Arthropods Of Rwanda on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed
 The
The  The most conspicuous specialization of segments is in the head. The four major groups of arthropods – Chelicerata ( sea spiders, horseshoe crabs and arachnids), Myriapoda (
The most conspicuous specialization of segments is in the head. The four major groups of arthropods – Chelicerata ( sea spiders, horseshoe crabs and arachnids), Myriapoda (
 Arthropod exoskeletons are made of
Arthropod exoskeletons are made of
 The exoskeleton cannot stretch and thus restricts growth. Arthropods, therefore, replace their exoskeletons by undergoing
The exoskeleton cannot stretch and thus restricts growth. Arthropods, therefore, replace their exoskeletons by undergoing
 Most arthropods have sophisticated visual systems that include one or more usually both of compound eyes and pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes"). In most cases ocelli are only capable of detecting the direction from which light is coming, using the shadow cast by the walls of the cup. However, the main eyes of spiders are pigment-cup ocelli that are capable of forming images, and those of jumping spiders can rotate to track prey.
Compound eyes consist of fifteen to several thousand independent
Most arthropods have sophisticated visual systems that include one or more usually both of compound eyes and pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes"). In most cases ocelli are only capable of detecting the direction from which light is coming, using the shadow cast by the walls of the cup. However, the main eyes of spiders are pigment-cup ocelli that are capable of forming images, and those of jumping spiders can rotate to track prey.
Compound eyes consist of fifteen to several thousand independent
 A few arthropods, such as
A few arthropods, such as  Most arthropods lay eggs, but scorpions are
Most arthropods lay eggs, but scorpions are
 It has been proposed that the
It has been proposed that the  The earliest fossil crustaceans date from about in the
The earliest fossil crustaceans date from about in the
 From 1952 to 1977, zoologist
From 1952 to 1977, zoologist
 Crustaceans such as
Crustaceans such as
Venomous Arthropods
chapter in United States Environmental Protection Agency and University of Florida/
Arthropods – Arthropoda
Insect Life Forms {{good article Extant Cambrian first appearances
appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body.
In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including anten ...
s. Arthropods form the phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature f ...
Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
made of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the l ...
. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species.
The haemocoel
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. Their nervous system is "ladder-like", with paired ventral nerve cords running through all segments and forming paired ganglia
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympatheti ...
in each segment. Their heads are formed by fusion of varying numbers of segments, and their brains are formed by fusion of the ganglia of these segments and encircle the esophagus. The respiratory and excretory systems of arthropods vary, depending as much on their environment as on the subphylum to which they belong.
Arthropods use combinations of compound eyes and pigment-pit ocelli for vision. In most species, the ocelli can only detect the direction from which light is coming, and the compound eyes are the main source of information, but the main eyes of spiders are ocelli that can form images and, in a few cases, can swivel to track prey. Arthropods also have a wide range of chemical and mechanical sensors, mostly based on modifications of the many bristles known as setae that project through their cuticles. Similarly, their reproduction and development are varied; all terrestrial species use internal fertilization, but this is sometimes by indirect transfer of the sperm via an appendage or the ground, rather than by direct injection. Aquatic species use either internal or external fertilization. Almost all arthropods lay eggs, but many species give birth to live young after the eggs have hatched inside the mother, and a few are genuinely viviparous, such as aphids. Arthropod hatchlings vary from miniature adults to grubs and caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
s that lack jointed limbs and eventually undergo a total metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
to produce the adult form. The level of maternal care for hatchlings varies from nonexistent to the prolonged care provided by social insects
Eusociality (from Greek εὖ ''eu'' "good" and social), the highest level of organization of sociality, is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping genera ...
.
The evolutionary ancestry of arthropods dates back to the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
period. The group is generally regarded as monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
, and many analyses support the placement of arthropods with cycloneuralia
Cycloneuralia is a clade of ecdysozoan animals including the Scalidophora (Kinorhynchans, Loriciferans, Priapulids) and the Nematoida (nematodes, Nematomorphs). It may be paraphyletic, or may be a sister group to Panarthropoda. Or perhaps Pana ...
ns (or their constituent clades) in a superphylum Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa () is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda (insects, chelicerata, crustaceans, and myriapods), Nematoda, and several smaller phyla. They were first defined by Aguinaldo ''et al.'' in 1997, based mainly on phylogenetic tr ...
. Overall, however, the basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
relationships of animals are not yet well resolved. Likewise, the relationships between various arthropod groups are still actively debated. Today, Arthropods contribute to the human food supply both directly as food, and more importantly, indirectly as pollinators of crops. Some species are known to spread severe disease to humans, livestock, and crops.
Etymology
The word ''arthropod'' comes from the Greek ''árthron'', " joint", and ''pous'' (gen.
The Book of Genesis (from Greek language, Greek ; Hebrew language, Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its i ...
''podos (ποδός)''), i.e. "foot" or " leg", which together mean "jointed leg". The designation "Arthropoda" was coined in 1848 by the German physiologist and zoologist Karl Theodor Ernst von Siebold
Prof Karl (Carl) Theodor Ernst von Siebold FRS(For) HFRSE (16 February 1804 – 7 April 1885) was a German physiologist and zoologist. He was responsible for the introduction of the taxa Arthropoda and Rhizopoda, and for defining the taxon Protoz ...
(1804–1885).
In common parlance, terrestrial arthropods are often called bugs. The term is also occasionally extended to colloquial names for freshwater or marine crustaceans (e.g. Balmain bug, Moreton Bay bug
''Thenus orientalis'' is a species of slipper lobster from the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans.
''T. orientalis'' is known by a number of common names. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization prefers the na ...
, mudbug
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the clade Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. In some locations, they are also known as crawfish, craydids, crawdaddies, crawdads, freshwater lobsters, mountain lobsters, rock lobsters, mu ...
) and used by physicians and bacteriologists for disease-causing germs (e.g. superbug
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. P ...
s), but entomologists reserve this term for a narrow category of " true bugs", insects of the order Hemiptera
Hemiptera (; ) is an order (biology), order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising over 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, Reduviidae, assassin bugs, Cimex, bed bugs, and shield bugs. ...
(which does not include ants, bees, beetles, butterflies or moths).
Description
Arthropods are invertebrates with segmented bodies and jointed limbs. The exoskeleton orcuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
s consists of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, a polymer of glucosamine. The cuticle of many crustaceans, beetle mites, and millipedes (except for bristly millipedes) is also biomineralized with calcium carbonate. Calcification of the endosternite, an internal structure used for muscle attachments, also occur in some opiliones.
Diversity
Estimates of the number of arthropod species vary between 1,170,000 and 5 to 10 million and account for over 80 percent of all known living animal species. The number of species remains difficult to determine. This is due to the census modeling assumptions projected onto other regions in order to scale up from counts at specific locations applied to the whole world. A study in 1992 estimated that there were 500,000 species of animals and plants in Costa Rica alone, of which 365,000 were arthropods. They are important members of marine, freshwater, land and air ecosystems, and are one of only two major animal groups that have adapted to life in dry environments; the other isamniote
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are disti ...
s, whose living members are reptiles, birds and mammals. Ruppert, Fox & Barnes (2004), pp. 518–522 One arthropod sub-group, insects, is the most species-rich member of all ecological guilds in land and freshwater environments. The lightest insects weigh less than 25 micrograms (millionths of a gram), while the heaviest weigh over . Some living malacostracans are much larger; for example, the legs of the Japanese spider crab may span up to , with the heaviest of all living arthropods being the American lobster
The American lobster (''Homarus americanus'') is a species of lobster found on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of North America, chiefly from Labrador to New Jersey. It is also known as Atlantic lobster, Canadian lobster, true lobster, norther ...
, topping out at over 20 kg (44 lbs).
Segmentation
 The
The embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
s of all arthropods are segmented, built from a series of repeated modules. The last common ancestor of living arthropods probably consisted of a series of undifferentiated segments, each with a pair of appendages that functioned as limbs. However, all known living and fossil arthropods have grouped segments into tagmata in which segments and their limbs are specialized in various ways.
The three-part appearance of many insect bodies and the two-part appearance of spiders is a result of this grouping; Gould (1990), pp. 102–106 in fact there are no external signs of segmentation in mites. Arthropods also have two body elements that are not part of this serially repeated pattern of segments, an ocular somite at the front, where the mouth and eyes originated, and a telson at the rear, behind the anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
.
Originally it seems that each appendage-bearing segment had two separate pairs of appendages: an upper, unsegmented exite and a lower, segmented endopod. These would later fuse into a single pair of biramous appendages united by a basal segment (protopod or basipod), with the upper branch acting as a gill while the lower branch was used for locomotion. The appendages of most crustaceans and some extinct taxa such as trilobites
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the At ...
have another segmented branch known as exopods, but whether these structures have a single origin remain controversial. In some segments of all known arthropods the appendages have been modified, for example to form gills, mouth-parts, antennae for collecting information, or claws for grasping; arthropods are "like Swiss Army knives, each equipped with a unique set of specialized tools." In many arthropods, appendages have vanished from some regions of the body; it is particularly common for abdominal appendages to have disappeared or be highly modified.
 The most conspicuous specialization of segments is in the head. The four major groups of arthropods – Chelicerata ( sea spiders, horseshoe crabs and arachnids), Myriapoda (
The most conspicuous specialization of segments is in the head. The four major groups of arthropods – Chelicerata ( sea spiders, horseshoe crabs and arachnids), Myriapoda (symphylan
Symphylans, also known as garden centipedes or pseudocentipedes, are soil-dwelling arthropods of the class Symphyla in the subphylum Myriapoda. Symphylans resemble centipedes, but are very small, non-venomous, and only distantly related to both ...
, pauropods, millipedes and centipede
Centipedes (from New Latin , "hundred", and Latin , " foot") are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda (Ancient Greek , ''kheilos'', lip, and New Latin suffix , "foot", describing the forcipules) of the subphylum Myriapoda, an ...
s), Crustacea
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
(oligostracan
Oligostraca is a superclass of crustaceans. It includes the seed shrimp, mystacocarids, branchiura
The family Argulidae, whose members are commonly known as carp lice or fish lice, are parasitic crustaceans in the class Ichthyostraca. It is ...
s, copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s, malacostracans, branchiopods, hexapods, etc.), and the extinct Trilobita – have heads formed of various combinations of segments, with appendages that are missing or specialized in different ways. Despite myriapods and hexapods both having similar head combinations, hexapods are deeply nested within crustacea while myriapods are not, so these traits are believed to have evolved separately. In addition, some extinct arthropods, such as '' Marrella'', belong to none of these groups, as their heads are formed by their own particular combinations of segments and specialized appendages. Summarised in Gould (1990), pp. 107–121.
Working out the evolutionary stages by which all these different combinations could have appeared is so difficult that it has long been known as "the arthropod head problem". In 1960, R. E. Snodgrass even hoped it would not be solved, as he found trying to work out solutions to be fun.
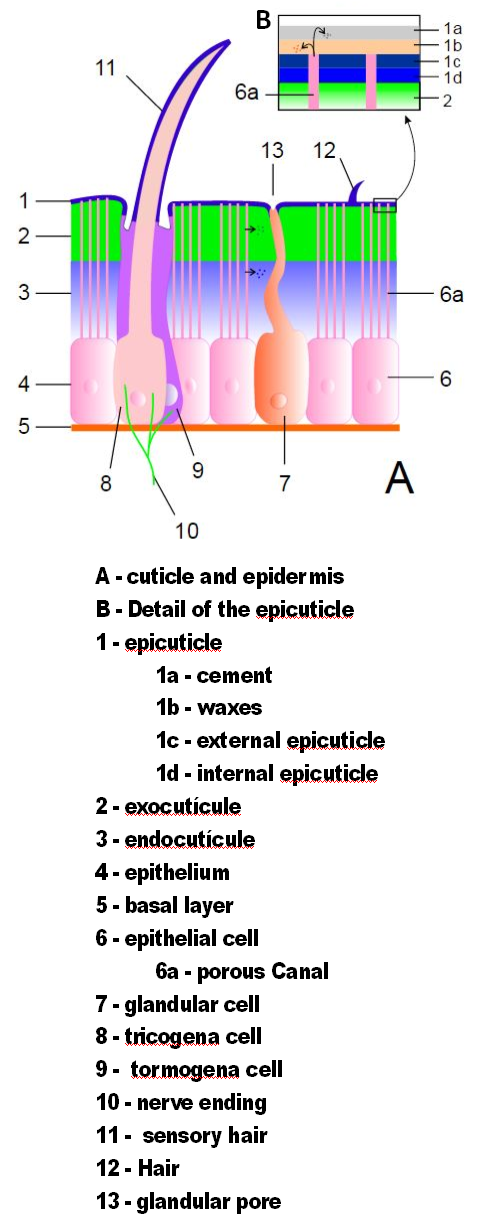
Exoskeleton
cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
, a non-cellular material secreted by the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
. Their cuticles vary in the details of their structure, but generally consist of three main layers: the epicuticle, a thin outer waxy coat that moisture-proofs the other layers and gives them some protection; the exocuticle, which consists of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
and chemically hardened proteins; and the endocuticle
The cuticle forms the major part of the integument of the Arthropoda. It includes most of the material of the exoskeleton of the insects, Crustacea, Arachnida, and Myriapoda.
Morphology
In arthropods, the integument, the external "skin", or "s ...
, which consists of chitin and unhardened proteins. The exocuticle and endocuticle together are known as the procuticle. Each body segment and limb section is encased in hardened cuticle. The joints between body segments and between limb sections are covered by flexible cuticle.
The exoskeletons of most aquatic crustaceans are biomineralized with calcium carbonate extracted from the water. Some terrestrial crustaceans have developed means of storing the mineral, since on land they cannot rely on a steady supply of dissolved calcium carbonate. Biomineralization generally affects the exocuticle and the outer part of the endocuticle. Two recent hypotheses about the evolution of biomineralization in arthropods and other groups of animals propose that it provides tougher defensive armor, and that it allows animals to grow larger and stronger by providing more rigid skeletons; and in either case a mineral-organic composite exoskeleton is cheaper to build than an all-organic one of comparable strength.
The cuticle may have setae (bristles) growing from special cells in the epidermis. Setae are as varied in form and function as appendages. For example, they are often used as sensors to detect air or water currents, or contact with objects; aquatic arthropods use feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
-like setae to increase the surface area of swimming appendages and to filter food particles out of water; aquatic insects, which are air-breathers, use thick felt-like coats of setae to trap air, extending the time they can spend under water; heavy, rigid setae serve as defensive spines.
Although all arthropods use muscles attached to the inside of the exoskeleton to flex their limbs, some still use hydraulic pressure to extend them, a system inherited from their pre-arthropod ancestors; for example, all spiders extend their legs hydraulically and can generate pressures up to eight times their resting level.
Moulting
 The exoskeleton cannot stretch and thus restricts growth. Arthropods, therefore, replace their exoskeletons by undergoing
The exoskeleton cannot stretch and thus restricts growth. Arthropods, therefore, replace their exoskeletons by undergoing ecdysis
Ecdysis is the moulting of the cuticle in many invertebrates of the clade Ecdysozoa. Since the cuticle of these animals typically forms a largely inelastic exoskeleton, it is shed during growth and a new, larger covering is formed. The remna ...
(moulting), or shedding the old exoskeleton after growing a new one that is not yet hardened. Moulting cycles run nearly continuously until an arthropod reaches full size. Ruppert, Fox & Barnes (2004), pp. 523–524
The developmental stages between each moult (ecdysis) until sexual maturity is reached is called an instar. Differences between instars can often be seen in altered body proportions, colors, patterns, changes in the number of body segments or head width. After moulting, i.e. shedding their exoskeleton, the juvenile arthropods continue in their life cycle until they either pupate or moult again.
In the initial phase of moulting, the animal stops feeding and its epidermis releases moulting fluid, a mixture of enzymes that digests the endocuticle
The cuticle forms the major part of the integument of the Arthropoda. It includes most of the material of the exoskeleton of the insects, Crustacea, Arachnida, and Myriapoda.
Morphology
In arthropods, the integument, the external "skin", or "s ...
and thus detaches the old cuticle. This phase begins when the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
has secreted a new epicuticle to protect it from the enzymes, and the epidermis secretes the new exocuticle while the old cuticle is detaching. When this stage is complete, the animal makes its body swell by taking in a large quantity of water or air, and this makes the old cuticle split along predefined weaknesses where the old exocuticle was thinnest. It commonly takes several minutes for the animal to struggle out of the old cuticle. At this point, the new one is wrinkled and so soft that the animal cannot support itself and finds it very difficult to move, and the new endocuticle has not yet formed. The animal continues to pump itself up to stretch the new cuticle as much as possible, then hardens the new exocuticle and eliminates the excess air or water. By the end of this phase, the new endocuticle has formed. Many arthropods then eat the discarded cuticle to reclaim its materials.
Because arthropods are unprotected and nearly immobilized until the new cuticle has hardened, they are in danger both of being trapped in the old cuticle and of being attacked by predators. Moulting may be responsible for 80 to 90% of all arthropod deaths.
Internal organs
Arthropod bodies are also segmented internally, and the nervous, muscular, circulatory, and excretory systems have repeated components. Arthropods come from a lineage of animals that have acoelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it r ...
, a membrane-lined cavity between the gut and the body wall that accommodates the internal organs. The strong, segmented limbs of arthropods eliminate the need for one of the coelom's main ancestral functions, as a hydrostatic skeleton, which muscles compress in order to change the animal's shape and thus enable it to move. Hence the coelom of the arthropod is reduced to small areas around the reproductive and excretory systems. Its place is largely taken by a hemocoel
The blood circulatory system is a organ system, system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascula ...
, a cavity that runs most of the length of the body and through which blood flows. Ruppert, Fox & Barnes (2004), pp. 527–528
Respiration and circulation
Arthropods have open circulatory systems, although most have a few short, open-ended arteries. In chelicerates and crustaceans, the blood carries oxygen to the tissues, while hexapods use a separate system oftracheae
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the ...
. Many crustaceans, but few chelicerates and tracheates, use respiratory pigments to assist oxygen transport. The most common respiratory pigment in arthropods is copper-based hemocyanin; this is used by many crustaceans and a few centipede
Centipedes (from New Latin , "hundred", and Latin , " foot") are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda (Ancient Greek , ''kheilos'', lip, and New Latin suffix , "foot", describing the forcipules) of the subphylum Myriapoda, an ...
s. A few crustaceans and insects use iron-based hemoglobin, the respiratory pigment used by vertebrates. As with other invertebrates, the respiratory pigments of those arthropods that have them are generally dissolved in the blood and rarely enclosed in corpuscles as they are in vertebrates.
The heart is typically a muscular tube that runs just under the back and for most of the length of the hemocoel. It contracts in ripples that run from rear to front, pushing blood forwards. Sections not being squeezed by the heart muscle are expanded either by elastic ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal li ...
s or by small muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
s, in either case connecting the heart to the body wall. Along the heart run a series of paired ostia, non-return valves that allow blood to enter the heart but prevent it from leaving before it reaches the front.
Arthropods have a wide variety of respiratory systems. Small species often do not have any, since their high ratio of surface area to volume enables simple diffusion through the body surface to supply enough oxygen. Crustacea usually have gills that are modified appendages. Many arachnids have book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open ventral abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and conn ...
s. Tracheae, systems of branching tunnels that run from the openings in the body walls, deliver oxygen directly to individual cells in many insects, myriapods and arachnids.
Nervous system
Living arthropods have paired main nerve cords running along their bodies below the gut, and in each segment the cords form a pair ofganglia
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympatheti ...
from which sensory
Sensory may refer to:
Biology
* Sensory ecology, how organisms obtain information about their environment
* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli
* Sensory perception, the process of acquiri ...
and motor nerves run to other parts of the segment. Although the pairs of ganglia in each segment often appear physically fused, they are connected by commissures (relatively large bundles of nerves), which give arthropod nervous systems a characteristic "ladder-like" appearance. The brain is in the head, encircling and mainly ''above'' the esophagus. It consists of the fused ganglia of the acron and one or two of the foremost segments that form the head – a total of three pairs of ganglia in most arthropods, but only two in chelicerates, which do not have antennae or the ganglion connected to them. The ganglia of other head segments are often close to the brain and function as part of it. In insects these other head ganglia combine into a pair of subesophageal ganglia The suboesophageal ganglion (acronym: SOG; synonym: ''subesophageal ganglion'') of arthropods and in particular insects is part of the arthropod central nervous system (CNS). As indicated by its name, it is located ''below the'' ''oesophagus'', insi ...
, under and behind the esophagus. Spiders take this process a step further, as ''all'' the segmental ganglia
The segmental ganglia (singular: s. ganglion) are ganglia of the annelid and arthropod central nervous system that lie in the segmented ventral nerve cord
The ventral nerve cord is a major structure of the invertebrate central nervous system. It i ...
are incorporated into the subesophageal ganglia, which occupy most of the space in the cephalothorax (front "super-segment"). Ruppert, Fox & Barnes (2004), pp. 531–532
Excretory system
There are two different types of arthropod excretory systems. In aquatic arthropods, the end-product of biochemical reactions thatmetabolise
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
nitrogen is ammonia, which is so toxic that it needs to be diluted as much as possible with water. The ammonia is then eliminated via any permeable membrane, mainly through the gills. All crustaceans use this system, and its high consumption of water may be responsible for the relative lack of success of crustaceans as land animals. Ruppert, Fox & Barnes (2004), pp. 529–530 Various groups of terrestrial arthropods have independently developed a different system: the end-product of nitrogen metabolism is uric acid, which can be excreted as dry material; the Malpighian tubule system filters the uric acid and other nitrogenous waste out of the blood in the hemocoel, and dumps these materials into the hindgut, from which they are expelled as feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
. Most aquatic arthropods and some terrestrial ones also have organs called nephridia ("little kidneys"), which extract other wastes for excretion as urine.
Senses
The stiffcuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
s of arthropods would block out information about the outside world, except that they are penetrated by many sensors or connections from sensors to the nervous system. In fact, arthropods have modified their cuticles into elaborate arrays of sensors. Various touch sensors, mostly setae, respond to different levels of force, from strong contact to very weak air currents. Chemical sensors provide equivalents of taste and smell
Smell may refer to;
* Odor, airborne molecules perceived as a scent or aroma
* Sense of smell, the scent also known scientifically as olfaction
* "Smells" (''Bottom''), an episode of ''Bottom''
* The Smell, a music venue in Los Angeles, Californ ...
, often by means of setae. Pressure sensors often take the form of membranes that function as eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the extern ...
s, but are connected directly to nerves rather than to auditory ossicle
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea). The absence of the auditory ...
s. The antennae of most hexapods include sensor packages that monitor humidity, moisture and temperature. Ruppert, Fox & Barnes (2004), pp. 532–537
Most arthropods lack balance and acceleration sensors, and rely on their eyes to tell them which way is up. The self-righting behavior of cockroaches is triggered when pressure sensors on the underside of the feet report no pressure. However, many malacostracan crustaceans have statocysts, which provide the same sort of information as the balance and motion sensors of the vertebrate inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
.
The proprioceptors of arthropods, sensors that report the force exerted by muscles and the degree of bending in the body and joints, are well understood. However, little is known about what other internal sensors arthropods may have.
Optical
 Most arthropods have sophisticated visual systems that include one or more usually both of compound eyes and pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes"). In most cases ocelli are only capable of detecting the direction from which light is coming, using the shadow cast by the walls of the cup. However, the main eyes of spiders are pigment-cup ocelli that are capable of forming images, and those of jumping spiders can rotate to track prey.
Compound eyes consist of fifteen to several thousand independent
Most arthropods have sophisticated visual systems that include one or more usually both of compound eyes and pigment-cup ocelli ("little eyes"). In most cases ocelli are only capable of detecting the direction from which light is coming, using the shadow cast by the walls of the cup. However, the main eyes of spiders are pigment-cup ocelli that are capable of forming images, and those of jumping spiders can rotate to track prey.
Compound eyes consist of fifteen to several thousand independent ommatidia
The compound eyes of arthropods like insects, crustaceans and millipedes are composed of units called ommatidia (singular: ommatidium). An ommatidium contains a cluster of photoreceptor cells surrounded by support cells and pigment cells. The ou ...
, columns that are usually hexagonal in cross section. Each ommatidium is an independent sensor, with its own light-sensitive cells and often with its own lens and cornea. Compound eyes have a wide field of view, and can detect fast movement and, in some cases, the polarization of light
Polarization (also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the ...
. On the other hand, the relatively large size of ommatidia makes the images rather coarse, and compound eyes are shorter-sighted than those of birds and mammals – although this is not a severe disadvantage, as objects and events within are most important to most arthropods. Several arthropods have color vision, and that of some insects has been studied in detail; for example, the ommatidia of bees contain receptors for both green and ultra-violet.
Olfaction
Reproduction and development
barnacle
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in eros ...
s, are hermaphroditic, that is, each can have the organs of both sex
Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones (ova, oft ...
es. However, individuals of most species remain of one sex their entire lives. A few species of insects and crustaceans can reproduce by parthenogenesis, especially if conditions favor a "population explosion". However, most arthropods rely on sexual reproduction, and parthenogenetic species often revert to sexual reproduction when conditions become less favorable. The ability to undergo meiosis is widespread among arthropods including both those that reproduce sexually and those that reproduce parthenogenetically
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development ...
. Although meiosis is a major characteristic of arthropods, understanding of its fundamental adaptive benefit has long been regarded as an unresolved problem, that appears to have remained unsettled.
Aquatic arthropods may breed by external fertilization, as for example frogs do, or by internal fertilization, where the ova remain in the female's body and the sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, whi ...
must somehow be inserted. All known terrestrial arthropods use internal fertilization. Opiliones (harvestmen), millipedes, and some crustaceans use modified appendages such as gonopods or penises
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males do n ...
to transfer the sperm directly to the female. However, most male terrestrial arthropods produce spermatophores, waterproof packets of sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, whi ...
, which the females take into their bodies. A few such species rely on females to find spermatophores that have already been deposited on the ground, but in most cases males only deposit spermatophores when complex courtship rituals look likely to be successful. Ruppert, Fox & Barnes (2004), pp. 537–539
 Most arthropods lay eggs, but scorpions are
Most arthropods lay eggs, but scorpions are ovoviparous
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ...
: they produce live young after the eggs have hatched inside the mother, and are noted for prolonged maternal care. Newly born arthropods have diverse forms, and insects alone cover the range of extremes. Some hatch as apparently miniature adults (direct development), and in some cases, such as silverfish
The silverfish (''Lepisma saccharinum'') is a species of small, primitive, wingless insect in the order Zygentoma (formerly Thysanura). Its common name derives from the insect's silvery light grey colour, combined with the fish-like appearance ...
, the hatchlings do not feed and may be helpless until after their first moult. Many insects hatch as grubs or caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
s, which do not have segmented limbs or hardened cuticles, and metamorphose into adult forms by entering an inactive phase in which the larval tissues are broken down and re-used to build the adult body. Dragonfly
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threate ...
larvae have the typical cuticles and jointed limbs of arthropods but are flightless water-breathers with extendable jaws. Crustaceans commonly hatch as tiny nauplius larvae that have only three segments and pairs of appendages.
Evolutionary history
Last common ancestor
Based on the distribution of sharedplesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and ...
features in extant and fossil taxa, the last common ancestor of all arthropods is inferred to have been as a modular organism with each module covered by its own sclerite (armor plate) and bearing a pair of biramous limbs. However, whether the ancestral limb was uniramous or biramous is far from a settled debate.
This Ur-arthropod had a ventral mouth, pre-oral antennae and dorsal eyes at the front of the body. It was assumed to have been a non-discriminatory sediment feeder, processing whatever sediment came its way for food, but fossil findings hint that the last common ancestor of both arthropods and priapulida shared the same specialized mouth apparatus; a circular mouth with rings of teeth used for capturing animal prey.
Fossil record
 It has been proposed that the
It has been proposed that the Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and th ...
animals ''Parvancorina
''Parvancorina'' is a genus of shield-shaped bilaterally symmetrical fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran seafloor. It has some superficial similarities with the Cambrian trilobite-like arthropods.
Etymology
The generic name is derived ...
'' and ''Spriggina
''Spriggina'' is a genus of early bilaterian animals whose relationship to living animals is unclear. Fossils of ''Spriggina'' are known from the late Ediacaran period in what is now South Australia. ''Spriggina floundersi'' is the official fossi ...
'', from around , were arthropods, but later study shows that their affinities of being origin of arthropods are not reliable. Small arthropods with bivalve-like shells have been found in Early Cambrian fossil beds dating in China and Australia. The earliest Cambrian trilobite fossils are about 530 million years old, but the class was already quite diverse and worldwide, suggesting that they had been around for quite some time. In the Maotianshan shales, which date to between 530 and 520 million years ago, fossils of arthropods such as '' Kylinxia'' and '' Erratus'' have been found that seem to show a transitional split between lobopodia and other more primitive stem arthropods. Re-examination in the 1970s of the Burgess Shale fossils from about identified many arthropods, some of which could not be assigned to any of the well-known groups, and thus intensified the debate about the Cambrian explosion
The Cambrian explosion, Cambrian radiation, Cambrian diversification, or the Biological Big Bang refers to an interval of time approximately in the Cambrian Period when practically all major animal phyla started appearing in the fossil recor ...
.Whittington, H. B. (1979). Early arthropods, their appendages and relationships. In M. R. House (Ed.), The origin of major invertebrate groups (pp. 253–268). The Systematics Association Special Volume, 12. London: Academic Press. Gould (1990) A fossil of '' Marrella'' from the Burgess Shale has provided the earliest clear evidence of moulting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
.
 The earliest fossil crustaceans date from about in the
The earliest fossil crustaceans date from about in the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
, and fossil shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
from about apparently formed a tight-knit procession across the seabed. Crustacean fossils are common from the Ordovician period onwards. They have remained almost entirely aquatic, possibly because they never developed excretory systems that conserve water. In 2020 scientists announced the discovery of '' Kylinxia'', a five-eyed ~5 cm long shrimp-like animal living 518 Mya that – with multiple distinctive features – appears to be a key ‘ missing link’ of the evolution from '' Anomalocaris'' to true arthropods and could be at the evolutionary root of true arthropods.
Arthropods provide the earliest identifiable fossils of land animals, from about in the Late Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
, and terrestrial tracks from about appear to have been made by arthropods. Arthropods possessed attributes that were easy coopted for life on land; their existing jointed exoskeletons provided protection against desiccation, support against gravity and a means of locomotion that was not dependent on water. Around the same time the aquatic, scorpion-like eurypterids became the largest ever arthropods, some as long as .
The oldest known arachnid is the trigonotarbid '' Palaeotarbus jerami'', from about in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
period. ''Attercopus
''Attercopus'' is an extinct genus of arachnids, containing one species ''Attercopus fimbriunguis'', known from flattened cuticle fossils from the Panther Mountain Formation in Upstate New York. It is placed in the extinct order Uraraneida, sp ...
fimbriunguis'', from in the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ...
period, bears the earliest known silk-producing spigots, but its lack of spinnerets means it was not one of the true spiders, which first appear in the Late Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ...
over . The Jurassic and Cretaceous periods provide a large number of fossil spiders, including representatives of many modern families. Fossils of aquatic scorpions with gills appear in the Silurian and Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ...
periods, and the earliest fossil of an air-breathing scorpion with book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open ventral abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and conn ...
s dates from the Early Carboniferous period.
The oldest possible insect fossil is the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ...
''Rhyniognatha hirsti
''Rhyniognatha'' is an extinct genus of arthropod of disputed placement. It has been considered in some analyses as the oldest insect known, as well as possibly being a flying insect. ''Rhyniognatha'' is known from a partial head with preserved m ...
'', dated at , but its mandibles are of a type found only in winged insects, which suggests that the earliest insects appeared in the Silurian period, although later study shows possibility that ''Rhyniognatha'' can be myriapod, not an insect. The Mazon Creek lagerstätten from the Late Carboniferous, about , include about 200 species, some gigantic by modern standards, and indicate that insects had occupied their main modern ecological niches as herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
s, detritivore
Detritivores (also known as detrivores, detritophages, detritus feeders, or detritus eaters) are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus (decomposing plant and animal parts as well as feces). There are many kinds of invertebrates, ...
s and insectivore
A robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects.
The first vertebrate insectivores wer ...
s. Social termites and ants first appear in the Early Cretaceous, and advanced social bees have been found in Late Cretaceous rocks but did not become abundant until the Middle Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
.
Evolutionary family tree
 From 1952 to 1977, zoologist
From 1952 to 1977, zoologist Sidnie Manton
Sidnie Milana Manton (4 May 1902 – 2 January 1979) was an influential British zoologist. She is known for making advances in the field of functional morphology. She is regarded as being one of the most outstanding zoologists of the twentieth ...
and others argued that arthropods are polyphyletic, in other words, that they do not share a common ancestor that was itself an arthropod. Instead, they proposed that three separate groups of "arthropods" evolved separately from common worm-like ancestors: the chelicerate
The subphylum Chelicerata (from New Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. It contains the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mite ...
s, including spiders and scorpions; the crustaceans; and the uniramia, consisting of onychophorans, myriapods and hexapods. These arguments usually bypassed trilobites, as the evolutionary relationships of this class were unclear. Proponents of polyphyly argued the following: that the similarities between these groups are the results of convergent evolution, as natural consequences of having rigid, segmented exoskeletons; that the three groups use different chemical means of hardening the cuticle; that there were significant differences in the construction of their compound eyes; that it is hard to see how such different configurations of segments and appendages in the head could have evolved from the same ancestor; and that crustaceans have biramous limbs with separate gill and leg branches, while the other two groups have uniramous limbs in which the single branch serves as a leg.
Further analysis and discoveries in the 1990s reversed this view, and led to acceptance that arthropods are monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
, in other words they are inferred to share a common ancestor that was itself an arthropod. For example, Graham Budd
Graham Edward Budd is a British palaeontologist. He is Professor and head of palaeobiology at Uppsala University.
Budd's research focuses on the Cambrian explosion and on the evolution and development, anatomy, and patterns of diversificati ...
's analyses of '' Kerygmachela'' in 1993 and of ''Opabinia
''Opabinia regalis'' is an extinct, stem group arthropod found in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale Lagerstätte (505 million years ago) of British Columbia. ''Opabinia'' was a soft-bodied animal, measuring up to 7 cm in body length, and it ...
'' in 1996 convinced him that these animals were similar to onychophorans and to various Early Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
"lobopod
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as ...
s", and he presented an "evolutionary family tree" that showed these as "aunts" and "cousins" of all arthropods. These changes made the scope of the term "arthropod" unclear, and Claus Nielsen proposed that the wider group should be labelled " Panarthropoda" ("all the arthropods") while the animals with jointed limbs and hardened cuticles should be called "Euarthropoda" ("true arthropods").
A contrary view was presented in 2003, when Jan Bergström and Xian-Guang Hou argued that, if arthropods were a "sister-group" to any of the anomalocarids, they must have lost and then re-evolved features that were well-developed in the anomalocarids. The earliest known arthropods ate mud in order to extract food particles from it, and possessed variable numbers of segments with unspecialized appendages that functioned as both gills and legs. Anomalocarids were, by the standards of the time, huge and sophisticated predators with specialized mouths and grasping appendages, fixed numbers of segments some of which were specialized, tail fins, and gills that were very different from those of arthropods. In 2006, they suggested that arthropods were more closely related to lobopod
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as ...
s and tardigrades than to anomalocarids. In 2014, research indicated that tardigrades were more closely related to arthropods than velvet worms.
Higher up the "family tree", the Annelida have traditionally been considered the closest relatives of the Panarthropoda, since both groups have segmented bodies, and the combination of these groups was labelled Articulata. There had been competing proposals that arthropods were closely related to other groups such as nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
s, priapulids and tardigrades, but these remained minority views because it was difficult to specify in detail the relationships between these groups.
In the 1990s, molecular phylogenetic
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
analyses of DNA sequences produced a coherent scheme showing arthropods as members of a superphylum labelled Ecdysozoa ("animals that moult"), which contained nematodes, priapulids and tardigrades but excluded annelids. This was backed up by studies of the anatomy and development of these animals, which showed that many of the features that supported the Articulata hypothesis showed significant differences between annelids and the earliest Panarthropods in their details, and some were hardly present at all in arthropods. This hypothesis groups annelids with molluscs and brachiopods in another superphylum, Lophotrochozoa
Lophotrochozoa (, "crest/wheel animals") is a clade of protostome animals within the Spiralia. The taxon was established as a monophyletic group based on molecular evidence. The clade includes animals like annelids, molluscs, bryozoans, brachi ...
.
If the Ecdysozoa hypothesis is correct, then segmentation of arthropods and annelids either has evolved convergently or has been inherited from a much older ancestor and subsequently lost in several other lineages, such as the non-arthropod members of the Ecdysozoa.
Phylogeny of stem-group arthropods
Modern interpretations of the basal, extinct stem-group of Arthropoda recognised the following groups, from most basal to most crownward: * The "Giant" or "Siberiid Lobopodians", such as '' Jianshanopodia'', ''Siberion
''Siberion'' is an extinct genus of lobopodian from the Sinsk biota of Russia. Its anatomy, including the proboscis-like organ projecting from the face and prominent grasping first pair of appendages, suggests that xenusians like this organism ma ...
'' and ''Megadictyon
''Megadictyon'' is a genus of Cambrian lobopodian with similarities to ''Jianshanopodia'' and '' Siberion''.
Occasionally mis-spelt ''Magadictyon''.
Megadictyon is a large lobopodian, with body length (excluding appendages) possibly up to 20 c ...
'', are the most basal grade in the total-group Arthropoda.
* The "Gilled Lobopodians", such as '' Kerygmachela'', '' Pambdelurion'' and ''Opabinia
''Opabinia regalis'' is an extinct, stem group arthropod found in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale Lagerstätte (505 million years ago) of British Columbia. ''Opabinia'' was a soft-bodied animal, measuring up to 7 cm in body length, and it ...
'', are the second most basal grade.
* The Radiodonta, which traditionally known as anomalocaridids come in third position, and are thought to be monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
.
* A possible "upper stem-group" assemblage of more uncertain position but contained within Deuteropoda
Deuteropoda or "upper stem group arthropods" is a proposed clade of arthropods whose members are distinguished by an anatomical reorganization of the head region, namely the appearance of a differentiated first appendage pair (the ' deutocerebr ...
: the Fuxianhuiida, Megacheira, and multiple "bivalved forms" including Isoxyida ('' Isoxys'' and ''Surusicaris
''Surusicaris'' is an extinct genus of bivalved arthropod, known from the Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. It is considered to be closely related to ''Isoxys,'' and like it has spined grasping frontal appendages.
Description
...
'') and Hymenocarina.
The Deuteropoda
Deuteropoda or "upper stem group arthropods" is a proposed clade of arthropods whose members are distinguished by an anatomical reorganization of the head region, namely the appearance of a differentiated first appendage pair (the ' deutocerebr ...
is a recently established clade uniting the crown-group (living) arthropods with these possible "upper stem-group" fossils taxa. The clade is defined by important changes to the structure of the head region such as the appearance of a differentiated deutocerebral appendage pair.
However, recent analyses since late 2010s also show that these "upper stem-groups" might be inside the crown-group: isoxyids might nested with the crown-group itself, Megacheira have been recovered as more closely related to Chelicerates, some bivalved forms such as Hymenocarina are consistently shown to be mandibulates, and similarly Fuxianhuiida might also be mandibulates as well.
The following cladogram shows the probable relationships between crown-group Arthropoda and stem-group Arthropoda according to O’Flynn et al. 2022, including two new fossils found to be the most early branches of Deuteropoda
Deuteropoda or "upper stem group arthropods" is a proposed clade of arthropods whose members are distinguished by an anatomical reorganization of the head region, namely the appearance of a differentiated first appendage pair (the ' deutocerebr ...
(the "upper stem-groups" in previous studies are marked in asterisk, living groups are marked in bold):
Note that the subphylum Artiopoda, containing the trilobites
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the At ...
, is closer to mandibulates than to chelicerates in the cladogram above, but older analyses place them as the sister group of chelicerates united under the clade Arachnomorpha.
Phylogeny of living arthropods
The following cladogram shows the internal relationships between all the living classes of arthropods as of late 2010s, as well as the estimated timing for some of the clades:Classification
The phylum Arthropoda is typically subdivided into foursubphyla
In zoological nomenclature, a subphylum is a taxonomic rank below the rank of phylum.
The taxonomic rank of " subdivision" in fungi and plant taxonomy is equivalent to "subphylum" in zoological taxonomy. Some plant taxonomists have also used th ...
, of which one is extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
:
# Artiopods are an extinct group of formerly numerous marine animals that disappeared in the Permian–Triassic extinction event, though they were in decline prior to this killing blow, having been reduced to one order in the Late Devonian extinction. They contain groups such as the trilobites
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the At ...
.
# Chelicerate
The subphylum Chelicerata (from New Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. It contains the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mite ...
s comprise the marine sea spiders and horseshoe crabs, along with the terrestrial arachnids such as mites, harvestmen, spiders, scorpions and related organisms characterized by the presence of chelicerae, appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body.
In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including anten ...
s just above/in front of the mouthparts
Mouthparts may refer to:
* The parts of a mouth
** Arthropod mouthparts
*** Insect mouthparts
{{disambig ...
. Chelicerae appear in scorpions and horseshoe crabs as tiny claws that they use in feeding, but those of spiders have developed as fang
A fang is a long, pointed tooth. In mammals, a fang is a modified maxillary tooth, used for biting and tearing flesh. In snakes, it is a specialized tooth that is associated with a venom gland (see snake venom). Spiders also have external fang ...
s that inject venom.
# Myriapods comprise millipedes, centipede
Centipedes (from New Latin , "hundred", and Latin , " foot") are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda (Ancient Greek , ''kheilos'', lip, and New Latin suffix , "foot", describing the forcipules) of the subphylum Myriapoda, an ...
s, pauropods and symphylan
Symphylans, also known as garden centipedes or pseudocentipedes, are soil-dwelling arthropods of the class Symphyla in the subphylum Myriapoda. Symphylans resemble centipedes, but are very small, non-venomous, and only distantly related to both ...
s, characterized by having numerous body segments each of which bearing one or two pairs of legs (or in a few cases being legless). All members are exclusively terrestrial.
# Pancrustacea
Pancrustacea is the clade that comprises all crustaceans and hexapods. This grouping is contrary to the Atelocerata hypothesis, in which Myriapoda and Hexapoda are sister taxa, and Crustacea are only more distantly related. As of 2010, the Pan ...
ns comprise ostracods, barnacle
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in eros ...
s, copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor) ...
s, malacostracans, cephalocaridan
The Cephalocarida are a class (biology), class in the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea comprising only 12 Benthic zone, benthic species. They were discovered in 1955 by Howard L. Sanders, and are commonly referred to as horseshoe shrimp. They hav ...
s, branchiopods, remipedes
Remipedia is a class of blind crustaceans found in coastal aquifers which contain saline groundwater, with populations identified in almost every ocean basin so far explored, including in Australia, the Caribbean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean. The ...
and hexapods. Most groups are primarily aquatic (two notable exceptions being woodlice and hexapods, which are both purely terrestrial) and are characterized by having biramous appendages. The most abundant group of pancrustaceans are the terrestrial hexapods, which comprise insects, diplurans, springtails
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Ent ...
, and proturans, with six thoracic legs.
Aside from these major groups, a number of fossil forms, mostly from the early Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
period, are difficult to place taxonomically, either from lack of obvious affinity to any of the main groups or from clear affinity to several of them. '' Marrella'' was the first one to be recognized as significantly different from the well-known groups.
The phylogeny of the major extant arthropod groups has been an area of considerable interest and dispute. Recent studies strongly suggest that Crustacea, as traditionally defined, is paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
, with Hexapoda having evolved from within it, so that Crustacea and Hexapoda form a clade, Pancrustacea
Pancrustacea is the clade that comprises all crustaceans and hexapods. This grouping is contrary to the Atelocerata hypothesis, in which Myriapoda and Hexapoda are sister taxa, and Crustacea are only more distantly related. As of 2010, the Pan ...
. The position of Myriapoda, Chelicerata and Pancrustacea remains unclear . In some studies, Myriapoda is grouped with Chelicerata (forming Myriochelata
The Myriochelata or Paradoxopoda, is a proposed grouping of arthropods comprising the Myriapoda (including millipedes and centipedes) and Chelicerata (including spiders and scorpions). If this proposition holds true, the Myriochelata are the sister ...
); in other studies, Myriapoda is grouped with Pancrustacea (forming Mandibulata), or Myriapoda may be sister to Chelicerata plus Pancrustacea.
Phylogenetic relationships of the major extant arthropod groups according to Regier et al. (2010); traditional subphyla in bold
The placement of the extinct trilobites is also a frequent subject of dispute. One of the newer hypotheses is that the chelicerae have originated from the same pair of appendages that evolved into antennae in the ancestors of Mandibulata, which would place trilobites, which had antennae, closer to Mandibulata than Chelicerata.
Since the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature recognises no priority above the rank of family, many of the higher-level groups can be referred to by a variety of different names.
Interaction with humans
crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s, lobster
Lobsters are a family (biology), family (Nephropidae, Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs ...
s, crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the clade Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. In some locations, they are also known as crawfish, craydids, crawdaddies, crawdads, freshwater lobsters, mountain lobsters, rock lobsters, mu ...
, shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
, and prawns have long been part of human cuisine, and are now raised commercially. Insects and their grubs are at least as nutritious as meat, and are eaten both raw and cooked in many cultures, though not most European, Hindu, and Islamic cultures. Cooked tarantulas are considered a delicacy in Cambodia, and by the Piaroa Indians of southern Venezuela, after the highly irritant hairs – the spider's main defense system – are removed. Humans also unintentionally eat arthropods in other foods, and food safety regulations lay down acceptable contamination levels for different kinds of food material. The intentional cultivation of arthropods and other small animals for human food, referred to as minilivestock
Insect farming is the practice of raising and breeding insects as livestock, also referred to as ''minilivestock'' or ''micro stock''. Insects may be farmed for the commodities they produce (like silk, honey, lac or insect tea), or for them themse ...
, is now emerging in animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starti ...
as an ecologically sound concept. Commercial butterfly breeding
Commercial butterfly breeding or captive butterfly breeding is the practice of breeding butterflies and moths in controlled environments to supply the stock to research facilities, universities, zoos, insectariums, elementary and secondary schools ...
provides Lepidoptera stock to butterfly conservatories, educational exhibits, schools, research facilities, and cultural events.
However, the greatest contribution of arthropods to human food supply is by pollination: a 2008 study examined the 100 crops that FAO lists as grown for food, and estimated pollination's economic value as €153 billion, or 9.5 per cent of the value of world agricultural production used for human food in 2005. Besides pollinating, bee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyly, monophyletic lineage within the ...
s produce honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
, which is the basis of a rapidly growing industry and international trade.
The red dye cochineal, produced from a Central American species of insect, was economically important to the Aztecs and Mayans. While the region was under Spanish control, it became Mexico's second most-lucrative export, and is now regaining some of the ground it lost to synthetic competitors. Shellac, a resin secreted by a species of insect native to southern Asia, was historically used in great quantities for many applications in which it has mostly been replaced by synthetic resins, but it is still used in woodworking and as a food additive. The blood of horseshoe crabs contains a clotting agent, Limulus Amebocyte Lysate, which is now used to test that antibiotics and kidney machines are free of dangerous bacteria, and to detect spinal meningitis and some cancers. Forensic entomology uses evidence provided by arthropods to establish the time and sometimes the place of death of a human, and in some cases the cause. Recently insects have also gained attention as potential sources of drugs and other medicinal substances.
The relative simplicity of the arthropods' body plan, allowing them to move on a variety of surfaces both on land and in water, have made them useful as models for robotics. The redundancy provided by segments allows arthropods and biomimetic robots to move normally even with damaged or lost appendages.
Although arthropods are the most numerous phylum on Earth, and thousands of arthropod species are venomous, they inflict relatively few serious bites and stings on humans. Far more serious are the effects on humans of diseases like malaria carried by blood-sucking insects. Other blood-sucking insects infect livestock with diseases that kill many animals and greatly reduce the usefulness of others. Ticks can cause tick paralysis
Tick paralysis is the only tick-borne disease that is not caused by an infectious organism. The illness is caused by a neurotoxin produced in the tick's salivary gland. After prolonged attachment, the engorged tick transmits the toxin to its host. ...
and several parasite-borne diseases in humans. A few of the closely related mites also infest humans, causing intense itching, and others cause allergic diseases, including hay fever
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, i ...
, asthma, and eczema.
Many species of arthropods, principally insects but also mites, are agricultural and forest pests. The mite '' Varroa destructor'' has become the largest single problem faced by beekeepers worldwide. Efforts to control arthropod pests by large-scale use of pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampri ...
s have caused long-term effects on human health and on biodiversity. Increasing arthropod resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
to pesticides has led to the development of integrated pest management using a wide range of measures including biological control. Predatory mites may be useful in controlling some mite pests.
As predators
Even amongst arthropods usually thought of as obligate predators,floral
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism ...
food sources (nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists ...
and to a lesser degree pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
) are often useful adjunct sources. It was noticed in one study that adult '' Adalia bipunctata'' (predator and common biocontrol of '' Ephestia kuehniella'') could survive on flowers but never completed the life cycle, so a meta-analysis was done to find such an overall trend in previously published data, if it existed. In some cases floral resources are outright necessary. Overall, floral resources (and an imitation, i.e. sugar water) increase longevity
The word " longevity" is sometimes used as a synonym for "life expectancy" in demography. However, the term ''longevity'' is sometimes meant to refer only to especially long-lived members of a population, whereas ''life expectancy'' is always d ...
and fecundity, meaning even predatory population numbers can depend on non-prey food abundance. Thus biocontrol success may surprisingly depend on nearby flowers.
See also
*Dorsal lobe
The dorsal lobe of arthropods is also known as the ''Antenna (biology), antennal mechanosensory center'' in contrast to the Optic lobe (arthropods), Optic lobe (visual center) and the antennal lobe (olfactory center). Together with the antennal lob ...
*Invertebrate paleontology
Invertebrate paleontology (also spelled invertebrate palaeontology) is sometimes described as invertebrate paleozoology or invertebrate paleobiology.
Whether it is considered to be a subfield of paleontology, paleozoology, or paleobiology, this d ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *External links
*Venomous Arthropods
chapter in United States Environmental Protection Agency and University of Florida/
Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences
The University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (UF/IFAS) is a teaching, research and Extension scientific organization focused on agriculture and natural resources. It is a partnership of federal, state, and county governmen ...
National Public Health Pesticide Applicator Training Manual
Arthropods – Arthropoda
Insect Life Forms {{good article Extant Cambrian first appearances