Adelaide Cemeteries Authority on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Adelaide ( ) is the capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The
 The area around modern-day Adelaide was originally inhabited by the Indigenous Kaurna people, one of many
The area around modern-day Adelaide was originally inhabited by the Indigenous Kaurna people, one of many

 South Australia was officially established as a British Province in England in February 1836. The first governor
proclaimed the commencement of colonial government in South Australia on 28 December 1836, near The Old Gum Tree in what is now the suburb of
South Australia was officially established as a British Province in England in February 1836. The first governor
proclaimed the commencement of colonial government in South Australia on 28 December 1836, near The Old Gum Tree in what is now the suburb of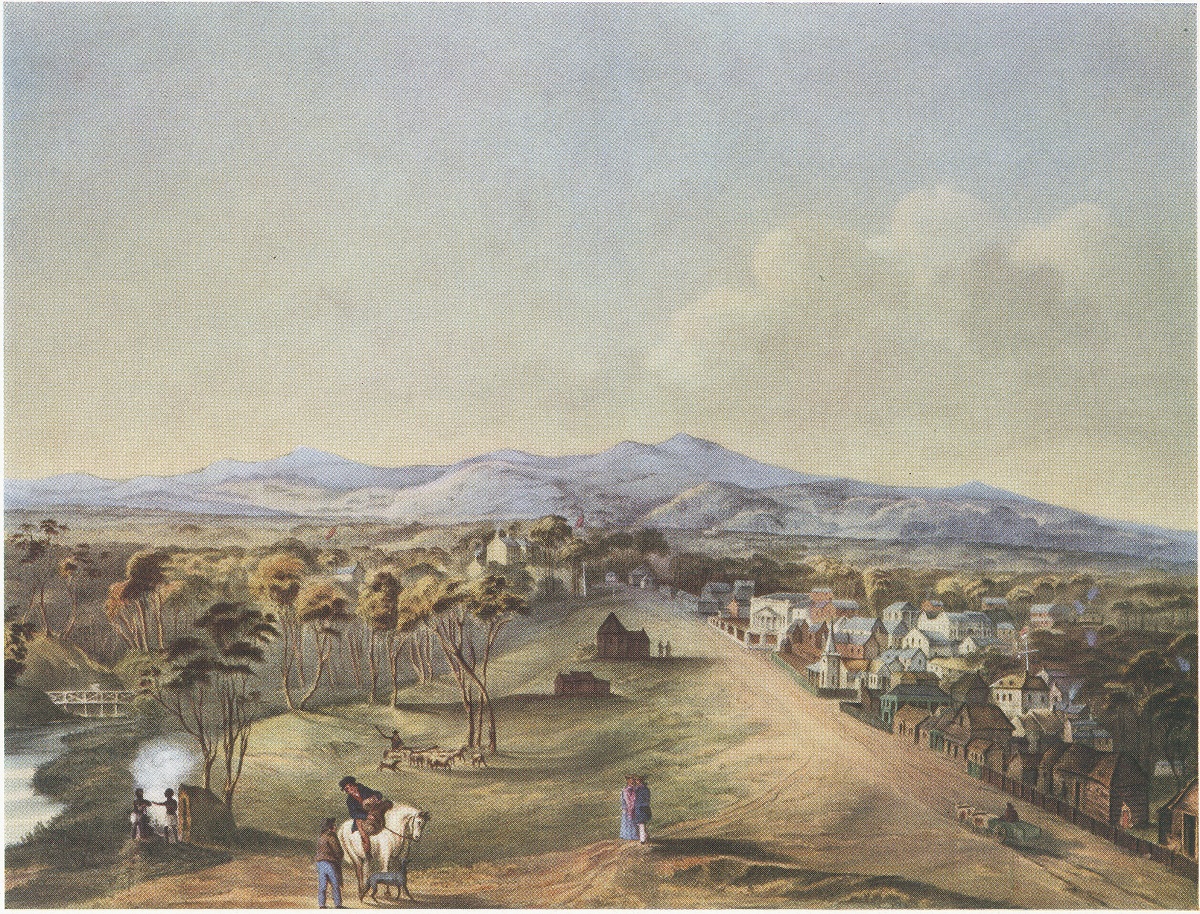  As it was believed that in a colony of free settlers there would be little crime, no provision was made for a gaol in Colonel Light's 1837 plan. But by mid-1837 the ''
As it was believed that in a colony of free settlers there would be little crime, no provision was made for a gaol in Colonel Light's 1837 plan. But by mid-1837 the ''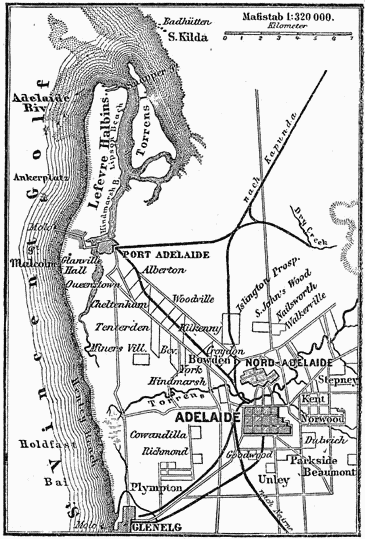 George Gawler took over from Hindmarsh in late 1838 and, despite being under orders from the ''Select Committee on South Australia'' in Britain not to undertake any public works, promptly oversaw construction of a governor's house, the Adelaide Gaol, police barracks, a hospital, a customs house and a wharf at
George Gawler took over from Hindmarsh in late 1838 and, despite being under orders from the ''Select Committee on South Australia'' in Britain not to undertake any public works, promptly oversaw construction of a governor's house, the Adelaide Gaol, police barracks, a hospital, a customs house and a wharf at
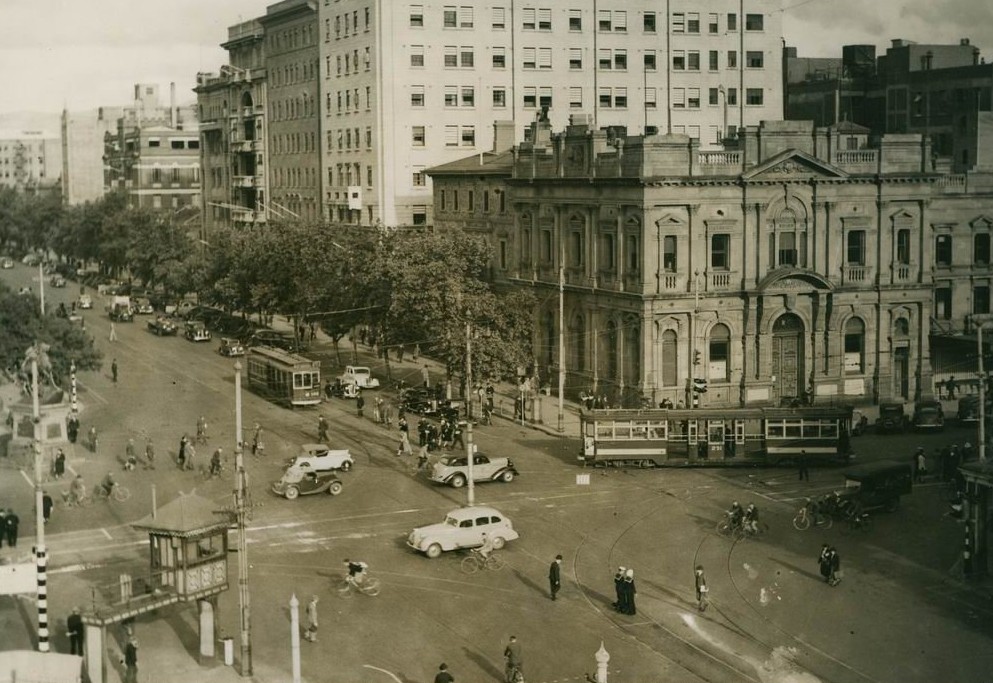 Adelaide was Australia's third largest city for most of the 20th century. Electric street lighting was introduced in 1900 and electric trams were transporting passengers in 1909. 28,000 men were sent to fight in World War I. Historian F. W. Crowley examined the reports of visitors in the early 20th century, noting that "many visitors to Adelaide admired the foresighted planning of its founders", as well as pondering the riches of the young city. Adelaide enjoyed a postwar boom, entering a time of relative prosperity. Its population grew, and it became the third most populous metropolitan area in the country, after Sydney and Melbourne. Its prosperity was short-lived, with the return of droughts and the
Adelaide was Australia's third largest city for most of the 20th century. Electric street lighting was introduced in 1900 and electric trams were transporting passengers in 1909. 28,000 men were sent to fight in World War I. Historian F. W. Crowley examined the reports of visitors in the early 20th century, noting that "many visitors to Adelaide admired the foresighted planning of its founders", as well as pondering the riches of the young city. Adelaide enjoyed a postwar boom, entering a time of relative prosperity. Its population grew, and it became the third most populous metropolitan area in the country, after Sydney and Melbourne. Its prosperity was short-lived, with the return of droughts and the

 Much of Adelaide was bushland before British settlement, with some variation – sandhills, swamps and marshlands were prevalent around the coast. The loss of the sandhills to urban development had a particularly destructive effect on the coastline due to erosion. Where practical, the government has implemented programs to rebuild and vegetate sandhills at several of Adelaide's beachside suburbs. Much of the original vegetation has been cleared with what is left to be found in reserves such as the Cleland National Park and
Much of Adelaide was bushland before British settlement, with some variation – sandhills, swamps and marshlands were prevalent around the coast. The loss of the sandhills to urban development had a particularly destructive effect on the coastline due to erosion. Where practical, the government has implemented programs to rebuild and vegetate sandhills at several of Adelaide's beachside suburbs. Much of the original vegetation has been cleared with what is left to be found in reserves such as the Cleland National Park and
File:Adelaide South Australia - panoramio.jpg, The Adelaide city centre was built on a
File:Adelaide-NthTce-EastEnd-TerraceHouses-Aug08.jpg, Terraced housing on North Terrace.
File:Fitzroy sa bluestone 1.jpg, A bluestone villa, typical of the housing in Fitzroy.
File:Maison à Adelaide.JPG, Heritage-listed house showing wrought-iron lacework and corrugated-iron verandah.
 Adelaide has a Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: Csa). The city has hot, dry summers and cool winters with moderate rainfall. Most precipitation falls in the winter months, leading to the suggestion that the climate be classified as a "cold monsoon". Rainfall is unreliable, light and infrequent throughout summer, although heavy falls can occur. In contrast, the winter has fairly reliable rainfall with June being the wettest month of the year, averaging around 80 mm.
Adelaide has a Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: Csa). The city has hot, dry summers and cool winters with moderate rainfall. Most precipitation falls in the winter months, leading to the suggestion that the climate be classified as a "cold monsoon". Rainfall is unreliable, light and infrequent throughout summer, although heavy falls can occur. In contrast, the winter has fairly reliable rainfall with June being the wettest month of the year, averaging around 80 mm.
 Adelaide was consistently ranked in the world's 10 most liveable cities through the 2010s by The Economist Intelligence Unit.
In June 2021, ''The Economist'' ranked Adelaide the third most liveable city in the world, behind Auckland and Osaka.
In December 2021, Adelaide was named the world's second National Park City, after the state government had lobbied for this title.
It was ranked the most liveable city in Australia by the Property Council of Australia, based on surveys of residents’ views of their own city, between 2010 and 2013, dropping to second place in 2014.
Adelaide was consistently ranked in the world's 10 most liveable cities through the 2010s by The Economist Intelligence Unit.
In June 2021, ''The Economist'' ranked Adelaide the third most liveable city in the world, behind Auckland and Osaka.
In December 2021, Adelaide was named the world's second National Park City, after the state government had lobbied for this title.
It was ranked the most liveable city in Australia by the Property Council of Australia, based on surveys of residents’ views of their own city, between 2010 and 2013, dropping to second place in 2014.
 Adelaide, as the capital of South Australia, is the seat of the
Adelaide, as the capital of South Australia, is the seat of the
 Adelaide's inhabitants are known as Adelaideans.
Compared with Australia's other state capitals, Adelaide is growing at a rate similar to Sydney, Canberra, and Hobart (see
Adelaide's inhabitants are known as Adelaideans.
Compared with Australia's other state capitals, Adelaide is growing at a rate similar to Sydney, Canberra, and Hobart (see

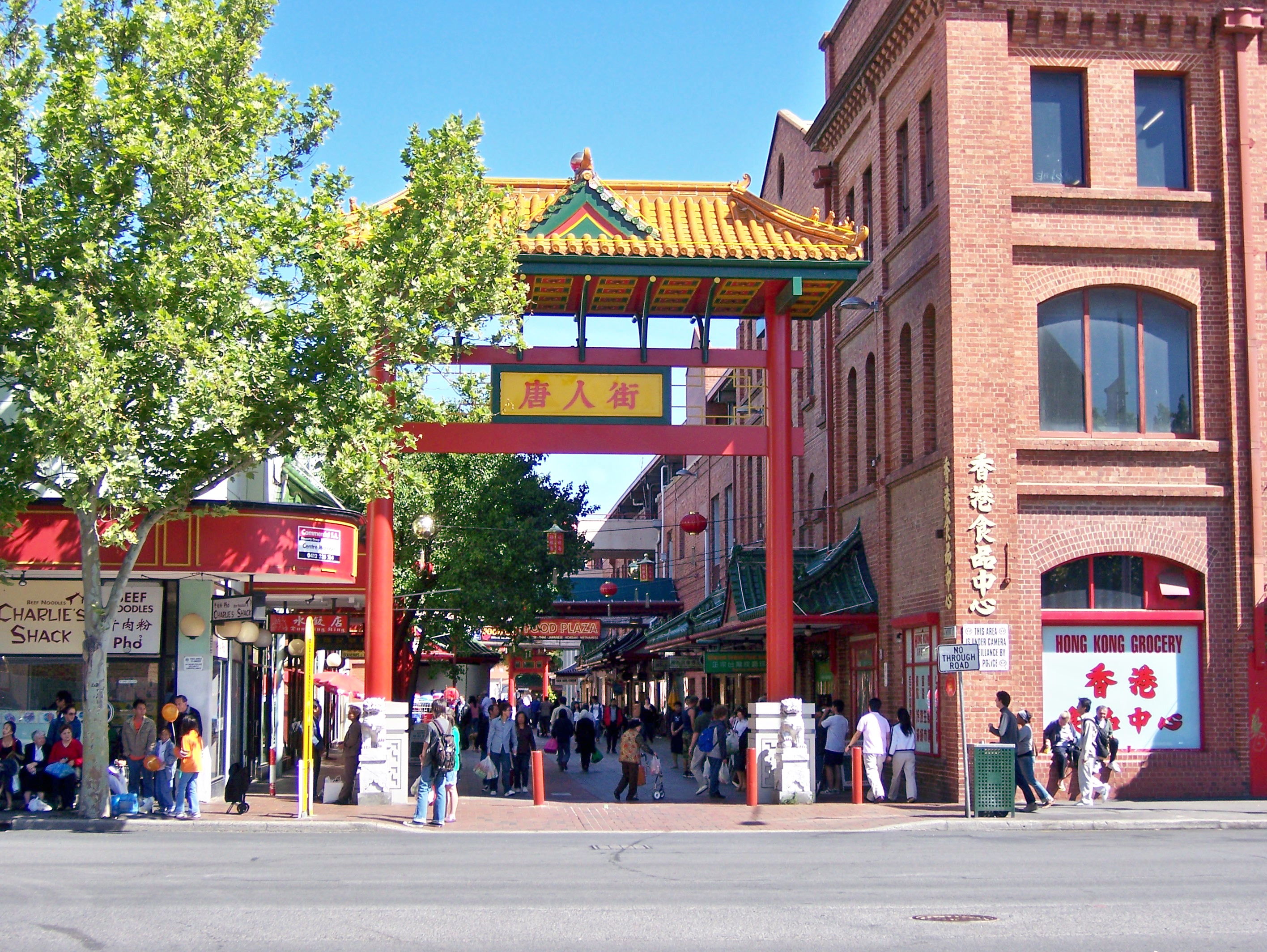
 Adelaide was founded on a vision of religious tolerance that attracted a wide variety of religious practitioners. This led to it being known as ''The City of Churches''. But approximately 28% of the population expressed no religious affiliation in the 2011 Census, compared with the national average of 22.3%, making Adelaide one of Australia's least religious cities. Over half of the population of Adelaide identifies as Christian, with the largest denominations being Catholic (21.3%),
Adelaide was founded on a vision of religious tolerance that attracted a wide variety of religious practitioners. This led to it being known as ''The City of Churches''. But approximately 28% of the population expressed no religious affiliation in the 2011 Census, compared with the national average of 22.3%, making Adelaide one of Australia's least religious cities. Over half of the population of Adelaide identifies as Christian, with the largest denominations being Catholic (21.3%),
, Jewish Virtual Library, Encyclopaedia Judica, 2008. A synagogue was built in 1871, when 435 Jews lived in the city. Many took part in the city councils, such as Judah Moss Solomon (1852–66) and others after him. Three Jews have been elected to the position of city mayor. In 1968, the Jewish population of Adelaide numbered about 1,200; in 2001, according to the Australian census, 979 persons declared themselves to be Jewish by religion. In 2011, over 1,000 Jews were living in the city, operating an Orthodox and a Reform school, in addition to a virtual Jewish museum. The " Afghan" community in Australia first became established in the 1860s when camels and their Pathan, Punjabi, Baluchi and Sindhi handlers began to be used to open up settlement in the continent's arid interior. Until eventually superseded by the advent of the railways and motor vehicles, camels played an invaluable economic and social role in transporting heavy loads of goods to and from isolated settlements and mines. This is acknowledged by the name of The Ghan, the passenger train operating between Adelaide, Alice Springs, and Darwin. The
 South Australia's largest employment sectors are health care and social assistance, surpassing manufacturing in SA as the largest employer since 2006–07. In 2009–10, manufacturing in SA had average annual employment of 83,700 persons compared with 103,300 for health care and social assistance. Health care and social assistance represented nearly 13% of the state average annual employment.1345.4 – SA Stats, Apr 2011
South Australia's largest employment sectors are health care and social assistance, surpassing manufacturing in SA as the largest employer since 2006–07. In 2009–10, manufacturing in SA had average annual employment of 83,700 persons compared with 103,300 for health care and social assistance. Health care and social assistance represented nearly 13% of the state average annual employment.1345.4 – SA Stats, Apr 2011
. abs.gov.au. Retrieved 26 July 2013. The Adelaide Hills wine region is an iconic and viable economic region for both the state and country in terms of wine production and sale. The 2014 vintage is reported as consisting of red grapes crushed valued at A$8,196,142 and white grapes crushed valued at $14,777,631.PGIBSA, 2014, page 25 The retail trade is the second largest employer in SA (2009–10), with 91,900 jobs, and 12 per cent of the state workforce. Manufacturing, defence technology, high-tech electronic systems and research, commodity export and corresponding service industries all play a role in the SA economy. Almost half of all cars produced in Australia were made in Adelaide at the General Motors Holden plant in Elizabeth. The site ceased operating in November 2017. The collapse of the State Bank in 1992 resulted in large levels of state public debt (as much as A$4 billion). The collapse meant that successive governments enacted lean budgets, cutting spending, which was a setback to the further economic development of the city and state. The debt has more recently been reduced with the State Government once again receiving a AAA+ Credit Rating. The global media conglomerate News Corporation was founded in, and until 2004 incorporated in, Adelaide and it is still considered its "spiritual" home by its founder, Rupert Murdoch. Australia's largest oil company, Santos, prominent South Australian brewery, Coopers, and national retailer Harris Scarfe also call Adelaide their home. In 2018, at which time more than 80 organisations employed 800 people in the space sector in South Australia, Adelaide was chosen for the headquarters of a new
 Education forms an increasingly important part of the city's economy, with the South Australian Government and educational institutions attempting to position Adelaide as "Australia's education hub" and marketing it as a "Learning City." The number of international students studying in Adelaide has increased rapidly in recent years to 30,726 in 2015, of which 1,824 were secondary school students. In addition to the city's existing institutions, foreign institutions have been attracted to set up campuses to increase its attractiveness as an education hub. Adelaide is the birthplace of three Nobel laureates, more than any other Australian city: physicist William Lawrence Bragg and pathologists
Education forms an increasingly important part of the city's economy, with the South Australian Government and educational institutions attempting to position Adelaide as "Australia's education hub" and marketing it as a "Learning City." The number of international students studying in Adelaide has increased rapidly in recent years to 30,726 in 2015, of which 1,824 were secondary school students. In addition to the city's existing institutions, foreign institutions have been attracted to set up campuses to increase its attractiveness as an education hub. Adelaide is the birthplace of three Nobel laureates, more than any other Australian city: physicist William Lawrence Bragg and pathologists
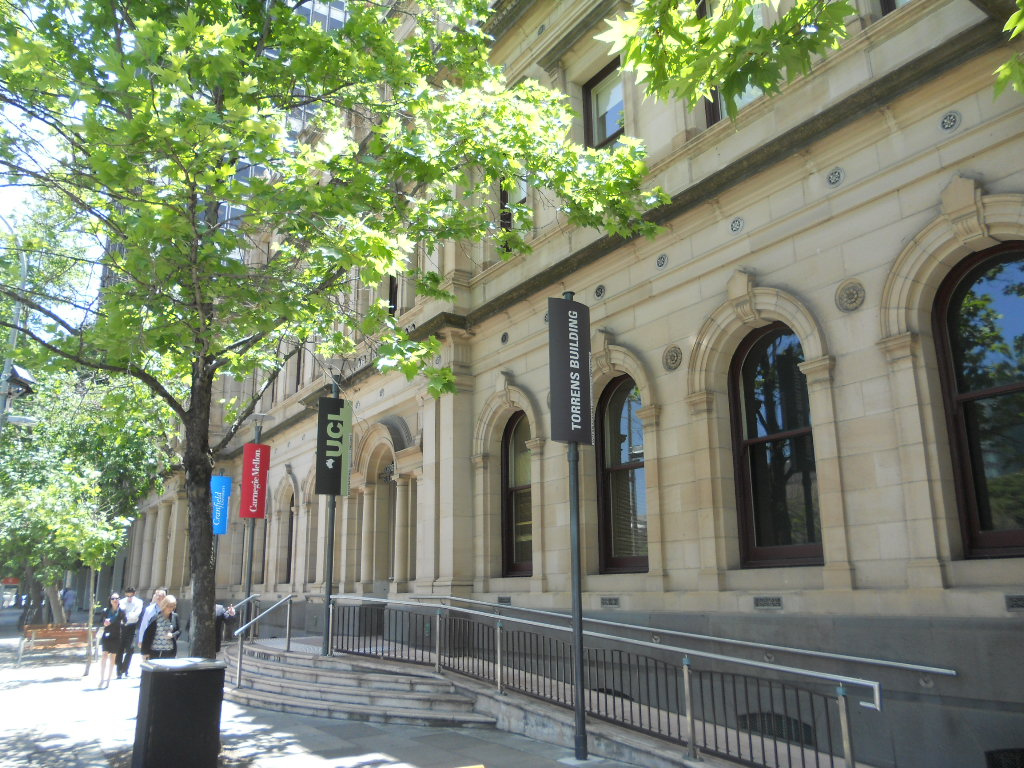 There are three public universities local to Adelaide, as well as one private university and three constituent colleges of foreign universities.
There are three public universities local to Adelaide, as well as one private university and three constituent colleges of foreign universities.
File:Bonython Hall.jpg, The Mitchell Building and Bonython Hall, University of Adelaide
File:Hawke Building, UniSA.jpg, The Hawke Building, part of the UniSA, City West Campus
File:Flinders from hill 3.jpg,

 While established as a British province, and very much English in terms of its culture, Adelaide attracted immigrants from other parts of Europe early on, including German and other European non-conformists escaping religious persecution. The first German Lutherans arrived in 1838, bringing with them the vine cuttings that they used to found the acclaimed wineries of the Barossa Valley.
The Royal Adelaide Show is an annual agricultural show and state fair, established in 1839 and now a huge event held in the Adelaide Showground annually.
Adelaide's arts scene flourished in the 1960s and 1970s with the support of successive premiers from both major political parties. The renowned
While established as a British province, and very much English in terms of its culture, Adelaide attracted immigrants from other parts of Europe early on, including German and other European non-conformists escaping religious persecution. The first German Lutherans arrived in 1838, bringing with them the vine cuttings that they used to found the acclaimed wineries of the Barossa Valley.
The Royal Adelaide Show is an annual agricultural show and state fair, established in 1839 and now a huge event held in the Adelaide Showground annually.
Adelaide's arts scene flourished in the 1960s and 1970s with the support of successive premiers from both major political parties. The renowned 
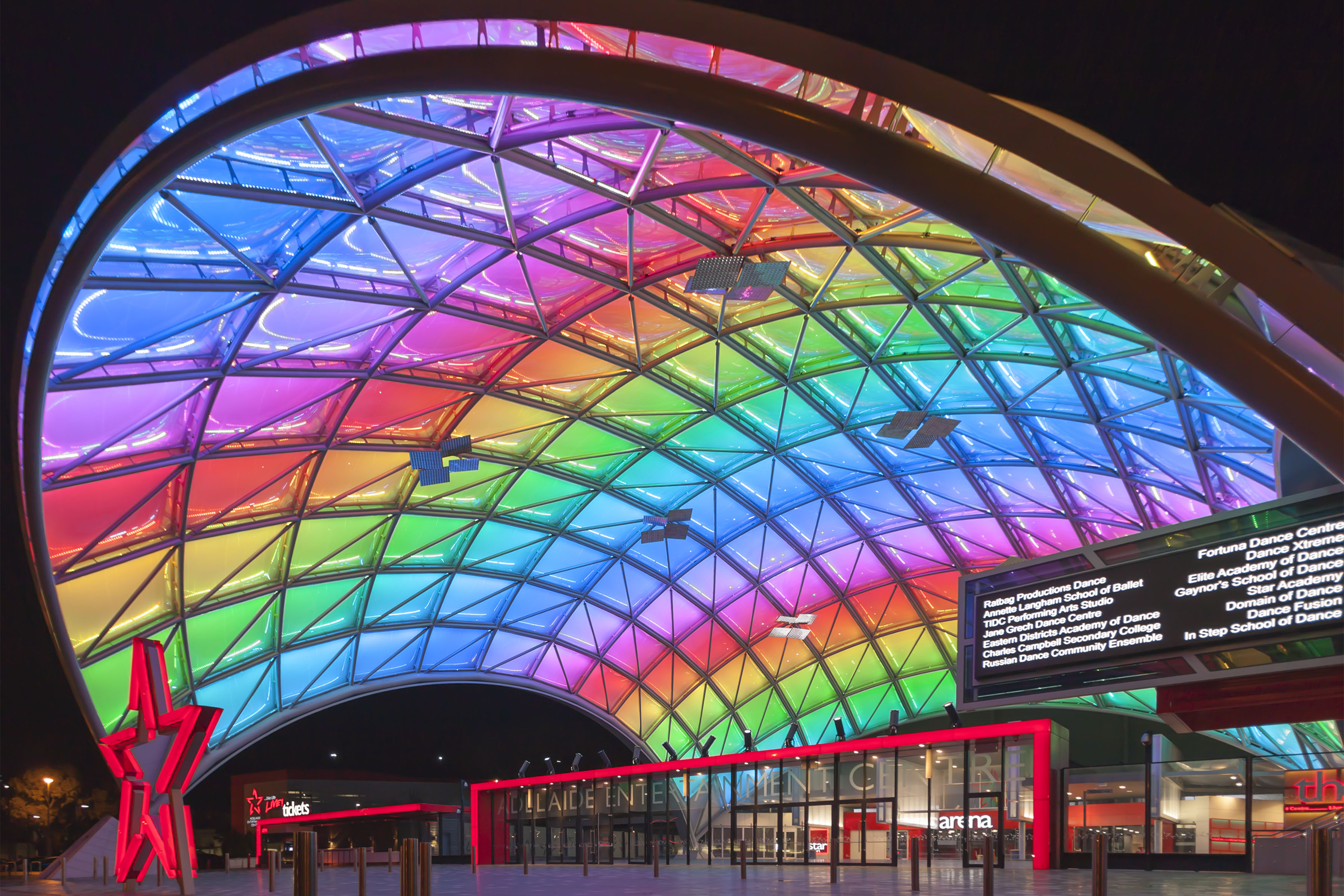
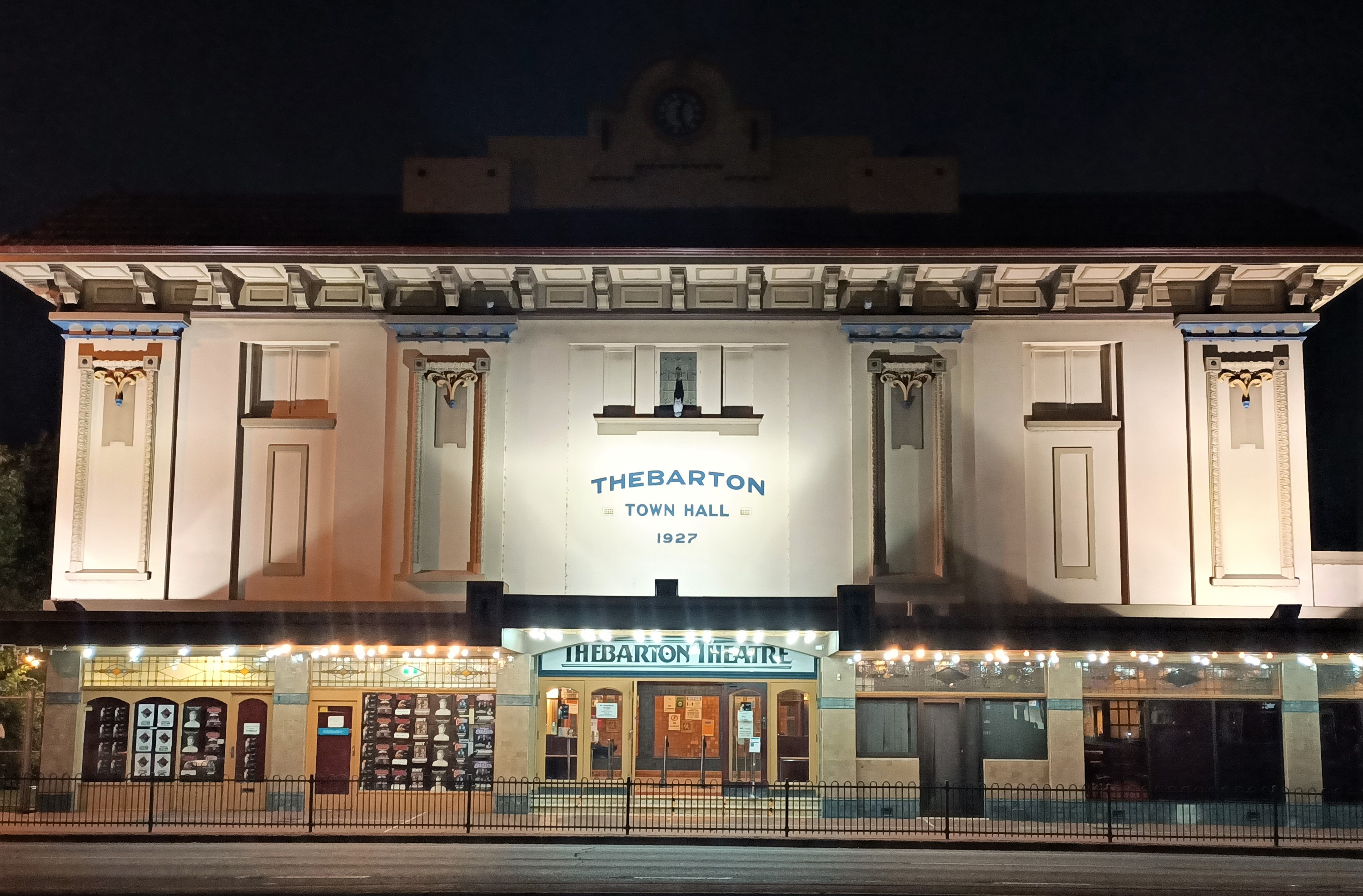
 The Adelaide Festival Centre (which includes the Dunstan Playhouse, Festival Theatre and Space Theatre), on the banks of the Torrens, is the focal point for much of the cultural activity in the city and home to the State Theatre Company of South Australia. Other live music and theatre venues include the Adelaide Entertainment Centre; Adelaide Oval; Memorial Drive Park; Thebarton Theatre;
The Adelaide Festival Centre (which includes the Dunstan Playhouse, Festival Theatre and Space Theatre), on the banks of the Torrens, is the focal point for much of the cultural activity in the city and home to the State Theatre Company of South Australia. Other live music and theatre venues include the Adelaide Entertainment Centre; Adelaide Oval; Memorial Drive Park; Thebarton Theatre;
 In 2015, it was said that there were now more live music venues per capita in Adelaide than any other capital city in the southern hemisphere, '' Lonely Planet'' labelled Adelaide "Australia's live music city", and the city was recognised as a " City of Music" by the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
In addition to its own WOMADelaide, Adelaide attracts several touring music festivals, including Creamfields, Laneway and Groovin'.
