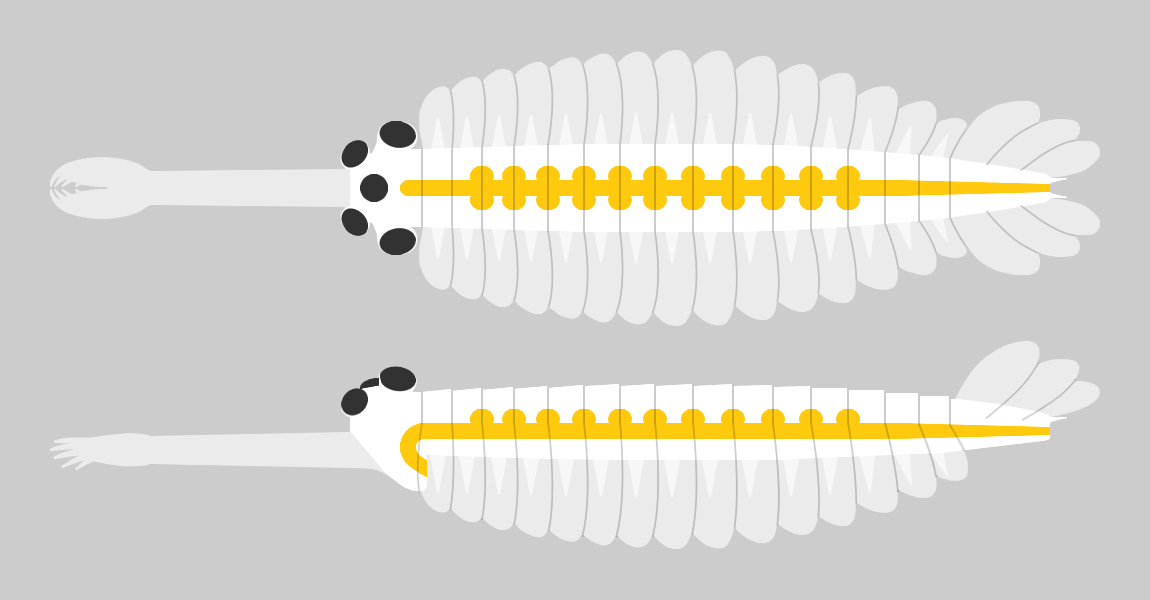
|
Deuteropoda
Deuteropoda or "upper stem group arthropods" is a proposed clade of arthropods whose members are distinguished by an anatomical reorganization of the head region, namely the appearance of a differentiated first appendage pair (the ' deutocerebral' pair), a multisegmented head, and a hypostome/ labrum complex. The clade contains all living arthropods (i.e. chelicerates and mandibulates) as well as several fossil groups that share these characteristics (e.g. fuxianhuiids, megacheirans and Artiopoda), while excluding other fossil groups that are more 'basal' or 'primitive' (e.g. anomalocarids and lobopodians). Defining characteristics Members of Deuteropoda are characterized by the presence of a differentiated labrum and a differentiated first ' deutocerebral' pair of appendages. In contrast, lobopodians (part of the "lower stem group") and onychophorans have a pair of pre-ocular or ' protocerebral' appendages, which presumably have evolved to be the labrum of modern livi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropoda
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erratus
''Erratus'' is an extinct genus of marine arthropod from the Cambrian of China. Its type and only species is ''Erratus sperare''. ''Erratus'' is likely one of the most basal known arthropods, and its discovery has helped scientists understand the early evolution of arthropod trunk appendages. Some of the stem-arthropods like radiodonts did not have legs, instead they had flap like appendages that helped them swim. ''Erratus'' on the other hand had not only flaps but also a set of primitive legs. It also supported the theory that the gills of aquatic arthropods probably evolved into the wings and lungs of terrestrial arthropods later in the Paleozoic. Fossils of ''Erratus'' have been found in the Chengjiang Lagerstätte of China, dating to around 520 million years ago. ''Erratus'' was a small, nektonic organism with a bivalved carapace that probably ate by deposit feeding or filter feeding. History of study The holotype consists of specimens XDBZ101 and XDBZ102. The paratype spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fengzhengia
''Fengzhengia'' is an extinct genus of arthropod known from a single species, ''Fengzhengia mamingae'' from the Cambrian aged Chengjiang Biota of Yunnan, China. It is thought to be a basal arthropod, as one of the most basal members of Deuteropoda. Like other basal deuteropods such as ''Kylinxia'', ''Fengzhengia'' has an upward curling pair of "frontal appendages", contrasting with the downward curving pair of frontal appendages possessed by radiodonts. The head has a pair of stalked eyes. The trunk had 15 tergites the first nine of which had upward facing spines, with the trunk terminating with a tail fan. The trunk seemingly had pairs of biramous limbs, with paddle-shaped exopod The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plur ...s. It is thought to have been nektobenthic (swimmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kylinxia Zhangi
''Kylinxia'' is a genus of extinct arthropod described in 2020. It was described from six specimens discovered in Yu'anshan Formation (Maotianshan Shales) in southern China. The specimens are assigned to one species ''Kylinxia zhangi.'' Dated to 518 million years, the fossils falls under the Cambrian period. Announcing the discovery on 4 November 2020 at a press conference, Zeng Han of the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology, said that the animal "bridges the evolutionary gap from ''Anomalocaris'' to true arthropods and forms a key ‘ missing link’ in the origin of arthropods," which was "predicted by Darwin’s evolutionary theory." The same day the formal description was published in ''Nature''. Discovery ''Kylinxia zhangi'' was discovered among the Maotianshan Shales from Yu'anshan Formation at Yunnan in southern China in 2019. Zeng Han, Zhao Fangchen, and Huang Diying of the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, made the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiodonta
Radiodonta is an extinct Order (biology), order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris, Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia, Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', ''Titanokorys gainesii, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster, Cambroraster falcatus'' and ''Amplectobelua, Amplectobelua symbrachiata'', the Ordovician ''Aegirocassis, Aegiroca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opabinia
''Opabinia regalis'' is an extinct, stem group arthropod found in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale Lagerstätte (505 million years ago) of British Columbia. ''Opabinia'' was a soft-bodied animal, measuring up to 7 cm in body length, and its segmented trunk had flaps along the sides and a fan-shaped tail. The head shows unusual features: five eyes, a mouth under the head and facing backwards, and a clawed proboscis that probably passed food to the mouth. ''Opabinia'' probably lived on the seafloor, using the proboscis to seek out small, soft food. Free abstract at Fewer than twenty good specimens have been described; 3 specimens of ''Opabinia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they constitute less than 0.1% of the community. When the first thorough examination of ''Opabinia'' in 1975 revealed its unusual features, it was thought to be unrelated to any known phylum, or perhaps a relative of arthropod and annelid ancestors. However, later studies since late 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pambdelurion
''Pambdelurion'' is an extinct genus of panarthropod from the Cambrian aged Sirius Passet site in northern Greenland. Like the morphologically similar ''Kerygmachela'' from the same locality, ''Pambdelurion'' is thought to be closely related to arthropods, combining characteristics of " lobopodians" with those of primitive arthropods. Description ''Pambdelurion'' was large for a Cambrian animal, and is estimated to have reached a length of . ''Omnidens'', an organism from China that closely resembles ''Pambdelurion'' and may even be synonymous with it, reached even larger sizes, estimated to be based on the proportions of ''Pambdelurion''. The head of ''Pambdelurion'' bore a large pair of frontal appendages, homologous to the antennae of onychophorans and frontal appendages of radiodonts. These frontal appendages were weakly muscled and relatively soft, suggesting they may have served primarily as sensory organs, rather than for grasping prey. Between the appendages are a pair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerygmachela
''Kerygmachela kierkegaardi'' is a gilled lobopodian from the Cambrian Stage 3 aged Sirius Passet Lagerstätte in northern Greenland. Its anatomy strongly suggests that it, along with its relative ''Pambdelurion whittingtoni'', was a close relative of radiodont (anomalocaridids) and euarthropods. The generic name "Kerygmachela" derives from the Greek words ''Kerygma'' (proclamation) and ''Chela'' (claw), in reference to the flamboyant frontal appendages. The specific name, "kierkegaardi" honors Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard. Morphology The head of ''Kerygmachela'' possesses a pair of well-developed frontal appendages which correspond to those of other dinocaridids and siberiid lobopodians. Each of them terminates in a series of long spines. A pair of sessile, slit-like compound eyes is located slightly behind the base of these appendages. A small anterior-facing mouth is located below the head and bears a pair of stylet-like structures. The head also possesses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jianshanopodia
''Jianshanopodia decora'' is a Cambrian lobopodian. Its frontal, grasping appendages bear wedge-shaped plates. Its limbs branch, instead of being tipped with claws as many lobopods' are. It has a sediment-filled gut surrounded by serially repeated diverticulae. It is thought to have sucked up prey with its short 'trunk'. It mainly crawled on the sea floor, but could swim when necessary. Its mouth resembles those of anomalocaridids and priapulid Priapulida (priapulid worms, from Gr. πριάπος, ''priāpos'' 'Priapus' + Lat. ''-ul-'', diminutive), sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility ...s. References Prehistoric protostome genera Fossil taxa described in 2006 Lobopodia {{Cambrian-animal-stub Cambrian genus extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megadictyon
''Megadictyon'' is a genus of Cambrian lobopodian with similarities to ''Jianshanopodia'' and '' Siberion''. Occasionally mis-spelt ''Magadictyon''. Megadictyon is a large lobopodian, with body length (excluding appendages) possibly up to 20 centimeters in total. The head has a pair of robust frontal appendages associated with rows of spine and terminal claws. Underside the head is a radiodont-like mouthpart forming by multiple layers of plates and teeth-like structures. The trunk is wide and annulated, with a pair of well-developed lobopodous limbs on each body segment. Only 8 segment/limb pairs are countable in the incomplete fossil materials which lacking posterior region, so it may have had more (possibly up to 11 to 13) in nature. It also has pairs of digestive glands similar to those of basal arthropod Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberion
''Siberion'' is an extinct genus of lobopodian from the Sinsk biota of Russia. Its anatomy, including the proboscis-like organ projecting from the face and prominent grasping first pair of appendages, suggests that xenusians like this organism may have been phylogenetically related to anomalocaridids, like ''Anomalocaris ''Anomalocaris'' ("unlike other shrimp", or "abnormal shrimp") is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group arthropods. The first fossils of ''Anomalocaris'' were discovered in the ''Ogygopsis'' Shale of the Stephen F ...''.Dzik, Jerzy (2011)"The xenusian-to-anomalocaridid transition within the lobopodians" ''Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana'', 50(1): 65-74. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q7507030 Xenusia Lobopodia Cambrian genus extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tardigrada
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them Kleiner Wasserbär ("little water bear"). In 1777, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada (), which means "slow steppers". They have been found in diverse regions of Earth's biospheremountaintops, the deep sea, tropical rainforests, and the Antarctic. Tardigrades are among the most resilient animals known, with individual species able to survive extreme conditions – such as exposure to extreme temperatures, extreme pressures (both high and low), air deprivation, radiation, dehydration, and starvation – that would quickly kill most other known forms of life. Tardigrades have survived exposure to outer space. There are about 1,300 known species in the phylum Tardigrada, a part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa consisting of animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |