|
Stanchester Hoard
The Stanchester Hoard is a hoard of 1,166 Roman coins dating from the fourth to early fifth century found in 2000 at Wilcot, in the Vale of Pewsey, Wiltshire, England. The find was considered important because of the large quantity of unclipped silver coins contained within. It was also the latest dated example of Roman coins found in Wiltshire. Discovery The hoard was discovered in a field on 25 July 2000 by John and David Philpotts, using metal detectors. It had been buried in a flagon made from pottery of the Alice Holt type. The hoard was named after the former Stanchester villa, a nearby Roman villa with which the hoard was likely to have been associated, along with the Wansdyke earthwork. Excavations of the villa in 1931 and 1969 revealed a wall and evidence for a Roman central heating system. Roof and flue tiles and pottery shards were dated by associated coins, which were from the 2nd to the 4th centuries. The Wiltshire Museum in Devizes acquired the hoard for £50, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
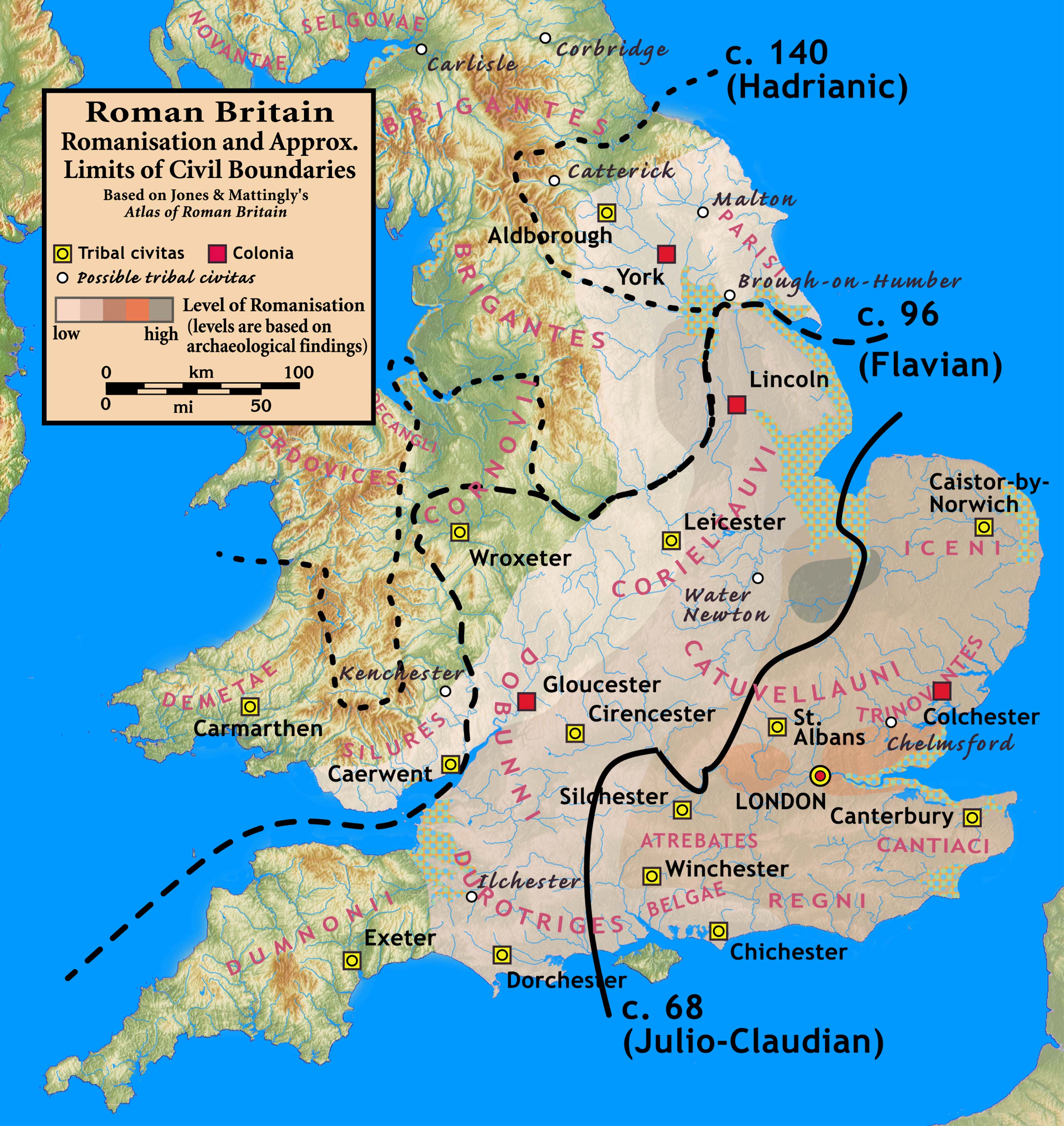
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanchester
Stanchester Academy, formerly Stanchester Community School, is an academy for children between the ages of 11 and 16 in Stoke-sub-Hamdon, Somerset ( en, All The People of Somerset) , locator_map = , coordinates = , region = South West England , established_date = Ancient , established_by = , preceded_by = , origin = , lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset , lord_ ..., England. As of September 2021 it had 791 students. Stanchester Academy has a range of technology facilities. Transport Somerset County Council provides free transport for students in Years 7 – 11 to attend their catchment or nearest appropriate school and they live more than 3 miles shortest available walking distance from home to Stanchester Academy. This is run by the School Transport Department which organises the routes and contract buses. It is possible for other students to apply for a spare seat on a contract bus operated by Somerset School Transport. History The neo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nummus
''Nummus'' ( el, νοῦμμος, ''noummos''), plural ''nummi'' () is a Latin term meaning "coin", but used technically by modern writers for a range of low-value copper coins issued by the Roman and Byzantine empires during Late Antiquity. It comes from the Greek ''nomos'' via its Western Doric form ''noummos'', which was used to describe a coin in some parts of southern Italy. The word was also used during the later years of the Roman Republic and the early Empire, either as a general word for a coin, or to describe the sestertius, which was the standard unit for keeping accounts. History In circa 294 AD, during the Tetrarchy, a new large bronze coin of circa 10 grams weight and 30 mm diameter appeared. Its official name was apparently ''nummus'', although it has until recently been known among numismatists as the ''follis''. The term ''nummus'' is now usually applied solely to the 5th–7th century Byzantine issues. These were small, badly struck coins, weighing le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siliqua