Adelaide has produced musical groups and individuals who have achieved national and international fame. These include the
In 2015, it was said that there were now more live music venues per capita in Adelaide than any other capital city in the southern hemisphere, '' Lonely Planet'' labelled Adelaide "Australia's live music city", and the city was recognised as a " City of Music" by the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
In addition to its own WOMADelaide, Adelaide attracts several touring music festivals, including Creamfields, Laneway and Groovin'.
Adelaide has produced musical groups and individuals who have achieved national and international fame. These include the

 The main sports played professionally in Adelaide are
The main sports played professionally in Adelaide are  Since 1999 Adelaide and its surrounding areas have hosted the Tour Down Under bicycle race, organised and directed by Adelaide-based Michael Turtur. Turtur won an Olympic
Since 1999 Adelaide and its surrounding areas have hosted the Tour Down Under bicycle race, organised and directed by Adelaide-based Michael Turtur. Turtur won an Olympic
 Being centrally located on the Australian mainland, Adelaide forms a strategic transport hub for east–west and north–south routes. The city itself has a metropolitan public transport system managed by and known as the Adelaide Metro. The Adelaide Metro consists of a contracted bus system including the O-Bahn Busway, 6 commuter rail lines (diesel and electric), and a small tram network operating between inner suburb
Being centrally located on the Australian mainland, Adelaide forms a strategic transport hub for east–west and north–south routes. The city itself has a metropolitan public transport system managed by and known as the Adelaide Metro. The Adelaide Metro consists of a contracted bus system including the O-Bahn Busway, 6 commuter rail lines (diesel and electric), and a small tram network operating between inner suburb  The Adelaide metropolitan area has one freeway and four expressways. In order of construction, they are:
* The South Eastern Freeway (M1), connects the south-east corner of the Adelaide Plain to the Adelaide Hills and beyond to
The Adelaide metropolitan area has one freeway and four expressways. In order of construction, they are:
* The South Eastern Freeway (M1), connects the south-east corner of the Adelaide Plain to the Adelaide Hills and beyond to
 The Adelaide metropolitan area has two commercial airports, Adelaide Airport and Parafield Airport. Adelaide Airport, in Adelaide's south-western suburbs, serves in excess of 8 million passengers annually. Parafield Airport, Adelaide's second airport north of the city centre, is used for small aircraft, pilot training and recreational aviation purposes. Parafield Airport served as Adelaide's main aerodrome until the opening of the Adelaide Airport in February 1955. Adelaide airport serves many international and domestic destinations including all Australian state capitals.
Adelaide is also home to a military airport, known as Edinburgh Airport, located in the northern suburbs. It was built in 1955 in a joint initiative with the UK for weapon development.
The Adelaide metropolitan area has two commercial airports, Adelaide Airport and Parafield Airport. Adelaide Airport, in Adelaide's south-western suburbs, serves in excess of 8 million passengers annually. Parafield Airport, Adelaide's second airport north of the city centre, is used for small aircraft, pilot training and recreational aviation purposes. Parafield Airport served as Adelaide's main aerodrome until the opening of the Adelaide Airport in February 1955. Adelaide airport serves many international and domestic destinations including all Australian state capitals.
Adelaide is also home to a military airport, known as Edinburgh Airport, located in the northern suburbs. It was built in 1955 in a joint initiative with the UK for weapon development.
 Adelaide's two largest hospitals are the Royal Adelaide Hospital (RAH) in the city centre, a teaching hospital affiliated with the University of Adelaide (800 beds), and the Flinders Medical Centre (580 beds) in Bedford Park, affiliated with Flinders University. The RAH also operates additional campuses for specialist care throughout the suburbs including the Hampstead Rehabilitation Centre (150 beds) in Northfield and the Glenside Campus (129 beds) for acute mental health services. Other major public hospitals are the
Adelaide's two largest hospitals are the Royal Adelaide Hospital (RAH) in the city centre, a teaching hospital affiliated with the University of Adelaide (800 beds), and the Flinders Medical Centre (580 beds) in Bedford Park, affiliated with Flinders University. The RAH also operates additional campuses for specialist care throughout the suburbs including the Hampstead Rehabilitation Centre (150 beds) in Northfield and the Glenside Campus (129 beds) for acute mental health services. Other major public hospitals are the  The largest provider of community health care within Adelaide is the not-for-profit Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), which provides out of hospital care and hospital avoidance care.
The largest provider of community health care within Adelaide is the not-for-profit Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), which provides out of hospital care and hospital avoidance care.
 The provision of water services is by the government-owned SA Water. Adelaide's water is supplied from its seven reservoirs: Mount Bold, Happy Valley, Myponga, Millbrook, Hope Valley, Little Para and South Para. The yield from these reservoir catchments can be as little as 10% of the city's requirements (90GL per annum) in drought years and about 60% in average years. The remaining demand is met by the pumping of water from the
The provision of water services is by the government-owned SA Water. Adelaide's water is supplied from its seven reservoirs: Mount Bold, Happy Valley, Myponga, Millbrook, Hope Valley, Little Para and South Para. The yield from these reservoir catchments can be as little as 10% of the city's requirements (90GL per annum) in drought years and about 60% in average years. The remaining demand is met by the pumping of water from the
Adelaide City Council > Official City Guide
Adelaide City Council
Kids in Adelaide
Retrieved 12 May 2020. {{Authority control 1836 establishments in Australia Australian capital cities Cities in South Australia Coastal cities in Australia Planned capitals Populated places established in 1836 Metropolitan areas of Australia
demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Traditional Owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna people. The area of the city centre and surrounding parklands is called ' in the Kaurna language.
Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains
The Adelaide Plains (Kaurna name Tarndanya) is a plain in South Australia lying between the coast (Gulf St Vincent) on the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges on the east. The southernmost tip of the plain is in the southern seaside suburbs of Ade ...
north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south.
Named in honour of Queen Adelaide, the city was founded in 1836 as the planned capital
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
for the only freely-settled British province in Australia. Colonel William Light, one of Adelaide's founding fathers, designed the city centre and chose its location close to the River Torrens. Light's design, now listed as national heritage, set out the city centre in a grid layout known as " Light's Vision", interspaced by wide boulevards and large public squares, and entirely surrounded by parklands.
Early colonial Adelaide was shaped by the diversity and wealth of its free settlers, in contrast to the convict history of other Australian cities. Until the post-war
In Western usage, the phrase post-war era (or postwar era) usually refers to the time since the end of World War II. More broadly, a post-war period (or postwar period) is the interval immediately following the end of a war. A post-war period c ...
era, it was Australia's third most populated city. It has been noted for its leading examples of religious freedom and progressive political reforms, and became known as the "City of Churches" due to its diversity of faiths. Today, Adelaide is known by its many festivals and sporting events, its food and wine, its coastline and hills, and its large defence and manufacturing sectors. Adelaide's quality of life has ranked consistently highly in various measures through the 21st century, at one stage being named Australia's most liveable city.
As South Australia's government and commercial centre, Adelaide is the site of many governmental and financial institutions. Most of these are concentrated in the city centre
A city centre is the commercial, cultural and often the historical, political, and geographic heart of a city. The term "city centre" is primarily used in British English, and closely equivalent terms exist in other languages, such as "" in Fren ...
along the cultural boulevards of North Terrace and King William Street.
History
Before European settlement
 The area around modern-day Adelaide was originally inhabited by the Indigenous Kaurna people, one of many
The area around modern-day Adelaide was originally inhabited by the Indigenous Kaurna people, one of many Aboriginal
Aborigine, aborigine or aboriginal may refer to:
*Aborigines (mythology), in Roman mythology
* Indigenous peoples, general term for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area
*One of several groups of indigenous peoples, see ...
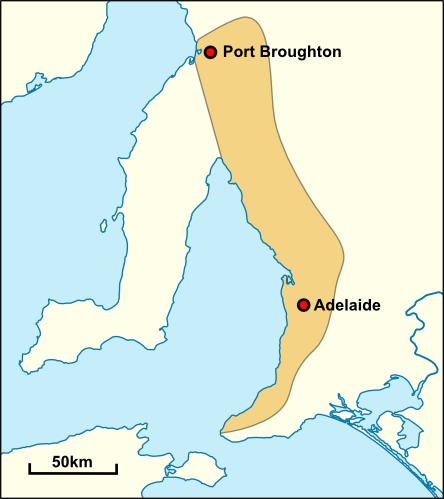
nations in South Australia. The city and parklands area was known as Tarntanya, Tandanya (now the short name of Tandanya National Aboriginal Cultural Institute), Tarndanya, or Tarndanyangga (now the dual name for Victoria Square) in the Kaurna language. The surrounding area was an open grassy plain with patches of trees and shrub which had been managed by hundreds of generations. Kaurna country encompassed the plains which stretched north and south of Tarntanya as well as the wooded foothills of the Mt Lofty Ranges
The Mount Lofty Ranges are a range of mountains in the Australian state of South Australia which for a small part of its length borders the east of Adelaide. The part of the range in the vicinity of Adelaide is called the Adelaide Hills ...
. The River Torrens was known as the Karrawirra Pari (Red Gum forest river). About 300 Kaurna populated the Adelaide area, and were referred to by the settlers as the Cowandilla.
There were more than 20 local clans across the plain who lived semi-nomadic lives, with extensive mound settlements where huts were built repeatedly over centuries and a complex social structure including a class of sorcerers separated from regular society.
Within a few decades of European settlement of South Australia, Kaurna culture was almost completely destroyed; the last speaker of Kaurna language died in 1929. Extensive documentation by early missionaries and other researchers has enabled a modern revival of both, which has included a commitment by local and state governments to rename or include Kaurna names for many local places.
19th century

 South Australia was officially established as a British Province in England in February 1836. The first governor
proclaimed the commencement of colonial government in South Australia on 28 December 1836, near The Old Gum Tree in what is now the suburb of
South Australia was officially established as a British Province in England in February 1836. The first governor
proclaimed the commencement of colonial government in South Australia on 28 December 1836, near The Old Gum Tree in what is now the suburb of Glenelg North
Glenelg North is a seaside suburb of Adelaide, South Australia. It is located in both the City of Holdfast Bay and the City of West Torrens.
Demographics
The 2011 Census by the Australian Bureau of Statistics counted 5,699 persons in Glenelg N ...
. The event is commemorated in South Australia as Proclamation Day. The site of the colony's capital was surveyed and laid out by Colonel William Light, the first Surveyor-General of South Australia, with his own original, unique, topographically sensitive design. The city was named after Queen Adelaide.
Adelaide was established as a planned colony of free immigrants, promising civil liberties and freedom from religious persecution, based upon the ideas of Edward Gibbon Wakefield. Wakefield had read accounts of Australian settlement while in prison in London for attempting to abduct an heiress, and realised that the eastern colonies suffered from a lack of available labour, due to the practice of giving land grants to all arrivals. Wakefield's idea was for the Government to survey and sell the land at a rate that would maintain land values high enough to be unaffordable for labourers and journeymen. Funds raised from the sale of land were to be used to bring out working-class emigrants, who would have to work hard for the monied settlers to ever afford their own land. As a result of this policy, Adelaide does not share the convict settlement history of other Australian cities like Sydney, Brisbane and Hobart
Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/Palawa kani: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-small ...
.
 As it was believed that in a colony of free settlers there would be little crime, no provision was made for a gaol in Colonel Light's 1837 plan. But by mid-1837 the ''
As it was believed that in a colony of free settlers there would be little crime, no provision was made for a gaol in Colonel Light's 1837 plan. But by mid-1837 the ''South Australian Register
''The Register'', originally the ''South Australian Gazette and Colonial Register'', and later ''South Australian Register,'' was South Australia's first newspaper. It was first published in London in June 1836, moved to Adelaide in 1837, and f ...
'' was warning of escaped convicts from New South Wales and tenders for a temporary gaol were sought. Following a burglary, a murder, and two attempted murders in Adelaide during March 1838, Governor Hindmarsh created the South Australian Police Force (now the South Australia Police) in April 1838 under 21-year-old Henry Inman. The first sheriff, Samuel Smart, was wounded during a robbery, and on 2 May 1838 one of the offenders, Michael Magee, became the first person to be hanged in South Australia. William Baker Ashton was appointed governor of the temporary gaol in 1839, and in 1840 George Strickland Kingston was commissioned to design Adelaide's new gaol. Construction of Adelaide Gaol commenced in 1841.
Adelaide's early history was marked by economic uncertainty and questionable leadership. The first governor of South Australia, John Hindmarsh
Rear-Admiral Sir John Hindmarsh KH (baptised 22 May 1785 – 29 July 1860) was a naval officer and the first Governor of South Australia, from 28 December 1836 to 16 July 1838.
Family
His grandfather William Hindmarsh was a gardener in Con ...
, clashed frequently with others, in particular the Resident Commissioner, James Hurtle Fisher. The rural area surrounding Adelaide was surveyed by Light in preparation to sell a total of over of land. Adelaide's early economy started to get on its feet in 1838 with the arrival of livestock from Victoria, New South Wales and Tasmania. Wool production provided an early basis for the South Australian economy. By 1860, wheat farms had been established from Encounter Bay in the south to Clare Clare may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Clare Range, a mountain range in Victoria Land
Australia
* Clare, South Australia, a town in the Clare Valley
* Clare Valley, South Australia
Canada
* Clare (electoral district), an electoral district
* Cl ...
in the north.
 George Gawler took over from Hindmarsh in late 1838 and, despite being under orders from the ''Select Committee on South Australia'' in Britain not to undertake any public works, promptly oversaw construction of a governor's house, the Adelaide Gaol, police barracks, a hospital, a customs house and a wharf at
George Gawler took over from Hindmarsh in late 1838 and, despite being under orders from the ''Select Committee on South Australia'' in Britain not to undertake any public works, promptly oversaw construction of a governor's house, the Adelaide Gaol, police barracks, a hospital, a customs house and a wharf at Port Adelaide
Port Adelaide is a port-side region of Adelaide, approximately northwest of the Adelaide CBD. It is also the namesake of the City of Port Adelaide Enfield council, a suburb, a federal and state electoral division and is the main port for the ...
. Gawler was recalled and replaced by George Edward Grey in 1841. Grey slashed public expenditure against heavy opposition, although its impact was negligible at this point: silver was discovered in Glen Osmond that year, agriculture was well underway, and other mines sprung up all over the state, aiding Adelaide's commercial development. The city exported meat, wool, wine, fruit and wheat by the time Grey left in 1845, contrasting with a low point in 1842 when one-third of Adelaide houses were abandoned.
Trade links with the rest of the Australian states were established after the Murray River was successfully navigated in 1853 by Francis Cadell, an Adelaide resident. South Australia became a self-governing colony in 1856 with the ratification of a new constitution by the British parliament. Secret ballot
The secret ballot, also known as the Australian ballot, is a voting method in which a voter's identity in an election or a referendum is anonymous. This forestalls attempts to influence the voter by intimidation, blackmailing, and potential vote ...
s were introduced, and a bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
parliament was elected on 9 March 1857, by which time 109,917 people lived in the province.
In 1860, the Thorndon Park reservoir was opened, finally providing an alternative water source to the now turbid River Torrens. Gas street lighting was implemented in 1867, the University of Adelaide was founded in 1874, the South Australian Art Gallery opened in 1881 and the Happy Valley Reservoir opened in 1896. In the 1890s Australia was affected by a severe economic depression, ending a hectic era of land booms and tumultuous expansionism. Financial institutions in Melbourne and banks in Sydney closed. The national fertility rate fell and immigration was reduced to a trickle. The value of South Australia's exports nearly halved. Drought and poor harvests from 1884 compounded the problems, with some families leaving for Western Australia. Adelaide was not as badly hit as the larger gold-rush cities of Sydney and Melbourne, and silver and lead discoveries at Broken Hill
Broken Hill is an inland mining city in the far west of outback New South Wales, Australia. It is near the border with South Australia on the crossing of the Barrier Highway (A32) and the Silver City Highway (B79), in the Barrier Range. It is ...
provided some relief. Only one year of deficit was recorded, but the price paid was retrenchments and lean public spending. Wine and copper were the only industries not to suffer a downturn.
20th century
 Adelaide was Australia's third largest city for most of the 20th century. Electric street lighting was introduced in 1900 and electric trams were transporting passengers in 1909. 28,000 men were sent to fight in World War I. Historian F. W. Crowley examined the reports of visitors in the early 20th century, noting that "many visitors to Adelaide admired the foresighted planning of its founders", as well as pondering the riches of the young city. Adelaide enjoyed a postwar boom, entering a time of relative prosperity. Its population grew, and it became the third most populous metropolitan area in the country, after Sydney and Melbourne. Its prosperity was short-lived, with the return of droughts and the
Adelaide was Australia's third largest city for most of the 20th century. Electric street lighting was introduced in 1900 and electric trams were transporting passengers in 1909. 28,000 men were sent to fight in World War I. Historian F. W. Crowley examined the reports of visitors in the early 20th century, noting that "many visitors to Adelaide admired the foresighted planning of its founders", as well as pondering the riches of the young city. Adelaide enjoyed a postwar boom, entering a time of relative prosperity. Its population grew, and it became the third most populous metropolitan area in the country, after Sydney and Melbourne. Its prosperity was short-lived, with the return of droughts and the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
of the 1930s. It later returned to fortune under strong government leadership. Secondary industries helped reduce the state's dependence on primary industries
The primary sector of the economy includes any industry involved in the extraction and production of raw materials, such as farming, logging, fishing, forestry and mining.
The primary sector tends to make up a larger portion of the economy in ...
. World War II brought industrial stimulus and diversification to Adelaide under the Playford Government, which advocated Adelaide as a safe place for manufacturing due to its less vulnerable location. Shipbuilding was expanded at the nearby port of Whyalla.
The South Australian Government in this period built on former wartime manufacturing industries but neglected cultural facilities which meant South Australia's economy lagged behind. International manufacturers like General Motors Holden
Holden, formerly known as General Motors-Holden, was an Australian subsidiary company of General Motors. It was an Australian automobile manufacturer, importer, and exporter which sold cars under its own marque in Australia. In its last thre ...
and Chrysler
Stellantis North America (officially FCA US and formerly Chrysler ()) is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automoti ...
made use of these factories around the Adelaide area in suburbs like Elizabeth, completing its transformation from an agricultural service centre to a 20th-century motor city. The Mannum–Adelaide pipeline brought River Murray
The Murray River (in South Australia: River Murray) (Ngarrindjeri: ''Millewa'', Yorta Yorta: ''Tongala'') is a river in Southeastern Australia. It is Australia's longest river at extent. Its tributaries include five of the next six longest r ...
water to Adelaide in 1955 and an airport opened at West Beach in 1955. Flinders University
Flinders University is a public research university based in Adelaide, South Australia, with a footprint extending across 11 locations in South Australia and the Northern Territory. Founded in 1966, it was named in honour of British navigator ...
and the Flinders Medical Centre were established in the 1960s at Bedford Park, south of the city. Today, Flinders Medical Centre is one of the largest teaching hospitals in South Australia. In the post-war years around the early 1960s, Adelaide was surpassed by Brisbane as Australia's third largest city.
The Dunstan Governments of the 1970s saw something of an Adelaide 'cultural revival', establishing a wide array of social reforms. The city became noted for its progressivism as South Australia became the first Australian state or territory to decriminalise homosexuality between consenting adults in 1975. It also became a centre for the arts, building upon the biennial "Adelaide Festival of Arts
The Adelaide Festival of Arts, also known as the Adelaide Festival, an arts festival, takes place in the South Australian capital of Adelaide in March each year. Started in 1960, it is a major celebration of the arts and a significant cultural ...
" that commenced in 1960. Adelaide hosted the Formula One Australian Grand Prix
The Australian Grand Prix is an annual motor racing event which is under contract to host Formula One until 2035. One of the oldest surviving motorsport competitions held in Australia, the Grand Prix has moved frequently with 23 different venu ...
between 1985 and 1995 on a street circuit in the city's east parklands; it moved to Melbourne in 1996. The State Bank collapsed in 1991 during an economic recession; the effects lasted until 2004, when Standard & Poor's
S&P Global Ratings (previously Standard & Poor's and informally known as S&P) is an American credit rating agency (CRA) and a division of S&P Global that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks, bonds, and commodities. S&P is con ...
reinstated South Australia's AAA credit rating. From 1999
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school shootin ...
until 2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, COVID- ...
, the Adelaide 500 Supercars
A supercar – also called exotic car – is a loosely defined description of street-legal, high-performance sports cars. Since the 2010s, the term hypercar has come into use for the highest performing supercars. Supercars commonly serve as t ...
race has made use of sections of the former Formula One circuit. Adelaide's tallest building, completed in 2020, is called the Adelaidean and is located at 11 Frome Street.
21st century
In the early years of the 21st century, a significant increase in the state government's spending on Adelaide's infrastructure occurred. The Rann government invested A$535 million in a major upgrade of the Adelaide Oval to enableAustralian Football League
The Australian Football League (AFL) is the only fully professional competition of Australian rules football. Through the AFL Commission, the AFL also serves as the sport's governing body and is responsible for controlling the laws of the gam ...
to be played in the city centre and more than A$2 billion to build a new Royal Adelaide Hospital on land adjacent to the Adelaide Railway Station. The Glenelg tramline was extended through the city to Hindmarsh down to East Terrace and the suburban railway line extended south to Seaford.
Following a period of stagnation in the 1990s and 2000s, Adelaide began several major developments and redevelopments. The Adelaide Convention Centre was redeveloped and expanded at a cost of A$350 million beginning in 2012. Three historic buildings were adapted for modern use: the Torrens Building in Victoria Square as the Adelaide campus for Carnegie Mellon University, University College London, and Torrens University; the Stock Exchange building as the Science Exchange of the Royal Institution Australia; and the Glenside Psychiatric Hospital as the Adelaide Studios of the SA Film Corporation. The government also invested more than A$2 billion to build a desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
plant, powered by renewable energy, as an 'insurance policy' against droughts affecting Adelaide's water supply. The Adelaide Festival, Fringe, and Womadelaide became annual events.
The COVID-19 Pandemic had an impact the economy and resident life of the city. Comparing to other major cities in Australia, Adelaide is less affected. The city only went to fully lockdown twice since the beginning of the pandemic, once in November 2020 (4 days) and another once in July 2021 (7 days), despite being the nearest city to Melbourne ( 262 days of lockdown) with 1 million or more population.

Geography
Adelaide is north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, on the Adelaide Plains between the Gulf St Vincent and the low-lying Mount Lofty Ranges. The city stretches from the coast to the foothills, and from Gawler at its northern extent to Sellicks Beach in the south. According to the Regional Development Australia, an Australian government planning initiative, the "Adelaide Metropolitan Region" has a total land area of , while a more expansive definition by the Australian Bureau of Statistics defines a "Greater Adelaide" statistical area totalling . The city sits at an average elevation of above sea level. Mount Lofty, east of the Adelaide metropolitan region in the Adelaide Hills at an elevation of , is the tallest point of the city and in the state south of Burra. The city borders the Temperate Grassland of South Australia in the east, an endangered vegetation community. Much of Adelaide was bushland before British settlement, with some variation – sandhills, swamps and marshlands were prevalent around the coast. The loss of the sandhills to urban development had a particularly destructive effect on the coastline due to erosion. Where practical, the government has implemented programs to rebuild and vegetate sandhills at several of Adelaide's beachside suburbs. Much of the original vegetation has been cleared with what is left to be found in reserves such as the Cleland National Park and
Much of Adelaide was bushland before British settlement, with some variation – sandhills, swamps and marshlands were prevalent around the coast. The loss of the sandhills to urban development had a particularly destructive effect on the coastline due to erosion. Where practical, the government has implemented programs to rebuild and vegetate sandhills at several of Adelaide's beachside suburbs. Much of the original vegetation has been cleared with what is left to be found in reserves such as the Cleland National Park and Belair National Park
Belair National Park (formerly known as the National Park and as Belair Recreation Park) is a protected area in Belair, South Australia, southeast of Adelaide city centre; it covers an area of . It was proclaimed in 1891 and was the first nation ...
. A number of creeks and rivers flow through the Adelaide region. The largest are the Torrens and Onkaparinga catchments. Adelaide relies on its many reservoirs for water supply with the Happy Valley Reservoir supplying around 40% and the much larger Mount Bold Reservoir 10% of Adelaide's domestic requirements respectively.
Geology
Adelaide and its surrounding area is one of the most seismically active regions in Australia. On 1 March 1954 at 3:40 am Adelaide experienced its largest recorded earthquake to date, with the epicentre 12 km from the city centre atDarlington
Darlington is a market town in the Borough of Darlington, County Durham, England. The River Skerne flows through the town; it is a tributary of the River Tees. The Tees itself flows south of the town.
In the 19th century, Darlington underwen ...
, and a reported magnitude of 5.6. There have been smaller earthquakes in 2010, 2011, 2014, 2017, and 2018.
The uplands of the Adelaide Hills, part of the southern Mount Lofty Ranges to the east of Adelaide, are defined on their western side by a number of arcuate faults (the Para, Eden, Clarendon and Willunga Faults), and consist of rocks such as siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.Blatt ''et al.'' 1980, p ...
, dolomite and quartzite, dating from the Neoproterozoic to the middle Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
, laid down in the Adelaide Rift Complex, the oldest part of the Adelaide Superbasin.
Most of the Adelaide metropolitan area lies in the downthrown St Vincent Basin and its embayments, including the Adelaide Plains
The Adelaide Plains (Kaurna name Tarndanya) is a plain in South Australia lying between the coast (Gulf St Vincent) on the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges on the east. The southernmost tip of the plain is in the southern seaside suburbs of Ade ...
Sub-basin, and the Golden Grove, Noarlunga and Willunga Embayments. These basins contain deposits of Tertiary marine and non-marine sands and limestones, which form important aquifers. These deposits are overlain by Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
alluvial fans and piedmont slope deposits, derived from erosion of the uplands, consisting of sands, clays and gravels, interfingering to the west with transgressive
Transgressive may mean:
*Transgressive art, a name given to art forms that violate perceived boundaries
*Transgressive fiction, a modern style in literature
*Transgressive Records, a United Kingdom-based independent record label
*Transgressive (l ...
Pleistocene to Holocene marine sands and coastal sediments of the shoreline of Gulf St Vincent.
Urban layout
Adelaide is a planned city, designed by the first Surveyor-General of South Australia, Colonel William Light. His plan, sometimes referred to as "Light's Vision" (also the name of a statue of him on Montefiore Hill), arranged Adelaide in a grid, with five squares in the Adelaide city centre and a ring of parks, known as the Adelaide Parklands, surrounding it. Light's selection of the location for the city was initially unpopular with the early settlers, as well as South Australia's first governor, John Hindmarsh, due to its distance from the harbour at Port Adelaide, and the lack of fresh water there. Light successfully persisted with his choice of location against this initial opposition. Recent evidence suggests that Light worked closely with George Kingston as well as a team of men to set out Adelaide, using various templates for city plans going back to Ancient Greece, including Italian Renaissance designs and the similar layouts of the American cities Philadelphia andSavannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the Canopy (forest), canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to rea ...
–which, like Adelaide, follow the same layout of a central city square, four complementing city squares surrounding it and a parklands area that surrounds the city centre.
The benefits of Light's design are numerous: Adelaide has had wide multi-lane roads from its beginning, an easily navigable cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
grid layout and an expansive green ring around the city centre. There are two sets of ring road
A ring road (also known as circular road, beltline, beltway, circumferential (high)way, loop, bypass or orbital) is a road or a series of connected roads encircling a town, city, or country. The most common purpose of a ring road is to assist i ...
s in Adelaide that have resulted from the original design. The inner ring route ( A21) borders the parklands, and the outer route ( A3/ A13/ A16/ A17) completely bypasses the inner city via (in clockwise order) Grand Junction Road, Hampstead Road, Ascot Avenue, Portrush Road, Cross Road and South Road.
Suburban expansion has to some extent outgrown Light's original plan. Numerous former outlying villages and "country towns", as well as the satellite city of Elizabeth, have been enveloped by its suburban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
. Expanding developments in the Adelaide Hills region led to the construction of the South Eastern Freeway to cope with growth, which has subsequently led to new developments and further improvements to that transport corridor. Similarly, the booming development in Adelaide's South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
led to the construction of the Southern Expressway
Southern Expressway may refer to:
*Southern Expressway (Adelaide), South Australia
* E01 expressway (Sri Lanka)
*A portion of U.S. Route 219 in New York
U.S. Route 219 (US 219) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from Rich ...
.
New roads are not the only transport infrastructure developed to cope with the urban growth. The O-Bahn Busway is an example of a unique solution to Tea Tree Gully's transport woes in the 1980s. The development of the nearby suburb of Golden Grove in the late 1980s is an example of well-thought-out urban planning.
In the 1960s, a Metropolitan Adelaide Transport Study Plan was proposed to cater for the future growth of the city. The plan involved the construction of freeways, expressways
Expressway may refer to:
*Controlled-access highway, the highest-grade type of highway with access ramps, lane markings, etc., for high-speed traffic.
*Limited-access road, a lower grade of highway or arterial road.
*Expressway, the fictional slide ...
and the upgrade of certain aspects of the public transport system. The then premier Steele Hall approved many parts of the plan and the government went as far as purchasing land for the project. The later Labor government elected under Don Dunstan shelved the plan, but allowed the purchased land to remain vacant, should the future need for freeways arise. In 1980, the Liberal party won government and premier David Tonkin committed his government to selling off the land acquired for the MATS plan, ensuring that even when needs changed, the construction of most MATS-proposed freeways would be impractical. Some parts of this land have been used for transport, (e.g. the O-Bahn Busway and Southern Expressway), while most has been progressively subdivided for residential use.
In 2008, the SA Government announced plans for a network of transport-oriented developments across the Adelaide metropolitan area and purchased a 10 hectare industrial site at Bowden for $52.5 million as the first of these developments. The site covers 102,478 square metres, or about 10 hectares, and is bounded by Park Terrace to the south, the Adelaide to Outer Harbour railway line to the west, Drayton Street to the north and Sixth and Seventh Streets to the east.
grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
, known as ''Light's Vision''
File:Cnr of Pulteney and North Terrace, Adelaide.png, The corner of North Terrace (right) and Pulteney Street (left), looking south-west from near Bonython Hall.
File:Transformers - Victoria Square Adelaide SA - panoramio.jpg, Aerial view of Victoria Square, one of the five main squares in the city centre and considered the heart of Adelaide's grid layout.
Housing
Historically, Adelaide's suburban residential areas have been characterised by single-storey detached houses built on blocks. A relative lack of suitable, locally-available timber for construction purposes led to the early development of a brick-making industry, as well as the use of stone, for houses and other buildings. By 1891, 68% of houses were built of stone, 15% of timber, and 10% of brick, with brick also being widely used in stone houses for quoins, door and window surrounds, and chimneys and fireplaces. There is a wide variety in the styles of these houses. Until the 1960s, most of the more substantial houses were built of red brick, though many front walls were of ornamental stone. Then cream bricks became fashionable, and in the 1970s, deep red and brown bricks became popular. Until the 1970s, roofs tended to be clad with (painted) corrugated iron or tiles (cement or clay, usually red "terracotta"). Since then,Colorbond
BlueScope Steel Limited is an Australian flat product steel producer that was Corporate spin-off, spun-off from BHP, BHP Billiton in 2002.
History
BlueScope was formed when BHP, BHP Billiton Corporate spin-off, spun-off its steel assets on 15 ...
corrugated steel has dominated. Most roofs are pitched; flat roofs are not common. Up to the 1970s, most houses were of "double brick" construction on concrete footings, with timber floors laid on joists supported by "dwarf walls". Later houses have mainly been of " brick veneer" construction – structural timber or, more recently, lightweight steel frame on a concrete slab foundation, lined with Gyprock
Drywall (also called plasterboard, dry lining, wallboard, sheet rock, gypsum board, buster board, custard board, and gypsum panel) is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or without additives, typically extruded between thick ...
, and with an outer skin of brickwork,Rosemary Cadden: ''Building South Australia: celebrating 125 years''. Solstice Media. pp. 77, 87. to cope with Adelaide's reactive soils, particularly Keswick Clay, black earth and some red-brown earth soils. The use of precast concrete panels for floor and wall construction has also increased. In addition to this, a significant factor in Adelaide's suburban history is the role of the South Australian Housing Trust.
Climate
 Adelaide has a Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: Csa). The city has hot, dry summers and cool winters with moderate rainfall. Most precipitation falls in the winter months, leading to the suggestion that the climate be classified as a "cold monsoon". Rainfall is unreliable, light and infrequent throughout summer, although heavy falls can occur. In contrast, the winter has fairly reliable rainfall with June being the wettest month of the year, averaging around 80 mm.
Adelaide has a Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: Csa). The city has hot, dry summers and cool winters with moderate rainfall. Most precipitation falls in the winter months, leading to the suggestion that the climate be classified as a "cold monsoon". Rainfall is unreliable, light and infrequent throughout summer, although heavy falls can occur. In contrast, the winter has fairly reliable rainfall with June being the wettest month of the year, averaging around 80 mm. Frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
s are occasional, with the most notable occurrences in 1908 and 1982. Hail is also common in winter.
Adelaide is a windy city with significant wind chill
Wind chill or windchill (popularly wind chill factor) is the lowering of body temperature due to the passing-flow of lower-temperature air.
Wind chill numbers are always lower than the air temperature for values where the formula is valid. When ...
in winter, which makes the temperature seem colder than it actually is. Snowfall in the metropolitan area is extremely uncommon, although light and sporadic falls in the nearby hills and at Mount Lofty occur during winter. Dewpoints in the summer typically range from . There are usually several days in summer where the temperature reaches or above; the frequency of these temperatures has been increasing in recent years. Temperature extremes range from -0.4 °C (31.4 °F), 8 June 1982 to 47.7 °C (117.9 °F), 24 January 2019. The city features 90.6 clear days annually.
The average sea temperature ranges from in August to in February.
Liveability
 Adelaide was consistently ranked in the world's 10 most liveable cities through the 2010s by The Economist Intelligence Unit.
In June 2021, ''The Economist'' ranked Adelaide the third most liveable city in the world, behind Auckland and Osaka.
In December 2021, Adelaide was named the world's second National Park City, after the state government had lobbied for this title.
It was ranked the most liveable city in Australia by the Property Council of Australia, based on surveys of residents’ views of their own city, between 2010 and 2013, dropping to second place in 2014.
Adelaide was consistently ranked in the world's 10 most liveable cities through the 2010s by The Economist Intelligence Unit.
In June 2021, ''The Economist'' ranked Adelaide the third most liveable city in the world, behind Auckland and Osaka.
In December 2021, Adelaide was named the world's second National Park City, after the state government had lobbied for this title.
It was ranked the most liveable city in Australia by the Property Council of Australia, based on surveys of residents’ views of their own city, between 2010 and 2013, dropping to second place in 2014.
Governance
 Adelaide, as the capital of South Australia, is the seat of the
Adelaide, as the capital of South Australia, is the seat of the Government of South Australia
The Government of South Australia, also referred to as the South Australian Government, SA Government or more formally, His Majesty’s Government, is the Australian state democratic administrative authority of South Australia. It is modelled o ...
as well as the bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
Parliament of South Australia, which consists of the lower house
A lower house is one of two Debate chamber, chambers of a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has co ...
known as the House of Assembly and the upper house known as the Legislative Council. General elections are held every four years, the last being the 2022 South Australian state election
The 2022 South Australian state election was held on 19 March 2022 to elect members to the 55th Parliament of South Australia. All 47 seats in the House of Assembly (the lower house, whose members were elected at the 2018 election), and half th ...
. As Adelaide is South Australia's capital and most populous city, the State Government
A state government is the government that controls a subdivision of a country in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, or ...
co-operates extensively with the City of Adelaide. In 2006, the Ministry for the City of Adelaide was created to facilitate the State Government's collaboration with the Adelaide City Council
The City of Adelaide, also known as the Corporation of the City of Adelaide and Adelaide City Council is a local government area in the metropolitan area of greater Adelaide, South Australia and is legally defined as the capital city of Sout ...
and the Lord Mayor to improve Adelaide's image. The State Parliament's Capital City Committee is also involved in the governance of the City of Adelaide, being primarily concerned with the planning of Adelaide's urban development and growth.
Reflecting South Australia's status as Australia's most centralised state, Adelaide elects a substantial majority of the South Australian House of Assembly. Of the 47 seats in the chamber, 34 seats (three-quarters of the legislature) are based in Adelaide, and two rural seats include Adelaide suburbs.
Local governments
The Adelaide metropolitan area is divided between nineteen local government areas. At its centre, the City of Adelaide administers the Adelaide city centre, North Adelaide, and the surrounding Adelaide Parklands. It is the oldest municipal authority in Australia and was established in 1840, when Adelaide and Australia's first mayor, James Hurtle Fisher, was elected. From 1919 onwards, the city has had a Lord Mayor, the current being Lord Mayor ''The Right Honourable''Sandy Verschoor
Sandra Maaike Jayne Verschoor (born 25 April 1959) is an Australian businesswoman who was the Lord Mayor of Adelaide in South Australia from 12 November 2018 until November 2022. Prior to this, she was Deputy Lord Mayor and a General Manager at ...
.
Demography
 Adelaide's inhabitants are known as Adelaideans.
Compared with Australia's other state capitals, Adelaide is growing at a rate similar to Sydney, Canberra, and Hobart (see
Adelaide's inhabitants are known as Adelaideans.
Compared with Australia's other state capitals, Adelaide is growing at a rate similar to Sydney, Canberra, and Hobart (see List of cities in Australia by population
This list of Australian cities by population provides rankings of Australian cities and towns according to various systems defined by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. The eight Greater Capital City Statistical Areas are listed for the stat ...
). In 2020, it had a metropolitan population (including suburbs) of more than 1,376,601, Estimated resident population, 30 June 2018. making it Australia's fifth-largest city. Some 77% of the population of South Australia are residents of the Adelaide metropolitan area, making South Australia one of the most centralised states.
Major areas of population growth in recent years have been in outer suburbs such as Mawson Lakes and Golden Grove. Adelaide's inhabitants occupy 366,912 houses, 57,695 semi-detached, row terrace or town houses and 49,413 flats, units or apartments.
About one sixth (17.1%) of the population had university qualifications. The number of Adelaideans with vocational qualifications (such as tradespersons) fell from 62.1% of the labour force in the 1991 census to 52.4% in the 2001 census.
Adelaide is ageing more rapidly than other Australian capital cities. More than a quarter (27.5%) of Adelaide's population is aged 55 years or older, in comparison to the national average of 25.6%. Adelaide has the lowest number of children (under-15-year-olds), who comprised 17.7% of the population, compared to the national average of 19.3%.
Ancestry and immigration
At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated ancestries were: Overseas-born Adelaideans composed 31.3% of the total population at the 2021 census. The five largest groups of overseas-born were from England (5.7%), India (3.1%), Mainland China (1.8%), Vietnam (1.2%) and Italy (1.1%). Suburbs includingNewton
Newton most commonly refers to:
* Isaac Newton (1642–1726/1727), English scientist
* Newton (unit), SI unit of force named after Isaac Newton
Newton may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Newton'' (film), a 2017 Indian film
* Newton ( ...
, Payneham
Payneham is an eastern suburb of Adelaide in the City of Norwood Payneham St Peters. It is part of a string of suburbs in Adelaide's east with a high proportion of Adelaide's Italian-Australian and French-Australian residents, many of whom can be ...
and Campbelltown in the east and Torrensville, West Lakes and Fulham
Fulham () is an area of the London Borough of Hammersmith & Fulham in West London, England, southwest of Charing Cross. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames, bordering Hammersmith, Kensington and Chelsea. The area faces Wandsworth ...
to the west, have large Greek and Italian communities. The Italian consulate is located in the eastern suburb of Payneham
Payneham is an eastern suburb of Adelaide in the City of Norwood Payneham St Peters. It is part of a string of suburbs in Adelaide's east with a high proportion of Adelaide's Italian-Australian and French-Australian residents, many of whom can be ...
. Large Vietnamese populations are settled in the north-western suburbs of Woodville, Kilkenny
Kilkenny (). is a city in County Kilkenny, Ireland. It is located in the South-East Region and in the province of Leinster. It is built on both banks of the River Nore. The 2016 census gave the total population of Kilkenny as 26,512.
Kilken ...
, Pennington, Mansfield Park and Athol Park and also Parafield Gardens
Parafield Gardens is a suburb of Adelaide, South Australia. The suburb is largely residential, with a pocket of industrial land in the southwest corner. There are two small shopping centres in the area, one on Salisbury Highway, and another on S ...
and Pooraka in Adelaide's north. Migrants from India and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
have settled into inner suburban areas of Adelaide including the inner northern suburbs of Blair Athol, Kilburn and Enfield and the inner southern suburbs of Plympton, Park Holme
Park Holme is a south-western suburb of Adelaide in the City of Marion, South Australia, located about 8 km (5 mi) from the Adelaide city centre. It is bordered to the east by Marion Road, to the west by Hendrie Street, to the south b ...
and Kurralta Park.
Suburbs such as Para Hills
Para Hills is a residential suburb of Adelaide, South Australia. There is a light aircraft airport close to its boundary, and numerous sporting facilities, abundant parks and schools and two medium-sized shopping centres. Most of the suburb is i ...
, Salisbury, Ingle Farm and Blair Athol in the north and Findon, West Croydon and Seaton and other Western suburbs have sizeable Afghan communities. Chinese migrants favour settling in the eastern and north eastern suburbs including Kensington Gardens
Kensington Gardens, once the private gardens of Kensington Palace, are among the Royal Parks of London. The gardens are shared by the City of Westminster and the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea and sit immediately to the west of Hyde P ...
, Greenacres Greenacres can refer to:
*Greenacres, California, a town in the Central Valley (United States)
*Harold Lloyd Estate, 'Greenacres', the legendary 1920s Harold Lloyd Estate in Beverly Hills, California (United States)
*Greenacres, Florida, town in th ...
, Modbury and Golden Grove. Mawson Lakes has a large international student population, due to its proximity to the University of South Australia campus.
At the 2021 census, 1.7% of Adelaide's population identified as being Indigenous — Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders.
Language
At the 2016 census, 75.4% of the population spoke English at home. The other languages most commonly spoken at home were Italian (2.1%),Standard Mandarin
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standar ...
(2.1%), Greek (1.7%) Vietnamese (1.4%), and Cantonese (0.7%). The Kaurna language, spoken by the area's original inhabitants, had no living speakers in the middle of the 20th century, but since the 1990's there has been a sustained revival effort from academics and Kaurna elders.
Religion

 Adelaide was founded on a vision of religious tolerance that attracted a wide variety of religious practitioners. This led to it being known as ''The City of Churches''. But approximately 28% of the population expressed no religious affiliation in the 2011 Census, compared with the national average of 22.3%, making Adelaide one of Australia's least religious cities. Over half of the population of Adelaide identifies as Christian, with the largest denominations being Catholic (21.3%),
Adelaide was founded on a vision of religious tolerance that attracted a wide variety of religious practitioners. This led to it being known as ''The City of Churches''. But approximately 28% of the population expressed no religious affiliation in the 2011 Census, compared with the national average of 22.3%, making Adelaide one of Australia's least religious cities. Over half of the population of Adelaide identifies as Christian, with the largest denominations being Catholic (21.3%), Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
(12.6%), Uniting Church (7.6%) and Eastern Orthodox (3.5%).
The Jewish community of the city dates back to 1840. Eight years later, 58 Jews lived in the city.Adelaide, Jewish Virtual Library, Encyclopaedia Judica, 2008. A synagogue was built in 1871, when 435 Jews lived in the city. Many took part in the city councils, such as Judah Moss Solomon (1852–66) and others after him. Three Jews have been elected to the position of city mayor. In 1968, the Jewish population of Adelaide numbered about 1,200; in 2001, according to the Australian census, 979 persons declared themselves to be Jewish by religion. In 2011, over 1,000 Jews were living in the city, operating an Orthodox and a Reform school, in addition to a virtual Jewish museum. The " Afghan" community in Australia first became established in the 1860s when camels and their Pathan, Punjabi, Baluchi and Sindhi handlers began to be used to open up settlement in the continent's arid interior. Until eventually superseded by the advent of the railways and motor vehicles, camels played an invaluable economic and social role in transporting heavy loads of goods to and from isolated settlements and mines. This is acknowledged by the name of The Ghan, the passenger train operating between Adelaide, Alice Springs, and Darwin. The
Central Adelaide Mosque
The Central Adelaide Mosque, also known as Adelaide City Mosque or Adelaide Mosque, and formerly known as the Afghan Chapel, is a mosque located in Adelaide, South Australia. The mosque was built in 1888–1889, with its four distinctive minare ...
is regarded as Australia's oldest permanent mosque; an earlier mosque at Marree in northern South Australia, dating from 1861 to 1862 and subsequently abandoned or demolished, has now been rebuilt.
Economy
 South Australia's largest employment sectors are health care and social assistance, surpassing manufacturing in SA as the largest employer since 2006–07. In 2009–10, manufacturing in SA had average annual employment of 83,700 persons compared with 103,300 for health care and social assistance. Health care and social assistance represented nearly 13% of the state average annual employment.1345.4 – SA Stats, Apr 2011
South Australia's largest employment sectors are health care and social assistance, surpassing manufacturing in SA as the largest employer since 2006–07. In 2009–10, manufacturing in SA had average annual employment of 83,700 persons compared with 103,300 for health care and social assistance. Health care and social assistance represented nearly 13% of the state average annual employment.1345.4 – SA Stats, Apr 2011. abs.gov.au. Retrieved 26 July 2013. The Adelaide Hills wine region is an iconic and viable economic region for both the state and country in terms of wine production and sale. The 2014 vintage is reported as consisting of red grapes crushed valued at A$8,196,142 and white grapes crushed valued at $14,777,631.PGIBSA, 2014, page 25 The retail trade is the second largest employer in SA (2009–10), with 91,900 jobs, and 12 per cent of the state workforce. Manufacturing, defence technology, high-tech electronic systems and research, commodity export and corresponding service industries all play a role in the SA economy. Almost half of all cars produced in Australia were made in Adelaide at the General Motors Holden plant in Elizabeth. The site ceased operating in November 2017. The collapse of the State Bank in 1992 resulted in large levels of state public debt (as much as A$4 billion). The collapse meant that successive governments enacted lean budgets, cutting spending, which was a setback to the further economic development of the city and state. The debt has more recently been reduced with the State Government once again receiving a AAA+ Credit Rating. The global media conglomerate News Corporation was founded in, and until 2004 incorporated in, Adelaide and it is still considered its "spiritual" home by its founder, Rupert Murdoch. Australia's largest oil company, Santos, prominent South Australian brewery, Coopers, and national retailer Harris Scarfe also call Adelaide their home. In 2018, at which time more than 80 organisations employed 800 people in the space sector in South Australia, Adelaide was chosen for the headquarters of a new
Australian Space Agency
The Australian Space Agency is an agency under the Australian Government responsible for the development of Australia's commercial space industry, coordinating domestic activities, identifying opportunities and facilitating international spac ...
. The agency opened its in 2020. It is working to triple the size of the Australian space industry and create 20,000 new jobs by 2030.
Defence industry
Adelaide is home to a large proportion of Australia's defence industries, which contribute over A$1 billion to South Australia's Gross State Product. The principal government military research institution, the Defence Science and Technology Organisation, and other defence technology organisations such as BAE Systems Australia and Lockheed Martin Australia, are north of Salisbury and west of Elizabeth in an area now called "Edinburgh Parks", adjacent to RAAF Base Edinburgh. Others, such as Saab Systems and Raytheon, are in or near Technology Park. ASC Pty Ltd, is based in the industrial suburb ofOsborne
Osborne may refer to:
* Osborne (name)
Places Australia
* Osborne, South Australia (disambiguation), places associated with the suburb in the Adelaide metropolitan area
* Osborne, New South Wales, a rural community in the Riverina region
Can ...
and is also a part of Technology Park. South Australia was charged with constructing Australia's s and more recently the A$6 billion contract to construct the Royal Australian Navy's new air-warfare destroyers.
Employment statistics
, Greater Adelaide had an unemployment rate of 7.4% with a youth unemployment rate of 15%. The median weekly individual income for people aged 15 years and over was $447 per week in 2006, compared with $466 nationally. The median family income was $1,137 per week, compared with $1,171 nationally. Adelaide's housing and living costs are substantially lower than that of other Australian cities, with housing being notably cheaper. The median Adelaide house price is half that of Sydney and two-thirds that of Melbourne. The three-month trend unemployment rate to March 2007 was 6.2%. The Northern suburbs' unemployment rate is disproportionately higher than the other regions of Adelaide at 8.3%, while the East and South are lower than the Adelaide average at 4.9% and 5.0% respectively.House prices
Over the decade March 2001 – March 2010, Metropolitan Adelaide median house prices approximately tripled. (approx. 285% – approx. 11%p.a. compounding) In the five years March 2007 – March 2012, prices increased by approx. 27% – approx. 5%p.a. compounding. March 2012 – March 2017 saw a further increase of 19% – approx. 3.5%p.a. compounding. In summary: Each quarter,The Alternative and Direct Investment Securities Association
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in En ...
(ADISA) publishes a list of median house sale prices by suburb and Local Government Area
A local government area (LGA) is an administrative division of a country that a local government is responsible for. The size of an LGA varies by country but it is generally a subdivision of a State (administrative division), state, province, divi ...
. (Previously, this was done by REISA) Due to the small sizes of many of Adelaide's suburbs, the low volumes of sales in these suburbs, and (over time) the huge variations in the numbers of sales in a suburb in a quarter, statistical analysis of "the most expensive suburb" is unreliable; the suburbs appearing in the "top 10 most expensive suburbs this quarter" list is constantly varying. Quarterly Reports for the last two years can be found on the REISA website.
Education and research
 Education forms an increasingly important part of the city's economy, with the South Australian Government and educational institutions attempting to position Adelaide as "Australia's education hub" and marketing it as a "Learning City." The number of international students studying in Adelaide has increased rapidly in recent years to 30,726 in 2015, of which 1,824 were secondary school students. In addition to the city's existing institutions, foreign institutions have been attracted to set up campuses to increase its attractiveness as an education hub. Adelaide is the birthplace of three Nobel laureates, more than any other Australian city: physicist William Lawrence Bragg and pathologists
Education forms an increasingly important part of the city's economy, with the South Australian Government and educational institutions attempting to position Adelaide as "Australia's education hub" and marketing it as a "Learning City." The number of international students studying in Adelaide has increased rapidly in recent years to 30,726 in 2015, of which 1,824 were secondary school students. In addition to the city's existing institutions, foreign institutions have been attracted to set up campuses to increase its attractiveness as an education hub. Adelaide is the birthplace of three Nobel laureates, more than any other Australian city: physicist William Lawrence Bragg and pathologists Howard Florey
Howard Walter Florey, Baron Florey (24 September 189821 February 1968) was an Australian pharmacologist and pathologist who shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Sir Ernst Chain and Sir Alexander Fleming for his role in ...
and Robin Warren, all of whom completed secondary and tertiary education at St Peter's College and the University of Adelaide.
Primary and secondary education
At the level of primary and secondary education, there are two systems of school education. There is a public system operated by the South Australian Government and a private system of independent and Catholic schools. South Australian schools provide education under the Australian Curriculum for reception to Year 10 students. In Years 10 to 12, students study for the South Australian Certificate of Education (SACE). They have the option of incorporating vocational education and training (VET) courses or a flexible learning option (FLO). South Australia also has 24 schools that use International Baccalaureate programs as an alternative to the Australian Curriculum or SACE. These programs include the IB Primary Years Programme, the IB Middle Years Programme, and the IB Diploma Programme. For South Australian students who cannot attend a traditional school, including students who live in rural or remote areas, the state government runs the Open Access College (OAC), which provides virtual teaching. The OAC has a campus in Marden which caters to students from reception to Year 12 and adults who haven't been able to complete their SACE. Guardians are also able to apply for their child to be educated from home as long as they provide an education program which meets the same requirements as the Australian Curriculum as well as opportunities for social interaction.Tertiary education
 There are three public universities local to Adelaide, as well as one private university and three constituent colleges of foreign universities.
There are three public universities local to Adelaide, as well as one private university and three constituent colleges of foreign universities. Flinders University of South Australia
Flinders University is a public research university based in Adelaide, South Australia, with a footprint extending across 11 locations in South Australia and the Northern Territory. Founded in 1966, it was named in honour of British navigator M ...
, the University of Adelaide, the University of South Australia and Torrens University Australia—part of the Laureate International Universities
Laureate Education, Inc. is a corporation based in Miami, Florida, United States. The firm owns and operates Laureate International Universities, with campuses in Mexico and Peru.
The company is publicly traded on the Nasdaq.
Corporate history ...
are based in Adelaide. The University of Adelaide was ranked in the top 150 universities worldwide. Flinders ranked in the top 250 and Uni SA in the top 300. Torrens University Australia is part of an international network of over 70 higher education institutions in more than 30 countries worldwide. The historic Torrens Building in Victoria Square houses Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. One of its predecessors was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools; it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology ...
's Heinz College Australia, and University College London's School of Energy and Resources (Australia), and constitute the city's international university precinct.
The University of Adelaide, with 25,000 students, is Australia's third-oldest university and a member of the leading " Group of Eight". It has five campuses throughout the state, including two in the city-centre, and a campus in Singapore. The University of South Australia, with 37,000 students, has two North Terrace campuses, three other campuses in the metropolitan area and campuses in the regional cities of Whyalla and Mount Gambier. Flinders University
Flinders University is a public research university based in Adelaide, South Australia, with a footprint extending across 11 locations in South Australia and the Northern Territory. Founded in 1966, it was named in honour of British navigator ...
, with 25,184 students, is based in the southern suburb of Bedford Park, alongside the Flinders Medical Centre, with additional campuses in neighbouring Tonsley and in Victoria Square in the city centre.
The Adelaide College of Divinity is at Brooklyn Park.
There are several South Australian TAFE
Technical and further education or simply TAFE (), is the common name in English-speaking countries in Oceania for vocational education, as a subset of tertiary education. TAFE institutions provide a wide range of predominantly vocational cours ...
(Technical and Further Education) campuses in the metropolitan area that provide a range of vocational education and training. The Adelaide College of the Arts, as a school of TAFE SA, provides nationally recognised training in visual and performing arts.
Research
In addition to the universities, Adelaide is home to research institutes, including theRoyal Institution of Australia
The Royal Institution of Australia (RiAus) is a national scientific not-for-profit organisation with a mission to "bring science to people and people to science". It opened in October 2009.
Concept
The concept of a Royal Institution of Austral ...
, established in 2009 as a counterpart to the two-hundred-year-old Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
of Great Britain. Many of the organisations involved in research tend to be geographically clustered throughout the Adelaide metropolitan area:
* The east end of North Terrace: SA Pathology; Hanson Institute; National Wine Centre.
* The west end of North Terrace: South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI), located next to the Royal Adelaide Hospital.
* The Waite Research Precinct: SARDI Head Office and Plant Research Centre; AWRI
The Australian Wine Research Institute (AWRI) is a research institute with a focus on Australian wine, based in Adelaide, South Australia.
Location
It is based at the Wine Innovation Cluster, situated in the Waite Research Precinct, in the Adela ...
; ACPFG; CSIRO
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government
The Australian Government, also known as the Commonwealth Government, is the national government of Australia, a federal parliamentar ...
research laboratories. SARDI also has establishments at Glenside and West Beach.
* Edinburgh, South Australia: DSTO; BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. ...
(Australia); Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
Australia Electronic Systems.
* Technology Park ( Mawson Lakes): BAE Systems; Optus; Raytheon; Topcon; Lockheed Martin Australia Electronic Systems.
* Research Park at Thebarton: businesses involved in materials engineering, biotechnology, environmental services, information technology, industrial design, laser/optics technology, health products, engineering services, radar systems, telecommunications and petroleum services.
* Science Park (adjacent to Flinders University): Playford Capital.
* The Basil Hetzel Institute for Translational Health Research in Woodville the research arm of the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Adelaide
* The Joanna Briggs Institute, a global research collaboration for evidence-based healthcare with its headquarters in North Adelaide.
Flinders University
Flinders University is a public research university based in Adelaide, South Australia, with a footprint extending across 11 locations in South Australia and the Northern Territory. Founded in 1966, it was named in honour of British navigator ...
buildings from the campus hills
File:Torrens Building, Victoria Square.jpg, Torrens University
File:SAHMRI.jpg, South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI)
Cultural life

 While established as a British province, and very much English in terms of its culture, Adelaide attracted immigrants from other parts of Europe early on, including German and other European non-conformists escaping religious persecution. The first German Lutherans arrived in 1838, bringing with them the vine cuttings that they used to found the acclaimed wineries of the Barossa Valley.
The Royal Adelaide Show is an annual agricultural show and state fair, established in 1839 and now a huge event held in the Adelaide Showground annually.
Adelaide's arts scene flourished in the 1960s and 1970s with the support of successive premiers from both major political parties. The renowned
While established as a British province, and very much English in terms of its culture, Adelaide attracted immigrants from other parts of Europe early on, including German and other European non-conformists escaping religious persecution. The first German Lutherans arrived in 1838, bringing with them the vine cuttings that they used to found the acclaimed wineries of the Barossa Valley.
The Royal Adelaide Show is an annual agricultural show and state fair, established in 1839 and now a huge event held in the Adelaide Showground annually.
Adelaide's arts scene flourished in the 1960s and 1970s with the support of successive premiers from both major political parties. The renowned Adelaide Festival of Arts
The Adelaide Festival of Arts, also known as the Adelaide Festival, an arts festival, takes place in the South Australian capital of Adelaide in March each year. Started in 1960, it is a major celebration of the arts and a significant cultural ...
was established in 1960 under Thomas Playford, which in the same year spawned an unofficial uncurated series of performances and exhibits which grew into the Adelaide Fringe. Construction of the Adelaide Festival Centre
Adelaide Festival Centre, Australia's first multi-purpose arts centre and the home of South Australia's performing arts, was built in the 1970s, designed by Hassell Architects. The Festival Theatre opened in June 1973 with the rest of the centr ...
began under Steele Hall in 1970 and was completed under the subsequent government of Don Dunstan, who also established the South Australian Film Corporation
South Australian Film Corporation (SAFC) is a South Australian Government statutory corporation established in 1972 to engage in film production and promote the film industry, located in Adelaide, South Australia. The Adelaide Studios are managed ...
in 1972 and the State Opera of South Australia in 1976.
Over time, the Adelaide Festival expanded to include Adelaide Writers' Week and WOMADelaide, and other separate festivals were established, such as the Adelaide Cabaret Festival (2002), the Adelaide Festival of Ideas (1999), the Adelaide Film Festival (2013), FEAST (1999, a queer culture), Tasting Australia (1997, a food and wine affair), and Illuminate Adelaide (2021). With the Festival, the Fringe, WOMADelaide, Writers' Week and the Adelaide 500 street motor racing event (along with evening music concerts) all happening in early March, the period became known colloquially as "Mad March".
In 2014, Ghil'ad Zuckermann
Ghil'ad Zuckermann ( he, גלעד צוקרמן, ; ) is an Israeli-born language revivalist and linguist who works in contact linguistics, lexicology and the study of language, culture and identity. Zuckermann is Professor of Linguistics and Ch ...
founded the Adelaide Language Festival
The Adelaide Language Festival is a language festival that celebrates linguistic diversity and encourages people to learn about the cognitive and cultural advantages of multilingualism. It consists of keynote presentations, musical performances, We ...
.
There are many international cultural fairs, most notably the German Schützenfest
A Schützenfest (, '' marksmen's festival'') is a traditional festival or fair featuring a target shooting competition in the cultures of Germany, the Netherlands and Switzerland.
At a Schützenfest, contestants compete based on their shooting ...
and Greek Glendi. Adelaide holds an annual Christmas pageant, the world's largest Christmas parade.

North Terrace institutions
As the state capital, Adelaide has a great number of cultural institutions, many of them along the boulevard of North Terrace. TheArt Gallery of South Australia
The Art Gallery of South Australia (AGSA), established as the National Gallery of South Australia in 1881, is located in Adelaide. It is the most significant visual arts museum in the Australian state of South Australia. It has a collection of ...
, with about 35,000 works, holds Australia's second largest state-based collection. Adjacent are the South Australian Museum and State Library of South Australia
The State Library of South Australia, or SLSA, formerly known as the Public Library of South Australia, located on North Terrace, Adelaide, is the official library of the Australian state of South Australia. It is the largest public research l ...
. The Adelaide Botanic Garden, National Wine Centre and Tandanya National Aboriginal Cultural Institute are nearby in the East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
of the city. In the back of the State Library lies the Migration Museum, Australia's oldest museum of its kind.
Further west, the Lion Arts Centre is home to ACE Open
ACE Open is a contemporary visual art organisation based in Adelaide, South Australia, established in 2017 after the Contemporary Art Centre of South Australia and the Australian Experimental Art Foundation (AEAF) were merged, creating a new org ...
, which showcases contemporary art; Dance Hub SA; and other studios and arts industry spaces. The Mercury Cinema and the JamFactory ceramics and design gallery are just around the corner.
Performing arts and music venues

 The Adelaide Festival Centre (which includes the Dunstan Playhouse, Festival Theatre and Space Theatre), on the banks of the Torrens, is the focal point for much of the cultural activity in the city and home to the State Theatre Company of South Australia. Other live music and theatre venues include the Adelaide Entertainment Centre; Adelaide Oval; Memorial Drive Park; Thebarton Theatre;
The Adelaide Festival Centre (which includes the Dunstan Playhouse, Festival Theatre and Space Theatre), on the banks of the Torrens, is the focal point for much of the cultural activity in the city and home to the State Theatre Company of South Australia. Other live music and theatre venues include the Adelaide Entertainment Centre; Adelaide Oval; Memorial Drive Park; Thebarton Theatre; Adelaide Town Hall
Adelaide Town Hall is a landmark building on King William Street in Adelaide, South Australia, Australia. The City of Adelaide Town Hall complex includes the Town Hall and the office building at 25 Pirie Street.
Description and history
Adelai ...
; Her Majesty's Theatre; Queen's Theatre; Holden Theatres and the Hopgood Theatre.
The Lion Arts Factory
The Lion Arts Centre, also known as Fowler's Lion Factory and Fowlers Building, with the main music venue within known as the Lion Arts Factory (formerly Fowler's Live), is a multi-purpose arts centre, including studios, galleries, music and per ...
, within the Lion Arts Centre, hosts contemporary music in a wide range of genres, as does " The Gov" in Hindmarsh
Hindmarsh is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Alfred Hindmarsh, MP for Wellington South (New Zealand electorate) and first leader of the New Zealand Labour Party
*Ian Hindmarsh, Australian rugby league player
* Jean Hindm ...
. The city also has numerous smaller theatres, pubs and cabaret bars which host performances.
Live music
 In 2015, it was said that there were now more live music venues per capita in Adelaide than any other capital city in the southern hemisphere, '' Lonely Planet'' labelled Adelaide "Australia's live music city", and the city was recognised as a " City of Music" by the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
In addition to its own WOMADelaide, Adelaide attracts several touring music festivals, including Creamfields, Laneway and Groovin'.
Adelaide has produced musical groups and individuals who have achieved national and international fame. These include the
In 2015, it was said that there were now more live music venues per capita in Adelaide than any other capital city in the southern hemisphere, '' Lonely Planet'' labelled Adelaide "Australia's live music city", and the city was recognised as a " City of Music" by the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
In addition to its own WOMADelaide, Adelaide attracts several touring music festivals, including Creamfields, Laneway and Groovin'.
Adelaide has produced musical groups and individuals who have achieved national and international fame. These include the Adelaide Symphony Orchestra
The Adelaide Symphony Orchestra (ASO) is a South Australian performing arts organisation comprising 75 full-time musicians, established in 1936.
Based in Adelaide, South Australia, the orchestra's primary performance venue is the Adelaide Town Ha ...
, the Adelaide Youth Orchestra, rock bands The Angels, Atlas Genius, Cold Chisel, The Superjesus, Wolf & Cub, roots/blues group The Audreys, internationally acclaimed metal acts I Killed The Prom Queen
I Killed the Prom Queen were an Australian metalcore band from Adelaide, formed in 2000. They were prominent in the Australian live music scene and toured the US, Japan and parts of Europe several times. They issued three studio albums: ''When ...
and Double Dragon, popular Australian hip-hop outfit Hilltop Hoods, pop acts like Sia, Orianthi, Guy Sebastian, and Wes Carr, as well as internationally successful tribute act, The Australian Pink Floyd Show.
Noted rocker Jimmy Barnes (formerly lead vocalist with Cold Chisel) spent most of his youth in the northern suburb of Elizabeth. Paul Kelly grew up in Adelaide and was head prefect at Rostrevor College. The first ''Australian Idol
''Australian Idol'' is an Australian singing competition, which began its first season in July 2003 and ended its initial run in November 2009. As part of the ''Idol'' franchise, Australian Idol originated from the reality program ''Pop Idol' ...
'' winner, Guy Sebastian, hails from the north-eastern suburb of Golden Grove.
Television
Adelaide is served by numerous digital free-to-air television channels: # ABC # ABC HD (ABC broadcast in HD) # ABC TV Plus # ABC Me # ABC News # SBS # SBS HD (SBS broadcast in HD) # SBS World Movies HD # SBS Viceland HD # SBS Food # NITV # SBS WorldWatch # Seven # 7HD (Seven broadcast in HD) # 7Two # 7mate # 7flix #Racing.com
Racing.com (stylised as RACING.COM) is an Australian free-to-air standard-definition digital television channel, owned and operated by the Seven Network and Racing Victoria. The channel broadcasts live Victorian and South Australian horse racing ...
# Nine
# 9HD (Nine broadcast in HD)
# 9Gem
# 9Go!
# 9Life
# 9Gem HD
# 9Rush
# Extra
# 10
# 10 HD
10 HD is an Australian free-to-air television channel that was originally launched on 16 December 2007 on channel 1. The channel was available to high definition digital television viewers through Network 10 owned-and-operated stations. The ...
(10 broadcast in HD)
# 10 Bold
10 Bold is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel owned by Network 10. It originally launched on 26 March 2009 as One HD with a focus on broadcasting sports-based programming and events, but rebranded to One in April 2011 to ...
# 10 Peach
10 Peach is an Australian free-to-air television channel operated by Network 10. It was launched on 11 January 2011 as Eleven. It is owned by ElevenCo, which was established as a joint venture between Ten Network Holdings and CBS Studios Inter ...
# 10 Shake
10 Shake is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel owned by Network 10. It launched on 27 September 2020 at 6am.
The channel includes a mix of shows for people aged forty and under. It broadcasts programming for children fro ...
# TVSN
# Gecko TV
# C44 Adelaide (Adelaide's community TV station)
All of the five Australian national television networks broadcast both high-definition digital and standard-definition digital television
Standard-definition television (SDTV, SD, often shortened to standard definition) is a television system which uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. "Standard" refers to it being the prevailing sp ...
services in Adelaide. They share three transmission towers on the ridge near the summit of Mount Lofty. There are two other transmission sites at 25 Grenfell Street, Adelaide and Elizabeth Downs
Elizabeth Downs is a northern suburb of Adelaide, South Australia in the City of Playford. It is east of Main North Road, bounded by Main North Road, Uley Road, Adams Road, Yorktown Road and Garlick Road. The suburb contains two government prima ...
. The two government-funded stations are run by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation ( ABC South Australia) and the Special Broadcasting Service (SBS). The Seven Network and Network Ten
Network 10 (commonly known as Ten Network, Channel 10 or simply 10) is an Australian commercial television network owned by Ten Network Holdings, a division of the Paramount Networks UK & Australia subsidiary of Paramount Global. One of five ...
both own their Adelaide stations ( SAS-7 and ADS-10 respectively). Adelaide's NWS-9 is part of the Nine Network
The Nine Network (stylised 9Network, commonly known as Channel Nine or simply Nine) is an Australian commercial free-to-air television network. It is owned by parent company Nine Entertainment and is one of five main free-to-air television netw ...
. Adelaide also has a community television station, Channel 44.
As part of a nationwide phase-out of analogue television in Australia, Adelaide's analogue television service was shut down on 2 April 2013.
The Foxtel
Foxtel is an Australian pay television company—operating in cable television, direct broadcast satellite television, and IPTV streaming services. It was formed in April 2018, superseding an earlier company from 1995. The service was establi ...
pay TV service is also available via cable or satellite to the entire metropolitan area.
All the major broadcasting networks also operate online on-demand television services, alongside internet-only services such as Stan
Stan or STAN may refer to:
People
* Stan (given name), a list of people with the given name
** Stan Laurel (1890–1965), English comic actor, part of duo Laurel and Hardy
* Stan (surname), a Romanian surname
* Stan! (born 1964), American author ...
, Fetch TV
Fetch TV is an Australian IPTV provider that delivers a subscription television service over a user's regular internet service. Fetch TV launched in 2010 backed by its Malaysian parent Astro Malaysia Holdings. On 2 August 2022, Telstra acquire ...
, Netflix, YouTube, Disney+, and Kayo Sports.
Radio
There are 20 radio stations that serve the metropolitan area, as well as four stations that serve only parts of the metropolitan area; six commercial stations, six community stations, six national stations and two narrowcast stations.DAB+
DAB, dab, dabs, or dabbing may refer to:
Dictionaries
* ''Dictionary of American Biography'', published under the auspices of the American Council of Learned Societies
* ''Dictionary of Australian Biography'', published since 1949
Places
* Dąb, ...
digital radio has been broadcasting in metropolitan Adelaide since 20 May 2009, and currently offers a choice of 41 stations all operated by the existing licensed radio broadcasters, which includes high-quality simulcast of all AM and FM stations.
Sport

 The main sports played professionally in Adelaide are
The main sports played professionally in Adelaide are Australian Rules football
Australian football, also called Australian rules football or Aussie rules, or more simply football or footy, is a contact sport played between two teams of 18 players on an oval field, often a modified cricket ground. Points are scored by k ...
, association football (soccer), cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
, netball, and basketball. Adelaide is the home of two Australian Football League
The Australian Football League (AFL) is the only fully professional competition of Australian rules football. Through the AFL Commission, the AFL also serves as the sport's governing body and is responsible for controlling the laws of the gam ...
teams: the Adelaide Football Club
The Adelaide Crows (officially the Adelaide Football Club) are a professional Australian rules football team based in Adelaide, South Australia. Founded in 1990. The Crows has fielded a men's team in the Australian Football League (AFL) since ...
and Port Adelaide Football Club
Port Adelaide Football Club is a professional Australian rules football club based in Alberton, South Australia, Alberton, South Australia. The club's senior men's team plays in the Australian Football League (AFL), where they are nicknamed ...
, and one A-League
A-League Men (known as the Isuzu UTE A-League for sponsorship reasons) is the highest-level professional men's soccer league in Australia and New Zealand. At the top of the Australian league system, it is the country's premier men's competiti ...
soccer team, Adelaide United. A local Australian rules football
Australian football, also called Australian rules football or Aussie rules, or more simply football or footy, is a contact sport played between two teams of 18 players on an oval field, often a modified cricket ground. Points are scored by k ...
league, the SANFL, is made up of 10 teams from around Adelaide. The SANFL has been in operation since 1877 when it began as the South Australian Football Association (SAFL) before changing its name to the SANFL in 1927. The SANFL is the oldest surviving football league of any code played in Australia.
Adelaide has developed a strong culture of attracting crowds to major sporting events. Until the completion of the 2012–14 renovation and upgrade of the Adelaide Oval, most large sporting events took place at either Football Park (the then home base of the Adelaide Crows, and the then Port Adelaide
Port Adelaide is a port-side region of Adelaide, approximately northwest of the Adelaide CBD. It is also the namesake of the City of Port Adelaide Enfield council, a suburb, a federal and state electoral division and is the main port for the ...
home game venue), or the historic Adelaide Oval, home of the South Australia Redbacks and the Adelaide Strikers cricket teams. Since completion of the upgrade, home games for Adelaide Crows and Port Adelaide now take place at Adelaide Oval.
Since 1884, Adelaide Oval has also hosted an international cricket test every summer, along with a number of One Day International
A One Day International (ODI) is a form of limited overs cricket, played between two teams with international status, in which each team faces a fixed number of overs, currently 50, with the game lasting up to 9 hours. The Cricket World C ...
cricket matches. Memorial Drive Park, adjacent to the Adelaide Oval, used to host Davis Cup and other major tennis events, including the Australian Open and the Adelaide International. Adelaide's professional association football team, Adelaide United, play in the A-League. Founded in 2003, their home ground is Hindmarsh Stadium, which has a capacity of 17,000 and is one of the few purpose-built soccer stadia in Australia. Prior to United's foundation, Adelaide City and West Adelaide represented the city in the National Soccer League
The National Soccer League (NSL) was the top-level soccer league in Australia, run by Soccer Australia and later the Australian Soccer Association. The NSL, the A-League's predecessor, spanned 28 seasons from its inception in 1977 until its d ...
. The two sides, which contest the Adelaide derby against one another, now play in the National Premier Leagues South Australia.
For two years, 1997 and 1998, Adelaide was represented in Australia's top level rugby league, after the New South Wales Rugby League had played a single game per season at the Adelaide Oval for five years starting in 1991. The Adelaide Rams were formed and played in the breakaway Super League
The Super League (officially known as the Betfred Super League due to sponsorship from Betfred and legally known as Super League Europe), is the top-level of the British rugby league system. At present the league consists of twelve teams, of wh ...
(SL) competition in 1997
File:1997 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The movie set of ''Titanic'', the highest-grossing movie in history at the time; ''Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone'', is published; Comet Hale-Bopp passes by Earth and becomes one of t ...
before moving to the new National Rugby League in 1998
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''.
Events January
* January 6 – The '' Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently ...
. Initially playing at the Adelaide Oval, the club moved to the more suitable Hindmarsh Stadium late in the 1998 season. As part of a peace deal with the Australian Rugby League to end the Super League war, the club's owners News Limited (who were also owners of the SL) suddenly closed the club only weeks before the start of the 1999 season.
Adelaide has two professional basketball teams, the men's team being the Adelaide 36ers which plays in the National Basketball League (NBL) and the women's team, the Adelaide Lightning which plays in the Women's National Basketball League
The Women's National Basketball League (WNBL) is the pre-eminent professional women's basketball league in Australia. It is currently composed of eight teams. The league was founded in 1981 and is the women's counterpart to the National Baske ...
(WNBL). Both teams play their home games at the Titanium Security Arena. Adelaide has a professional netball team, the Adelaide Thunderbirds, which plays in the national netball competition, the Suncorp Super Netball championship, with home games played at Priceline Stadium. The Thunderbirds occasionally play games or finals at the Titanium Security Arena, while international netball matches are usually played at the 10,500 seat Adelaide Entertainment Centre. The Titanium Security Arena has a capacity of 8,000 and is the largest purpose-built basketball stadium in Australia.
 Since 1999 Adelaide and its surrounding areas have hosted the Tour Down Under bicycle race, organised and directed by Adelaide-based Michael Turtur. Turtur won an Olympic
Since 1999 Adelaide and its surrounding areas have hosted the Tour Down Under bicycle race, organised and directed by Adelaide-based Michael Turtur. Turtur won an Olympic gold medal
A gold medal is a medal awarded for highest achievement in a non-military field. Its name derives from the use of at least a fraction of gold in form of plating or alloying in its manufacture.
Since the eighteenth century, gold medals have bee ...
for Australia in the 4000 m team pursuit at the 1984 Los Angeles Olympics
The 1984 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXIII Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1984) were an international multi-sport event held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles, California, United States. It marked the secon ...
. The Tour Down Under is the largest cycling event outside Europe and was the first event outside Europe to be granted UCI ProTour status.
Adelaide maintains a franchise in the Australian Baseball League, the Adelaide Giants. They have been playing since 2009, and their home stadium (until 2016) was Norwood Oval
Norwood Oval (currently known as Coopers Stadium due to sponsorship from the Adelaide-based Coopers Brewery) is a suburban oval in the western end of Norwood, an inner eastern suburb of Adelaide, South Australia. It is owned by Norwood, Payn ...
. From 2016 the team moved to the Diamond Sports Stadium located near the Adelaide International Airport due to renovations at Norwood.
Adelaide also has an ice hockey team, Adelaide Adrenaline in the Australian Ice Hockey League (AIHL). It was national champions in 2009 and plays its games at the IceArenA.
The Australian Grand Prix
The Australian Grand Prix is an annual motor racing event which is under contract to host Formula One until 2035. One of the oldest surviving motorsport competitions held in Australia, the Grand Prix has moved frequently with 23 different venu ...
for World Championship Formula One racing was hosted by Adelaide from 1985 to 1995 on the Adelaide Street Circuit which was laid out in the city's East End as well as the eastern parklands including the Victoria Park Racecourse. The Grand Prix became a source of pride, and losing the event to Melbourne in a surprise announcement in mid-1993 left a void that has since been filled with the highly successful Clipsal 500 for V8 Supercar racing, held on a modified version of the same street circuit. The Classic Adelaide, a rally of classic sporting vehicles, is also held in the city and its surrounds.
Adelaide formerly had three horse racing venues. Victoria Park, Cheltenham Park Racecourse, both of which have now closed, and Morphettville Racecourse that remains the home of the South Australian Jockey Club
South Australian Jockey Club is the principal race club in South Australia.
First racing events
The first horse racing events in South Australia took place at a well-attended picnic meeting held over 1 and 2 January 1838. In August 1838, ridin ...
. It also has Globe Derby Park for Harness racing
Harness racing is a form of horse racing in which the horses race at a specific gait (a trot or a pace). They usually pull a two-wheeled cart called a sulky, or spider, or chariot occupied by a driver. In Europe, and less frequently in Australi ...
that opened in 1969, and by 1973 had become Adelaide's premier harness racing venue taking over from the Wayville Showgrounds, as well as Greyhound Park for greyhound racing
Greyhound racing is an organized, competitive sport in which greyhounds are raced around a track. There are two forms of greyhound racing, track racing (normally around an oval track) and coursing; the latter is now banned in most countries. Tra ...
that opened in 1972.
The World Solar Challenge race attracts teams from around the world, most of which are fielded by universities or corporations, although some are fielded by high schools. The race has a 20-years' history spanning nine races, with the inaugural event taking place in 1987. Adelaide hosted the 2012 World Bowls Championships at Lockleys Bowling Club, becoming the third city in the world to have held the championships twice, having previously hosted the event in 1996.
Dirt track speedway is also popular in Adelaide with three operating speedways. Adelaide Motorsport Park, located adjacent to the Adelaide International Raceway road racing circuit at Virginia ( north of the city centre) has been in continuous operation since 1979 after the closure of the popular Rowley Park Speedway. Gillman Speedway located in the semi-industrial suburb of Gillman, has been in operation since 1998 and caters to Motorcycle speedway
Motorcycle speedway, usually referred to simply as speedway, is a motorcycle sport involving four and sometimes up to six riders competing over four anti-clockwise laps of an oval circuit. The motorcycles are specialist machines that use only ...
and Sidecars, while the Sidewinders Speedway located in Wingfield is also a motorcycle speedway dedicated to Under-16 riders and has been in operation since 1978. In 2016, backed my South Australia's Peregrine Group owners of OTR (On the run service stations and 24/7-hour convenient stores) opened up a multi-purpose facility; a state-of-the-art motorsporting park and a hotel alongside its newer OTR service station outside a small township of Tailem Bend currently named The Bend Motorsport Park. Design for thrill seekers and rev-heads the facility currently host South Australia's second V8 Supercars motoring event during a round in August and hopes to bring in other major international motoring events such as SBK Superbikes SBK may refer to:
*SBK Records, former record label
*ShoreBank insolvent US community development bank acquired by the Urban Partnership Bank
*Silver Bells Killer
*Superbike World Championship
*'' SBK: Snowboard Kids'', video game
*South Brooklyn Ra ...
and other well established FIA motoring events.
Adelaide is home to the Great Southern Slam, the world's largest roller derby
Roller derby is a roller skating contact sport played by two teams of fifteen members. Roller derby is played by approximately 1,250 amateur leagues worldwide, mostly in the United States.
Game play consists of a series of short scrimmages (jam ...
tournament. The tournament has been held biennially over Australia's Queen's Birthday holiday weekend since 2010. In 2014, and 2016 the tournament featured 45 teams playing in two divisions. In 2018, the tournament has expanded to 48 teams competing in three divisions.
Infrastructure
Transport
Hindmarsh
Hindmarsh is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Alfred Hindmarsh, MP for Wellington South (New Zealand electorate) and first leader of the New Zealand Labour Party
*Ian Hindmarsh, Australian rugby league player
* Jean Hindm ...
, the city centre, and seaside Glenelg. Tramways were largely dismantled in the 1950s, but saw a revival in the 2010s with upgrades and extensions.
Road transport in Adelaide has historically been easier than many of the other Australian cities, with a well-defined city layout and wide multiple-lane roads from the beginning of its development. Adelaide was known as a "twenty-minute city", with commuters having been able to travel from metropolitan outskirts to the city proper in roughly twenty minutes. However, such arterial roads often experience traffic congestion as the city grows.
 The Adelaide metropolitan area has one freeway and four expressways. In order of construction, they are:
* The South Eastern Freeway (M1), connects the south-east corner of the Adelaide Plain to the Adelaide Hills and beyond to
The Adelaide metropolitan area has one freeway and four expressways. In order of construction, they are:
* The South Eastern Freeway (M1), connects the south-east corner of the Adelaide Plain to the Adelaide Hills and beyond to Murray Bridge Murray Bridge may refer to.
*Murray Bridge, South Australia, a city and locality
*Rural City of Murray Bridge, a local government area in South Australia
*Corporate Town of Murray Bridge, a former local government area in South Australia
See also
...
and Tailem Bend, where it then continues as National Highway 1 south-east to Melbourne.
* The Southern Expressway
Southern Expressway may refer to:
*Southern Expressway (Adelaide), South Australia
* E01 expressway (Sri Lanka)
*A portion of U.S. Route 219 in New York
U.S. Route 219 (US 219) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from Rich ...
(M2), connecting the outer southern suburbs with the inner southern suburbs and the city centre. It duplicates the route of South Road.
* The North-South Motorway (M2), is an ongoing major project that will become the major north–south corridor, replacing most of what is now South Road, connecting the Southern Expressway
Southern Expressway may refer to:
*Southern Expressway (Adelaide), South Australia
* E01 expressway (Sri Lanka)
*A portion of U.S. Route 219 in New York
U.S. Route 219 (US 219) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from Rich ...
and the Northern Expressway via a motorway with no traffic lights. As of 2020 the motorway's northern half is complete (save for a small link under construction at Croydon Park), connecting the Northern Expressway to Adelaide's inner north-west; the section running through Adelaide's inner west and inner south-west is awaiting funding.
* The Port River Expressway (A9), connects Port Adelaide and Outer Harbor to Port Wakefield Road at the northern "entrance" to the metropolitan area.
* The Northern Expressway (Max Fatchen Expressway) (M2), is the northern suburbs bypass route connecting the Sturt Highway (National Highway 20) via the Gawler Bypass to Port Wakefield Road at a point a few kilometres north of the Port River Expressway connection.
* The Northern Connector, completed in 2020, links the North South Motorway to the Northern Expressway.
Airports
 The Adelaide metropolitan area has two commercial airports, Adelaide Airport and Parafield Airport. Adelaide Airport, in Adelaide's south-western suburbs, serves in excess of 8 million passengers annually. Parafield Airport, Adelaide's second airport north of the city centre, is used for small aircraft, pilot training and recreational aviation purposes. Parafield Airport served as Adelaide's main aerodrome until the opening of the Adelaide Airport in February 1955. Adelaide airport serves many international and domestic destinations including all Australian state capitals.
Adelaide is also home to a military airport, known as Edinburgh Airport, located in the northern suburbs. It was built in 1955 in a joint initiative with the UK for weapon development.
The Adelaide metropolitan area has two commercial airports, Adelaide Airport and Parafield Airport. Adelaide Airport, in Adelaide's south-western suburbs, serves in excess of 8 million passengers annually. Parafield Airport, Adelaide's second airport north of the city centre, is used for small aircraft, pilot training and recreational aviation purposes. Parafield Airport served as Adelaide's main aerodrome until the opening of the Adelaide Airport in February 1955. Adelaide airport serves many international and domestic destinations including all Australian state capitals.
Adelaide is also home to a military airport, known as Edinburgh Airport, located in the northern suburbs. It was built in 1955 in a joint initiative with the UK for weapon development.
Health
 Adelaide's two largest hospitals are the Royal Adelaide Hospital (RAH) in the city centre, a teaching hospital affiliated with the University of Adelaide (800 beds), and the Flinders Medical Centre (580 beds) in Bedford Park, affiliated with Flinders University. The RAH also operates additional campuses for specialist care throughout the suburbs including the Hampstead Rehabilitation Centre (150 beds) in Northfield and the Glenside Campus (129 beds) for acute mental health services. Other major public hospitals are the
Adelaide's two largest hospitals are the Royal Adelaide Hospital (RAH) in the city centre, a teaching hospital affiliated with the University of Adelaide (800 beds), and the Flinders Medical Centre (580 beds) in Bedford Park, affiliated with Flinders University. The RAH also operates additional campuses for specialist care throughout the suburbs including the Hampstead Rehabilitation Centre (150 beds) in Northfield and the Glenside Campus (129 beds) for acute mental health services. Other major public hospitals are the Women's and Children's Hospital
The Women's and Children's Hospital is located on King William Road in North Adelaide, Australia.
It is one of the major hospitals in Adelaide and is a teaching hospital of the University of Adelaide, the University of South Australia and Flin ...
(305 beds), in North Adelaide; the Queen Elizabeth Hospital (340 beds) in Woodville; Modbury Hospital (178 beds) in Modbury; and the Lyell McEwin Hospital (198 beds) in Elizabeth. Numerous private hospitals are also located throughout the city, with the largest operators being not-for-profits Adelaide Community Healthcare Alliance
Adelaide Community Healthcare Alliance is a South Australian private hospital group incorporated on 9 November 1999. Healthscope has had day-to-day operational responsibility for the hospitals since 2003.
It comprises the following hospitals:
* ...
(3 hospitals) and Calvary Care (4 hospitals).
In 2017, the RAH was relocated from the city's East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
to a new AU$2.3 billion facility built over former railyards in the West End. The state-of-the-art hospital forms part of a new biomedical precinct called BioMed City
BioMed Central (BMC) is a United Kingdom-based, for-profit scientific open access publisher that produces over 250 scientific journals. All its journals are published online only. BioMed Central describes itself as the first and largest open a ...
that collocates the South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI), the University of Adelaide Health and Medical Sciences building, the University of South Australia's Health Innovation Building, and the state's Dental Hospital. SAHMRI is building a $300 million second facility due to be completed by 2022 to house the Australian Bragg Centre with Australia's first proton therapy
In medicine, proton therapy, or proton radiotherapy, is a type of particle therapy that uses a beam of protons to irradiate diseased tissue, most often to treat cancer. The chief advantage of proton therapy over other types of external beam ra ...
unit. There are also plans for the Women's and Children's Hospital
The Women's and Children's Hospital is located on King William Road in North Adelaide, Australia.
It is one of the major hospitals in Adelaide and is a teaching hospital of the University of Adelaide, the University of South Australia and Flin ...
to be relocated to the precinct adjacent the RAH by 2024.
 The largest provider of community health care within Adelaide is the not-for-profit Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), which provides out of hospital care and hospital avoidance care.
The largest provider of community health care within Adelaide is the not-for-profit Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), which provides out of hospital care and hospital avoidance care.
Energy
Adelaide's energy requirements were originally met by the Adelaide Electric Supply Company, which was nationalised by the Playford government in 1946, becoming the Electricity Trust of South Australia (ETSA). Despite significant public opposition and the Labor party's anti-privatisation stance which left the Liberal party one vote short of the numbers needed to pass the legislation, ETSA was privatised by theOlsen Olsen or Ölsen may refer to:
*Olsen (surname), people with the surname ''Olsen''
* Fred. Olsen & Co., a large shipping company with worldwide headquarters in Oslo, Norway
*Ölsen, municipality in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
* Olsen House, a his ...
Government in 1999 by way of a 200-year lease for the distribution network (ETSA Utilities, later renamed SA Power Networks) and the outright purchase of ETSA Power by the Cheung Kong Holdings for $3.5 billion (11 times ETSA's annual earnings) after Labor MP Trevor Crothers
Trevor Crothers (20 May 1938 – 9 July 2002) was a South Australian politician. Crothers entered the South Australian Legislative Council in 1987 to fill a Labor Party vacancy, and then was re-elected as a Labor candidate in 1993. However h ...
resigned from the party and voted with the government.
The electricity retail market was opened to competition in 2003 and although competition was expected to result in lower retail costs, prices increased by 23.7% in the market's first year. In 2004, the privatisation was deemed to be a failure with consumers paying 60% more for their power and with the state government estimated to lose $3 billion in power generation net income in the first ten years of privatisation. In 2012, the industry came under scrutiny for allegedly reducing supply by shutting down generators during periods of peak demand to force prices up. Increased media attention also revealed that in 2009 the state government had approved a 46% increase in retail prices to cover expected increases in the costs of generation while generation costs had in fact fallen 35% by 2012. South Australia has the highest retail price for electricity in the country.
Privatisation led to competition from a variety of companies who now separately provide for the generation, transmission, distribution and retail sales of gas and electricity. Electricity generation comes from a range of technologies and operators. ElectraNet operates the high-voltage electricity transmission network. SA Power Networks distributes electricity to end users. The largest electricity and gas retailing companies are also the largest generating companies.
The largest fossil fuel power stations are the Torrens Island Power Station gas-fired plant operated by AGL Energy
AGL Energy Ltd () is an Australian listed public company involved in both the generation and retailing of electricity and gas for residential and commercial use. AGL is Australia's largest electricity generator, and the nation's largest carbo ...
and the Pelican Point Power Station operated by Engie. South Australia also has wind and solar power and connections to the national grid. Gas is supplied from the Moomba Gas Processing Plant in the Cooper Basin via the Moomba Adelaide Pipeline System and the SEAGas pipeline
The SEA Gas pipeline ''(South East Australia Gas pipeline)'' is a 687 km natural gas pipeline from the Iona Gas Plant near Port Campbell in Victoria to the Pelican Point Power Station at Port Adelaide. It connects Adelaide's gas supply to s ...
from Victoria.
In 2011, South Australia generated 18% of its electricity from wind power, and had 51% of the installed capacity of wind generators in Australia.
Due to almost universal blackouts within the city during September 2016, the state worked with Tesla to produce the world's largest electricity battery at Hornsdale Power Reserve which has increased that state's electrical security to the extent in which large blackouts are no longer an event.
Water
 The provision of water services is by the government-owned SA Water. Adelaide's water is supplied from its seven reservoirs: Mount Bold, Happy Valley, Myponga, Millbrook, Hope Valley, Little Para and South Para. The yield from these reservoir catchments can be as little as 10% of the city's requirements (90GL per annum) in drought years and about 60% in average years. The remaining demand is met by the pumping of water from the
The provision of water services is by the government-owned SA Water. Adelaide's water is supplied from its seven reservoirs: Mount Bold, Happy Valley, Myponga, Millbrook, Hope Valley, Little Para and South Para. The yield from these reservoir catchments can be as little as 10% of the city's requirements (90GL per annum) in drought years and about 60% in average years. The remaining demand is met by the pumping of water from the River Murray
The Murray River (in South Australia: River Murray) (Ngarrindjeri: ''Millewa'', Yorta Yorta: ''Tongala'') is a river in Southeastern Australia. It is Australia's longest river at extent. Its tributaries include five of the next six longest r ...
.
A sea-water desalination plant capable of supplying 100GL per annum was built during the 2001–2009 drought; however, it operated at about 8% of its capacity until 2019. In December 2018, the State and Federal Governments agreed to fund a $2m study to determine how the plant could be used to reduce reliance on river water, in an effort to help save the Murray River basin and mouth (including the Coorong) from further ecological damage.
Communications
AdelaideFree WiFi is a citywide free Wi-Fi network covering most of the inner city areas of Adelaide, primarily theAdelaide CBD
Adelaide city centre (Kaurna language, Kaurna: Tarndanya) is the inner city locality of Adelaide, Greater Adelaide, the capital city of South Australia. It is known by locals simply as "the City" or "Town" to distinguish it from Greater Adelaid ...
and Northern Adelaide precincts. It was officially launched at the Adelaide Central Markets on Tuesday 25 June 2014. It is provided by Internode, with infrastructure provided by outdoor Cisco WiFi N access points attached to the top of lighting poles, as well as inside cafes and businesses across the city.
See also
* Adelaide city centre includes chart of major streets and squares, street widths, and town acres * Adelaide Hills * City of Adelaide * Music of Adelaide *Port Adelaide
Port Adelaide is a port-side region of Adelaide, approximately northwest of the Adelaide CBD. It is also the namesake of the City of Port Adelaide Enfield council, a suburb, a federal and state electoral division and is the main port for the ...
; Lists
* Images of Adelaide
* List of Adelaide obsolete suburb names
__NOTOC__
This List of Adelaide obsolete suburb names gives suburb names which were officially discontinued before 1994, and their new names or the suburbs into which they were incorporated.
Notes
References
Sources
*''Directory of South ...
* List of Adelaide parks and gardens
* List of Adelaide railway stations
* List of Adelaide suburbs
* List of films shot in Adelaide
This is a list of films shot in Adelaide or in the state of South Australia.
Films
See also
* Australian Film Commission
* Cinema of Australia
* Film Australia
* Screen Australia
* South Australian Film Corporation
* World cinema
* List of Au ...
* List of people from Adelaide
This is a list of notable people from Adelaide.
Arts and music
Prominent intellectuals, writers, artists, bands, and musicians to hail from Adelaide include:
Actors
*Dame Judith Anderson - '' Rebecca'', ''And Then There Were None''; Tony and ...
* List of protected areas in Adelaide
* List of public art in South Australia
This is a list of public art in South Australia organized by town. This list is focused only on outdoor public art, and thus does not encompass works contained within private collections, art galleries or museums.
Adelaide
Kapunda
Port Noa ...
* List of public transport routes in Adelaide
Public transport in Adelaide, South Australia, is managed by the State Government's Department for Infrastructure & Transport, branded as Adelaide Metro. Today bus services are operated by contractors: Busways, SouthLink, Torrens Connect and T ...
* List of South Australian commercial icons
There have been many Adelaide and South Australian icons, some of which still exist, but few of which are still South Australian owned.
With the start of the 21st century, and in conjunction with the National Trust (SA), BankSA launched its ann ...
* List of sporting clubs in Adelaide
The following is a partial list of sports clubs in Adelaide, the capital of South Australia.
Athletics
* Adelaide University Athletics Club
*Adelaide Eagles Little Athletics Club
*Flinders Athletics Club
Australian rules football
Australian Fo ...
* List of tallest buildings in Adelaide
* Sister cities of the City of Adelaide (the Local government area that governs the city centre)
* Tourist attractions in South Australia
Notes
References
Further reading
* * (full text) * * *External links
Adelaide City Council > Official City Guide
Adelaide City Council
Kids in Adelaide
Retrieved 12 May 2020. {{Authority control 1836 establishments in Australia Australian capital cities Cities in South Australia Coastal cities in Australia Planned capitals Populated places established in 1836 Metropolitan areas of Australia