|
Elne
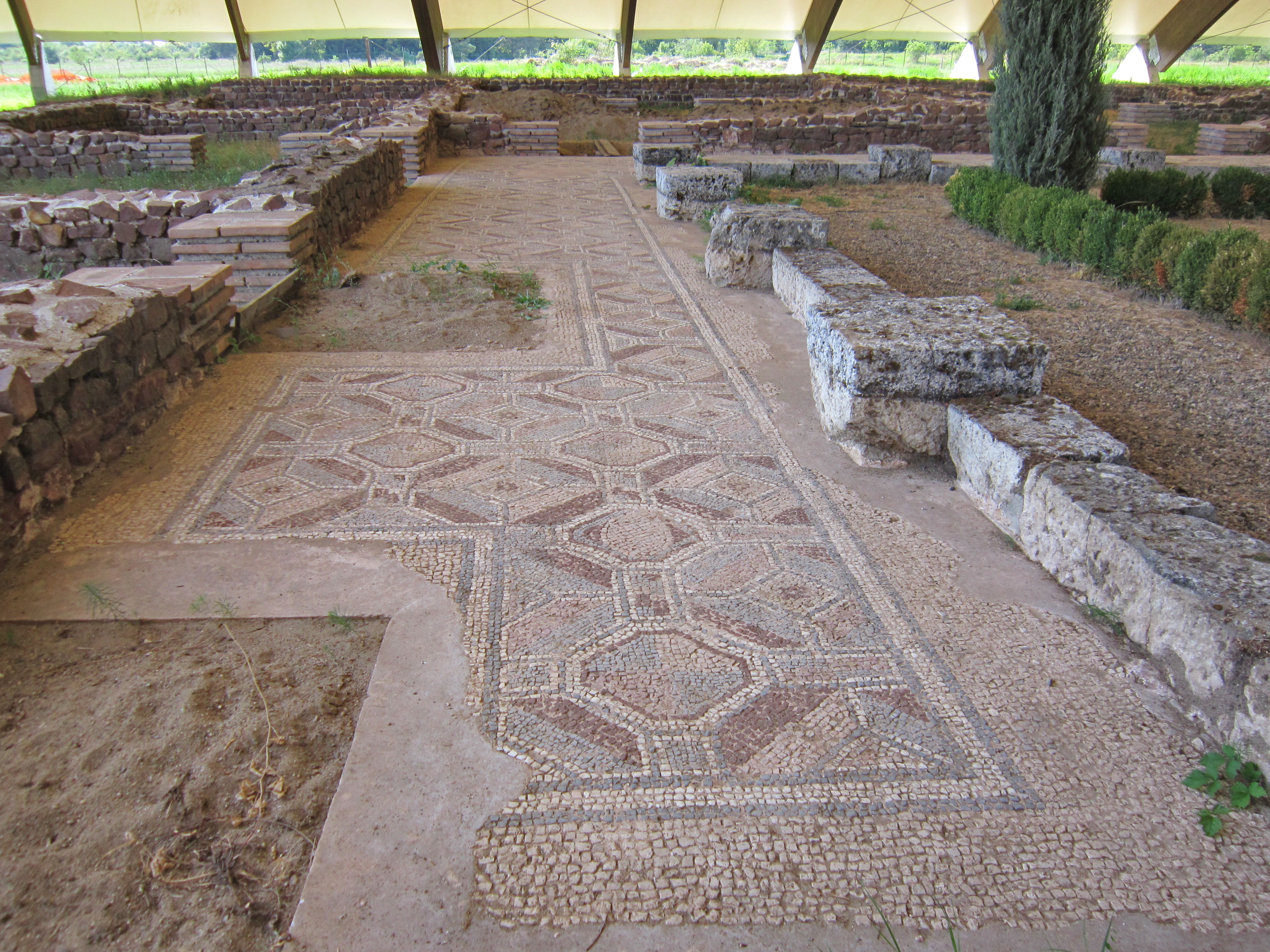
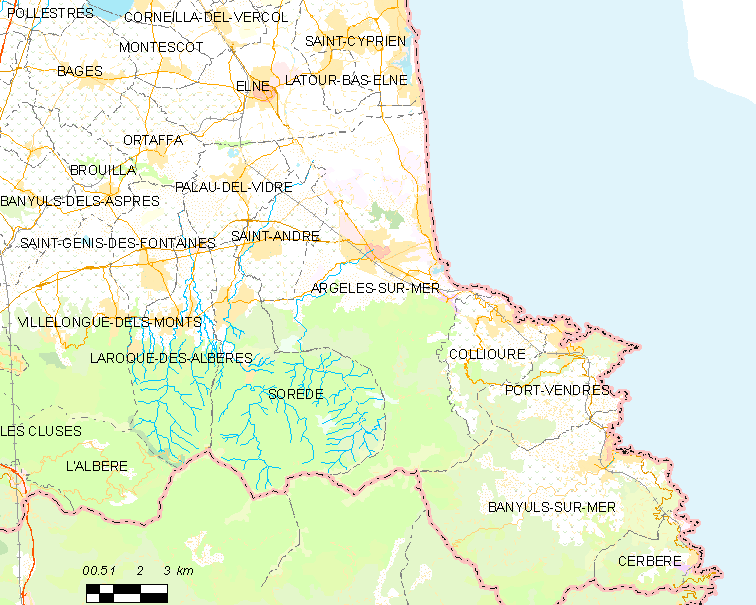
Elne (; ca, Elna ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France. It lies in the former province of Roussillon, of which it was the first capital, being later replaced by Perpignan. Its inhabitants are still called ''Illibériens'' in reference to the city's Iberian name, Illiberis, one that it shared with the Illiberis that became Granada, Spain. Geography Elne is located in the canton of La Plaine d'Illibéris and in the arrondissement of Perpignan. It is situated from the Mediterranean near the Tech River, in Pyrénées-Orientales, from Perpignan and from Argelès. History Elne, from the heights of its fortified site, dominates the narrow plain of Roussillon between the Pyrenees and the Mediterranean. Numerous archeological researches have shown that the surrounding countryside has been occupied since Neolithic times. Elne was an Iberian ''oppidum'' or fortified town. Elne is the oldest town in Roussillon and since it is situated on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of La Plaine D'Illibéris
The Canton of La Plaine d'Illibéris is a French canton of Pyrénées-Orientales department, in Occitanie. At the French canton reorganisation which came into effect in March 2015, the canton of La Plaine d'Illibéris was created including 5 communes from the canton of Elne and 2 from the canton of La Côte Radieuse. Composition *Alénya *Bages *Corneilla-del-Vercol *Elne *Latour-Bas-Elne *Montescot *Ortaffa *Théza *Villeneuve-de-la-Raho Villeneuve-de-la-Raho (; ca, Vilanova de Raó) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department, southern France. Geography Villeneuve-de-la-Raho is located in the canton of La Plaine d'Illibéris and in the arrondissement of Perpignan. Th ... References Plaine d'Illiberis {{PyrénéesOrientales-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constans
Flavius Julius Constans ( 323 – 350), sometimes called Constans I, was Roman emperor from 337 to 350. He held the imperial rank of ''caesar'' from 333, and was the youngest son of Constantine the Great. After his father's death, he was made ''augustus'' alongside his brothers in September 337. Constans was given the administration of the praetorian prefectures of Italy, Illyricum, and Africa. He defeated the Sarmatians in a campaign shortly afterwards. Quarrels over the sharing of power led to a civil war with his eldest brother and co-emperor Constantine II, who invaded Italy in 340 and was killed in battle with Constans's forces near Aquileia. Constans gained from him the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. Thereafter there were tensions with his remaining brother and co-''augustus'' Constantius II (), including over the exiled bishop Athanasius of Alexandria. In the following years he campaigned against the Franks, and in 343 he visited Roman Britain, the last legitimate emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. The region was also variously known as Gallia, Arbuna or Narbonensis. The territory of Septimania roughly corresponds with the modern French former administrative region of Languedoc-Roussillon that merged into the new administrative region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie. Septimania was conquered by the Muslims in the 8th century, when it was known as Arbuna and was made part of Al-Andalus. It passed briefly to the Emirate of Córdoba, which had been expanding from the south during the eighth century, before its subsequent conquest by the Franks, who by the end of the ninth century termed it Gothia or the Gothic March (''Marca Gothica''). Septimania became a March (territorial ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argelès-sur-Mer
Argelès-sur-Mer (, literally ''Argelès on Sea''; ca, Argelers de la Marenda or ; oc, Argelers de Mar), commonly known as Argelès, is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in the administrative region of Occitania, France. It is about 25 km from Perpignan. Geography Argelès-sur-Mer is located in the canton of La Côte Vermeille and in the arrondissement of Céret. Argelès-sur-Mer is on the Côte Vermeille at the foot of the Albères mountain range, close to the Spanish border. It has the longest beach in the Pyrenées Orientales. History During World War II, Argelès-sur-Mer was the location of a concentration camp, where up to 100,000 defeated Spanish Republicans were interned next to a windy beach in abysmal sanitary conditions by the French government after the defeat of the Spanish Republic. The refugees streamed to the camp from the winter of 1938/39 after the collapse of the Catalan front following the rebel offensive. Government and politics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tech River
The Tech (; ca, Tec ) is a river in southern France, very close to the French-Spanish border. It runs through a valley in the Pyrénées-Orientales, in the former Roussillon, and is long. Its source is the Parcigoule Valley, elevation , and it feeds the Mediterranean Sea. At Céret, the medieval ''Devil's bridge'', once the largest bridge arch in the world, spans the river in an arc of in length. Geography The Tech flows through 25 different towns, from its source to the sea: Prats-de-Mollo-la-Preste, Serralongue, Le Tech, Saint-Laurent-de-Cerdans, Montferrer, Corsavy, Arles-sur-Tech, Montbolo, Amélie-les-Bains-Palalda, Reynès, Céret, Saint-Jean-Pla-de-Corts, Maureillas-las-Illas, Le Boulou, Tresserre, Saint-Génis-des-Fontaines, Montesquieu-des-Albères, Banyuls-dels-Aspres, Villelongue-dels-Monts, Brouilla, Ortaffa, Palau-del-Vidre, Elne and Argelès-sur-Mer. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea between Saint-Cyprien and Argelès-sur-Mer, southeast of Perpignan Perpig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrénées-Orientales
Pyrénées-Orientales (; ca, Pirineus Orientals ; oc, Pirenèus Orientals ; ), also known as Northern Catalonia, is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France, adjacent to the northern Spanish frontier and the Mediterranean Sea. It also surrounds the tiny Spanish exclave of Llívia, and thus has two distinct borders with Spain. In 2019, it had a population of 479,979.Populations légales 2019: 66 Pyrénées-Orientales INSEE Some parts of the Pyrénées-Orientales (like the ) are part of the . It is na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Biclarum
John of Biclaro, Biclar, or Biclarum (''c.'' 540 – after 621), also ''Iohannes Biclarensis'', was a Visigoth chronicler. He was born in Lusitania, in the city of ''Scallabis'' (modern Santarém in Portugal). He was also bishop of Girona. Early life He was educated at Constantinople, where he devoted between 7-17 years to the study of Latin and Greek. Career Imprisonment When he returned to his homeland, he was imprisoned for several years in Barcelona. Isidore of Seville ascribes this to his refusal to join the Arian Church of the Visigothic realm in Hispania. Modern historians note that other contemporary Iberian sources, including John's own ''Chronicle'' do not attest a Visigothic campaign of persecution of Catholics until the revolt of Hermenegild divided Visigothic loyalties. The Visigothic persecutions of dissenters and Jews may be a more recent Catholic myth. Indeed, John wrote that, in 578, "Leovigild had peace to reside with his own people." A more likely re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Toledo
From the 5th century to the 7th century AD, about thirty synods, variously counted, were held at Toledo (''Concilia toletana'') in what would come to be part of Spain. The earliest, directed against Priscillianism, assembled in 400. The "third" synod of 589 marked the epoch-making conversion of King Reccared from Arianism to orthodox Chalcedonian Christianity. The " fourth", in 633, probably under the presidency of the noted Isidore of Seville, regulated many matters of discipline and decreed uniformity of liturgy throughout the kingdom. The British Celts of Galicia accepted the Latin rite and stringent measures were adopted against baptized Jews who had gone back to their former faith. The "twelfth" council in 681 assured to the archbishop of Toledo the primacy of Hispania (present Iberian Peninsula). As nearly one hundred early canons of Toledo found a place in the ''Decretum Gratiani'', they exerted an important influence on the development of ecclesiastical law. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Ancient Rome, Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in 753 BC through the reign of Augustus in Livy's own lifetime. He was on familiar terms with members of the Julio-Claudian dynasty and a friend of Augustus, whose young grandnephew, the future emperor Claudius, he exhorted to take up the writing of history. Life Livy was born in Patavium in northern Italy (Roman Empire), Italy, now modern Padua, probably in 59 BC. At the time of his birth, his home city of Patavium was the second wealthiest on the Italian peninsula, and the largest in the province of Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy). Cisalpine Gaul was merged in Roman Italy, Italy proper during his lifetime and its inhabitants were given Roman citizenship by Julius Caesar. In his works, Livy often expressed his deep affection an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toulouges
Toulouges (; ca, Toluges, ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France. Geography Toulouges is located between Thuir and Perpignan, in the canton of Perpignan-6 and in the arrondissement of Perpignan. The town covers an area of , with 669 inhabitants per km2. Toulouges borders the following municipalities: Perpignan, Canohès, Thuir, El Soler, and Baho. History Toulouges probably grew upon a Roman villa. It was first mentioned in 904 at the same time mentioning the church called Tulogias. Other names that are presumably Toulouges are Tologis (in a 937 document), Tulujes (1027), Tuluges (1030), Toluges (1119). Toulouges hosted an ecumenical council known as the Council of Elge-Toulouges in 1027. It aimed to promote peace among the feudal lords of France by declaring the Truce of God, attempting to limit the days of the week and times of year that the nobility could engage in violence. During the 14th and 15th centuries Toulouges grew rapidly. A w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I (emperor)
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, was a Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine became emperor. He was acclaimed by his army at Eboracum (York, England), and eventually emerged victorious in the civil wars against emperors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helena (empress)
Flavia Julia Helena ''Augusta'' (also known as Saint Helena and Helena of Constantinople, ; grc-gre, Ἑλένη, ''Helénē''; AD 246/248– c. 330) was an '' Augusta'' and Empress of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the lower classes''Anonymus Valesianus'1.2 "Origo Constantini Imperatoris". traditionally in the Greek city of Drepanon, Bithynia, in Asia Minor, which was renamed Helenopolis in her honor, though several locations have been proposed for her birthplace and origin. Helena ranks as an important figure in the history of Christianity. In her final years, she made a religious tour of Syria Palaestina and Jerusalem, during which ancient tradition claims that she discovered the True Cross. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodox Churches, and Anglican Communion revere her as a saint, and the Lutheran Church commemorates her. Early life Sources agree that Helena was a Greek, probably from Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |