St. Tewdric on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tewdrig ap Teithfallt (; la, Theodoricus), known simply as Tewdrig, was a king of the post-Roman
 There are three theories about the origins of name Tewdrig:
* a variant of the Germanic name Theodoric;
* it may have been North British, as the name
There are three theories about the origins of name Tewdrig:
* a variant of the Germanic name Theodoric;
* it may have been North British, as the name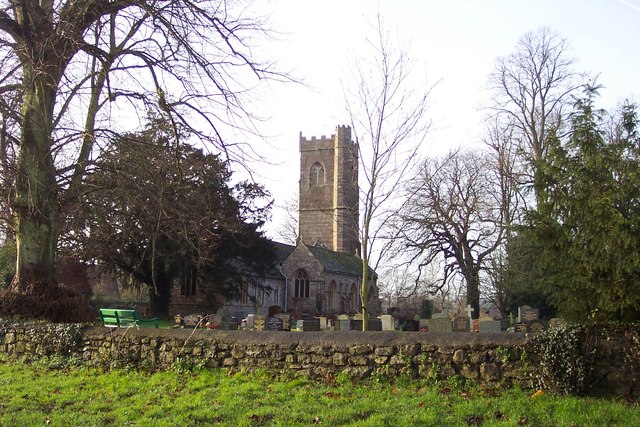  There is a minor hagiographic element in this story from the ''Book of Llandaff''. On returning to secular service due to military necessity, Tewdrig is given the prophecy that he will be successful but will be mortally wounded; that a vehicle pulled by two
There is a minor hagiographic element in this story from the ''Book of Llandaff''. On returning to secular service due to military necessity, Tewdrig is given the prophecy that he will be successful but will be mortally wounded; that a vehicle pulled by two
Kingdom of Glywysing
Glywysing was, from the sub-Roman period to the Early Middle Ages, a petty kingdom in south-east Wales. Its people were descended from the Iron Age tribe of the Silures, and frequently in union with Gwent, merging to form Morgannwg.
Name an ...
. He abdicated in favour of his son Meurig Meurig is a Welsh name of Brittonic origin and may refer to:
*Meurig ap Tewdrig (, the son of Tewdrig (St. Tewdrig), and a king of the early Welsh kingdoms of Gwent and Glywysing
*Meurig ap Idnerth, king of Buellt, a Welsh kingdom from c. 510 to 54 ...
(Maurice) and retired to live a hermitical life, but was recalled to lead his son's army against an intruding Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
force. He won the battle, but was mortally wounded.
The context of the battle is one of Britons versus invading Saxons, without explicit religious overtones. Since Tewdrig held to a religious lifestyle and was killed while defending a Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
kingdom against pagans Pagans may refer to:
* Paganism, a group of pre-Christian religions practiced in the Roman Empire
* Modern Paganism, a group of contemporary religious practices
* Order of the Vine, a druidic faction in the ''Thief'' video game series
* Pagan's ...
, by the standards of that day Tewdrig is considered to be a martyr and a saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
. The Latin form of his name is given as 'Theodoric' and his feast day is 1 April.
Tewdrig's name appears in a genealogy of Jesus College MS 20, in the line of one of his descendants, but the only substantive information about the person comes from the twelfth century '' Book of Llandaff''.
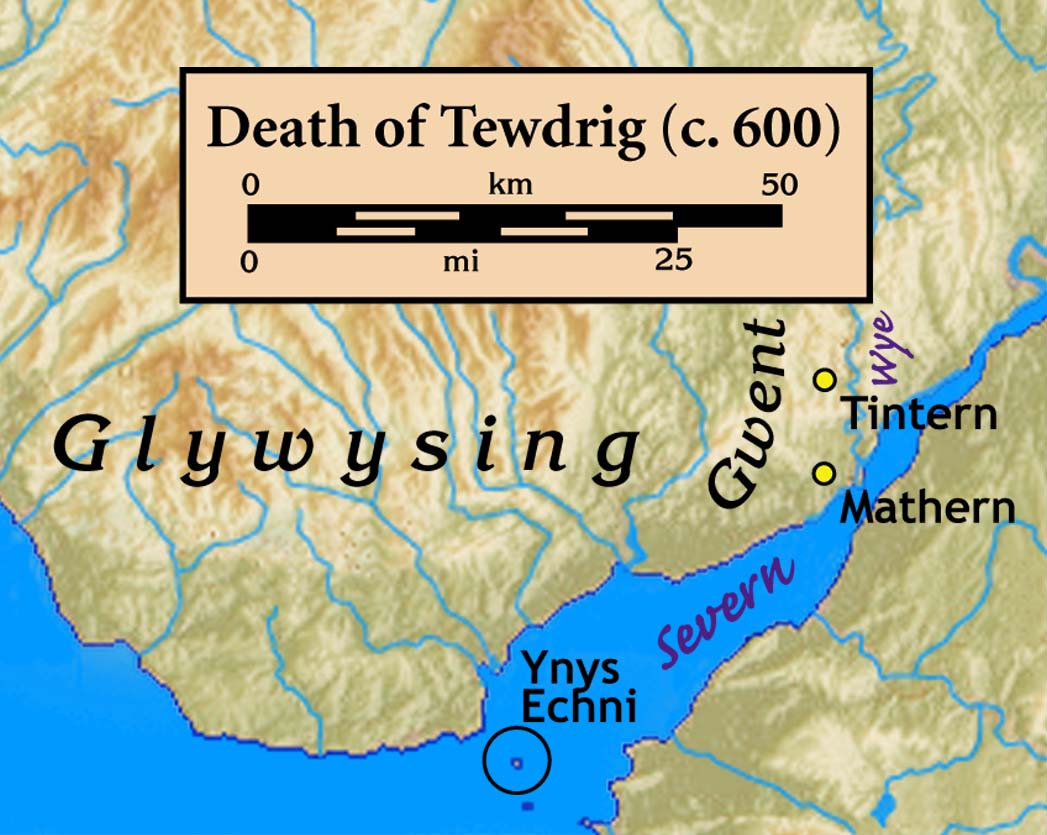
The ''Book of Llandaff'' places Tewdrig's story in the territory of the historical Kingdom of Gwent (the southeastern part of modern Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire ( cy, Sir Fynwy) is a county in the south-east of Wales. The name derives from the historic county of the same name; the modern county covers the eastern three-fifths of the historic county. The largest town is Abergavenny, with ...
), though it states that he was a king of Glywysing. The ancient histories of the kingdoms of Gwent and Glywysing are intertwined, and he may have ruled both kingdoms.
Life
 There are three theories about the origins of name Tewdrig:
* a variant of the Germanic name Theodoric;
* it may have been North British, as the name
There are three theories about the origins of name Tewdrig:
* a variant of the Germanic name Theodoric;
* it may have been North British, as the name Theodric
Theodoric is a Germanic given name. First attested as a Gothic name in the 5th century, it became widespread in the Germanic-speaking world, not least due to its most famous bearer, Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths.
Overview
The name ...
had been a royal name in Bernicia and/or;
* or the Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
royal name ''Theuderic''.
Tewdrig's father, Teithfallt, had also been a king, and the ''Book of Llandaff'' notes that during his reign the Saxons had devastated the border regions, chiefly to the northwest near Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. With a population ...
(i.e., in the historical Kingdom of Ergyng), and also along the River Wye
The River Wye (; cy, Afon Gwy ) is the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn estuary. For much of its length the river forms part of Wal ...
.
While king of Glywysing, Tewdrig ap Teithfallt had been a patron of the Church at Llandaff, with a history of success in battle. At some point in his reign, he abdicated in favour of his son Meurig Meurig is a Welsh name of Brittonic origin and may refer to:
*Meurig ap Tewdrig (, the son of Tewdrig (St. Tewdrig), and a king of the early Welsh kingdoms of Gwent and Glywysing
*Meurig ap Idnerth, king of Buellt, a Welsh kingdom from c. 510 to 54 ...
in order to live a hermitical life at Tintern, a rocky place near a ford across the River Wye
The River Wye (; cy, Afon Gwy ) is the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn estuary. For much of its length the river forms part of Wal ...
. When a Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
threat to the kingdom emerged, he returned to lead a defence. He was successful, but at a battle or skirmish at or near the ford (called ''Rhyd Tintern''), he was mortally wounded. He asked to be taken to Ynys Echni (called Flat Holm in English) for burial, but got no further than Mathern
Mathern ( cy, Matharn; older form: ''Merthyr Tewdrig'') is a historic community (parish) and village in Monmouthshire, south east Wales, about south west of the town of Chepstow, close to the Severn estuary, the Bristol Channel and the M48 mot ...
on an inlet of the Severn estuary, where he languished briefly and died. King Meurig built a church on the spot and buried his father's body there, giving the surrounding land to the Bishops of Llandaff; a bishops' palace was later built there. The place became known first as ''Merthyr Tewdrig'' ("Tewdrig the martyr"), and later as ''Mateyrn'' ("place of a king") or Mathern.E. T. Davies, ''A History of the Parish of Mathern'', 1990 Tewdrig's defence of his homeland was said to be sufficiently decisive that the Saxons would not dare to invade again for thirty years.