The siliqua (plural ''siliquae'') is the modern name given (without any ancient evidence to confirm the designation) to small, thin, Roman silver coins produced in the 4th century A.D. and later. When the coins were in circulation, the Latin word ''siliqua'' was a unit, perhaps of weight defined by one late Roman writer as one twenty-fourth of a Roman solidus. The term siliqua comes from the ''siliqua graeca'', the seed of the carob tree, which in the Roman weight system is equivalent to of a scruple ( of a Roman pound or about 0.19 grams). The term has been applied in modern times to various silver coins on the premise that the coins were valued at of the gold solidus (which weighed of a Roman pound) and therefore represented a siliqua of gold in value. Since gold was worth about 12 times as much as silver in ancient Rome (in Diocletian's ''Edict of Maxmimum Prices'' of 301),Bransbourg, Giles. "Inflation and monetary reforms in the fourth century: Diocletian's twin Edict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miliarense
The ''miliarense'' (neuter form of the late Latin ''miliarensis'', "pertaining to a thousand"; plural: ''miliarensia'') was a large silver coin, introduced to the late Roman monetary system in the early 4th century. It was struck with variable fineness, generally with a weight between 3.8 and 6.0 grams, and a diameter of c. 23–24 mm. The ''miliarense'' was struck first under Constantine the Great (r. 306–337). There were two kinds of ''miliarense'' coins: light and heavy. It took 14 heavy ''miliarensia'' and 18 light ''miliarensia'' to equal one gold ''solidus'' (as also introduced by Constantine). ''Miliarensia'' are highly desired by numismatists of the present day, due to both the rarity of the denomination (far less common than the '' siliqua'') and the often exquisite execution of both bust and reverse types, which led to many being used as pendants or mounted in antiquity. A variant of the original denomination was revived in the Byzantine silver coinage from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; ''solidi'') or nomisma ( grc-gre, νόμισμα, ''nómisma'', 'coin') was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Late Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire. Constantine introduced the coin, and its weight of about 4.5 grams remained relatively constant for seven centuries. In the Byzantine Empire, the solidus or nomisma remained a highly pure gold coin until the 11th century, when several Byzantine emperors began to strike the coin with less and less gold. The nomisma was finally abolished by Alexius I in 1092, who replaced it with the hyperpyron, which also came to be known as a "bezant". The Byzantine solidus also inspired the originally slightly less pure dinar issued by the Muslim Caliphate. In Western Europe, the solidus was the main gold coin of commerce from late Roman times to Pepin the Short's currency reform, which introduced the silver-based pound/ shilling/ penny system. In Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, the sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Δάφνῃ "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; la, Antiochia ad Orontem; hy, Անտիոք ''Antiokʽ''; syr, ܐܢܛܝܘܟܝܐ ''Anṭiokya''; he, אנטיוכיה, ''Anṭiyokhya''; ar, أنطاكية, ''Anṭākiya''; fa, انطاکیه; tr, Antakya. was a Hellenistic, and later, a Biblical Christian city, founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. This city served as the capital of the Seleucid Empire and later as regional capital to both the Roman and Byzantine Empire. During the Crusades, Antioch served as the capital of the Principality of Antioch, one of four Crusader states that were founded in the Levant. Its inhabitants were known as ''Antiochenes''; the city's ruin lies on the Orontes River, near Antaky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis ( Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of Macedonia, the administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek as (), literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the () or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the delta of the Axios. The municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical center, had a population of 317,778 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metropolitan area had 1,091,424 inhabitants in 2021. It is Greece's second major economic, industrial, commercial and political centre, and a major transportation hub for Greece and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians and Celts, it was conquered by the Romans in the 1st century BC and subsequently became the capital of the Roman province of Pannonia Inferior. In 294 AD, Sirmium was proclaimed one of four capitals of the Roman Empire. It was also the capital of the Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum and of Pannonia Secunda. The site is protected as an archaeological Site of Exceptional Importance. The modern region of Syrmia (Srem or Srijem) was named after the city. Sirmium purportedly had 100,000 inhabitants and was one of the largest cities of its time. Colin McEvedy, whose estimates for ancient cities are much lower than the general consensus, however, put the population at only 7,000, based on the size of the archaeological site. The amount of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sisak
Sisak (; hu, Sziszek ; also known by other alternative names) is a city in central Croatia, spanning the confluence of the Kupa, Sava and Odra rivers, southeast of the Croatian capital Zagreb, and is usually considered to be where the Posavina (Sava basin) begins, with an elevation of 99 m. The city's total population in 2011 was 47,768 of which 33,322 live in the urban settlement (naselje). Sisak is the administrative centre of the Sisak-Moslavina County, Croatia's biggest river port and a centre of river shipping industry (Dunavski Lloyd). It lies on the D36 state road and the Zagreb-Sisak-Novska railway. Sisak is a regional economic, cultural and historical center. The largest oil refinery in Croatia is here. Name Prior to belonging to the Roman Empire, which gave it the Latin name Siscia, the region was Celtic and Illyrian and the city there was named Segestica or Segesta. Writers in Greek referred to the city as grc, Σισκία, Siskía, Σεγέστα ''Segésta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquileia
Aquileia / / / / ;Bilingual name of ''Aquileja – Oglej'' in: vec, Aquiłeja / ; Slovenian: ''Oglej''), group=pron is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river Natiso (modern Natisone), the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times. Today, the city is small (about 3,500 inhabitants), but it was large and prominent in classical antiquity as one of the world's largest cities with a population of 100,000 in the 2nd century AD and is one of the main archaeological sites of northern Italy. In late antiquity the city was the first city in the Italian Peninsula to be sacked by Attila the Hun. History Classical Antiquity Roman Republic Aquileia was founded as a colony by the Romans in 180/181 BC along the Natiso River, on land south of the Julian Alps but about north of the lagoons. The colony served as a strategic frontier fortress at the north-east corner of transpadane Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |