Aude De Fanjeaux on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aude (; ) is a
INSEE Aude is a frequent feminine French given name in Francophone countries, deriving initially from Aude or Oda, a wife of Bertrand,
department
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
in Southern France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French language, French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi ...
, located in the Occitanie Occitanie may refer to:
*Occitania, a region in southern France called ''Occitanie'' in French
*Occitania (administrative region)
Occitania ( ; french: Occitanie ; oc, Occitània ; ca, Occitània ) is the southernmost administrative region of ...
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
and named after the river Aude
Aude (; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it "Ca ...
. The departmental council also calls it "Cathar
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Follow ...
Country" ( French: ''Pays cathare'') after a group of religious dissidents active in the 12th to 14th centuries.
Its prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
is Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
and its subprefectures are Limoux
Limoux (; oc, Limós ) is a commune and subprefecture in the Aude department, a part of the ancient Languedoc province and the present-day Occitanie region in southern France. Its vineyards are famous for being first to produce sparkling wi ...
and Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
. As of 2019, it had a population of 374,070.Populations légales 2019: 11 AudeINSEE Aude is a frequent feminine French given name in Francophone countries, deriving initially from Aude or Oda, a wife of Bertrand,
Duke of Aquitaine
The Duke of Aquitaine ( oc, Duc d'Aquitània, french: Duc d'Aquitaine, ) was the ruler of the medieval region of Aquitaine (not to be confused with modern-day Aquitaine) under the supremacy of Frankish, English, and later French kings.
As succe ...
, and mother of Eudo, brother of Saint Hubertus
Hubertus or Hubert ( 656 – 30 May 727 A.D.) was a Christian saint who became the first bishop of Liège in 708 A.D. He is the patron saint of hunters, mathematicians, opticians and metalworkers. Known as the "Apostle of the Ardennes", he was ...
. Aude was the name of Roland's fiancée in the ''chansons de geste''.
Geography
Location
Aude is located between theMediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
and the Pyrenees Mountains
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to C ...
.
It is part of the current region of Occitanie Occitanie may refer to:
*Occitania, a region in southern France called ''Occitanie'' in French
*Occitania (administrative region)
Occitania ( ; french: Occitanie ; oc, Occitània ; ca, Occitània ) is the southernmost administrative region of ...
. It is surrounded by the departments of Pyrénées-Orientales
Pyrénées-Orientales (; ca, Pirineus Orientals ; oc, Pirenèus Orientals ; ), also known as Northern Catalonia, is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France, adjacent to the northern Spanish frontier and the Mediterranean Sea. ...
, Ariège, Haute-Garonne
Haute-Garonne (; oc, Nauta Garona, ; en, Upper Garonne) is a department in the Occitanie region of Southwestern France. Named after the river Garonne, which flows through the department. Its prefecture and main city is Toulouse, the country's ...
, Tarn, and Hérault
Hérault (; oc, Erau, ) is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France. Named after the Hérault River, its prefecture is Montpellier. It had a population of 1,175,623 in 2019.Golfe du Lion on the east.
 The countryside in this department falls into several
The countryside in this department falls into several
 Each natural region of the Aude has its own particular landscape. In the east, lagoons or coastal lakes separate land and sea. These were formed by accumulations of sediments carried down by the rivers Aude, Orb and
Each natural region of the Aude has its own particular landscape. In the east, lagoons or coastal lakes separate land and sea. These were formed by accumulations of sediments carried down by the rivers Aude, Orb and
 The landscapes of Aude can be explained by its geology. In the south, there are
The landscapes of Aude can be explained by its geology. In the south, there are
 Aude is under the influence of a Mediterranean climate.
The autumn is characterized by violent and short storms.
The summer is often hot and dry, which is favorable to the culture of the vine and the olive-trees. Yet, the department has several contrasts in climate:
In the north, the Montagne Noire and, in the south, the Pays de Sault, have a mountainous climate with temperatures sometimes very low in winter.
In the west, the climate is under Aquitaine influence with heavier precipitation, while in the east the climate is purely Mediterranean.
In the centre, in the Limouxin, Carcassonnais and Razès areas, the climate is known as intermediary with significant exposure to winds.
The winds are often present in Aude. It is one of the windiest French departments, with 300 to 350 days of wind per year. This phenomenon is due mostly to the variations in relief north and south which create a kind of corridor.
In the north-west blows the
Aude is under the influence of a Mediterranean climate.
The autumn is characterized by violent and short storms.
The summer is often hot and dry, which is favorable to the culture of the vine and the olive-trees. Yet, the department has several contrasts in climate:
In the north, the Montagne Noire and, in the south, the Pays de Sault, have a mountainous climate with temperatures sometimes very low in winter.
In the west, the climate is under Aquitaine influence with heavier precipitation, while in the east the climate is purely Mediterranean.
In the centre, in the Limouxin, Carcassonnais and Razès areas, the climate is known as intermediary with significant exposure to winds.
The winds are often present in Aude. It is one of the windiest French departments, with 300 to 350 days of wind per year. This phenomenon is due mostly to the variations in relief north and south which create a kind of corridor.
In the north-west blows the
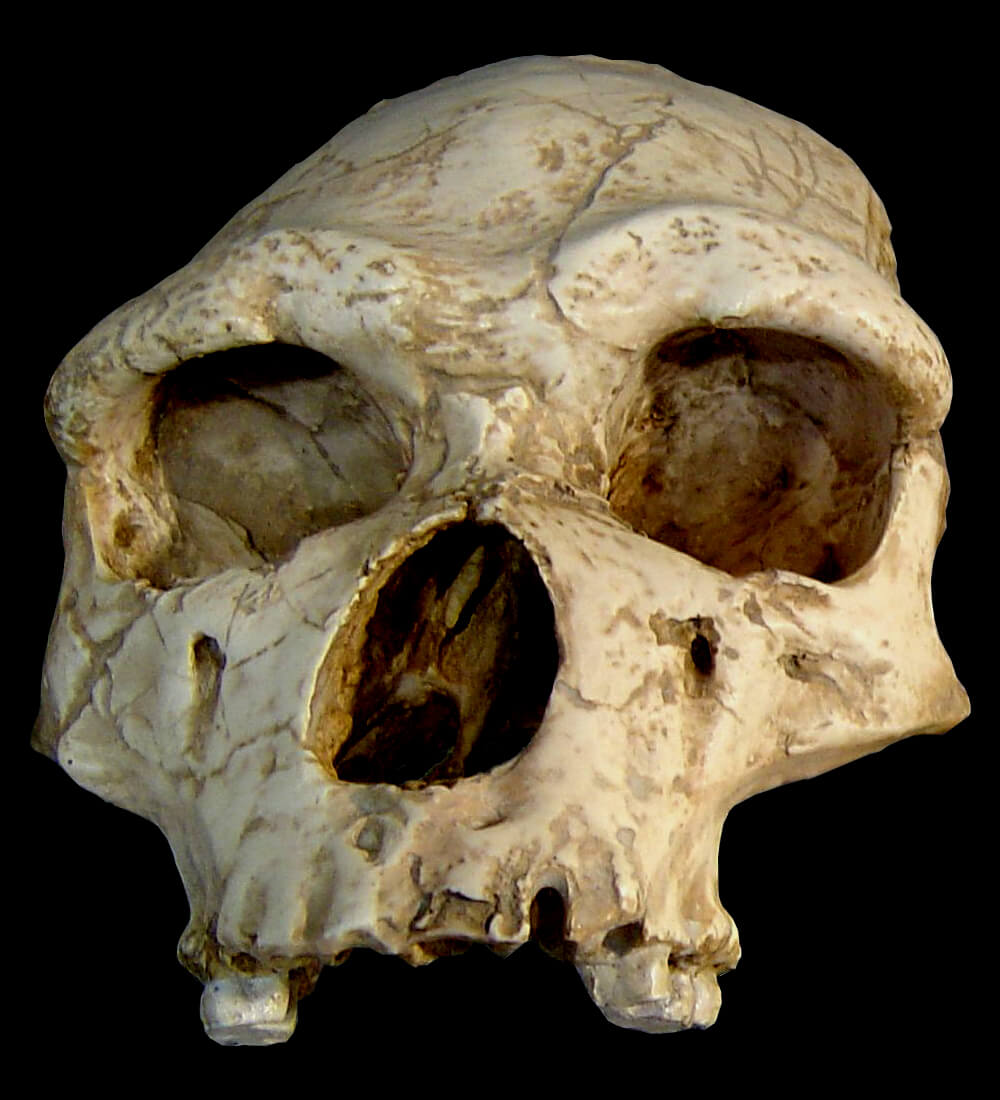 Hammers and worked tools have been found on the hill of Grazailles at Carcassonne, dating from between 690,000 and 300,000 years ago. Most interesting is the skull of
Hammers and worked tools have been found on the hill of Grazailles at Carcassonne, dating from between 690,000 and 300,000 years ago. Most interesting is the skull of
 Aude is an agricultural area dominated by vineyards. In the east are the wines of Corbieres and La Clape, in the centre are
Aude is an agricultural area dominated by vineyards. In the east are the wines of Corbieres and La Clape, in the centre are

 The people of Aude expressed
The people of Aude expressed
, accessed 25 June 2009, Ac-montpellier.fr, accessed 16 August 2010 Between 2000 and 2007, primary school enrollment steadily increased from 28,331 students to 30,491 students At secondary level, the department had 31 colleges and 17 public and private high schools for about 23,000 students in 2006. Education in Aude now includes teaching in the
Natural regions
 The countryside in this department falls into several
The countryside in this department falls into several natural region
A natural region (landscape unit) is a basic geographic unit. Usually, it is a region which is distinguished by its common natural features of geography, geology, and climate.
From the ecology, ecological point of view, the naturally occurring fl ...
s:
* 1 – Lauragais
The Lauragais () is an area of the south-west of France that is south-east of Toulouse.
The Lauragais, a former county in the south-west of France, takes its name from the town of Laurac and has a large area. It covers both sides of the Canal ...
* 2 – Montagne Noire
The Montagne Noire ( oc, Montanha Negra, known as the 'Black Mountain' in English) is a mountain range in central southern France. It is located at the southwestern end of the Massif Central at the juncture of the Tarn, Hérault and Aude departm ...
* 3 – Cabardès
* 4 – Carcassonais
* 5 – Razès
Razès (; oc, Rasés; ca, Rasès) is a historical area in southwestern France, in today's Aude ''département''.
Several communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of ...
* 6 – Quercorb
* 7 – Pays de Sault
Pays de Sault is a small natural region of France in the department of Aude. Geographically, this region is located between 990 and 1310 metres of elevation from the heart of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, ...
* 8 – Minervois
Minervois is an AOC in the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region, in the departments of the Aude and of the Herault. Historically, the region's capital has been the village of Minerve.
AOC regulations require the wine to be blended (at least 2 variet ...
* 9 – Corbières
* 10 – Narbonnais
Landscapes
 Each natural region of the Aude has its own particular landscape. In the east, lagoons or coastal lakes separate land and sea. These were formed by accumulations of sediments carried down by the rivers Aude, Orb and
Each natural region of the Aude has its own particular landscape. In the east, lagoons or coastal lakes separate land and sea. These were formed by accumulations of sediments carried down by the rivers Aude, Orb and Hérault
Hérault (; oc, Erau, ) is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France. Named after the Hérault River, its prefecture is Montpellier. It had a population of 1,175,623 in 2019.Halophile
The halophiles, named after the Greek word for "salt-loving", are extremophiles that thrive in high salt concentrations. While most halophiles are classified into the domain Archaea, there are also bacterial halophiles and some eukaryotic species, ...
(i.e., salt-loving) plants grow there. The area is also noted for the pink flamingo
Flamingos or flamingoes are a type of Wader, wading bird in the Family (biology), family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas ...
and the white stilt
Stilt is a common name for several species of birds in the family Recurvirostridae, which also includes those known as avocets. They are found in brackish or saline wetlands in warm or hot climates.
They have extremely long legs, hence the grou ...
.
Inland to the west, shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees ...
and scrub dominate the landscape of the drylands of the Aude and the Corbières Massif
The Corbières Massif (Catalan: ''Corberes''; french: Massif des Corbières, ) is a mountain range in the Pre-Pyrenees. It is the only true foothill of the Pyrenees on their northern side.
Geography
The Corbières are a mountain region in the ...
. This landscape is the result of forest clearance, maintained by the raising of livestock. The flora is varied and characterized by many species of orchids
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowering ...
. The Sault countryside is dominated by beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
groves and fir plantations up to the mountains. These forests are known for their mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans.
The standard for the name "mushroom" is t ...
s, and have a rich flora and fauna, including the Pyrenean lily, the euproctis moth and horsetail
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of ferns, which reproduce by spores rather than seeds.
''Equisetum'' is a "living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass Eq ...
of the woods.
To the north and west, the Black Mountain country is made up of forests of oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
and beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
. The Lauragais is a wooded landscape where grain farming has shaped the hills. There are bodies of water like the Lac de la Ganguise. Finally, the high valley of the Aude, otherwise called the Razès, consists of a riparian forest
A riparian forest or riparian woodland is a forested or wooded area of land adjacent to a body of water such as a river, stream, pond, lake, marshland, estuary, canal, sink or reservoir.
Etymology
The term riparian comes from the Latin word '' ...
made of beech, alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few sp ...
, poplar or ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
. It includes some peatlands
A mire, peatland, or quagmire is a wetland area dominated by living peat-forming plants. Mires arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to water-logging and subsequent anoxia. All types ...
that are very rare in southern France.
Geology
 The landscapes of Aude can be explained by its geology. In the south, there are
The landscapes of Aude can be explained by its geology. In the south, there are sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles t ...
folded during the formation of the Pyrenees. To the north and centre of Aude, the sedimentary rocks are less folded. At the extreme east, near the Mediterranean, the rocks are carved by normal collapse faults which are due to the opening of the Golfe du Lion.
In the north, the Black Mountain and Minervois consist of schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes o ...
and marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the ...
, forming the southern edge of the Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.
Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,00 ...
. These ancient rocks are over 300 million years old and were deformed by the formation of the Hercynian
The Variscan or Hercynian orogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.
Nomenclature
The name ''Variscan'', come ...
chain. The Montagne d'Alaric ( Alaric's Mountain) is an antiform fold in the shape of a vault and made of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
.
Climate
 Aude is under the influence of a Mediterranean climate.
The autumn is characterized by violent and short storms.
The summer is often hot and dry, which is favorable to the culture of the vine and the olive-trees. Yet, the department has several contrasts in climate:
In the north, the Montagne Noire and, in the south, the Pays de Sault, have a mountainous climate with temperatures sometimes very low in winter.
In the west, the climate is under Aquitaine influence with heavier precipitation, while in the east the climate is purely Mediterranean.
In the centre, in the Limouxin, Carcassonnais and Razès areas, the climate is known as intermediary with significant exposure to winds.
The winds are often present in Aude. It is one of the windiest French departments, with 300 to 350 days of wind per year. This phenomenon is due mostly to the variations in relief north and south which create a kind of corridor.
In the north-west blows the
Aude is under the influence of a Mediterranean climate.
The autumn is characterized by violent and short storms.
The summer is often hot and dry, which is favorable to the culture of the vine and the olive-trees. Yet, the department has several contrasts in climate:
In the north, the Montagne Noire and, in the south, the Pays de Sault, have a mountainous climate with temperatures sometimes very low in winter.
In the west, the climate is under Aquitaine influence with heavier precipitation, while in the east the climate is purely Mediterranean.
In the centre, in the Limouxin, Carcassonnais and Razès areas, the climate is known as intermediary with significant exposure to winds.
The winds are often present in Aude. It is one of the windiest French departments, with 300 to 350 days of wind per year. This phenomenon is due mostly to the variations in relief north and south which create a kind of corridor.
In the north-west blows the Cers
CERS (Centre for Relationship Marketing and Service Management) is a research and competence centre at the Hanken School of Economics in Helsinki, Finland. The centre operates in conjunction with the department of marketing, and specialises in re ...
, called Tramontane in Provence, which is a ground wind. It is a dry, somewhat violent wind and cold in winter. In the south-east blows the Autan, locally called the Marin
Marin (French) or Marín (Spanish "sailor") may refer to:
People
* Marin (name), including a list of persons with the given name or surname
* MaRin, in-game name of professional South Korean ''League of Legends'' player Jang Gyeong-hwan (born 19 ...
, which is hot and wet and comes from the sea.
These regular winds made it possible to install an industrial park of wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
s, as in the area of Avignonet-Lauragais.
Hydrography
The drainage system of Aude is dominated by its river of the same name. The river rises at the Roc d'Aude and passes through theMatemale
Matemale (; ca, Matamala) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.
Geography
Matemale is located in the canton of Les Pyrénées catalanes and in the arrondissement of Prades.
Population
See also
*Commun ...
and Puyvalador
Puyvalador (; ca, Puigbalador) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.
Geography
Puyvalador is in the canton of Les Pyrénées catalanes and in the arrondissement of Prades.
Population
See also
*Commu ...
dams on the Capcir
Capcir (; ) is a historical Catalan comarca of Northern Catalonia, now part of the French department of Pyrénées-Orientales. The capital of the comarca was Formiguera, and it borders the historical comarques of Conflent and Alta Cerdanya. Ca ...
plateau at 1500m, then crosses the department from south to north across Axat, Limoux, and Quillan following the upper valley of the Aude. At Carcassonne, the river changes direction toward the Mediterranean Sea to the east, where it empties near Fleury.
Principal towns
The most populous commune isNarbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
; the prefecture Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
is the second-most populous. As of 2019, there are 5 communes with more than 10,000 inhabitants:
History
Prehistory
 Hammers and worked tools have been found on the hill of Grazailles at Carcassonne, dating from between 690,000 and 300,000 years ago. Most interesting is the skull of
Hammers and worked tools have been found on the hill of Grazailles at Carcassonne, dating from between 690,000 and 300,000 years ago. Most interesting is the skull of Tautavel Man
Tautavel Man refers to the archaic humans which—from approximately 550,000 to 400,000 years ago—inhabited the Caune de l’Arago, a limestone cave in Tautavel, France. They are generally grouped as part of a long and highly variable lineag ...
, discovered in 1971 by Henry de Lumley
Henry de Lumley (born 1934 in Marseille) is a French archeologist, geologist and prehistorian. He is director of the Institute of Human Paleontology in Paris, and Professor Emeritus at the Museum of Natural History in Paris. He is also a corres ...
in the commune of Tautavel
Tautavel (; ca, Talteüll) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.
It is home to The European Centre for Prehistoric Research (CERP). Tautavel Man, an early hominid and some of the oldest human remains in Euro ...
in the Pyrénées-Orientales
Pyrénées-Orientales (; ca, Pirineus Orientals ; oc, Pirenèus Orientals ; ), also known as Northern Catalonia, is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France, adjacent to the northern Spanish frontier and the Mediterranean Sea. ...
department. It is the oldest-known skull in Europe. It dates from about 450,000 years BC. It is likely that Tautavel Man lived in all of this region.
Roman Era
TheRomans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, led by the consul-general Domitius Ahenobarbus, first occupied the oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (plural ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretchi ...
of Montlaurès in 118 BC, a few kilometres to the north of Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
. This became the provincial capital and a very active mercantile port. The position was strategically important since it stood at the crossroads of two Roman roads
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
, the Via Aquitania
The ''Via Aquitania'' was a Roman road created in 118 BC in the Roman province of Gaul. It started at Narbonne, where it connected to the ''Via Domitia''. It then went toward the Atlantic Ocean, via Toulouse and Bordeaux, covering approximately .
...
and the Via Domitia
The Via Domitia was the first Roman road built in Gaul, to link Italy and Hispania through Gallia Narbonensis, across what is now Southern France. The route that the Romans regularised and paved was ancient when they set out to survey it, and tr ...
, as well as by the sea near the mouth of the river Aude
Aude (; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it "Ca ...
. Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
became Latin in 30 BC with the creation of numerous grain farms. For almost two centuries, Aude enjoyed peace and strong economic growth.
Barbarian invasions
TheVisigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
invaded the area in 435 AD at a time when Flavius Aetius
Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 454) was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433454). He managed pol ...
, the Roman senator, was busy suppressing the Bagaudes, who were brigands or lawless types in central and northern Gaul. Roman authority was restored until 462. In 507, the victory of Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single kin ...
at the battle of Vouillé
The Battle of Vouillé (from Latin ''Campus Vogladensis'') was fought in the northern marches of Visigothic territory, at Vouillé, near Poitiers (Gaul), in the spring of 507 between the Franks, commanded by Clovis, and the Visigoths, command ...
permitted him to conquer Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Par ...
and Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January ...
. However, he could not recover the Aude territory, which, thanks to the help of the King of the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the larg ...
, remained in the hands of the Visigoths. His troops defeated Clovis's son in 508. The region was part of Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
, so called because it was composed of seven bishoprics
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
that the Visigoth kings had established there: Elne
Elne (; ca, Elna ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.
It lies in the former province of Roussillon, of which it was the first capital, being later replaced by Perpignan. Its inhabitants are still called ...
, Agde
Agde (; ) is a commune in the Hérault department in Southern France. It is the Mediterranean port of the Canal du Midi.
Location
Agde is located on the Hérault river, from the Mediterranean Sea, and from Paris. The Canal du Midi con ...
, Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
, Lodève
Lodève (; oc, Lodeva ) is a commune in the département of Hérault, in the Occitanie region in southern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department. The derivation of the city's name is from Gaulish ''Luteva'', composed of lut-, swamp, ...
, Béziers
Béziers (; oc, Besièrs) is a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Hérault Departments of France, department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region of Southern France. Every August Béziers hos ...
, Maguelonne, and Nîmes
Nîmes ( , ; oc, Nimes ; Latin: ''Nemausus'') is the prefecture of the Gard department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. Located between the Mediterranean Sea and Cévennes, the commune of Nîmes has an estimated population of 148,5 ...
. Septimania covered the Aude but also the whole region of Languedoc-Roussillon.
Middle Ages
In 817, Louis le Débonnaire detached Carcassès andRazès
Razès (; oc, Rasés; ca, Rasès) is a historical area in southwestern France, in today's Aude ''département''.
Several communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of ...
from Septimania to reunite them with the marquisate of Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Par ...
and the kingdom of Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January ...
. The first Count of Carcassonne was Oliba from the family of the Counts of Barcelona
The Count of Barcelona ( ca, Comte de Barcelona, es, Conde de Barcelona, french: Comte de Barcelone, ) was the ruler of the County of Barcelona and also, by extension and according with the Usages of Barcelona, usages and Catalan constitutions, of ...
. He established himself in 819. Razès was another county that was formed by an archbishop of Narbonne who had been chased from his town by the Saracens
file:Erhard Reuwich Sarazenen 1486.png, upright 1.5, Late 15th-century Germany in the Middle Ages, German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek language, Greek and Latin writings, to refer ...
. He had transferred his episcopal seat to Razès and had procured the honours of the feudal title for the area. Narbonne formed a third county. Thus, in the ninth century, the département of Aude consisted of three counties: Carcassonne, Razès and Narbonne. In 880, the County of Razès was united by marriage to that of Carcassonne, never to be separated.
Catharism in Aude
In the 13th century, the region saw the development ofCatharism
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Follow ...
: a dualistic Christian sect with similarities to Gnosticism
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people ...
. This religion was very quickly judged as heretical by the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Faced with its growing strength in the counties of Carcassonne and Toulouse, Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 J ...
in 1209 declared a crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
against the Albigensians
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Foll ...
. The barons of the north united to form an army under the command of Simon de Montfort
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester ( – 4 August 1265), later sometimes referred to as Simon V de Montfort to distinguish him from his namesake relatives, was a nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the ...
. Whereas the count of Toulouse Raymond VI received absolution, the Count of Carcassonne confronted the army alone. The city of Carcassonne became the refuge of numerous Cathars.
The Protestant crisis and economic expansion of the department
In 1561, religious troubles again arose atCarcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
in the form of a Protestant crisis. Duke Henri I de Montmorency
Henri I de Montmorency (15 June 1534 in Chantilly, Oise – 2 April 1614), Marshal of France, and Constable of France, seigneur of Damville, served as Governor of Languedoc from 1563 to 1614.
Biography
Born on 15 June 1534, Henri was the son ...
, the Governor of the Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (; , ; oc, Lengadòc ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately ...
, joined the Reformed
Reform is beneficial change
Reform may also refer to:
Media
* ''Reform'' (album), a 2011 album by Jane Zhang
* Reform (band), a Swedish jazz fusion group
* ''Reform'' (magazine), a Christian magazine
*''Reforme'' ("Reforms"), initial name of the ...
side in 1574. On the Catholic side, the Duke Anne de Joyeuse
Anne de Batarnay de Joyeuse, Baron d'Arques, Vicomte then Duke of Joyeuse (1560 – 20 October 1587) was a royal favourite and active participant in the French Wars of Religion.
An intimate friend of Henry III of France, he was keeper of the kin ...
became head of the Catholic League. In September 1632, Henri II de Montmorency
Henri II de Montmorency (1595 – 30 October 1632) was a French nobleman and military commander.
Biography
Born at Chantilly, Oise, Henri was the son of Henri I de Montmorency and Louise de Budos. He was the godson of Henri IV of France, Henri ...
fought against the royal troops at the Battle of Castelnaudary
Castelnaudary (; oc, Castèlnòu d'Arri) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region of southern France. It is located in the former province of the Lauragais and famous for cassoulet of which it claims to be the world capital ...
and was defeated. He was condemned to death and executed at Toulouse.
The creation of the department
The present department is one of the original 83 departments created by theConstituent Assembly
A constituent assembly (also known as a constitutional convention, constitutional congress, or constitutional assembly) is a body assembled for the purpose of drafting or revising a constitution. Members of a constituent assembly may be elected b ...
during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
on 4 March 1790. It was created from part of the former province of Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (; , ; oc, Lengadòc ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately ...
.
Administrative divisions were amended by the Act of 28 Pluviôse
Pluviôse (; also ''Pluviose'') was the fifth month in the French Republican Calendar. The month was named after the Latin word ''pluviosus'', which means ''rainy''.
Pluviôse was the second month of the winter quarter (''mois d'hiver''), star ...
of Year 8, which created four arrondissements (reduced to three by Premier Raymond Poincaré
Raymond Nicolas Landry Poincaré (, ; 20 August 1860 – 15 October 1934) was a French statesman who served as President of France from 1913 to 1920, and three times as Prime Minister of France.
Trained in law, Poincaré was elected deputy in 1 ...
in 1926) and reduced the number of cantons from 45 to 31.
The 20th century
The Aude enjoyed strong wine production whilst at the same time the grain farmers ofLauragais
The Lauragais () is an area of the south-west of France that is south-east of Toulouse.
The Lauragais, a former county in the south-west of France, takes its name from the town of Laurac and has a large area. It covers both sides of the Canal ...
faced great difficulties. However, the department suffered from overproduction and a slump in sales of wine. In 1907 the crisis produced a winemakers' revolt. This led to the establishment of many Winemaking cooperative
A winemaking cooperative is an agricultural cooperative which is involved in winemaking, and which in a similar way to other cooperatives is owned by its members. The members in a winemaking cooperative are usually vineyard owners, who deliver gr ...
s in Aude from 1909.
Heraldry
Economy
Overview
Agriculture and fisheries
 Aude is an agricultural area dominated by vineyards. In the east are the wines of Corbieres and La Clape, in the centre are
Aude is an agricultural area dominated by vineyards. In the east are the wines of Corbieres and La Clape, in the centre are Minervois
Minervois is an AOC in the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region, in the departments of the Aude and of the Herault. Historically, the region's capital has been the village of Minerve.
AOC regulations require the wine to be blended (at least 2 variet ...
and Côtes de Malepère, and in the south Limoux wine
Limoux wine is produced around the city of Limoux in Languedoc in southwestern France. Limoux wine is produced under four ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designations: Blanquette de Limoux, Blanquette méthode ancestrale, Crémant de ...
. In Lauragais
The Lauragais () is an area of the south-west of France that is south-east of Toulouse.
The Lauragais, a former county in the south-west of France, takes its name from the town of Laurac and has a large area. It covers both sides of the Canal ...
grain is predominant, whereas in the Montagne Noire
The Montagne Noire ( oc, Montanha Negra, known as the 'Black Mountain' in English) is a mountain range in central southern France. It is located at the southwestern end of the Massif Central at the juncture of the Tarn, Hérault and Aude departm ...
only sheep farming
Sheep farming or sheep husbandry is the raising and breeding of domestic sheep. It is a branch of animal husbandry. Sheep are raised principally for their meat (lamb and mutton), milk (sheep's milk), and fiber (wool). They also yield sheepskin an ...
is possible. More recently there has been an increase in cultivation of olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
trees for their oil.
Port-la-Nouvelle
Port-la-Nouvelle (; oc, La Novèla) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions a ...
is the biggest fishing port in the department followed by Gruissan. In 1996 there were 127 vessels in Aude including 75 in Port-la-Nouvelle and 52 in Gruissan. These vessels were as follows:
* Fishing trawler
A fishing trawler is a commercial fishing vessel designed to operate Trawling, fishing trawls. Trawling is a method of fishing that involves actively dragging or pulling a trawl through the water behind one or more trawlers. Trawls are fishing ...
s: 19 in Port-la-Nouvelle
* tuna boats: 2 in Port-la-Nouvelle
* small craft: 106 including 54 in Port-La-Nouvelle and 52 in Gruissan
Small craft are recreational boats such as dinghies with one man fishing a lake or motor launches with up to three people fishing in coastal waters. About 85% of small craft are intended for lake fishing as in the Étang de Thau
The Étang de Thau (; oc, Estanh de Taur) or Bassin de Thau is the largest of a string of lagoons (''étangs'') that stretch along the French coast from the Rhône river to the foothills of the Pyrenees and the border to Spain in the Languedoc- ...
.
Viticulture
Viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
is the main economic activity of the department due to its rich and varied soils. It was the Greeks who established vineyards in Aude and the Romans who determined the rights of exploitation. The first vines were planted in Minervois
Minervois is an AOC in the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region, in the departments of the Aude and of the Herault. Historically, the region's capital has been the village of Minerve.
AOC regulations require the wine to be blended (at least 2 variet ...
in the 1st century.
But the grapes and wines were not consumer products or self-sufficient for many years. Cereals and olive trees dominated the fertile plains of Aude. It was at the beginning of the 19th century that the wine industry developed in Aude and the rest of Languedoc-Roussillon. Wine then became a consumer product. Higher output was needed and vineyards replaced cereals on the plains. There was an initial period of prosperity to 1850 before phylloxera
Grape phylloxera is an insect pest of commercial grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America. Grape phylloxera (''Daktulosphaira vitifoliae'' (Fitch 1855) belong to the family Phylloxeridae, within the order Hemiptera, bugs ...
appeared towards 1870. At the end of the 19th century, Aude experienced a second period of prosperity but there was a wine crisis triggered in 1901 because of over-production, fraud, and slumping sales. It reached its peak during the winemakers revolt in 1907. The wine growers regrouped themselves into winemaking cooperative
A winemaking cooperative is an agricultural cooperative which is involved in winemaking, and which in a similar way to other cooperatives is owned by its members. The members in a winemaking cooperative are usually vineyard owners, who deliver gr ...
s to prevent fraud and deception. In 1919 then in 1935, a law of AOC
Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (; ; born October 13, 1989), also known by her initials AOC, is an American politician and activist. She has served as the U.S. representative for New York's 14th congressional district since 2019, as a member of ...
was adopted under the leadership of Jean Capus. The INAO was set up as a body to control the application of the new laws.
After the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the vineyards were revitalized and the region saw a mass of viticulture. The wine was produced in large quantities and satisfied a very demanding population. The product was supplied in large quantities at very low prices. In 1970 the market evolved replacing demand for quantity with demand for quality and causing a second wine crisis. Many events, negotiations, and attacks paralyzed the region and the economy. Emile Pouytès and the CRS Joel le Gof died at Montredon-des-Corbières
Montredon-des-Corbières is a commune in the Aude department in southern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territori ...
on 4 March 1976 during this crisis. A large change in the Aude viticulture business started with a reorganization of the profession and the wine-growing region. Quality had to become the mark of wine from Aude.
The rich and varied soil of Aude together with abundant sunshine abounds enables Aude to produce quality wines. Many wines emanate from the department, ranging in quality from table wine
Table wine (rarely abbreviated TW) is a wine term with two different meanings: a style of wine and a quality level within wine classification.
In the United States, the term primarily designates a wine style: an ordinary wine which is not fortif ...
s to AOCs, passing through vins de pays and VDQS.
There are seven main areas of production:
* Cabardès AOC (1),
* Corbières AOC
Corbières is an Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) for wine in the Languedoc-Roussillon, France, and it is this region's largest AOC, responsible for 46 per cent of the region's AOC wine production in 2005. Red wine dominates the producti ...
(6),
* Côtes Malepère AOC near Carcassonne (2),
* Coteaux du Languedoc
Languedoc-Roussillon wine, including the ''vin de pays'' labeled ''Vin de Pays d'Oc'', is produced in southern France. While "Languedoc" can refer to a specific historic region of France and Northern Catalonia, usage since the 20th century (esp ...
on the plain of Narbonnais (5),
* Fitou AOC
Fitou ( oc, Fiton) is a large French wine appellation in Languedoc-Roussillon, France. The dominant vine variety is Carignan which has to constitute 40% of any blend. Grenache, Lladoner Pelut (the 'hairy' Grenache), Mourvèdre and Syrah are al ...
(7),
* Limoux wine
Limoux wine is produced around the city of Limoux in Languedoc in southwestern France. Limoux wine is produced under four ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designations: Blanquette de Limoux, Blanquette méthode ancestrale, Crémant de ...
(3),
* Minervois AOC
Minervois is an AOC in the Languedoc-Roussillon wine region, in the departments of the Aude and of the Herault. Historically, the region's capital has been the village of Minerve.
AOC regulations require the wine to be blended (at least 2 variet ...
(4).
These areas produce different wines such as ''Blanquette de Limoux
Limoux wine is produced around the city of Limoux in Languedoc in southwestern France. Limoux wine is produced under four ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designations: Blanquette de Limoux, Blanquette méthode ancestrale, Crémant de ...
'', Chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern French wine, France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from English wine, Englan ...
and sparkling wine from Limoux, ''La Clape'', Corbières, Fitou
Fitou (; oc, Fitor) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France.
Population
Wine
Fitou has a red wine appellation; see Fitou AOC
Fitou ( oc, Fiton) is a large French wine appellation in Languedoc-Roussillon, France. The domi ...
, and Cabardès.
Industry and energy
Industrial activity is strong in the upper valley of the Aude. It has been especially prominent aroundLimoux
Limoux (; oc, Limós ) is a commune and subprefecture in the Aude department, a part of the ancient Languedoc province and the present-day Occitanie region in southern France. Its vineyards are famous for being first to produce sparkling wi ...
since the late nineteenth century; and the Lafarge
La Farge, LaFarge or Lafarge can refer to:
People
* Antoinette LaFarge (1966–), American artist and writer
* Christopher Grant LaFarge (1862–1938), American architect and partner in the firm Heins & LaFarge
* Christopher Grant La Farge ( ...
brick plant there is still booming.
Since the 1970s, however, the Aude has seen a rapid decline in its traditional industries such as shoe and hat making. More recent activity is mostly centred around Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
, particularly dock
A dock (from Dutch language, Dutch ''dok'') is the area of water between or next to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore) or such structures themselves. The ex ...
facilities and oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
depots in Port-la-Nouvelle
Port-la-Nouvelle (; oc, La Novèla) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions a ...
.
From 1889, the high valley of Aude became increasingly important in generating hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
power. Aude was the first department in France to transmit such power, from its plants at Alet-les-Bains
Alet-les-Bains (; ''Alet'' in Occitan, formerly spelt ''Aleth'') is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region in southern France.
Geography
Alet-les-Bains is located near a hot springs in Aude in the south of France. The vill ...
and Quillan
Quillan (; Languedocien: ''Quilhan'') is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. On 1 January 2016, the former commune of Brenac was merged into Quillan.Axat
Axat (; ''Atsat'' in Occitan) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region of southern France.
The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Axatois'' or ''Axatoises''.
Geography
Axat is located in Cathar country at the doors of ...
-Saint-Georges supplied the cities of Carcassonne and Narbonne at 20 kilovolts
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defi ...
.
Today Aude is the leading department in France for the number of wind turbines installed. There are 113 in operation. They produce some 91 megawatts
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt ...
, which is the domestic electricity consumption of about 100,000 people. With the proliferation of these machines, the prefecture is seeking to establish with stakeholders a charter of good conduct for wind turbines.
Crafts
Crafts
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale prod ...
are very well represented in Aude with 14.6% of the population involved. Some 5,400 businesses operating in 250 craft professions achieved in the late 1990s an annual turnover of 3 billion francs (400 million Euros).
Demography
The inhabitants of Aude are known as 'Audois'. The 1990 census confirmed a growth in population since the 1960s with about 700 people more per year. This growth is explained by the return of pensioners aged over 60 years to their place of origin and to immigration from the Mediterranean basin. At the last census, the population of Aude represented 0.5% of the French population and 14.1% of the population of Languedoc-Roussillon. It is predominantly rural with a density of 48 inhabitants per km2, which is slightly less than half the national average. The two main cities, Carcassonne and Narbonne, are medium-sized cities comprising only one third of the inhabitants of the department. In 2017, the department had 370,260 inhabitants.Transport
Two major roads cross the Aude. From west to east theA61 autoroute
The A61 autoroute is a French motorway forming part of the ''Autoroute de Deux Mers''. It is long.
It connects Narbonne (and a junction on A9) and Toulouse, where it becomes the A62 towards Bordeaux. It also has junctions with the A64 towards ...
(Autoroute des Deux Mers) connects Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
and Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Par ...
via Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
. From north to south, following the Mediterranean coast, the A9 autoroute
The A9 autoroute (La ''Languedocienne''/''La Catalane'') is a motorway in southern France.
The road forms part of the European route E15, as does the A9 road (Scotland). The road runs between Orange and Perthus, in the Pyrénées-Orientales ...
links Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the Departments of ...
with Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
.
The rail network follows the same route as the road network. It is a low speed system, but a project is under way to build a fast line to Spain as part of the Trans-European Rail network The Trans-European Rail network is made up of the Trans-European high-speed rail network as well as the Trans-European conventional rail network. The rail network is one of a number of the European Union's Trans-European transport networks (TEN-T). ...
.
Finally, Aude is crossed by the Canal du Midi
The Canal du Midi (; ) is a long canal in Southern France (french: le Midi). Originally named the ''Canal royal en Languedoc'' (Royal Canal in Languedoc) and renamed by French revolutionaries to ''Canal du Midi'' in 1789, the canal is considere ...
which is a major waterway that allows tourists to pass from the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea. It comes into the west of Aude at Seuil de Naurouze
The Seuil de Naurouze, or Col de Naurouze, is the highest point (190 m above sea level) of the Canal du Midi in southern France. It is the watershed point identified by Pierre-Paul Riquet when he designed and built the canal. Water falling on ...
then joins the Mediterranean at Sète
Sète (; oc, Seta, ), also historically spelt ''Cette'' (official until 1928) and ''Sette'', is a commune in the Hérault department, in the region of Occitania, southern France. Its inhabitants are called ''Sétois'' (male) and ''Sétoises' ...
.
Politics
royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governme ...
opinions until the end of the Bourbon Restoration Bourbon Restoration may refer to:
France under the House of Bourbon:
* Bourbon Restoration in France (1814, after the French revolution and Napoleonic era, until 1830; interrupted by the Hundred Days in 1815)
Spain under the Spanish Bourbons:
* ...
. In 1830 republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
ideas began to develop and made this department a bastion of the left
Left may refer to:
Music
* ''Left'' (Hope of the States album), 2006
* ''Left'' (Monkey House album), 2016
* "Left", a song by Nickelback from the album ''Curb'', 1996
Direction
* Left (direction), the relative direction opposite of right
* L ...
. This growth is symbolized by two men, Armand Barbès
Armand Barbès (18 September 1809 – 26 June 1870) was a French Republican revolutionary and an opponent of the July monarchy (1830–1848). He is remembered as a man whose life centers on two days:
* ''12 May 1839'', the day of the uprising ...
and Theophile Marcou. Armand Barbès is a symbol of the struggle for a social democratic
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote soci ...
Republic.
It was in Aude that François Mitterrand
François Marie Adrien Maurice Mitterrand (26 October 19168 January 1996) was President of France, serving under that position from 1981 to 1995, the longest time in office in the history of France. As First Secretary of the Socialist Party, he ...
had his highest score in the 1981 presidential election with just over 63% of the vote.
Only affluent coastal areas surrounding Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
and the department's prefecture, Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
give consideration to the right.
The President of the Departmental Council is Hélène Sandragné of the Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of th ...
.
Current National Assembly Representatives
Education
Aude department in 2008 had 364 primary schools (schools of the first degree) serving 30,771 students. Academic inspection of the Aude, accessed 25 June 2009, Ac-montpellier.fr, accessed 16 August 2010 Between 2000 and 2007, primary school enrollment steadily increased from 28,331 students to 30,491 students At secondary level, the department had 31 colleges and 17 public and private high schools for about 23,000 students in 2006. Education in Aude now includes teaching in the
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
language.
Culture
Festivals and traditions
TheCarnival of Limoux
The Carnival of Limoux (french: Carnaval de Limoux) is an annual festival held in Limoux, Languedoc-Roussillon, France. It takes place for three months on the weekends between January and Mardi Gras and is conducted in Occitan, the area's trad ...
is an Aude festival which takes place over a period of ten weeks or more. This is one of the longest carnivals in the world. It takes place in the town of Limoux
Limoux (; oc, Limós ) is a commune and subprefecture in the Aude department, a part of the ancient Languedoc province and the present-day Occitanie region in southern France. Its vineyards are famous for being first to produce sparkling wi ...
on the Place de la République every weekend from mid-January to the end of March. It is characterized by bands in Pierrot
Pierrot ( , , ) is a stock character of pantomime and '' commedia dell'arte'', whose origins are in the late seventeenth-century Italian troupe of players performing in Paris and known as the Comédie-Italienne. The name is a diminutive of ''P ...
costumes (known as ''les fécos'') accompanied by musicians. In the region around Limoux a major celebration of gastronomy known as ''Toques et Clochers'' (literally, "Tall Hats & Steeples') organized by the winegrowers from Sieur d'Arques' takes place over the weekend of Palm Sunday
Palm Sunday is a Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter. The feast commemorates Christ's triumphal entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in each of the four canonical Gospels. Palm Sunday marks the first day of Holy ...
. It permits the sale of a large quantity of wine in order to enhance local patronage.
Sport
Aude is the land ofrugby league
Rugby league football, commonly known as just rugby league and sometimes football, footy, rugby or league, is a full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular field measuring 68 metres (75 yards) wide and 112 ...
(rugby à XIII) with the teams of Limoux, Carcassonne and Lézignan among the elite. Puig Aubert
Puig Aubert (born Robert Aubert Puig, 24 March 1925 – 3 June 1994), is often considered the best French rugby league footballer of all-time. Over a 16-year professional career he would play for Carcassonne, XIII Catalan, Celtic de Paris and Ca ...
(1925–1994) was a famous rugby league player who played with AS Carcassonne. There are numerous amateur rugby league clubs dotted all over the area.
Rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In its m ...
(rugby à XV) is also played in Aude. It appeared early in the twentieth century and the US-Quillan club dominated in the late 1920s. Jean Bourrel won the title in 1929 against Lézignan. After the Second World War, the Carcassonne team took the lead. Recently, however, rugby union in the Aude has faced an uphill struggle in a sport that has become both globalized and more professional. The Narbonne team (known as Racing Club Narbonne-Mediterranean) has nevertheless managed to develop in the Pro D2 championship.
Every 15 August, in Quillan
Quillan (; Languedocien: ''Quilhan'') is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. On 1 January 2016, the former commune of Brenac was merged into Quillan.Tour de l'Aude is one of the most important female cycling events in the calendar. It generally takes place in May.
 ''Fréginat'', a traditional type of fricasee of pork from Corbières, can be found throughout the department. It is made from pork and pig's liver with a local variety of white beans (Lingots de Castelnaudary) flavoured with garigue herbs. On the coast, eel stew (borrida d’anguilles) is a dish of choice. Finally, the
''Fréginat'', a traditional type of fricasee of pork from Corbières, can be found throughout the department. It is made from pork and pig's liver with a local variety of white beans (Lingots de Castelnaudary) flavoured with garigue herbs. On the coast, eel stew (borrida d’anguilles) is a dish of choice. Finally, the
Ràdio Lenga
(Occitan) at 95.5 FM.
 Aude is a tourist department with a rich cultural heritage and varied natural sites. Since the 1990s, the Aude has developed the attractiveness of its territory by focusing on the development of the publicity surrounding
Aude is a tourist department with a rich cultural heritage and varied natural sites. Since the 1990s, the Aude has developed the attractiveness of its territory by focusing on the development of the publicity surrounding
 The department has many castles that have been developed by the General Council of the Aude to stimulate tourism. The fortresses are often located on rocky peaks, such as the castles of Quéribus and Lastours, which gave them a strategic position. The city of Carcassonne was the logistical hub of the country at the time of conflict with the Kingdom of
The department has many castles that have been developed by the General Council of the Aude to stimulate tourism. The fortresses are often located on rocky peaks, such as the castles of Quéribus and Lastours, which gave them a strategic position. The city of Carcassonne was the logistical hub of the country at the time of conflict with the Kingdom of  Many abbeys exist throughout the department of Aude. The best known are
Many abbeys exist throughout the department of Aude. The best known are
File:Narbonne Cathedrale Saint Just et Saint Pasteur.jpg,
Logements et résidences principales en 2017
figures as at 1 January 2017 Communes with more than 10% Secondary Residences (2017)
Michel Gayraud
''Narbonne ancient origins at the end of the 3rd century''. Paris, De Boccard, Revue archéologique de Narbonnaise, Supplément 8, 1981, 591 p. * ''History of Narbonne'', Jacques Michaud and André Cabanis, Toulouse, Privat, 2004, 330 p. * ''Aude, Cathar Country'', collective work, Guides Gallimard, 2004 * Bilotte M. et Al., ''Géology of the Department of Aude'', Société d'études scientifiques de l'Aude, 1989 * ''I write to you of Carcassonne'', Claude Marti and Patrice Cartier, Du Mont, 2011
Departmental council website
Prefecture website
Aude official tourism website
*
Department of Aude Accounts for the communes and groupings
- Individual Data Principle budget only, Consolidated data in principle budget and annexes {{Authority control 1790 establishments in France Departments of Occitania (administrative region) States and territories established in 1790 Massif Central
Gastronomy
cassoulet
Cassoulet (, also , ; ; from Occitan and cognates with Spanish: ''cazoleta'' and Catalan: ''cassolet'') is a rich, slow-cooked stew containing meat (typically pork sausages, goose, duck and sometimes mutton), pork skin () and white beans (), ...
of Castelnaudary, made from white beans and sausage, is a typical dish of the Lauragais
The Lauragais () is an area of the south-west of France that is south-east of Toulouse.
The Lauragais, a former county in the south-west of France, takes its name from the town of Laurac and has a large area. It covers both sides of the Canal ...
.
Other specialties exist such as oysters
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not al ...
from Gruissan and Leucate
Leucate (; oc, Leucata) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. It lies between the Mediterranean Sea and the lagoon Étang de Leucate.
Geography
Leucate is on the Mediterranean coast of France. It is part of the eastern C ...
. Olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: f ...
is also very widespread in the Aude and is a speciality of Bize-Minervois
Bize-Minervois is a commune in the Aude department in southern France.
Geography
Located on the edge of the Haut-Minervois in the Cesse valley, Bize lies between the fertile sedimentary plain of Narbonne and the causses of the Minervois and ...
. ''Cartagena'' is a liqueur
A liqueur (; ; ) is an alcoholic drink composed of spirits (often rectified spirit) and additional flavorings such as sugar, fruits, herbs, and spices. Often served with or after dessert, they are typically heavily sweetened and un-aged beyond ...
marketed by some manufacturers. Finally, the Blanquette de Limoux
Limoux wine is produced around the city of Limoux in Languedoc in southwestern France. Limoux wine is produced under four ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designations: Blanquette de Limoux, Blanquette méthode ancestrale, Crémant de ...
is a sparkling white wine popular in the department whose origin dates back to the sixteenth century.
Occitan
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
is spoken in the Aude in its Languedoc variant. The language emerged during the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
used in the south of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.
In Aude, Occitan was rarely used in writing before the 11th century. However, several poets and troubadours
A troubadour (, ; oc, trobador ) was a composer and performer of Old Occitan lyric poetry during the High Middle Ages (1100–1350). Since the word ''troubadour'' is etymologically masculine, a female troubadour is usually called a ''trobairit ...
such as Raimon de Miraval
Raimon de Miraval(h) (c. 1135/1160 – c. 1220) was a troubadour (fl. 1180–1220) and, according to his '' vida'', "a poor knight from Carcassonne who owned less than a quarter of the castle of Miraval."Graham-Leigh, 28. Favoured by Raym ...
used language based on courtly love in the 12th and 13th centuries. In the 14th and 15th centuries, Occitan was used to draw up local administrative documents. In the 16th century, Occitan was used less than royal French, whose use was made compulsory by the edict of Villers-Cotterêts
Villers-Cotterêts () is a commune in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France, France. It is notable as the signing-place in 1539 of the ''Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts'' discontinuing the use of Latin in official French documents, and as the ...
in 1539. However, it survived very well among the people until the 19th century, when public schools were established with teaching solely in French.
In the 1970s and the 1980s, new demands were made for the dignity of the language and for its teaching. Occitan speech reached a wider audience and singers like Claudi Marti Claudi is a masculine given name which may refer to:
* Claudi Arimany (born 1955), Spanish/Catalan flautist
* Claudi L. H. Bockting (born 1969), Dutch clinical psychologist and professor
* Claudi Lorenzale (1814–1889), Spanish painter
* Claudi Ma ...
, ''Mans de Brèish'', and ''La Sauze'' promoted its use.
It was in Aude that the first Occitan radio station broadcast in the region of Languedoc-RoussillonRàdio Lenga
(Occitan) at 95.5 FM.
Tourism
 Aude is a tourist department with a rich cultural heritage and varied natural sites. Since the 1990s, the Aude has developed the attractiveness of its territory by focusing on the development of the publicity surrounding
Aude is a tourist department with a rich cultural heritage and varied natural sites. Since the 1990s, the Aude has developed the attractiveness of its territory by focusing on the development of the publicity surrounding Catharism
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Follow ...
. The Aude has been named ''Cathar Country'' by the General Council to mark the authentic and mysterious nature of the department, especially with its many Cathar castles
Cathar castles (in French ''Châteaux cathares'') are a group of medieval castles located in the Languedoc region. Some had a Cathar connection in that they offered refuge to dispossessed Cathars in the thirteenth century. Many of these sites were ...
.
Tourism is also promoted through a stock of hotel rooms in all categories of 313,500 beds available year-round. Aude estimates the number of tourist overnight stays to be 17.11 million in 2010 with a turnover of 842 million euros providing 5,800 full-time jobs and 9,500 seasonal jobs.
In a very limited section of the Orbiel Valley the department has had occasional pollution problems because of its abandoned gold mines (with mercury and arsenic).
Overview of tourist areas
Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
has been restored to much of its medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
appearance. Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
is a tourist destination due to its Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
ruins.
Other towns and villages worth visiting include Limoux
Limoux (; oc, Limós ) is a commune and subprefecture in the Aude department, a part of the ancient Languedoc province and the present-day Occitanie region in southern France. Its vineyards are famous for being first to produce sparkling wi ...
, Quillan
Quillan (; Languedocien: ''Quilhan'') is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. On 1 January 2016, the former commune of Brenac was merged into Quillan.Lézignan-Corbières
Lézignan-Corbières (; ) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region in southern France. Situated in the Corbières wine region not far from Narbonne, it has a Vine and Wine Museum (''Musée de la Vigne et du Vin'').
Geograph ...
, Lagrasse
Lagrasse (; oc, La Grassa) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. In 2016, it had a population of 560. Lagrasse is part of the Les Plus Beaux Villages de France ("The most beautiful villages of France" ...
, Sigean
Sigean (; oc, Sijan) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. It formerly laid on ''Route nationale'' 9 between Narbonne and Perpignan, but RN 9 (downgraded to ''route départementale'' 6009) now bypasses the town of Sigean and ...
and Leucate
Leucate (; oc, Leucata) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. It lies between the Mediterranean Sea and the lagoon Étang de Leucate.
Geography
Leucate is on the Mediterranean coast of France. It is part of the eastern C ...
.
Limoux
Limoux (; oc, Limós ) is a commune and subprefecture in the Aude department, a part of the ancient Languedoc province and the present-day Occitanie region in southern France. Its vineyards are famous for being first to produce sparkling wi ...
lies in the upper Aude valley, 24 km south of Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
. It is known for its local wine, Blanquette, a sparkling white wine which is said to have been the forerunner of Champagne. Limoux hosts an extensive and varied market each Friday.
Quillan
Quillan (; Languedocien: ''Quilhan'') is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. On 1 January 2016, the former commune of Brenac was merged into Quillan.Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
.
Lézignan-Corbières
Lézignan-Corbières (; ) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region in southern France. Situated in the Corbières wine region not far from Narbonne, it has a Vine and Wine Museum (''Musée de la Vigne et du Vin'').
Geograph ...
lies on the main road between Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
and Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
. It is called the capital of the Corbières and has a Wednesday morning market.
Lagrasse
Lagrasse (; oc, La Grassa) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. In 2016, it had a population of 560. Lagrasse is part of the Les Plus Beaux Villages de France ("The most beautiful villages of France" ...
stands on the River Orbieu and has an 8th-century abbey, two very attractive bridges and an unchanged and very compact and delightful medieval stone village centre.
Sigean
Sigean (; oc, Sijan) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. It formerly laid on ''Route nationale'' 9 between Narbonne and Perpignan, but RN 9 (downgraded to ''route départementale'' 6009) now bypasses the town of Sigean and ...
, 18 km south of Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
, lies between the A9 autoroute
The A9 autoroute (La ''Languedocienne''/''La Catalane'') is a motorway in southern France.
The road forms part of the European route E15, as does the A9 road (Scotland). The road runs between Orange and Perthus, in the Pyrénées-Orientales ...
and the coast and has an African Reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US vi ...
.
Leucate
Leucate (; oc, Leucata) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. It lies between the Mediterranean Sea and the lagoon Étang de Leucate.
Geography
Leucate is on the Mediterranean coast of France. It is part of the eastern C ...
is a hilltop village, about 30 km south of Narbonne, which has spread down to the coast where Leucate Plage is a popular beach resort.
The Corbières Massif
The Corbières Massif (Catalan: ''Corberes''; french: Massif des Corbières, ) is a mountain range in the Pre-Pyrenees. It is the only true foothill of the Pyrenees on their northern side.
Geography
The Corbières are a mountain region in the ...
forms the central part of the department. This is an area of dissected plateaux and escarpments which form an effective barrier to direct road communication. It is a very attractive and sometimes wild area of steep hills, hidden valleys, woodland and vines, and contains some of the most memorable Cathar
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Follow ...
sites including Quéribus, Peyrepertuse
Peyrepertuse (Languedocien dialect, Languedocien: ''Castèl de Pèirapertusa'') is a ruined fortress and one of the so-called Cathar castles located high in the French Pyrénées in the commune in France, commune of Duilhac-sous-Peyrepertuse, in th ...
and Villerouge-Termenès.
The Lauragais
The Lauragais () is an area of the south-west of France that is south-east of Toulouse.
The Lauragais, a former county in the south-west of France, takes its name from the town of Laurac and has a large area. It covers both sides of the Canal ...
, that spreads on both sides of the administrative border between Aude and Haute-Garonne
Haute-Garonne (; oc, Nauta Garona, ; en, Upper Garonne) is a department in the Occitanie region of Southwestern France. Named after the river Garonne, which flows through the department. Its prefecture and main city is Toulouse, the country's ...
, is a historic and cultural area known since the Middle Ages for its abundant agricultural productions. With Castelnaudary
Castelnaudary (; oc, Castèlnòu d'Arri) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region of southern France. It is located in the former province of the Lauragais and famous for cassoulet of which it claims to be the world capital ...
as a central and major city, this region is also famous for the role it played during the Albigensian Crusade
The Albigensian Crusade or the Cathar Crusade (; 1209–1229) was a military and ideological campaign initiated by Pope Innocent III to eliminate Catharism in Languedoc, southern France. The Crusade was prosecuted primarily by the French crown ...
and for its local heritage: Canal du Midi
The Canal du Midi (; ) is a long canal in Southern France (french: le Midi). Originally named the ''Canal royal en Languedoc'' (Royal Canal in Languedoc) and renamed by French revolutionaries to ''Canal du Midi'' in 1789, the canal is considere ...
and its springs, abbeys and churches, castles, disk-shaped steles, dovecotes, windmills, bastides, etc.
Wine production is extensive across Aude, and local chateaux and domaines provide free tastings as well as sales of wine and other local produce. With the decline of some local wine production, local government policy is now to attract more tourists to the area, and to assist with this the Corbières area is now labelled on maps and road signs as Cathar
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Follow ...
country.
Architectural heritage
The Aude has about fifteenbastides
Bastides are fortified new towns built in medieval Languedoc, Gascony, Aquitaine, England and Wales during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, although some authorities count Mont-de-Marsan and Montauban, which was founded in 1144, as the fir ...
which were built after the Treaty of Meaux
The Treaty of Paris, also known as Treaty of Meaux, was signed on 12 April 1229 between Raymond VII of Toulouse and Louis IX of France in Meaux near Paris. Louis was still a minor, and it was his mother Blanche of Castile, as regent, who was ins ...
in 1229 when the region was attached to the Capetian
The Capetian dynasty (; french: Capétiens), also known as the House of France, is a dynasty of Franks, Frankish origin, and a branch of the Robertians. It is among the largest and oldest dynasty, royal houses in Europe and the world, and cons ...
crown of France. The bastide is a type of town based on a grid created in one building project on a greenfield site. The purpose of such construction was to weaken the local lords and attract people to new economic centres. These bastides came into competition with fortified villages based on ecclesiastical or seigneurial power. Chalabre
Chalabre (; Languedocien: ''Eissalabra'') is a commune in the Aude department in southern France.
The capital of the Quercorb region, it is a relatively unspoilt ''bastide'' with shady streets and quiet alleyways.
The local industry died ou ...
, Camps-sur-l'Agly
Camps-sur-l'Agly (Languedocien: ''Camps d’Aglin'') is a commune in the Aude department in southern France.
Population
See also
* Pic de Bugarach
The Pic de Bugarach () or Pech de Bugarach () (''puèg de Bugarag'' in Occitan, i.e. "Peak ...
and the Bastide Saint-Louis in Carcassonne are examples of bastides in the Aude.
 The department has many castles that have been developed by the General Council of the Aude to stimulate tourism. The fortresses are often located on rocky peaks, such as the castles of Quéribus and Lastours, which gave them a strategic position. The city of Carcassonne was the logistical hub of the country at the time of conflict with the Kingdom of
The department has many castles that have been developed by the General Council of the Aude to stimulate tourism. The fortresses are often located on rocky peaks, such as the castles of Quéribus and Lastours, which gave them a strategic position. The city of Carcassonne was the logistical hub of the country at the time of conflict with the Kingdom of Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
.
 Many abbeys exist throughout the department of Aude. The best known are
Many abbeys exist throughout the department of Aude. The best known are Fontfroide Abbey
Fontfroide Abbey (french: Abbaye Sainte-Marie de Fontfroide; la, Fons frigidus) is a former Cistercian monastery in France, situated 15 kilometers south-west of Narbonne near to the Spanish border.
It was founded in 1093 by Aimery I, Visc ...
, Lagrasse Abbey
The Abbey of St. Mary of Lagrasse (French: ''Abbaye Sainte-Marie de Lagrasse'' or ''Abbaye Sainte-Marie-d'Orbieu'') is a Romanesque abbey in Lagrasse, southern France, whose origins date to the 7th century. It is located in Languedoc, near the C ...
, the abbey of Sainte-Marie Villelongue-d'Aude, and the Abbey of Saint-Hilaire.
Narbonne Cathedral
Narbonne Cathedral (''Cathédrale Saint-Just-et-Saint-Pasteur de Narbonne'') is a Roman Catholic church located in the town of Narbonne, France. The cathedral is a national monument and dedicated to Saints Justus and Pastor.
It was the seat of t ...
is a remarkable Gothic cathedral and remains unfinished. It is a symbol of the French presence in Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (; , ; oc, Lengadòc ) is a former province of France.
Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately ...
in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
.
Caving
Aude has many caves suitable for speleological exploration. The ''Pays de Sault'' consists of one of the largest limestone areas of the Pyrenees. This geology lends itself to the formation of cavities and there are many 'barrencs' (the local name forPit cave
A pit cave, shaft cave or vertical cave—or often simply called a pit (in the US) and pothole or pot (in the UK); jama in South Slavic languages scientific and colloquial vocabulary (borrowed since early research in the Western Balkan Dinaric ...
s). This plateau is home to a cave, the TM71, which is a superb cavity classified as a natural reserve since 1987. This is unique in France.
Other natural cavities of the Aude contain concretions
A concretion is a hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. Concretions are often ovoid or spherical in shape, although irregular ...
like the Pit cave of Cabrespine
Cabrespine (; oc, Cabrespina) is a commune in the Aude department in southern France.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Aude department
The following is a list of the 433 communes of the Aude department of France.
The communes coope ...
, the Aguzou Grotto, and the grotto of Limousis. The latter contains the largest block of aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including prec ...
yet discovered. In the Massif of Corbières on the plateau of Lacamp there are cavities formed by detrital rocks (marls
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part ...
, clays
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
and puddingstone) carved by erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
.
Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
File:Castelnaudary bassin canal.jpg, Castelnaudary
Castelnaudary (; oc, Castèlnòu d'Arri) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region of southern France. It is located in the former province of the Lauragais and famous for cassoulet of which it claims to be the world capital ...
File:France-Lagrasse-Village et Pont Vieux - 2005-12-27.jpg, Lagrasse
Lagrasse (; oc, La Grassa) is a commune in the Aude department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. In 2016, it had a population of 560. Lagrasse is part of the Les Plus Beaux Villages de France ("The most beautiful villages of France" ...
Secondary housing
According to INSEE 25.4% of available housing in Aude consisted of secondary residences. The following table indicates the main communes in Aude (population more than 2,000) where second homes or occasional residences comprise more than 10% of total housing.figures as at 1 January 2017 Communes with more than 10% Secondary Residences (2017)
Arts
Cinema
The diversity of the landscape, its authenticity, and the uniqueness of its monuments have attracted many filmmakers. Thus, the city ofCarcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
has been the setting for many films. The excellent state of preservation of this city offers an outstanding setting for historical films. In 1908 filmmakers abandoned scenery on canvas and Louis Feuillade
Louis Feuillade (; 19 February 1873 – 25 February 1925) was a French filmmaker of the silent era. Between 1906 and 1924, he directed over 630 films. He is primarily known for the crime serials ''Fantômas'', ''Les Vampires'' and ''Judex'' ...
filmed in front of the city towers for the ''Return of the cross'', ''Engagement oath'', and ''Enchanted guitar''. In 1924 major films were produced such as '' Le Miracle des Loups'' by Raymond Bernard
Raymond Bernard (10 October 1891 – 12 December 1977) was a French film director and screenwriter whose career spanned more than 40 years. He is best remembered for several large-scale historical productions, including the silent films '' Le Mi ...
. In 1928 for the two thousandth anniversary of the city of Carcassonne, Jean Renoir
Jean Renoir (; 15 September 1894 – 12 February 1979) was a French film director, screenwriter, actor, producer and author. As a film director and actor, he made more than forty films from the silent film, silent era to the end of the 1960s. ...
made ''Le Tournoi dans la cité''. In 1965 the city of Carcassonne appeared in ''The Sucker
''The Sucker'' (french: link=no, Le Corniaud, ) is a French, Italian and Spanish comedy film by Gérard Oury starring Louis de Funès and Bourvil.
Plot
Leaving Paris for his summer vacation, the naïve Antoine Maréchal has his 2CV totally w ...
'' by Gerard Oury. In 1968 ''The Little Bather
''The Little Bather'' (french: Le Petit Baigneur), is a French comedy film from 1968, directed and written by Robert Dhéry, starring Louis de Funès and Andréa Parisy.
Cast
* Louis de Funès : Louis-Philippe Fourchaume
* Robert Dhéry : Andr ...
'' by Robert Dhéry
Robert Dhéry (27 April 1921 – 3 December 2004) (born Robert Léon Henri Fourrey or Robert Foullcy) was a French comedian, actor, director and screenwriter.
He was married to actor Colette Brosset, with whom he appeared onstage in ''La Plume de ...
(with Louis de Funès
Louis Germain David de Funès de Galarza (; 31 July 1914 – 27 January 1983) was a French actor and comedian. He is France's favourite actor, according to a series of polls conducted since the late 1960s, having played over 150 roles in fil ...
and Michel Galabru
Michel Louis Edmond Galabru (27 October 19224 January 2016) was a French actor.
Career
Galabru appeared in more than 250 films and worked with directors such as Bertrand Blier, Costa-Gavras, Luc Besson (for '' Subway''), and Jean-Luc Godard. ...
) shot at ''Cabanes de Fleury'' (at the mouth of the Aude).
More recently, the Count's castle in the city was the setting for '' The Visitors'' by Jean-Marie Poire
Jean-Marie is both a given name and a surname. Notable people with the name include:
* Jean-Marie Abgrall (born 1950), a French psychiatrist, criminologist, specialist in forensic medicine, cult expert, and graduate in criminal law
* Jean-Marie Ch ...
in 1972, while the Château de Puivert
The Château de Puivert ( Languedocien: ''Castèl de Puègverd'') is a so-called Cathar castle situated in the '' commune'' of Puivert, in the Aude ''département'' of France. The castle has been classified as a ''monument historique'' by the Fre ...
was used in ''La Passion Béatrice'' by Bertrand Tavernier
Bertrand Tavernier (25 April 1941 – 25 March 2021) was a French director, screenwriter, actor and producer.
Life and career
Tavernier was born in Lyon, France, the son of Geneviève (née Dumond) and René Tavernier, a publicist and writer, s ...
in 1987, and ''The Ninth Gate
''The Ninth Gate'' is a 1999 neo-noir horror thriller film directed, produced, and co-written by Roman Polanski. An international co-production between the United States, Portugal, France, and Spain, the film is loosely based upon Arturo Pére ...
'' by Roman Polanski
Raymond Roman Thierry Polański , group=lower-alpha, name=note_a (né Liebling; 18 August 1933) is a French-Polish film director, producer, screenwriter, and actor. He is the recipient of numerous accolades, including an Academy Award, two ...
in 1999. The Beach at Gruissan is present in Betty Blue
''Betty Blue'' (french: 37°2 le matin, lit=37.2°C in the morning) is a 1986 French erotic psychological drama film directed by Jean-Jacques Beineix, based on the 1985 novel ''37°2 le matin'' by Philippe Djian. The film stars Béatrice Dalle ...
by Jean-Jacques Beineix
Jean-Jacques Beineix (; 8 October 1946 – 13 January 2022) was a French film director best known for the films ''Diva'' and ''Betty Blue''. His work is regarded as a prime example of the '' cinéma du look'' film movement in France.
Early life ...
.
Painters
As for the cinema, it is the city of Carcassonne which attracts the greatest painters. Jacques Ourtal is the one who painted most of the city in trying to depict the city in different eras. Originally from Fontiers-Cabardès, the Aude painter ''Eugène Pech'' has created paintings of the city many times which are today scattered in various public and private collections. The four eras of the city can still be found in settings for "The City Hall". Another Aude artist, Marie-Louise Petiet, is known for her transcriptions of scenes of popular life such as ''La marchande d'oranges'' (The Orange Seller) or ''La jeune fille aux oies'' (The young girl and the geese). Several of her works are visible at the Petiet Museum in Limoux. ''Les blanchisseuses'' (The Laundresses) depicting a laundry lesson is particularly remarkable and well-known. Finally,Paul Sibra
Paul Sibra (10 September 1889 – 24 March 1951) was a French regionalist painter, painter of religious scenes, landscapes and portraits.
Paul Sibra is nicknamed “''le peintre du Lauragais''”, after his native region.
Biography
Paul Sibra ...
, an expert in landscape-painting, nicknamed "''le peintre du Lauragais''", produced thousands of paintings and drawings of scenes from or based on the rural life of the people of ''Lauragais'' in the 1940s.
Achilles Laugé (born 1861 in Arzens, died 1944 in Cailhau), misunderstood because of his pointillist technique, was able to show the dawning of spring especially with the broom
A broom (also known in some forms as a broomstick) is a cleaning tool consisting of usually stiff fibers (often made of materials such as plastic, hair, or corn husks) attached to, and roughly parallel to, a cylindrical handle, the broomstick. I ...
and almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree native to Iran and surrounding countries, including the Levant. The almond is also the name of the edible and widely cultivated seed of this tree. Within the genus ...
trees in bloom.
Another artist, Lina Bill (Louis Bonnot), born at Gruissan in 1855 and died in Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
in 1936, painted Provence and the Mediterranean (museums of Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of Franc ...
, Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
, and the Musée d'Orsay
The Musée d'Orsay ( , , ) ( en, Orsay Museum) is a museum in Paris, France, on the Left Bank of the Seine. It is housed in the former Gare d'Orsay, a Beaux-Arts railway station built between 1898 and 1900. The museum holds mainly French art ...
in Paris).
Notable people
*Publius Terentius Varro Atacinus Publius Terentius Varro Atacinus (; 82 – c. 35 BC) was a Roman poet, more polished in his style than the more famous and learned Varro Reatinus, his contemporary, and therefore more widely read by the Augustan writers.Charles Thomas Cruttwell'' ...
(82-37 BC), Roman epic poet
* Saint Prudent (3rd century), Archbishop of Narbonne and martyr
* Saint Sebastian
Saint Sebastian (in Latin: ''Sebastianus''; Narbo, Gallia Narbonensis, Roman Empire c. AD 255 – Rome, Italia, Roman Empire c. AD 288) was an early Christian saint and martyr. According to traditional belief, he was killed during the Dioclet ...
(3rd century AD), Christian martyr, according to legend from Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the ...
* Ermengarde de Narbonne (1127-1196), Vicountess of Narbonne
* Fabre d'Eglantine
Fabre or Fabré is a surname of Occitan French origin, and a given name. Notable people with the name include:
* André Fabre (born 1945), French thoroughbred horse racing trainer
* Cándido Fabré, Cuban musician, songwriter and singer
* Cath ...
(1750-1794), composer, actor, playwright, and politician, guillotined during the Terror
* Félix Barthe
Félix Barthe (28 July 1795 – 28 February 1863) was a French lawyer, Deputy, Minister of Public Education and then Minister of Justice. He was the first President of the Court of Accounts (1834–37, 1839–63) and became a Senator of the Second ...
(1795-1863), Minister of Education and Religious Affairs, Minister of Justice, and first president of the Court of Auditors
* Charles Cros
Charles Cros or Émile-Hortensius-Charles Cros (October 1, 1842 – August 9, 1888) was a French poet and inventor. He was born in Fabrezan, Aude.
Cros was a well-regarded poet and humorous writer. As an inventor, he was interested in the field ...
(1842-1888), poet and scientist, he originated the process of colour photography and the phonograph
* Marcelin Albert
Marcelin Albert (29 March 1851 – 21 December 1921) was a French cafe owner and winegrower considered the leader of the 1907 revolt of the Languedoc winegrowers.
Early years
Marcelin Albert was born on 29 March 1851 in Argeliers, Aude.
The v ...
(1851-1921), leader of the revolt of the wine growers in 1907
* Prosper Montagné
Prosper Montagné (; 14 November 1865 – 22 April 1948) was one of the most renowned French chefs of the Belle Époque and author of many books and articles on food, cooking, and gastronomy, notably Larousse Gastronomique (1938), an encyclopedic ...
(1865-1948), chef, author of numerous books on gastronomy
* Léon Blum
André Léon Blum (; 9 April 1872 – 30 March 1950) was a French socialist politician and three-time Prime Minister.
As a Jew, he was heavily influenced by the Dreyfus affair of the late 19th century. He was a disciple of French Socialist le ...
(1872–1950), politician, Member of Parliament for Narbonne who became Prime Minister in 1936
* Louis Barthas
Louis Barthas (; 14 July 1879 – 4 May 1952) was a French infantry corporal who served on the Western Front of World War I for nearly the entire duration of conflict, stationed on the front lines for a significant amount of time. He was ...
(1879-1952), cooper, author, and veteran of WWI
* Henri de Monfreid (1879-1974), adventurer and writer, author of numerous books including the Secrets of the Red Sea
* Loís Alibèrt
Adrien Louis Marie Alibert, known as Louis Alibert (''Loís Alibèrt'' in Occitan; 1884–1959) was a French linguist, born on October 12, 1884 in Bram in the Aude and died on April 16, 1959 in Montpellier. He specialized in Occitan and Langue ...
(1884-1959) Occitan linguist, notable author of a grammar and a dictionary based on classical standard Occitan
* Pierre Reverdy
Pierre Reverdy (; 13 September 1889 – 17 June 1960) was a French poet whose works were inspired by and subsequently proceeded to influence the provocative art movements of the day, Surrealism, Dadaism and Cubism. The loneliness and spiritual a ...
(1889-1960), writer, a precursor of surrealism
Surrealism is a cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists depicted unnerving, illogical scenes and developed techniques to allow the unconscious mind to express itself. Its aim was, according to l ...
* Joseph Delteil
Joseph Delteil (20 April 1894 – 16 April 1978) was a 20th-century French writer and poet.
Biography
Joseph Delteil was born in the farm of La Pradeille, from a woodcutter-charcoal father and a "buissonnière" mother. Joseph Delteil spent ...
(1894-1978) writer from Pieusse
* Joë Bousquet
Joë Bousquet (; 19 March 1897 – 28 September 1950) was a French poet.
Bousquet was born in Narbonne. Wounded on 27 May 1918 at Vailly near the Aisne battlelines at the end of the First World War, he was paralysed for the rest of his life, an ...
(1897-1950), poet and surrealist writer
* René Iché
René Iché (21 January 1897 – 23 December 1954) was a 20th-century French sculptor.
Life and work
René Iché was born in Sallèles-d'Aude, France. He fought in World War I, where he was injured and gassed. After the war, he earned a degre ...
(1897–1954), modern sculptor and French Résistance
The French Resistance (french: La Résistance) was a collection of organisations that fought the German occupation of France during World War II, Nazi occupation of France and the Collaborationism, collaborationist Vichy France, Vichy régim ...
fighter during WWII.
* Roger Peyrefitte
Roger is a given name, usually masculine, and a surname. The given name is derived from the Old French personal names ' and '. These names are of Germanic origin, derived from the elements ', ''χrōþi'' ("fame", "renown", "honour") and ', ' ( ...
(1907-2000) writer
* Charles Trenet
Louis Charles Augustin Georges Trenet (; 18 May 1913 – 19 February 2001) was a renowned French singer-songwriter who composed both the music and the lyrics to nearly a thousand songs over a career that lasted more than 60 years. These include ...
(1913–2001), singer and poet born at Narbonne, famous for the song La Mer
* Jean Cau (1925-1993), writer, columnist, journalist, born in Bram
Bram may refer to:
People
* Bram (given name)
* Bram (surname)
* Bram (wrestler) (born 1986), ring name of professional wrestler Thomas Raymond Latimer
* Bram Tchaikovsky (born 1950), stage name of British musician Peter Bramall
* Bram Stoker Iris ...
, he was secretary for Jean-Paul Sartre
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre (, ; ; 21 June 1905 – 15 April 1980) was one of the key figures in the philosophy of existentialism (and phenomenology), a French playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and litera ...
* Gérard Schivardi
Gérard Schivardi (born 17 April 1950) is a French politician. He contended in the French presidential election of 2007 under the colours of the Workers' Party (''Parti des Travailleurs'') of Trotskyist legacy. He came last in the first round of ...
(1950-), Mayor of Mailhac, candidate in the French Presidential election of 2007
* Olivia Ruiz
Olivia Blanc (born 1 January 1980), known as Olivia Ruiz, is a French pop singer of partial Spanish descent belonging to the nouvelle chanson genre.
(1980-), singer, born in Carcassonne
* Dimitri Szarzewski (1983-), Hooker on the French Rugby Union Team
* Camille Lacourt
Camille Lacourt (; born 22 April 1985) is a retired French competitive swimmer and backstroke specialist. He won the 50 metre backstroke at three consecutive world championships ( 2013 Barcelona, 2015 Kazan, and 2017 Budapest). He competed at t ...
(1985-), swimmer, born in Narbonne
* Spanghero Family, famous Rugby Union players, who began their careers at RC Narbonne
* Didier Codorniou
Didier Codorniou (born 13 February 1958 in Narbonne)Didier Codorniou player profile
ESPN ...
, former international rugby player
* ESPN ...
Amédée Domenech
Amédée Domenech (May 3, 1933, Narbonne – September 21, 2003 Brive-la-Gaillarde) was a French rugby union prop. He played for RC Vichy between 1954 and 1955. After one year he moved to CA Brive and helped the club to gain promotion to the f ...
, former international rugby player
See also
* County of Razès *Cantons of the Aude department
The following is a list of the 19 cantons of the Aude department, in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and t ...
* Communes of the Aude department
The following is a list of the 433 communes of the Aude department of France.
The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Arrondissements of the Aude department
The 3 arrondissements of the Aude department are:
# Arrondissement of Carcassonne, (prefecture of the Aude department: Carcassonne) with 186 communes. The population of the arrondissement was 159,539 in 2016.
# Arrondissement of Limoux, (subpr ...
* Diocese of Aude
The Diocese of Aude or, more fully, the Diocese of the Department of Aude is a former diocese of the Constitutional Church in France.
Created by the civil constitution of the clergy of 1790, it was suppressed following the Concordat of 1801. Its ...
References
Sources
* ''The Colours of Aude'', André Authier and Jean-Philippe Vidal, Pélican * ''Aude from prehistory to today'', Jacques Crémadeilis, Saint-Jean-d’Angély, 1989, 430 p. * ''Aude People: biographical dictionary'', Rémy Cazals and Daniel Fabre, Carcassonne, Association des Amis des Archives de l’Aude, Société d’études scientifiques de l’Aude, 1990, 347 p.Michel Gayraud
''Narbonne ancient origins at the end of the 3rd century''. Paris, De Boccard, Revue archéologique de Narbonnaise, Supplément 8, 1981, 591 p. * ''History of Narbonne'', Jacques Michaud and André Cabanis, Toulouse, Privat, 2004, 330 p. * ''Aude, Cathar Country'', collective work, Guides Gallimard, 2004 * Bilotte M. et Al., ''Géology of the Department of Aude'', Société d'études scientifiques de l'Aude, 1989 * ''I write to you of Carcassonne'', Claude Marti and Patrice Cartier, Du Mont, 2011
External links
Departmental council website
Prefecture website
Aude official tourism website
*
Department of Aude Accounts for the communes and groupings
- Individual Data Principle budget only, Consolidated data in principle budget and annexes {{Authority control 1790 establishments in France Departments of Occitania (administrative region) States and territories established in 1790 Massif Central