 There is a minor hagiographic element in this story from the ''Book of Llandaff''. On returning to secular service due to military necessity, Tewdrig is given the prophecy that he will be successful but will be mortally wounded; that a vehicle pulled by two
There is a minor hagiographic element in this story from the ''Book of Llandaff''. On returning to secular service due to military necessity, Tewdrig is given the prophecy that he will be successful but will be mortally wounded; that a vehicle pulled by two stag
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
s, yoked, will appear and carry him towards his destination of Ynys Echni, but that he will die in peace three days after the battle. Wherever the stags halted, fountains gushed forth, but as they approached the Severn the wagon was broken, a very clear stream gushed forth and here Tewdric died.Hando, F.J., (1958) "Out and About in Monmouthshire", R. H. Johns, Newport.
A number of sources, such as Ussher's ''Brittanicarum Ecclesiarum Antiquitates'' (1639), cite Bishop Godwin's 1615 account of the medieval church at Mathern. Godwin said that he discovered a stone coffin by the altar in the church, containing the saint's bones, and that the skull was badly fractured. Ussher also repeats the account of the ''Book of Llandaff''. In 1958 Hando also recounts the story told to him by an old lady who had lived in Mathern and who claimed to have seen for herself, in 1881, the stone coffin bearing the remains of St. Tewdrig with his mortal wound (a hole in the skull made by a spear-point) still visible.
Sources of information
The Book of Llandaff
The '' Book of Llandaff'' was written c. 1125, at a time when the bishopric at Llandaff was struggling against the competing bishoprics atSaint David's
St Davids or St David's ( cy, Tyddewi, , "David's house”) is a city and a community (named St Davids and the Cathedral Close) with a cathedral in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Alun. It is the resting place of Saint David, Wa ...
and Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. With a population ...
. The book was written specifically to justify the claims of Llandaff, and Tewdrig's story provides the reason why his son, Meurig ap Tewdrig, donated the lands near Mathern to the see
See or SEE may refer to:
* Sight - seeing
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Music:
** ''See'' (album), studio album by rock band The Rascals
*** "See", song by The Rascals, on the album ''See''
** "See" (Tycho song), song by Tycho
* Television
* ...
of Llandaff.
Other sources
Tewdrig is not mentioned byNennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
in the '' Historia Brittonum'' (c. 850). Lloyd
Lloyd, Lloyd's, or Lloyds may refer to:
People
* Lloyd (name), a variation of the Welsh word ' or ', which means "grey" or "brown"
** List of people with given name Lloyd
** List of people with surname Lloyd
* Lloyd (singer) (born 1986), American ...
's ''History of Wales'' (1911) mentions the ''Book of Llandaff's'' account of Tewdrig's combat at the crossing of the Wye, and notes that ''Merthyr Tewdrig'' is now called Mathern, but adds nothing further. Nedelec's ''History of the Early Cambro-British Christians'' (1879) retells the story from the ''Book of Llandaff'', adding a number of unattributed details which are colourful but inconsequential. Turner's ''History of the Anglo-Saxons'' (1799) repeats the accounts of the ''Book of Llandaff'' and Bishop Godwin (citing Ussher as the source), but then adds that the Saxons in question were those of Wessex, led by Ceolwulf Ceolwulf, occasionally spelt Ceolwulph, may refer to:
* Ceolwulf I of Mercia, King of Mercia
*Ceolwulf II of Mercia, King of Mercia
*Ceolwulf of Northumbria (Saint Ceolwulf), King of Northumbria
*Ceolwulf of Wessex
Ceolwulf (died 611) was a Kin ...
. No authority is provided for this claim.
The Iolo Manuscripts
The ''Iolo Manuscripts'' are a collection of manuscripts presented in the early nineteenth century by Edward Williams, who is better known as Iolo Morganwg. Containing elaborate genealogies that connect virtually everyone of note with everyone else of note (and with many connections to "Arthur"), they were at first accepted as genuine, but have since been shown to be an assortment of manuscripts, transcriptions, and fantasies, many invented by Iolo himself. There are many references to Tewdrig and his genealogy. A list of works tainted by their reliance on the material presented by Iolo (sometimes without attribution) would be quite long.Sources
Bibliography
* — from MSS. in the Libraries of Hengwrt, and of Jesus College (English translation) *References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tewdrig Monarchs of Morgannwg Monarchs of Gwent Medieval Welsh saints 6th-century Christian saints 6th-century Welsh monarchs Monarchs of Glywysing