|
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Londinium
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. It was originally a settlement established on the current site of the City of London around AD 47–50. It sat at a key crossing point over the River Thames which turned the city into a road nexus and major port, serving as a major commercial centre in Roman Britain until its abandonment during the 5th century. Following the foundation of the town in the mid-1st century, early Londinium occupied the relatively small area of , roughly half the area of the modern City of London and equivalent to the size of present-day Hyde Park. In the year 60 or 61, the rebellion of the Iceni under Boudica compelled the Roman forces to abandon the settlement, which was then razed. Following the defeat of Boudica by the Roman governor Gaius Suetonius Paulinus a military installation was established and the city was rebuilt. It had probably largely recovered within about a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
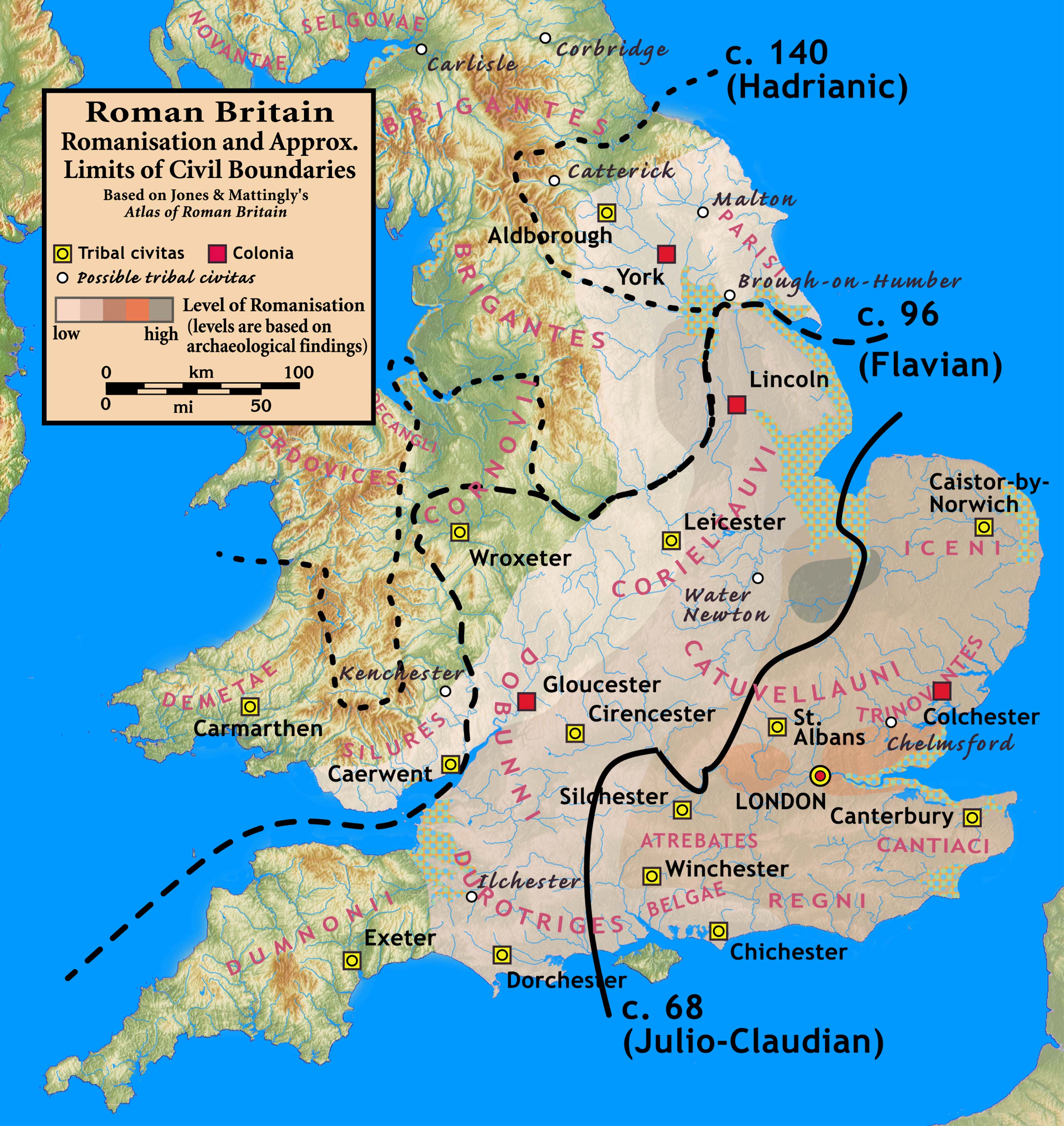
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was raised to the status of a Roman province. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by other Celtic tribes during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells ('' musculi'') according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea. Three years later, Claudius directed four legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain is the period of late antiquity in Great Britain between the end of Roman rule and the Anglo-Saxon settlement. The term was originally used to describe archaeological remains found in 5th- and 6th-century AD sites that hinted at the decay of locally made wares from a previous higher standard under the Roman Empire. It is now used to describe the period that commenced with the evacuation of Roman troops to Gaul by Constantine III in 407 and to have concluded with the Battle of Deorham in 577. Meaning of terms The period of sub-Roman Britain traditionally covers the history of the area which subsequently became England from the end of Roman imperial rule, traditionally dated to be in 410, to the arrival of Saint Augustine in 597. The date taken for the end of this period is arbitrary in that the sub-Roman culture continued in northern England until the merger of Rheged (the kingdom of the Brigantes) with Northumbria by dynastic marriage in 633, and longer i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, Cornish and Bretons (among others). They spoke the Common Brittonic language, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman writers and dates to the Iron Age.Koch, pp. 291–292. Celtic Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various hillforts. The Britons followed an Ancient Celtic religion overseen by druids. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Belgica, and minted their own coins. The Roman Empire conquered most of Britain in the 1st century, creating the province of Britannia. The Romans invaded northern Britain, but the Britons and Caledonians in the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
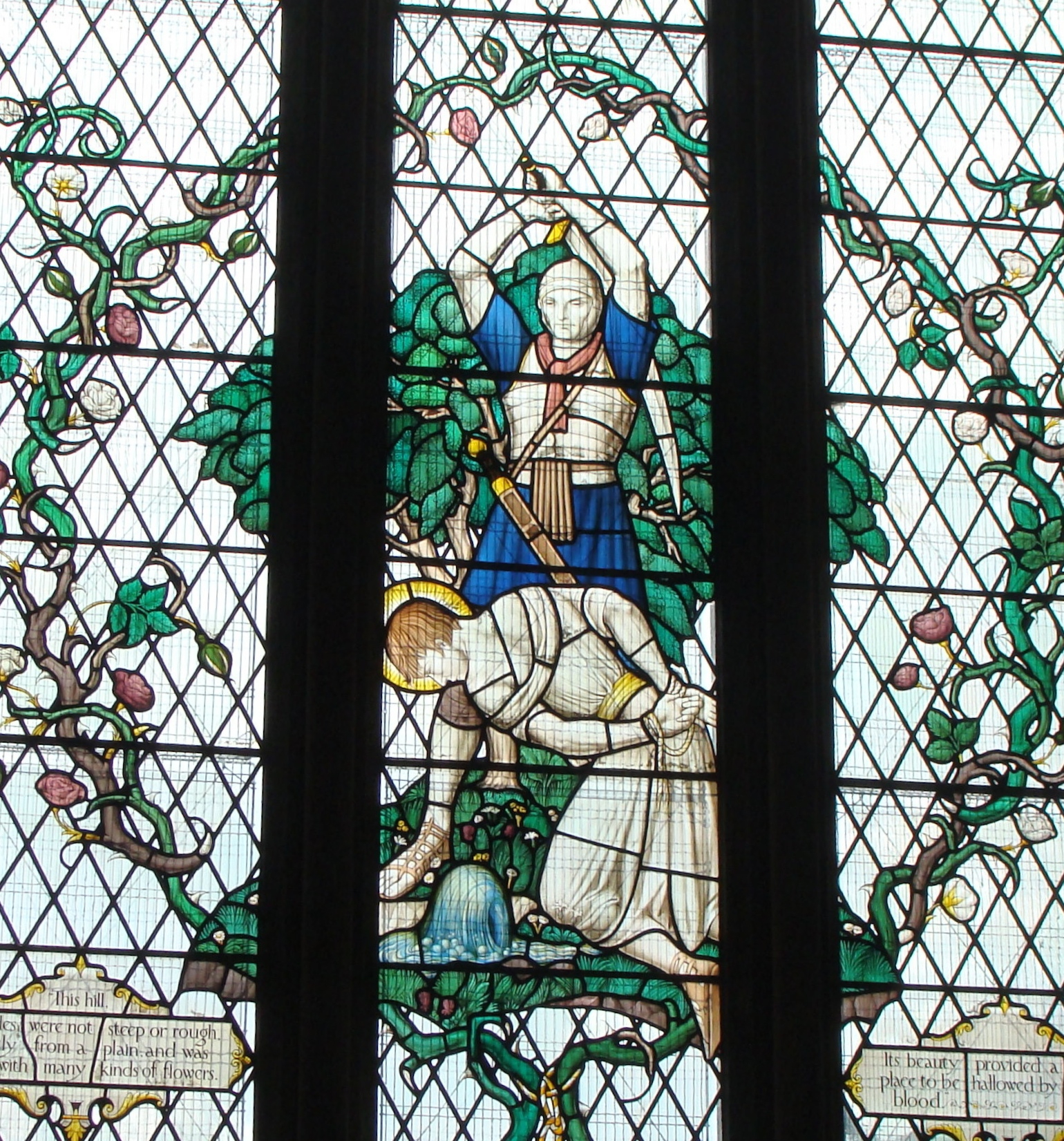
Saint Alban
Saint Alban (; la, Albanus) is venerated as the first-recorded British Christian martyr, for which reason he is considered to be the British protomartyr. Along with fellow Saints Julius and Aaron, Alban is one of three named martyrs recorded at an early date from Roman Britain (" Amphibalus" was the name given much later to the priest he was said to have been protecting). He is traditionally believed to have been beheaded in Verulamium (modern St Albans) sometime during the 3rd or 4th century, and his cult has been celebrated there since ancient times. Hagiography Alban lived in Roman Britain, but little is known about his religious affiliations, socioeconomic status, or citizenship. According to the most elaborate version of the tale found in Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', in the 3rd or 4th century (see dating controversy below), Christians began to suffer "cruel persecution", and Alban was living in Verulamium. However, Gildas says he crossed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustine Of Canterbury
Augustine of Canterbury (early 6th century – probably 26 May 604) was a monk who became the first Archbishop of Canterbury in the year 597. He is considered the "Apostle to the English" and a founder of the English Church.Delaney ''Dictionary of Saints'' pp. 67–68 Augustine was the prior of a monastery in Rome when Pope Gregory the Great chose him in 595 to lead a mission, usually known as the Gregorian mission, to Britain to Christianize King Æthelberht and his Kingdom of Kent from Anglo-Saxon paganism. Kent was probably chosen because Æthelberht had married a Christian princess, Bertha, daughter of Charibert I the King of Paris, who was expected to exert some influence over her husband. Before reaching Kent, the missionaries had considered turning back, but Gregory urged them on, and in 597, Augustine landed on the Isle of Thanet and proceeded to Æthelberht's main town of Canterbury. King Æthelberht converted to Christianity and allowed the missionaries t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened within Britain, and the identity was not merely imported. Anglo-Saxon identity arose from interaction between incoming groups from several Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes, both amongst themselves, and with Celtic Britons, indigenous Britons. Many of the natives, over time, adopted Anglo-Saxon culture and language and were assimilated. The Anglo-Saxons established the concept, and the Kingdom of England, Kingdom, of England, and though the modern English language owes somewhat less than 26% of its words to their language, this includes the vast majority of words used in everyday speech. Historically, the Anglo-Saxon period denotes the period in Britain between about 450 and 1066, after Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2021 of 3,107,500 and has a total area of . Wales has over of coastline and is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperateness, north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff. Welsh national identity emerged among the Celtic Britons after the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was formed as a Kingdom of Wales, kingdom under Gruffydd ap Llywelyn in 1055. Wales is regarded as one of the Celtic nations. The Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by Edward I of England was completed by 1283, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European part of Turkey), Egypt, Iran, the Levant (including Syria (region), Ash-Shām and Cyprus), Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), and the Socotra Governorate, Socotra Archipelago (a part of Yemen). The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and has been viewed by some to be discriminatory or too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia (including Iran), but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt (not just the Sina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 70,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing" division. Routledge is headquartered in the main T&F office in Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxfordshire and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by some, simply as the Continent. When Eurasia is regarded as a single continent, Europe is treated as a subcontinent, and called as European subcontinent. The old notion of Europe as a cultural term was centred on core Europe (''Kerneuropa''), the continental territory of the historical Carolingian Empire, corresponding to modern France, Italy, German-speaking Europe and the Benelux states (historical Austrasia). This historical core of "Carolingian Europe" was consciously invoked in the 1950s as the historical ethno-cultural basis for the prospective European integration (see also Multi-speed Europe). Usage The most common definition of Mainland Europe excludes these continental islands: the Greek Islands, Cyprus, Malta, Sicily, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |