimony of our senses."
The ''Ninth Bridgewater Treatise'' was quoted extensively in '' Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation''. The parallel with Babbage's computing machines is made explicit, as allowing plausibility to the theory that transmutation of species could be pre-programmed.
 Jonar Ganeri, author of ''Indian Logic'', believes Babbage may have been influenced by Indian thought; one possible route would be through
Jonar Ganeri, author of ''Indian Logic'', believes Babbage may have been influenced by Indian thought; one possible route would be through Henry Thomas Colebrooke
Henry Thomas Colebrooke FRS FRSE (15 June 1765 – 10 March 1837) was an English orientalist and mathematician. He has been described as "the first great Sanskrit scholar in Europe".
Biography
Henry Thomas Colebrooke was born on 15 June ...
. Mary Everest Boole argues that Babbage was introduced to Indian thought in the 1820s by her uncle George Everest:
Some time about 1825, verestcame to England for two or three years, and made a fast and lifelong friendship with Herschel and with Babbage, who was then quite young. I would ask any fair-minded mathematician to read Babbage's Ninth Bridgewater Treatise and compare it with the works of his contemporaries in England; and then ask himself whence came the peculiar conception of the nature of miracle which underlies Babbage's ideas of Singular Points on Curves (Chap, viii) – from European Theology or Hindu Metaphysic? Oh! how the English clergy of that day hated Babbage's book!
Religious views
Babbage was raised in the Protestant form of the Christian faith, his family having inculcated in him an orthodox form of worship. He explained: Rejecting theAthanasian Creed
The Athanasian Creed, also called the Pseudo-Athanasian Creed and sometimes known as ''Quicunque Vult'' (or ''Quicumque Vult''), which is both its Latin name and its opening words, meaning "Whosoever wishes", is a Christian statement of belief ...
as a "direct contradiction in terms", in his youth he looked to Samuel Clarke's works on religion, of which ''Being and Attributes of God'' (1704) exerted a particularly strong influence on him. Later in life, Babbage concluded that "the true value of the Christian religion rested, not on speculative heology… but … upon those doctrines of kindness and benevolence which that religion claims and enforces, not merely in favour of man himself but of every creature susceptible of pain or of happiness."
In his autobiography ''Passages from the Life of a Philosopher'' (1864), Babbage wrote a whole chapter on the topic of religion, where he identified three sources of divine knowledge:
# ''A priori'' or mystical experience
# From Revelation
# From the examination of the works of the Creator
He stated, on the basis of the design argument
The teleological argument (from ; also known as physico-theological argument, argument from design, or intelligent design argument) is an argument for the existence of God or, more generally, that complex functionality in the natural world wh ...
, that studying the works of nature had been the more appealing evidence, and the one which led him to actively profess the existence of God. Advocating for natural theology, he wrote:
Like Samuel Vince
Samuel Vince FRS (6 April 1749 – 28 November 1821) was an English clergyman, mathematician and astronomer at the University of Cambridge.
Life
He was born in Fressingfield. The son of a plasterer, Vince was admitted as a sizar to Caius Colle ...
, Babbage also wrote a defence of the belief in divine miracles. Against objections previously posed by David Hume, Babbage advocated for the belief of divine agency, stating "we must not measure the credibility or incredibility of an event by the narrow sphere of our own experience, nor forget that there is a Divine energy which overrides what we familiarly call the laws of nature." He alluded to the limits of human experience, expressing: "all that we see in a miracle is an effect which is new to our observation, and whose cause is concealed. The cause may be beyond the sphere of our observation, and would be thus beyond the familiar sphere of nature; but this does not make the event a violation of any law of nature. The limits of man's observation lie within very narrow boundaries, and it would be arrogance to suppose that the reach of man's power is to form the limits of the natural world."
Later life
 The British Association was consciously modelled on the Deutsche Naturforscher-Versammlung, founded in 1822. It rejected
The British Association was consciously modelled on the Deutsche Naturforscher-Versammlung, founded in 1822. It rejected romantic science
19th-century science was greatly influenced by Romanticism (or the Age of Reflection, 1800–40), an intellectual movement that originated in Western Europe as a counter-movement to the late-18th-century Enlightenment. Romanticism incorporated m ...
as well as metaphysics, and started to entrench the divisions of science from literature, and professionals from amateurs. Belonging as he did to the "Wattite" faction in the BAAS, represented in particular by James Watt the younger
James Watt junior, FRS (5 February 1769 – 2 June 1848) was a Scottish engineer, businessman and activist.
Early life
He was born on 5 February 1769, the son of James Watt by his first wife Margaret Miller, and half-brother of Gregory Wat ...
, Babbage identified closely with industrialists. He wanted to go faster in the same directions, and had little time for the more gentlemanly component of its membership. Indeed, he subscribed to a version of conjectural history Conjectural history is a type of historiography isolated in the 1790s by Dugald Stewart, who termed it "theoretical or conjectural history," as prevalent in the historians and early social scientists of the Scottish Enlightenment. As Stewart saw it, ...
that placed industrial society
In sociology, industrial society is a society driven by the use of technology and machinery to enable mass production, supporting a large population with a high capacity for division of labour. Such a structure developed in the Western world i ...
as the culmination of human development (and shared this view with Herschel). A clash with Roderick Murchison
Sir Roderick Impey Murchison, 1st Baronet, (19 February 1792 – 22 October 1871) was a Scotland, Scottish geologist who served as director-general of the British Geological Survey from 1855 until his death in 1871. He is noted for investigat ...
led in 1838 to his withdrawal from further involvement. At the end of the same year he sent in his resignation as Lucasian professor, walking away also from the Cambridge struggle with Whewell. His interests became more focussed, on computation and metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in Fran ...
, and on international contacts.
Metrology programme
A project announced by Babbage was to tabulate allphysical constant
A physical constant, sometimes fundamental physical constant or universal constant, is a physical quantity that is generally believed to be both universal in nature and have constant value in time. It is contrasted with a mathematical constant, ...
s (referred to as "constants of nature", a phrase in itself a neologism), and then to compile an encyclopaedic work of numerical information. He was a pioneer in the field of "absolute measurement". His ideas followed on from those of Johann Christian Poggendorff
Johann Christian Poggendorff (29 December 1796 – 24 January 1877), was a German physicist born in Hamburg. By far the greater and more important part of his work related to electricity and magnetism. Poggendorff is known for his electrostatic m ...
, and were mentioned to Brewster in 1832. There were to be 19 categories of constants, and Ian Hacking
Ian MacDougall Hacking (born February 18, 1936) is a Canadian philosopher specializing in the philosophy of science. Throughout his career, he has won numerous awards, such as the Killam Prize for the Humanities and the Balzan Prize, and been ...
sees these as reflecting in part Babbage's "eccentric enthusiasms". Babbage's paper ''On Tables of the Constants of Nature and Art'' was reprinted by the Smithsonian Institution in 1856, with an added note that the physical tables of Arnold Henry Guyot "will form a part of the important work proposed in this article".
Exact measurement was also key to the development of machine tools. Here again Babbage is considered a pioneer, with Henry Maudslay, William Sellers, and Joseph Whitworth.
Engineer and inventor
Through the Royal Society Babbage acquired the friendship of the engineer Marc Brunel. It was through Brunel that Babbage knew ofJoseph Clement
Joseph Clement (13 June 1779 – 28 February 1844) was a British engineer and industrialist, chiefly remembered as the maker of Charles Babbage's first difference engine, between 1824 and 1833.
Biography
Early life
Joseph Clement was born on ...
, and so came to encounter the artisans whom he observed in his work on manufactures. Babbage provided an introduction for Isambard Kingdom Brunel in 1830, for a contact with the proposed Bristol & Birmingham Railway. He carried out studies, around 1838, to show the superiority of the broad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS ...
for railways, used by Brunel's Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
.
In 1838, Babbage invented the pilot (also called a cow-catcher), the metal frame attached to the front of locomotives that clears the tracks of obstacles; he also constructed a dynamometer car. His eldest son, Benjamin Herschel Babbage, worked as an engineer for Brunel on the railways before emigrating to Australia in the 1850s.
Babbage also invented an ophthalmoscope, which he gave to Thomas Wharton Jones for testing. Jones, however, ignored it. The device only came into use after being independently invented by Hermann von Helmholtz.
Cryptography
Babbage achieved notable results in cryptography, though this was still not known a century after his death.Letter frequency
Letter frequency is the number of times letters of the alphabet appear on average in written language. Letter frequency analysis dates back to the Arab mathematician Al-Kindi (c. 801–873 AD), who formally developed the method to break ...
was category 18 of Babbage's tabulation project. Joseph Henry
Joseph Henry (December 17, 1797– May 13, 1878) was an American scientist who served as the first Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution. He was the secretary for the National Institute for the Promotion of Science, a precursor of the Smith ...
later defended interest in it, in the absence of the facts, as relevant to the management of movable type.
As early as 1845, Babbage had solved a cipher that had been posed as a challenge by his nephew Henry Hollier, and in the process, he made a discovery about ciphers that were based on Vigenère tables. Specifically, he realised that enciphering plain text with a keyword rendered the cipher text subject to modular arithmetic. During the Crimean War of the 1850s, Babbage broke Vigenère's autokey cipher
An autokey cipher (also known as the autoclave cipher) is a cipher that incorporates the message (the plaintext) into the key. The key is generated from the message in some automated fashion, sometimes by selecting certain letters from the text or ...
as well as the much weaker cipher that is called Vigenère cipher today. His discovery was kept a military secret, and was not published. Credit for the result was instead given to Friedrich Kasiski, a Prussian infantry officer, who made the same discovery some years later. However, in 1854, Babbage published the solution of a Vigenère cipher, which had been published previously in the ''Journal of the Society of Arts''. In 1855, Babbage also published a short letter, "Cypher Writing", in the same journal. Nevertheless, his priority was not established until 1985.
Public nuisances
Babbage involved himself in well-publicised but unpopular campaigns against public nuisances. He once counted all the broken panes of glass of a factory, publishing in 1857 a "Table of the Relative Frequency of the Causes of Breakage of Plate Glass Windows": Of 464 broken panes, 14 were caused by "drunken men, women or boys". Babbage's distaste for commoners (the Mob) included writing "Observations of Street Nuisances" in 1864, as well as tallying up 165 "nuisances" over a period of 80 days. He especially hatedstreet music
Street performance or busking is the act of performing in public places for gratuities
A gratuity (often called a tip) is a sum of money customarily given by a customer to certain service sector workers such as hospitality for the service ...
, and in particular the music of organ grinders, against whom he railed in various venues. The following quotation is typical:
Babbage was not alone in his campaign. A convert to the cause was the MP Michael Thomas Bass
Michael Thomas Bass, DL (6 July 1799 – 29 April 1884) was an English brewer and a Member of Parliament. Under his leadership, the Bass Brewery became the largest brewery in the world, and Bass the best known brand of beer in England. Bass r ...
.
In the 1860s, Babbage also took up the anti- hoop-rolling campaign. He blamed hoop-rolling boys for driving their iron hoops under horses' legs, with the result that the rider is thrown and very often the horse breaks a leg. Babbage achieved a certain notoriety in this matter, being denounced in debate in Commons in 1864 for "commencing a crusade against the popular game of tip-cat
Tip-cat (also called cat, cat and dog, one-a-cat, pussy, or piggy) is a pastime which consists of tapping a short billet of wood (usually no more than ) with a larger stick (similar to a baseball bat or broom handle); the shorter piece is tapered ...
and the trundling of hoops."
Computing pioneer
 Babbage's machines were among the first mechanical computers. That they were not actually completed was largely because of funding problems and clashes of personality, most notably with George Biddell Airy, the Astronomer Royal.
Babbage directed the building of some steam-powered machines that achieved some modest success, suggesting that calculations could be mechanised. For more than ten years he received government funding for his project, which amounted to £17,000, but eventually the Treasury lost confidence in him.
While Babbage's machines were mechanical and unwieldy, their basic architecture was similar to a modern computer. The data and program memory were separated, operation was instruction-based, the control unit could make conditional jumps, and the machine had a separate I/O unit.
Babbage's machines were among the first mechanical computers. That they were not actually completed was largely because of funding problems and clashes of personality, most notably with George Biddell Airy, the Astronomer Royal.
Babbage directed the building of some steam-powered machines that achieved some modest success, suggesting that calculations could be mechanised. For more than ten years he received government funding for his project, which amounted to £17,000, but eventually the Treasury lost confidence in him.
While Babbage's machines were mechanical and unwieldy, their basic architecture was similar to a modern computer. The data and program memory were separated, operation was instruction-based, the control unit could make conditional jumps, and the machine had a separate I/O unit.
Background on mathematical tables
In Babbage's time, printed mathematical tables were calculated by human computers; in other words, by hand. They were central to navigation, science and engineering, as well as mathematics. Mistakes were known to occur in transcription as well as calculation. At Cambridge, Babbage saw the fallibility of this process, and the opportunity of adding mechanisation into its management. His own account of his path towards mechanical computation references a particular occasion: There was another period, seven years later, when his interest was aroused by the issues around computation of mathematical tables. The French official initiative by Gaspard de Prony, and its problems of implementation, were familiar to him. After the Napoleonic Wars came to a close, scientific contacts were renewed on the level of personal contact: in 1819Charles Blagden
Sir Charles Brian Blagden FRS (17 April 1748 – 26 March 1820) was an English physician and chemist. He served as a medical officer in the Army (1776–1780) and later held the position of Secretary of the Royal Society (1784–1797). Blagd ...
was in Paris looking into the printing of the stalled de Prony project, and lobbying for the support of the Royal Society. In works of the 1820s and 1830s, Babbage referred in detail to de Prony's project.
Difference engine

 Babbage began in 1822 with what he called the difference engine, made to compute values of
Babbage began in 1822 with what he called the difference engine, made to compute values of polynomial function
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression (mathematics), expression consisting of indeterminate (variable), indeterminates (also called variable (mathematics), variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtrac ...
s. It was created to calculate a series of values automatically. By using the method of finite differences, it was possible to avoid the need for multiplication and division.
For a prototype difference engine, Babbage brought in Joseph Clement
Joseph Clement (13 June 1779 – 28 February 1844) was a British engineer and industrialist, chiefly remembered as the maker of Charles Babbage's first difference engine, between 1824 and 1833.
Biography
Early life
Joseph Clement was born on ...
to implement the design, in 1823. Clement worked to high standards, but his machine tools were particularly elaborate. Under the standard terms of business of the time, he could charge for their construction, and would also own them. He and Babbage fell out over costs around 1831.
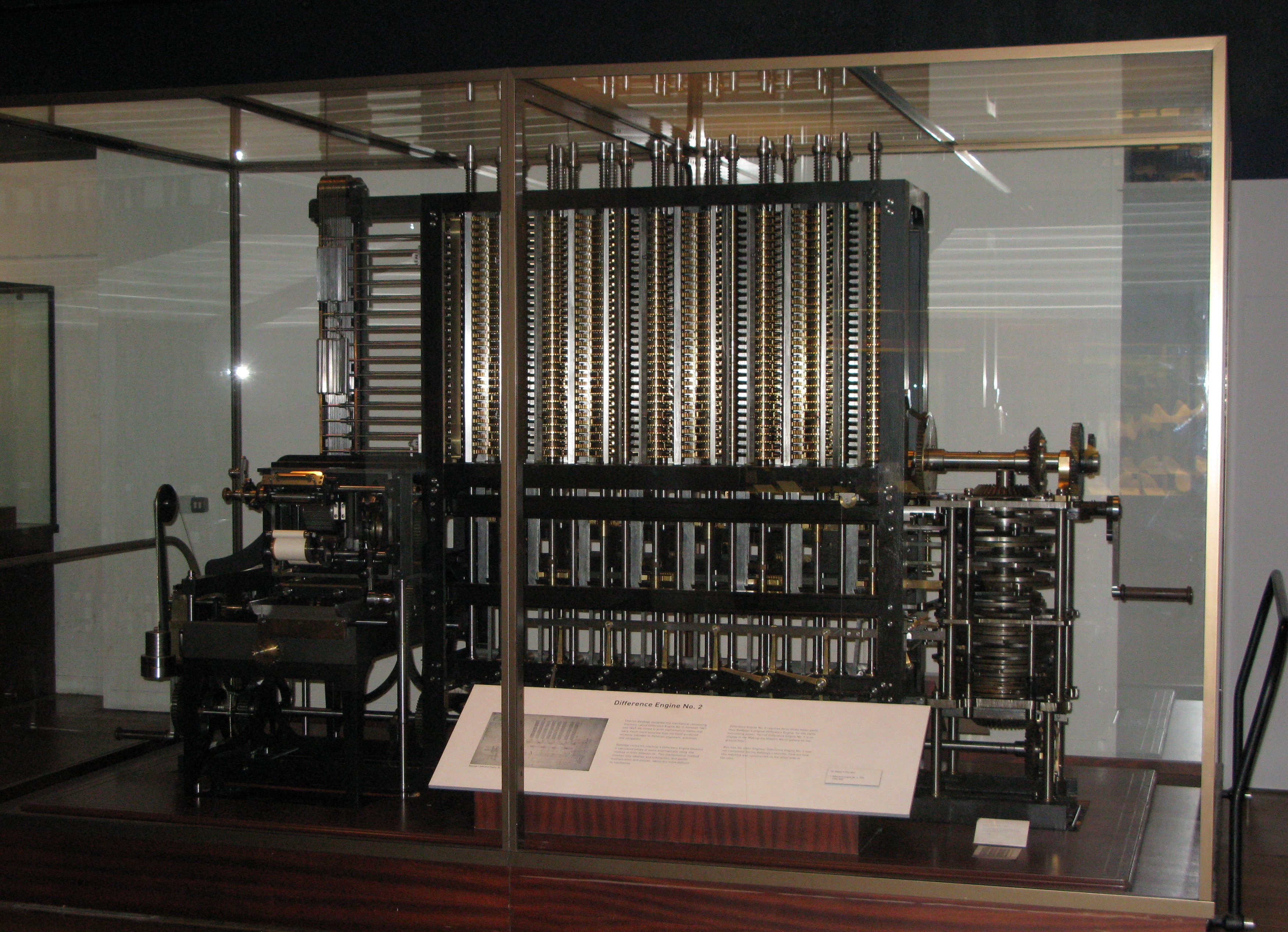
Some parts of the prototype survive in the Museum of the History of Science, Oxford. This prototype evolved into the "first difference engine". It remained unfinished and the finished portion is located at the Science Museum in London. This first difference engine would have been composed of around 25,000 parts, weighed , and would have been tall. Although Babbage received ample funding for the project, it was never completed. He later (1847–1849) produced detailed drawings for an improved version,"Difference Engine No. 2", but did not receive funding from the British government. His design was finally constructed in 1989–1991, using his plans and 19th-century manufacturing tolerances. It performed its first calculation at the Science Museum, London, returning results to 31 digits.
Nine years later, in 2000, the Science Museum completed the printer Babbage had designed for the difference engine.
Completed models
The Science Museum has constructed two Difference Engines according to Babbage's plans for the Difference Engine No 2. One is owned by the museum. The other, owned by the technology multimillionaire Nathan Myhrvold, went on exhibition at theComputer History Museum
The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a museum of computer history, located in Mountain View, California. The museum presents stories and artifacts of Silicon Valley and the information age, and explores the computing revolution and its impact on ...
in Mountain View, California on 10 May 2008. The two models that have been constructed are not replicas.
Analytical Engine
 After the attempt at making the first difference engine fell through, Babbage worked to design a more complex machine called the Analytical Engine. He hired C. G. Jarvis, who had previously worked for Clement as a draughtsman. The Analytical Engine marks the transition from mechanised arithmetic to fully-fledged general purpose computation. It is largely on it that Babbage's standing as computer pioneer rests.
The major innovation was that the Analytical Engine was to be programmed using punched cards: the Engine was intended to use loops of Jacquard's punched cards to control a mechanical calculator, which could use as input the results of preceding computations. The machine was also intended to employ several features subsequently used in modern computers, including sequential control, branching and looping. It would have been the first mechanical device to be, in principle, Turing-complete. The Engine was not a single physical machine, but rather a succession of designs that Babbage tinkered with until his death in 1871.
After the attempt at making the first difference engine fell through, Babbage worked to design a more complex machine called the Analytical Engine. He hired C. G. Jarvis, who had previously worked for Clement as a draughtsman. The Analytical Engine marks the transition from mechanised arithmetic to fully-fledged general purpose computation. It is largely on it that Babbage's standing as computer pioneer rests.
The major innovation was that the Analytical Engine was to be programmed using punched cards: the Engine was intended to use loops of Jacquard's punched cards to control a mechanical calculator, which could use as input the results of preceding computations. The machine was also intended to employ several features subsequently used in modern computers, including sequential control, branching and looping. It would have been the first mechanical device to be, in principle, Turing-complete. The Engine was not a single physical machine, but rather a succession of designs that Babbage tinkered with until his death in 1871.

Ada Lovelace and Italian followers
Ada Lovelace, who corresponded with Babbage during his development of the Analytical Engine, is credited with developing an algorithm that would enable the Engine to calculate a sequence of Bernoulli numbers.Robin Hammerman, Andrew L. Russell (2016). ''Ada's Legacy: Cultures of Computing from the Victorian to the Digital Age''. Association for Computing Machinery and Morgan & Claypool Publishers. Despite documentary evidence in Lovelace's own handwriting, some scholars dispute to what extent the ideas were Lovelace's own. For this achievement, she is often described as the firstcomputer programmer
A computer programmer, sometimes referred to as a software developer, a software engineer, a programmer or a coder, is a person who creates computer programs — often for larger computer software.
A programmer is someone who writes/creates ...
; though no programming language had yet been invented.
Lovelace also translated and wrote literature supporting the project. Describing the engine's programming by punch cards, she wrote: "We may say most aptly that the Analytical Engine weaves algebraical patterns just as the Jacquard loom
The Jacquard machine () is a device fitted to a loom that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with such complex patterns as brocade, damask and matelassé. The resulting ensemble of the loom and Jacquard machine is then called a Ja ...
weaves flowers and leaves."
Babbage visited Turin in 1840 at the invitation of Giovanni Plana
Giovanni Antonio Amedeo Plana (6 November 1781 – 20 January 1864) was an Italian astronomer and mathematician. He is considered one of the premiere Italian scientists of his age.
The crater Plana on the Moon is named in his honor.
Biograph ...
, who had developed in 1831 an analog computing machine that served as a perpetual calendar. Here in 1840 in Turin, Babbage gave the only public explanation and lectures about the Analytical Engine. In 1842 Charles Wheatstone approached Lovelace to translate a paper of Luigi Menabrea
Luigi Federico Menabrea (4 September 1809 – 24 May 1896), later made 1st Count Menabrea and 1st Marquess of Valdora, was an Italian general, statesman and mathematician who served as the seventh prime minister of Italy from 1867 to 1869.
B ...
, who had taken notes of Babbage's Turin talks; and Babbage asked her to add something of her own. Fortunato Prandi who acted as interpreter in Turin was an Italian exile and follower of Giuseppe Mazzini.
Swedish followers
Per Georg Scheutz
Pehr (Per) Georg Scheutz (23 September 1785 – 22 May 1873) was a Swedish lawyer, translator, and inventor, who is now best known for his pioneering work in computer technology.
Life
Scheutz studied law at Lund University, graduating in 1805. He ...
wrote about the difference engine in 1830, and experimented in automated computation. After 1834 and Lardner's ''Edinburgh Review'' article he set up a project of his own, doubting whether Babbage's initial plan could be carried out. This he pushed through with his son, Edvard Scheutz. Another Swedish engine was that of Martin Wiberg (1860).
Legacy
In 2011, researchers in Britain proposed a multimillion-pound project, "Plan 28", to construct Babbage's Analytical Engine. Since Babbage's plans were continually being refined and were never completed, they intended to engage the public in the project and crowd-source the analysis of what should be built. It would have the equivalent of 675 bytes of memory, and run at a clock speed of about 7 Hz. They hoped to complete it by the 150th anniversary of Babbage's death, in 2021. Advances in MEMS andnanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal o ...
have led to recent high-tech experiments in mechanical computation. The benefits suggested include operation in high radiation or high temperature environments. These modern versions of mechanical computation were highlighted in '' The Economist'' in its special "end of the millennium" black cover issue in an article entitled "Babbage's Last Laugh".
Due to his association with the town Babbage was chosen in 2007 to appear on the 5 Totnes pound note. An image of Babbage features in the British cultural icons section of the newly designed British passport
A British passport is a travel document issued by the United Kingdom or other British dependencies and territories to individuals holding any form of British nationality. It grants the bearer international passage in accordance with visa requ ...
in 2015.
Family
 On 25 July 1814, Babbage married Georgiana Whitmore, sister of British parliamentarian William Wolryche-Whitmore, at St. Michael's Church in Teignmouth, Devon. The couple lived at
On 25 July 1814, Babbage married Georgiana Whitmore, sister of British parliamentarian William Wolryche-Whitmore, at St. Michael's Church in Teignmouth, Devon. The couple lived at Dudmaston Hall
Dudmaston Hall is a 17th-century country house in the care of the National Trust in the Severn Valley, Shropshire, England.
Dudmaston Hall is located near the village of Quatt, a few miles south of the market town of Bridgnorth, just off the ...
, Shropshire (where Babbage engineered the central heating system), before moving to 5 Devonshire Street, London in 1815.
Charles and Georgiana had eight children, but only four – Benjamin Herschel, Georgiana Whitmore, Dugald Bromhead and Henry Prevost – survived childhood. Charles' wife Georgiana died in Worcester on 1 September 1827, the same year as his father, their second son (also named Charles) and their newborn son Alexander.
* Benjamin Herschel Babbage (1815–1878)
* Charles Whitmore Babbage (1817–1827)
* Georgiana Whitmore Babbage (1818 – 26 September 1834)
* Edward Stewart Babbage (1819–1821)
* Francis Moore Babbage (1821–????)
* Dugald Bromhead (Bromheald?) Babbage (1823–1901)
* (Maj-Gen) Henry Prevost Babbage (1824–1918)
* Alexander Forbes Babbage (1827–1827)
His youngest surviving son, Henry Prevost Babbage (1824–1918), went on to create six small demonstration pieces for Difference Engine No. 1 based on his father's designs, one of which was sent to Harvard University where it was later discovered by Howard H. Aiken
Howard Hathaway Aiken (March 8, 1900 – March 14, 1973) was an American physicist and a pioneer in computing, being the original conceptual designer behind IBM's Harvard Mark I computer.
Biography
Aiken studied at the University of Wisconsin ...
, pioneer of the Harvard Mark I
The Harvard Mark I, or IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator (ASCC), was a general-purpose electromechanical computer used in the war effort during the last part of World War II.
One of the first programs to run on the Mark I was initi ...
. Henry Prevost's 1910 Analytical Engine Mill, previously on display at Dudmaston Hall, is now on display at the Science Museum.
Death
 Babbage lived and worked for over 40 years at 1 Dorset Street, Marylebone, where he died, at the age of 79, on 18 October 1871; he was buried in London's Kensal Green Cemetery. According to Horsley, Babbage died "of renal inadequacy, secondary to cystitis." He had declined both a knighthood and baronetcy. He also argued against hereditary peerages, favouring life peerages instead.
Babbage lived and worked for over 40 years at 1 Dorset Street, Marylebone, where he died, at the age of 79, on 18 October 1871; he was buried in London's Kensal Green Cemetery. According to Horsley, Babbage died "of renal inadequacy, secondary to cystitis." He had declined both a knighthood and baronetcy. He also argued against hereditary peerages, favouring life peerages instead.
Autopsy report
In 1983, the autopsy report for Charles Babbage was discovered and later published by his great-great-grandson. A copy of the original is also available. Half of Babbage's brain is preserved at the Hunterian Museum in the Royal College of Surgeons in London. The other half of Babbage's brain is on display in the Science Museum, London.Memorials
 There is a black plaque commemorating the 40 years Babbage spent at 1 Dorset Street, London. Locations, institutions and other things named after Babbage include:
* The Moon crater
There is a black plaque commemorating the 40 years Babbage spent at 1 Dorset Street, London. Locations, institutions and other things named after Babbage include:
* The Moon crater Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer.
Babbage is considered ...
* The Charles Babbage Institute, an information technology archive and research center at the University of Minnesota
* The Charles Babbage Premium, an annual computing award
* British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British rai ...
named a locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
after him in the 1990s
* The Babbage Building at the University of Plymouth, where the university's school of computing is based
* The Babbage programming language for GEC 4000 series
The GEC 4000 was a series of 16/32-bit minicomputers produced by GEC Computers Ltd in the United Kingdom during the 1970s, 1980s and early 1990s.
History
GEC Computers was formed in 1968 as a business unit of the GEC conglomerate. It in ...
minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a class of smaller general purpose computers that developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, ...
s
* "Babbage", '' The Economist''s Science and Technology blog.
* The former chain retail computer and video-games store "Babbage's" (now GameStop
GameStop Corp. is an American video game, consumer electronics, and gaming merchandise retailer. The company is headquartered in Grapevine, Texas (a suburb of Dallas), and is the largest video game retailer worldwide. , the company operates 4,5 ...
) was named after him.
In fiction and film
Babbage frequently appears insteampunk
Steampunk is a subgenre of science fiction that incorporates retrofuturistic technology and aesthetics inspired by 19th-century industrial steam-powered machinery. Steampunk works are often set in an alternative history of the Victorian era or ...
works; he has been called an iconic figure of the genre. Other works in which Babbage appears include:
* The 2008 short film ''Babbage'', screened at the 2008 Cannes Film Festival
The 61st Annual Cannes Film Festival was held from 14 to 25 May 2008. The President of the Official Jury was American actor and director Sean Penn. Twenty two films from fourteen countries were selected to compete for the ''Palme d'Or''. The awards ...
, a 2009 finalist with Haydenfilms
Haydenfilms LLC is a producer and distributor of independent films. It was founded in 2001 by Hayden Craddolph, the current executive director of the Haydenfilms Institute (HFI). Haydenfilms is based in Lehigh Valley, Pennsylvania, at the TEK Par ...
, and shown at the 2009 HollyShorts Film Festival and other international film festivals. The film shows Babbage at a dinner party, with guests discussing his life and work.
* Sydney Padua
Melina Sydney Padua is a graphic artist and animator based in London, England. She is the author of '' The Thrilling Adventures of Lovelace and Babbage'' steampunk comic, and her animation work appears in several popular Hollywood films.
She ...
created ''The Thrilling Adventures of Lovelace and Babbage
''The Thrilling Adventures of Lovelace and Babbage: The (Mostly) True Story of the First Computer'' is a steampunk graphic novel written and drawn by Sydney Padua. It features Ada Lovelace and Charles Babbage in an alternative universe where they ...
'', a cartoon alternate history in which Babbage and Lovelace succeed in building the Analytical Engine. It quotes heavily from the writings of Lovelace, Babbage and their contemporaries.
* Kate Beaton, cartoonist of webcomic '' Hark! A Vagrant'', devoted one of her comic strips to Charles and Georgiana Babbage.
* The ''Doctor Who
''Doctor Who'' is a British science fiction television series broadcast by the BBC since 1963. The series depicts the adventures of a Time Lord called the Doctor, an extraterrestrial being who appears to be human. The Doctor explores the u ...
'' episode "Spyfall, Part 2
"Spyfall" is the two-part premiere of the twelfth series of the British science fiction television programme ''Doctor Who'', first broadcast on BBC One on 1 January 2020, and concluded on 5 January 2020. It was written by showrunner and executi ...
" (Season 12, episode 2) features Charles Babbage and Ada Gordon as characters who assist the Doctor when she's stuck in the year 1834.
Publications
* * * * * * (Reissued by Cambridge University Press 2009, .) * (The LOCOMAT site contains a reconstruction of this table.) * * * * * C. J. D. Roberts, Compiler.Charles Babbage's Lectures On Astronomy
/ref>
See also
* Babbage's congruence * List of pioneers in computer scienceNotes
References
* .External links
* * * * *The Babbage Papers
The papers held by the Science Museum Library and Archives which relate mostly to Babbage's automatic calculating engines
''The Babbage Engine''
Computer History Museum, Mountain View CA, USA. Multi-page account of Babbage, his engines and his associates, including a video of the Museum's functioning replica of the Difference Engine No 2 in action
Analytical Engine Museum
John Walker's (of AutoCAD fame) comprehensive catalogue of the complete technical works relating to Babbage's machine.
Charles Babbage
A history at the School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews Scotland.
Mr. Charles Babbage
obituary from ''The Times'' (1871)
The Babbage Pages
Charles Babbage, The Online Books Page, University of Pennsylvania
an overview of how it works
"On a Method of Expressing by Signs the Action of Machinery"
1826. Original edition
pages on "Who Was Charles Babbage?" including biographical note, description of Difference Engine No. 2, publications by Babbage, archival and published sources on Babbage, sources on Babbage and Ada Lovelace
''Babbage's Calculating Machine''
(1872) – full digital facsimile from Linda Hall Library
Author profile
in the database zbMATH
The 'difference engine' built by Georg & Edvard Scheutz in 1843
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Babbage, Charles 1791 births 1871 deaths 19th-century English mathematicians Alumni of Peterhouse, Cambridge Alumni of Trinity College, Cambridge British business theorists Burials at Kensal Green Cemetery Corresponding members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences English Christians English computer scientists English engineers Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Fellows of the Royal Astronomical Society Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Fellows of the Royal Society Lucasian Professors of Mathematics People educated at Totnes Grammar School People of the Industrial Revolution Recipients of the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society Mathematicians from London