|
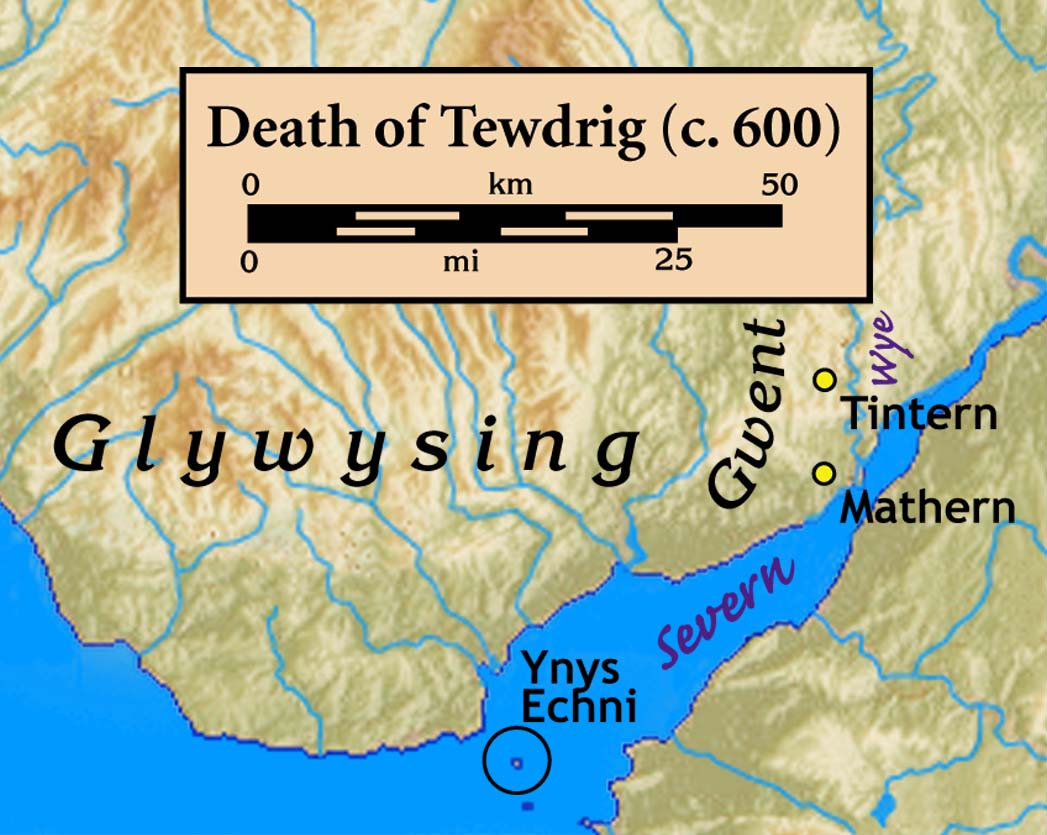
St. Tewdric
Tewdrig ap Teithfallt (; la, Theodoricus), known simply as Tewdrig, was a king of the post-Roman Kingdom of Glywysing. He abdicated in favour of his son Meurig (Maurice) and retired to live a hermitical life, but was recalled to lead his son's army against an intruding Saxon force. He won the battle, but was mortally wounded. The context of the battle is one of Britons versus invading Saxons, without explicit religious overtones. Since Tewdrig held to a religious lifestyle and was killed while defending a Christian kingdom against pagans, by the standards of that day Tewdrig is considered to be a martyr and a saint. The Latin form of his name is given as 'Theodoric' and his feast day is 1 April. Tewdrig's name appears in a genealogy of Jesus College MS 20, in the line of one of his descendants, but the only substantive information about the person comes from the twelfth century '' Book of Llandaff''. The ''Book of Llandaff'' places Tewdrig's story in the territory of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pewter
Pewter () is a malleable metal alloy consisting of tin (85–99%), antimony (approximately 5–10%), copper (2%), bismuth, and sometimes silver. Copper and antimony (and in antiquity lead) act as hardeners, but lead may be used in lower grades of pewter, imparting a bluish tint. Pewter has a low melting point, around , depending on the exact mixture of metals. The word ''pewter'' is probably a variation of the word ''spelter'', a term for zinc alloys (originally a colloquial name for zinc). History Pewter was first used around the beginning of the Bronze Age in the Near East. The earliest known piece of pewter was found in an Egyptian tomb, c. 1450 BC, but it is unlikely that this was the first use of the material. Pewter was used for decorative metal items and tableware in ancient times by the Egyptians and later the Romans, and came into extensive use in Europe from the Middle Ages until the various developments in pottery and glass-making during the 18th and 19th centuries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergyng
Ergyng (or Erging) was a Welsh kingdom of the sub-Roman and early medieval period, between the 5th and 7th centuries. It was later referred to by the English as ''Archenfield''. Location The kingdom lay mostly in what is now western Herefordshire (now in England), its heartland between the River Monnow and River Wye. However, it also spread into modern Monmouthshire and east of the Wye, where sits the old Roman town of ''Ariconium'' (Welsh: ''Ergyng'') at Weston under Penyard from which its name may derive; it may have been the first capital. Some maps show Ergyng extending across what is now the Forest of Dean to the River Severn. Monarchy After the withdrawal of the Roman legions from Britain in 410 AD, new smaller political entities took the place of the centralised structure. The area was originally part of the Kingdom of Glywysing (modern Glamorgan) and the Kingdom of Gwent, but seems to have become independent for a period under Peibio Clafrog in the 5th or 6th century an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. With a population of 53,112 in 2021 it is by far the largest settlement in Herefordshire. An early town charter from 1189, granted by Richard I of England, describes it as "Hereford in Wales". Hereford has been recognised as a city since time immemorial, with the status being reconfirmed as recently as October 2000. It is now known chiefly as a trading centre for a wider agricultural and rural area. Products from Hereford include cider, beer, leather goods, nickel alloys, poultry, chemicals and sausage rolls, as well as the famous Hereford breed of cattle. Toponymy The Herefordshire edition of Cambridge County Geographies states "a Welsh derivation of Hereford is more probable than a Saxon one" but the name "Hereford" is also said to come from the Angl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breton People
The Bretons (; br, Bretoned or ''Vretoned,'' ) are a Celtic ethnic group native to Brittany. They trace much of their heritage to groups of Brittonic speakers who emigrated from southwestern Great Britain, particularly Cornwall and Devon, mostly during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. They migrated in waves from the 3rd to 9th century (most heavily from 450 to 600) into Armorica, which was subsequently named Brittany after them. The main traditional language of Brittany is Breton (''Brezhoneg''), spoken in Lower Brittany (i.e., the western part of the peninsula). Breton is spoken by around 206,000 people as of 2013. The other principal minority language of Brittany is Gallo; Gallo is spoken only in Upper Brittany, where Breton is less dominant. As one of the Brittonic languages, Breton is related closely to Cornish and more distantly to Welsh, while the Gallo language is one of the Romance '' langues d'oïl''. Currently, most Bretons' native language is standard French. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England. The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English counties of Northumberland, Tyne and Wear, and Durham, as well as the Scottish counties of Berwickshire and East Lothian, stretching from the Forth to the Tees. In the early 7th century, it merged with its southern neighbour, Deira, to form the kingdom of Northumbria, and its borders subsequently expanded considerably. Brittonic ''Bryneich'' Etymologies Bernicia occurs in Old Welsh poetry as ''Bryneich'' or ''Brynaich'' and in the 9th-century ''Historia Brittonum'', (§ 61) as ''Berneich'' or ''Birneich''. This was most likely the name of the native Brittonic kingdom , whose name was then adopted by the Anglian settlers who rendered it in Old English as ''Bernice'' or ''Beornice'' . The coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodric Of Bernicia
Theodric or Ðeodric ruled from 572 to 579. He was the fifth known ruler of the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Bernicia. Theodric was the son of Ida of Bernicia, founder of the kingdom of Bernicia, and a brother of his predecessor, Æthelric of Bernicia, Æthelric. Little is known of Theodric's life and reign although Urien, the king of Rheged, was said to have subjected Theodric and his sons to a three-day siege on the island of Lindisfarne. Theodric has been identified with an Anglian ruler nicknamed ''Fflamddwyn'' in Welsh, who, according to medieval Welsh poetry such as ''Gweith Argoed Llwyfain'' (''The Battle of Argoed Llwyfain'' or ''Battle of Leeming Lane'') from the Book of Taliesin, was killed in battle by Urien's son, Owain mab Urien, after he demanded hostages and Owain refused to give in. The dates for Theodric's rule are conjecture; the earliest authorities differ widely on the order and the regnal years of the kings between the death of Ida and the beginning o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoric
Theodoric is a Germanic given name. First attested as a Gothic name in the 5th century, it became widespread in the Germanic-speaking world, not least due to its most famous bearer, Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. Overview The name was Latinisation of names, Latinized as ''Theodoricus'' or ''Theodericus'', originally from a Proto-Germanic language, Common Germanic form ''*wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/Þeudarīks, Þeudarīks'' ("people-ruler") from *''wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/þeudō, þeudō'' ("people") and *''wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/rīks, rīks'', which would have resulted in a Gothic language, Gothic *𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃 (*þiudareiks). Anglicized spellings of the name during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages include ''Theodoric'', ''Theoderic'', ''Theudoric'', ''Theuderic''. Gregory of Tours Latinized the name as ''Theodore (given name), Theodorus'', in origin the unrelated Greek name Theodore (given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic People
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and early medieval Germanic languages and are thus equated at least approximately with Germanic-speaking peoples, although different academic disciplines have their own definitions of what makes someone or something "Germanic". The Romans named the area belonging to North-Central Europe in which Germanic peoples lived ''Germania'', stretching East to West between the Vistula and Rhine rivers and north to south from Southern Scandinavia to the upper Danube. In discussions of the Roman period, the Germanic peoples are sometimes referred to as ''Germani'' or ancient Germans, although many scholars consider the second term problematic since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. The very concept of "Germanic peoples" has become the subject of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tewdrig
Tewdrig ap Teithfallt (; la, Theodoricus), known simply as Tewdrig, was a king of the post-Roman Kingdom of Glywysing. He abdicated in favour of his son Meurig (Maurice) and retired to live a hermitical life, but was recalled to lead his son's army against an intruding Saxon force. He won the battle, but was mortally wounded. The context of the battle is one of Britons versus invading Saxons, without explicit religious overtones. Since Tewdrig held to a religious lifestyle and was killed while defending a Christian kingdom against pagans, by the standards of that day Tewdrig is considered to be a martyr and a saint. The Latin form of his name is given as 'Theodoric' and his feast day is 1 April. Tewdrig's name appears in a genealogy of Jesus College MS 20, in the line of one of his descendants, but the only substantive information about the person comes from the twelfth century ''Book of Llandaff''. The ''Book of Llandaff'' places Tewdrig's story in the territory of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire ( cy, Sir Fynwy) is a county in the south-east of Wales. The name derives from the historic county of the same name; the modern county covers the eastern three-fifths of the historic county. The largest town is Abergavenny, with other towns and large villages being: Caldicot, Chepstow, Monmouth, Magor and Usk. It borders Torfaen, Newport and Blaenau Gwent to the west; Herefordshire and Gloucestershire to the east; and Powys to the north. Historic county The historic county of Monmouthshire was formed from the Welsh Marches by the Laws in Wales Act 1535 bordering Gloucestershire to the east, Herefordshire to the northeast, Brecknockshire to the north, and Glamorgan to the west. The Laws in Wales Act 1542 enumerated the counties of Wales and omitted Monmouthshire, implying that the county was no longer to be treated as part of Wales. However, for all purposes Wales had become part of the Kingdom of England, and the difference had little practical effect. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Gwent
Gwent ( owl, Guent) was a medieval Welsh kingdom, lying between the Rivers Wye and Usk. It existed from the end of Roman rule in Britain in about the 5th century until the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century. Along with its neighbour Glywyssing, it seems to have had a great deal of cultural continuity with the earlier Silures,Miranda Aldhouse-Green &al. ''Gwent In Prehistory and Early History: The Gwent County History'', Vol.1. 2004. . keeping their own courts and diocese separate from the rest of Wales until their conquest by Gruffydd ap Llywelyn. Although it recovered its independence after his death in 1063, Gwent was the first of the Welsh kingdoms to be overrun following the Norman conquest. History Establishment The area has been occupied since the Paleolithic, with Mesolithic finds at Goldcliff and evidence of growing activity throughout the Bronze and Iron Age. Gwent came into being after the Romans had left Britain, and was a successor state drawing on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |