|
Spatial Transcriptomics
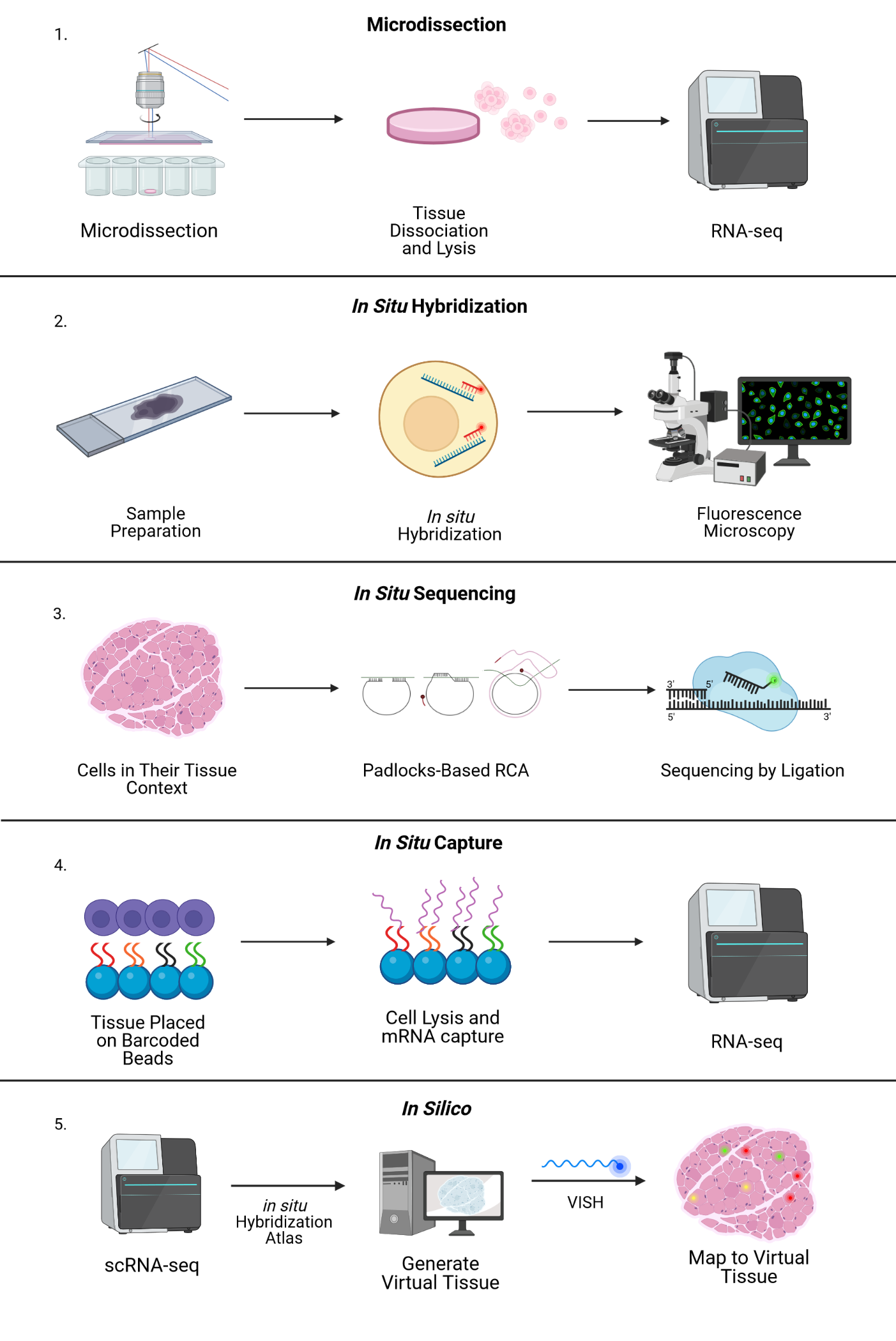
Spatial transcriptomics is a method for assigning cell types (identified by the mRNA readouts) to their locations in the histological sections. This method can also be used to determine subcellular localization of mRNA molecules. The term is a variation of Spatial Genomics, first described by Doyle, et al., in 2000 and then expanded upon by Ståhl et al. in a technique developed in 2016, which has since undergone a variety of improvements and modifications. The Ståhl method implies positioning individual tissue samples on the arrays of spatially barcoded reverse transcription primers able to capture mRNA with the tails. Besides tail and spatial barcode, which indicates the x and y position on the arrayed slide, the probe contains a cleavage site, amplification and sequencing handle, and unique molecular identifier. Commonly, histological samples are cut using cryotome, then fixed, stained, and put on the microarrays. After that, it undergoes enzymatic permeabilization, so tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dimensional structural configuration. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of ''individual'' genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of ''all'' of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Illinois At Chicago
The University of Illinois Chicago (UIC) is a Public university, public research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its campus is in the Near West Side, Chicago, Near West Side community area, adjacent to the Chicago Loop. The second campus established under the University of Illinois system, UIC is also the largest university in the Chicago metropolitan area, having more than 33,000 students enrolled in 16 colleges. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity." The roots of UIC can be traced to the establishment of the Chicago College of Pharmacy in 1859, which was joined in the 1800s by additional medical related schools. It began an undergraduate program toward the end of World War II, and developed its West side campus in the 1960s. In 1982, it consolidated the University of Illinois at Chicago Circle and the University of Illinois at the Medical Center into the present universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-Seq
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a sequencing technique which uses next-generation sequencing (NGS) to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample at a given moment, analyzing the continuously changing cellular transcriptome. Specifically, RNA-Seq facilitates the ability to look at alternative gene spliced transcripts, post-transcriptional modifications, gene fusion, mutations/SNPs and changes in gene expression over time, or differences in gene expression in different groups or treatments. In addition to mRNA transcripts, RNA-Seq can look at different populations of RNA to include total RNA, small RNA, such as miRNA, tRNA, and ribosomal profiling. RNA-Seq can also be used to determine exon/intron boundaries and verify or amend previously annotated 5' and 3' gene boundaries. Recent advances in RNA-Seq include single cell sequencing, in situ sequencing of fixed tissue, and native RNA molecule sequencing with single-molecule real-time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-cell Transcriptomics
Single-cell transcriptomics examines the gene expression level of individual cells in a given population by simultaneously measuring the RNA concentration (conventionally only messenger RNA (mRNA)) of hundreds to thousands of genes. Single-cell transcriptomics makes it possible to unravel heterogeneous cell populations, reconstruct cellular developmental pathways, and model transcriptional dynamics — all previously masked in bulk RNA sequencing. Background The development of high-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and microarrays has made gene expression analysis a routine. RNA analysis was previously limited to tracing individual transcripts by Northern blots or quantitative PCR. Higher throughput and speed allow researchers to frequently characterize the expression profiles of populations of thousands of cells. The data from bulk assays has led to identifying genes differentially expressed in distinct cell populations, and biomarker discovery. These studies are limited as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Cell Sequencing
Single-cell sequencing examines the sequence information from individual cells with optimized next-generation sequencing technologies, providing a higher resolution of cellular differences and a better understanding of the function of an individual cell in the context of its microenvironment. For example, in cancer, sequencing the DNA of individual cells can give information about mutations carried by small populations of cells. In development, sequencing the RNAs expressed by individual cells can give insight into the existence and behavior of different cell types. In microbial systems, a population of the same species can appear genetically clonal. Still, single-cell sequencing of RNA or epigenetic modifications can reveal cell-to-cell variability that may help populations rapidly adapt to survive in changing environments. Background A typical human cell consists of about 2 x 3.3 billion base pairs of DNA and 600 million mRNA bases. Usually, a mix of millions of cells is used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Institute
The Eli and Edythe L. Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard (IPA: , pronunciation respelling: ), often referred to as the Broad Institute, is a biomedical and genomic research center located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. The institute is independently governed and supported as a 501(c)(3) nonprofit research organization under the name Broad Institute Inc., and it partners with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Harvard University, and the five Harvard teaching hospitals. History The Broad Institute evolved from a decade of research collaborations among MIT and Harvard scientists. One cornerstone was the Center for Genome Research of Whitehead Institute at MIT. Founded in 1982, the Whitehead became a major center for genomics and the Human Genome Project. As early as 1995, scientists at the Whitehead started pilot projects in genomic medicine, forming an unofficial collaborative network among young scientists interested in genomic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockholm
Stockholm () is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, largest city of Sweden as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the Stockholm Municipality, municipality, with 1.6 million in the Stockholm urban area, urban area, and 2.4 million in the Metropolitan Stockholm, metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Mälaren, Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Outside the city to the east, and along the coast, is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the county seat of Stockholm County. For several hundred years, Stockholm was the capital of Finland as well (), which then was a part of Sweden. The population of the municipality of Stockholm is expected to reach o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Embryo Project
The Visible Embryo Project (VEP) is a multi-institutional, multidisciplinary research project originally created in the early 1990s as a collaboration between the Developmental Anatomy Center at the National Museum of Health and Medicine and the Biomedical Visualization Laboratory (BVL) at the University of Illinois at Chicago, "to develop software strategies for the development of distributed biostructural databases using cutting-edge technologies for high-performance computing and communications (HPCC), and to implement these tools in the creation of a large-scale digital archive of multidimensional data on normal and abnormal human development." This project related to BVL's other research in the areas of health informatics, educational multimedia, and biomedical imaging science. Over the following decades, the list of VEP collaborators grew to include over a dozen universities, national laboratories, and companies around the world. An early (1993) goal of the project was to ena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Mason University
George Mason University (George Mason, Mason, or GMU) is a public research university in Fairfax County, Virginia with an independent City of Fairfax, Virginia postal address in the Washington, D.C. Metropolitan Area. The university was originally founded in 1949 as a Northern Virginia regional branch of the University of Virginia. Named after Founding Father of the United States George Mason in 1959, it became an independent university in 1972. The school has since grown into the largest public university in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Mason operates four campuses in Virginia ( Fairfax, Arlington, Front Royal, and Prince William), as well as a campus in Incheon, South Korea. The flagship campus is in Fairfax. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Two professors were awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics during their time at George Mason University: James M. Buchanan in 1986 and Vernon L. Smith in 2002. Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eolas
Eolas (, meaning "Knowledge"; bacronym: "Embedded Objects Linked Across Systems") is a United States technology firm formed as a spin-off from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), in order to commercialize UCSF's patents for work done there by Eolas' co-founders, as part of the Visible Embryo Project. The company was founded in 1994 by Dr. Michael Doyle, Rachelle Tunik, David Martin, and Cheong Ang from the UCSF Center for Knowledge Management (CKM). The company was created at the request of UCSF, and was founded by the inventors of the university's patents. In addition to the work done while at UCSF, Dr. Doyle has led work at Eolas to create new technologies ranging from Spatial Genomics/Spatial transcriptomics, Code signing, transient-key cryptography, and blockchain to mobile AI assistants and automated audio conversation annotation. The University of California, San Francisco CKM team created an advanced early web browser that supported plugins, streaming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unique Molecular Identifier
Unique molecular identifiers (UMIs), or molecular barcodes (MBC) are short sequences or molecular "tags" added to DNA fragments in some next generation sequencing library preparation protocols to identify the input DNA molecule. These tags are added before PCR amplification, and can be used to reduce errors and quantitative bias introduced by the amplification. Applications include variant calling in ctDNA, gene expression in single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) and haplotyping via linked reads. See also * Batch effect * Multiplex (assay) In the biological sciences, a multiplex assay is a type of immunoassay that uses magnetic beads to simultaneously measure multiple analytes in a single experiment. A multiplex assay is a derivative of an ELISA using beads for binding the capture a ... References DNA sequencing {{genetics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14592057920).jpg)
_B2.jpg)




