|
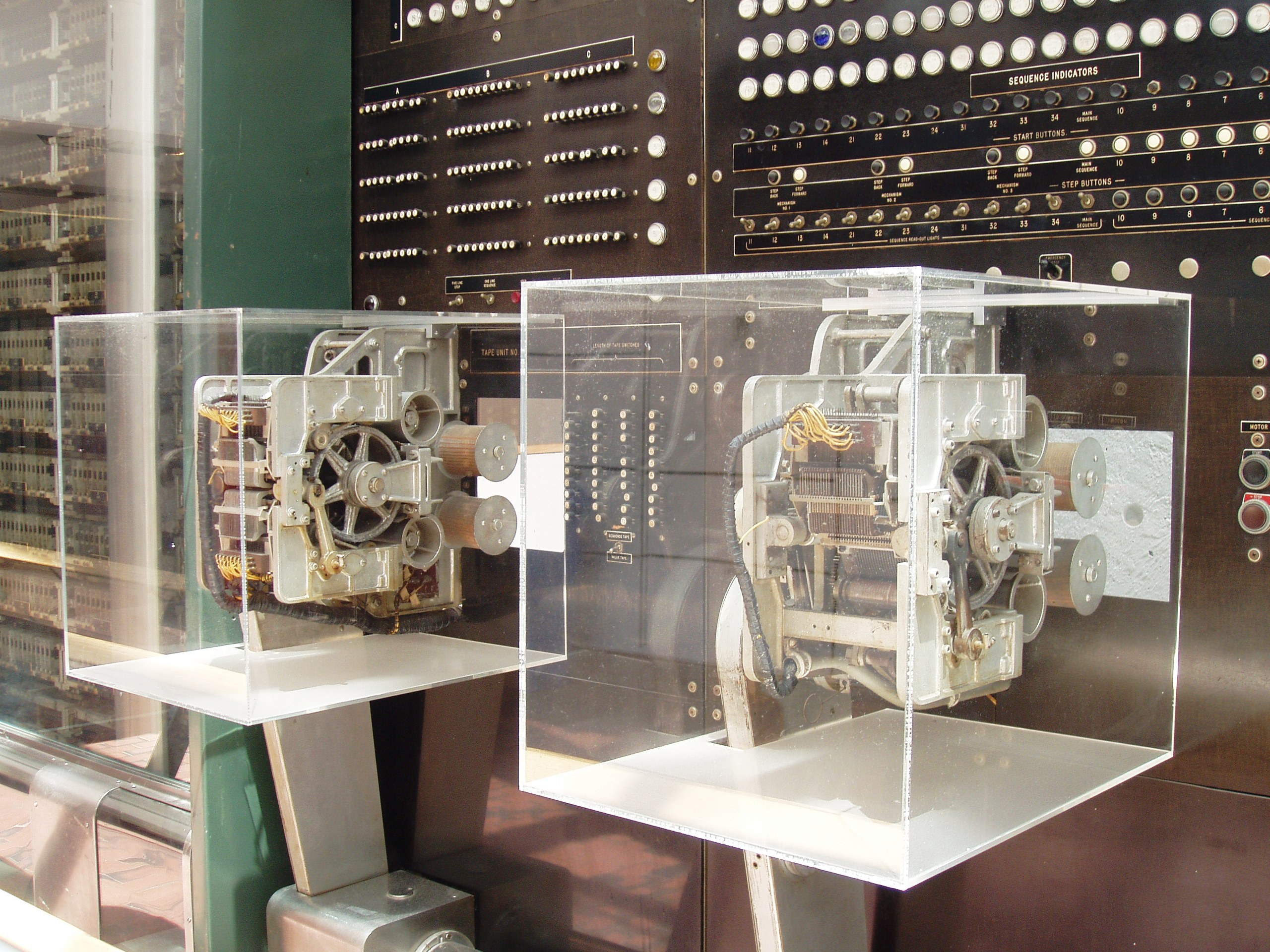
Howard H. Aiken
Howard Hathaway Aiken (March 8, 1900 – March 14, 1973) was an American physicist and a pioneer in computing. He was the original conceptual designer behind IBM's Harvard Mark I, the United States' first programmable computer. Biography Aiken was born on 8 March 1900, in Hoboken, New Jersey, to Daniel Aiken, who came from a wealthy and established Indiana family, and Margaret Emily Mierisch, whose parents were German immigrants. He grew up in Indianapolis where he graduated from Arsenal Technical High School in 1919. Aiken studied at the University of Wisconsin–Madison where he received his B.S. in electrical engineering in 1923. He later obtained his M.A. and Ph.D. degrees in physics from Harvard University in 1937 and 1939, respectively. During this time, he encountered differential equations that he could only solve numerically. Inspired by Charles Babbage's difference engine, he envisioned an electro-mechanical computing device that could do much of the tedious wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hoboken, New Jersey
Hoboken ( ; ) is a City (New Jersey), city in Hudson County, New Jersey, Hudson County in the U.S. state of New Jersey. Hoboken is part of the New York metropolitan area and is the site of Hoboken Terminal, a major transportation hub. As of the 2020 United States census, the city's population was 60,419, an increase of 10,414 (+20.8%) from the 2010 United States census, 2010 census count of 50,005, which in turn reflected an increase of 11,428 (+29.6%) from the 38,577 counted in the 2000 United States census, 2000 census. The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated a population of 57,010 for 2023, making it the List of United States cities by population, 708th-most populous municipality in the nation. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Pioneers In Computer Science
This is a list of people who made transformative breakthroughs in the creation, development and imagining of what computers could do. Pioneers ~ Items marked with a tilde are circa dates. See also * Computer Pioneer Award * IEEE John von Neumann Medal * Grace Murray Hopper Award * History of computing ** History of computing hardware ** History of computing hardware (1960s–present) ** History of software * List of computer science awards * List of computer scientists * List of Internet pioneers * List of people considered father or mother of a field § Computing * '' The Man Who Invented the Computer'' (2010 book) * List of Russian IT developers * List of Women in Technology International Hall of Fame inductees * Timeline of computing * Turing Award * Women in computing Women in computing were among the first programmers in the early 20th century, and contributed substantially to the industry. As technology and practices altered, the role of women as programme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Richard Milton Bloch
Richard Milton Bloch (June 18, 1921 – May 22, 2000) was a pioneering American computer programmer. Bloch, Grace Hopper, and Robert Campbell were the first programmers of the Harvard Mark I, an electromechanical computer which, when it began operation in 1944, was the first American programmable computer. Early life Bloch was born in Rochester, New York, on June 18, 1921, and grew up there, being graduated from Benjamin Franklin High School. He then attended Harvard University on a scholarship, majoring in mathematics, being graduated in 1943. He then immediately joined the Navy, as World War II was in progress, and was assigned to the Naval Research Institute. There, he was recruited by Howard Aiken to work on the Mark I project, moving to Harvard in March 1944. Mark I work The Harvard Mark I became operational in 1944, and was used for war work, including computation of ballistic tables, Bessel tables for electronics and other applications, and calculations used by the Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
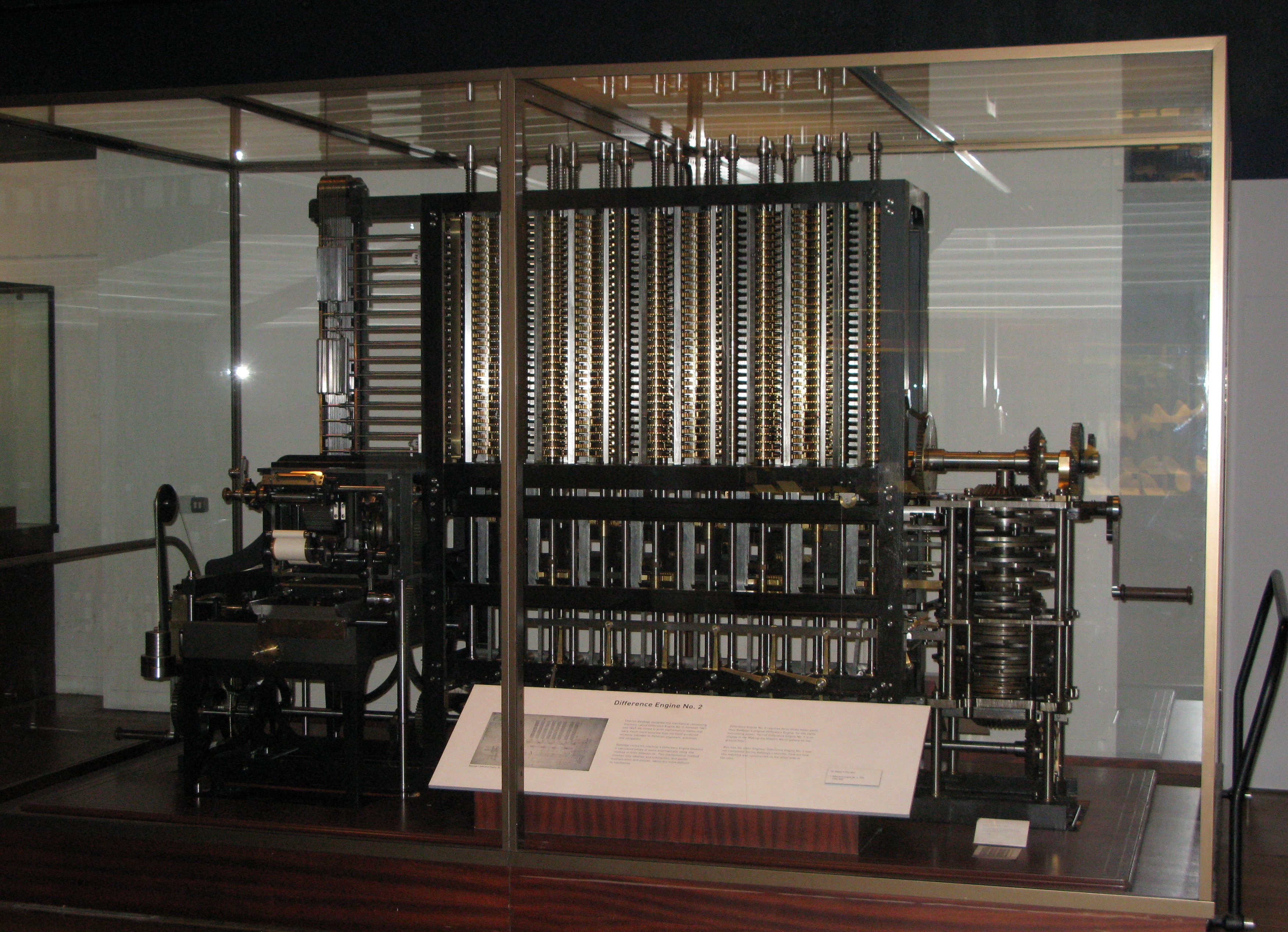
Difference Engine
A difference engine is an automatic mechanical calculator designed to tabulate polynomial functions. It was designed in the 1820s, and was created by Charles Babbage. The name ''difference engine'' is derived from the method of finite differences, a way to interpolate or tabulate functions by using a small set of polynomial co-efficients. Some of the most common mathematical functions used in engineering, science and navigation are built from logarithmic and trigonometric functions, which can be approximated by polynomials, so a difference engine can compute many useful tables. History The notion of a mechanical calculator for mathematical functions can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of the 2nd century BC, while early modern examples are attributed to Pascal and Leibniz in the 17th century. In 1784 J. H. Müller, an engineer in the Hessian army, devised and built an adding machine and described the basic principles of a difference machine in a book pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. Babbage is considered by some to be "List of pioneers in computer science, father of the computer". He is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the difference engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in his analytical engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. As part of his computer work, he also designed the first Printer (computing), computer printers. He had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his 1832 book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. He was an important figure in the social scene in London, and is credited with importing the "scientific soirée" from France with hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arsenal Technical High School
Arsenal Technical High School, commonly referred to as Tech or Arsenal Tech, is a public high school in Indianapolis, Indiana, United States, which is run by the Indianapolis Public Schools district. The school is located on a , multiple building campus east of downtown Indianapolis, and is the only such type school in Indiana. The school's campus originally served as a American Civil War, U.S. Civil War era arsenal from 1864 until 1903, when it was closed following the Spanish–American War. A few years later, the school opened in 1912 under founder Milo H. Stuart. A number of extant buildings dating back to military use are still open and serve academic purposes for the school, such as the Arsenal building and the Barracks. In addition, a number of additional buildings were built in the following decades to accommodate the school's functions. Due to the significance of the school's campus, facilities, and history, Arsenal Technical was placed on the National Register of Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indianapolis
Indianapolis ( ), colloquially known as Indy, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Indiana, most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the county seat of Marion County, Indiana, Marion County. Indianapolis is situated in the state's central till plain region along the west fork of the White River (Indiana), White River. The city's official slogan, "Crossroads of America", reflects its historic importance as a transportation hub and its relative proximity to other major North American markets. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the Indianapolis (balance), balance population was 887,642. Indianapolis is the List of United States cities by population, 16th-most populous city in the U.S., the third-most populous city in the Midwestern United States, Midwest after Chicago and Columbus, Ohio, and the fourth-most populous state capital in the nation after Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Austin, Texas, Austin, and Columbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, implemented in 1949 following the end of World War II, defines a German as a German nationality law, German citizen. During the 19th and much of the 20th century, discussions on German identity were dominated by concepts of a common language, culture, descent, and history.. "German identity developed through a long historical process that led, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, to the definition of the German nation as both a community of descent (Volksgemeinschaft) and shared culture and experience. Today, the German language is the primary though not exclusive criterion of German identity." Today, the German language is widely seen as the primary, though not exclusive, criterion of German identity. Estimates on the total number of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the south and southeast, and the Wabash River and Illinois to the west. Nicknamed "the Hoosier State", Indiana is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 38th-largest by area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 17th-most populous of the List of states and territories of the United States, 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the Union as the 19th state on December 11, 1816. Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous resistance to American settlement was broken with defeat of the Tecumseh's confederacy in 1813. The new settlers were primarily Americans of British people, British ancestry from the East Coast of the United States, eastern seaboard and the Upland South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Babbage Institute
The IT History Society (ITHS) is an organization that supports the history and scholarship of information technology by encouraging, fostering, and facilitating archival and historical research. Formerly known as the Charles Babbage Foundation, it advises historians, promotes collaboration among academic organizations and museums, and assists IT corporations in preparing and archiving their histories for future studies. Activities The IT History Society provides background information to those with an interest in the history of Information Technology, including papers that provide advice on how to perform historical work and how historical activities can benefit private sector organizations. It tracks historical projects seeking funding as well as projects underway and completed. It maintains online, publicly available, lists of events pertaining to IT history, IT history resources, an IT Honor Roll acknowledging more than 700 individuals who have made a noteworthy contribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |