|
Shinkansen0-n700
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond long-distance travel, some sections around the List of metropolitan areas in Japan, largest metropolitan areas are used as a commuter rail network. It is operated by five Japan Railways Group companies. Over the Shinkansen's 50-plus-year history, carrying over 10 billion passengers, there has been not a single passenger fatality or injury on board due to derailments or collisions. Starting with the Tokaido Shinkansen () in 1964, the network has expanded to currently consist of of lines with maximum speeds of , of Mini-Shinkansen lines with a maximum speed of , and of spur lines with Shinkansen services. The network presently links most major cities on the islands of Honshu and Kyushu, and Hakodate on northern island of Hokkaido, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinkansen0-n700
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond long-distance travel, some sections around the List of metropolitan areas in Japan, largest metropolitan areas are used as a commuter rail network. It is operated by five Japan Railways Group companies. Over the Shinkansen's 50-plus-year history, carrying over 10 billion passengers, there has been not a single passenger fatality or injury on board due to derailments or collisions. Starting with the Tokaido Shinkansen () in 1964, the network has expanded to currently consist of of lines with maximum speeds of , of Mini-Shinkansen lines with a maximum speed of , and of spur lines with Shinkansen services. The network presently links most major cities on the islands of Honshu and Kyushu, and Hakodate on northern island of Hokkaido, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
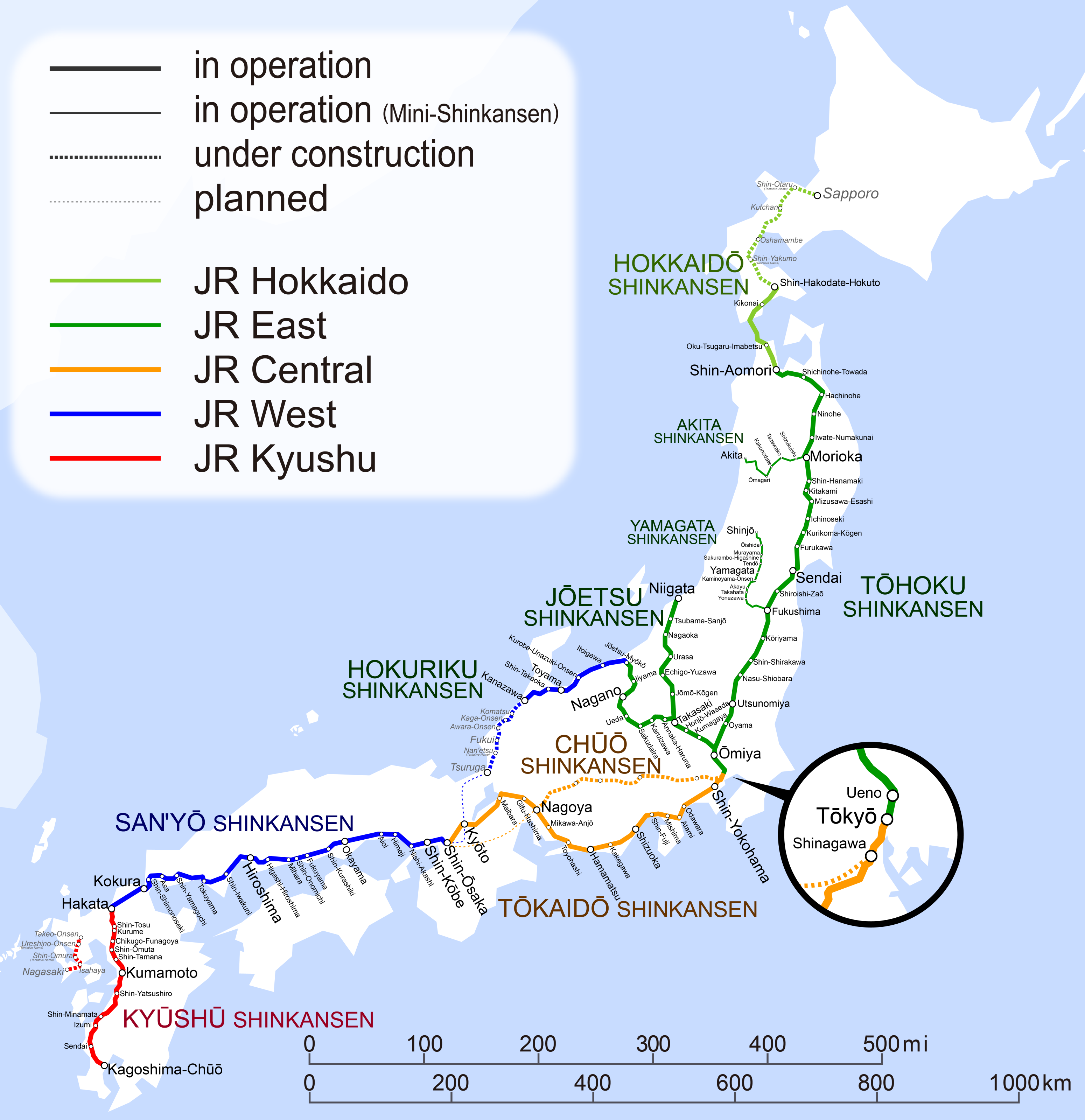
Shinkansen Map 201703 En
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond long-distance travel, some sections around the List of metropolitan areas in Japan, largest metropolitan areas are used as a commuter rail network. It is operated by five Japan Railways Group companies. Over the Shinkansen's 50-plus-year history, carrying over 10 billion passengers, there has been not a single passenger fatality or injury on board due to derailments or collisions. Starting with the Tokaido Shinkansen () in 1964, the network has expanded to currently consist of of lines with maximum speeds of , of Mini-Shinkansen lines with a maximum speed of , and of spur lines with Shinkansen services. The network presently links most major cities on the islands of Honshu and Kyushu, and Hakodate on northern island of Hokkaido, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
æ°å¹¹ç·
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond long-distance travel, some sections around the largest metropolitan areas are used as a commuter rail network. It is operated by five Japan Railways Group companies. Over the Shinkansen's 50-plus-year history, carrying over 10 billion passengers, there has been not a single passenger fatality or injury on board due to derailments or collisions. Starting with the Tokaido Shinkansen () in 1964, the network has expanded to currently consist of of lines with maximum speeds of , of Mini-Shinkansen lines with a maximum speed of , and of spur lines with Shinkansen services. The network presently links most major cities on the islands of Honshu and Kyushu, and Hakodate on northern island of Hokkaido, with an extension to Sapporo under constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
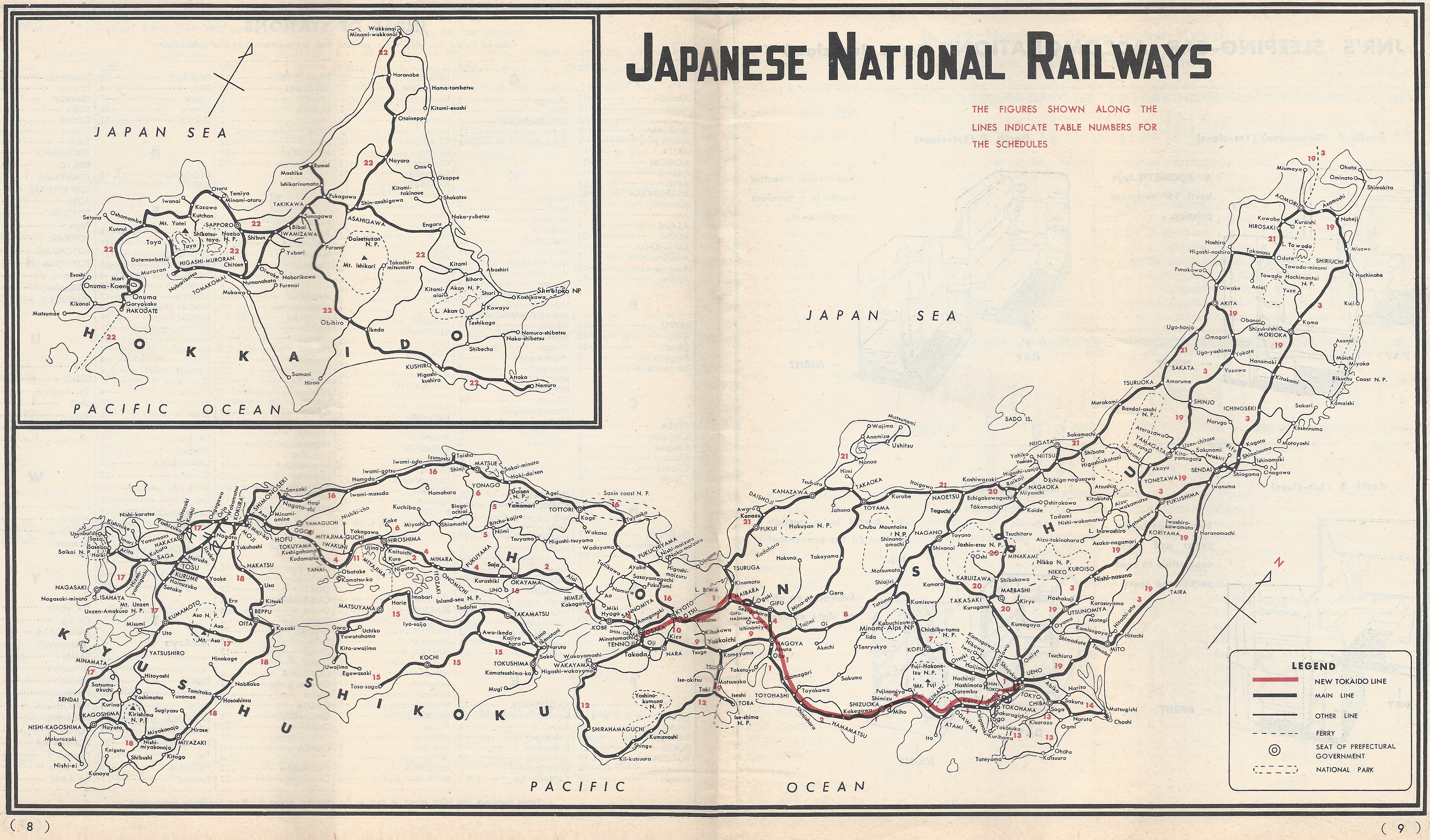
Central Japan Railway Company
is the main railway company operating in the ChÅ«bu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR TÅkai ( ja, JRæ±æµ·, links=no). ''TÅkai'' is a reference to the geographical region in which the company chiefly operates. JR Central's operational hub is Nagoya Station and the company's administrative headquarters are located in the JR Central Towers above the station. The busiest and longest railway line operated by JR Central is the TÅkaidÅ Main Line between and . The company also operates the TÅkaidÅ Shinkansen between and . Additionally it is responsible for the ChÅ«Å Shinkansen—a maglev service between Tokyo and Osaka, which is due to start operation between Tokyo and Nagoya in 2027. JR Central is Japan's most profitable and highest throughput high-speed-rail operator, carrying 138 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009, considerably more than the world's largest airline. Japan recorded a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TÅhoku Shinkansen
The is a Japanese high-speed Shinkansen rail line, connecting Tokyo with Aomori in Aomori Prefecture in a route length of , making it Japan's longest Shinkansen line. It runs through the more sparsely populated TÅhoku region of Japan's main island, Honshu, and was extended as the Hokkaido Shinkansen through the Seikan Tunnel to (this section opened March 2016) and is expected to be extended to Sapporo by 2030. It has two Mini-shinkansen branch lines, the Yamagata Shinkansen and Akita Shinkansen. The line is operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East). Services There are four services in operation: * ''Hayabusa'', Tokyo – Shin-Aomori/Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto limited-stop, starting 5 March 2011 * '' Hayate'', Morioka/Shin-Aomori - Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto limited-stop, starting 26 March 2016 (the name has been in use since 1 December 2002) * ''Yamabiko'', Tokyo – Sendai limited-stop, and all-stations to Morioka, starting June 1982 * ''Nasuno'', Tokyo – Oyama/Nas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Speed Record For Rail Vehicles
The world record for a conventional wheeled passenger train is held by France's TGV (''Train à Grande Vitesse''), set in 2007 when it reached on a section of track. Japan's experimental maglev train L0 Series achieved on a 42.8 km magnetic levitation track in 2015. World speed records Legend: ; Arr (Arrangement) : Disposition and number of elements forming the train. :; Loc:One locomotive pulling one or more cars) :; Multi :Multi Motorized Elements :; Single :Single rail vehicle ; Power: DC, DC 3rd rail, AC, Single phase, Triphase, Diesel-elec., Gas, Steam, Diesel-hydraulic, Propeller, Rocket, Jet. ; State: "Proto." (Prototype), "Unmod." (Unmodified from vehicles in service), "unknown" (Unknown), "Tuned" All passenger trains The following is a partial list of absolute world speed records for all trains designed to carry passengers, regardless of gauge, propulsion or type of rail, , - , , , , 1938-20-07 , , Bologna-Milano line between Pontenure and Piacenza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCMaglev
The SCMaglev (superconducting maglev, formerly called the MLU) is a magnetic levitation (maglev) railway system developed by Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central) and the Railway Technical Research Institute. On 21 April 2015, a manned seven-car L0 Series SCMaglev train reached a speed of , less than a week after the same train clocked , breaking the previous land speed record for rail vehicles of set by a JR Central MLX01 maglev train in December 2003. Technology The SCMaglev system uses an electrodynamic suspension (EDS) system. The trains' bogies have superconducting magnets installed, and the guideways contain two sets of metal coils. The current levitation system utilizes a series of coils wound into a "figure 8" along both walls of the guideway. These coils are also cross-connected underneath the track. As the train accelerates, the magnetic fields of its superconducting magnets induce a current into these coils due to the magnetic field induction effect. If th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most populous city of Aichi Prefecture, and is one of Japan's major ports along with those of Tokyo, Osaka, Kobe, Yokohama, and Chiba. It is the principal city of the ChūkyŠmetropolitan area, which is the third-most populous metropolitan area in Japan with a population of 10.11million in 2020. In 1610, the warlord Tokugawa Ieyasu, a retainer of Oda Nobunaga, moved the capital of Owari Province from Kiyosu to Nagoya. This period saw the renovation of Nagoya Castle. The arrival of the 20th century brought a convergence of economic factors that fueled rapid growth in Nagoya, during the Meiji Restoration, and became a major industrial hub for Japan. The traditional manufactures of timepieces, bicycles, and sewing machines were followed by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2.7 million in the 2020 census, it is also the largest component of the Keihanshin Metropolitan Area, which is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan and the 10th largest urban area in the world with more than 19 million inhabitants. Osaka was traditionally considered Japan's economic hub. By the Kofun period (300â538) it had developed into an important regional port, and in the 7th and 8th centuries, it served briefly as the imperial capital. Osaka continued to flourish during the Edo period (1603â1867) and became known as a center of Japanese culture. Following the Meiji Restoration, Osaka greatly expanded in size and underwent rapid industrialization. In 1889, Osaka was officially established as a municipality. The construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
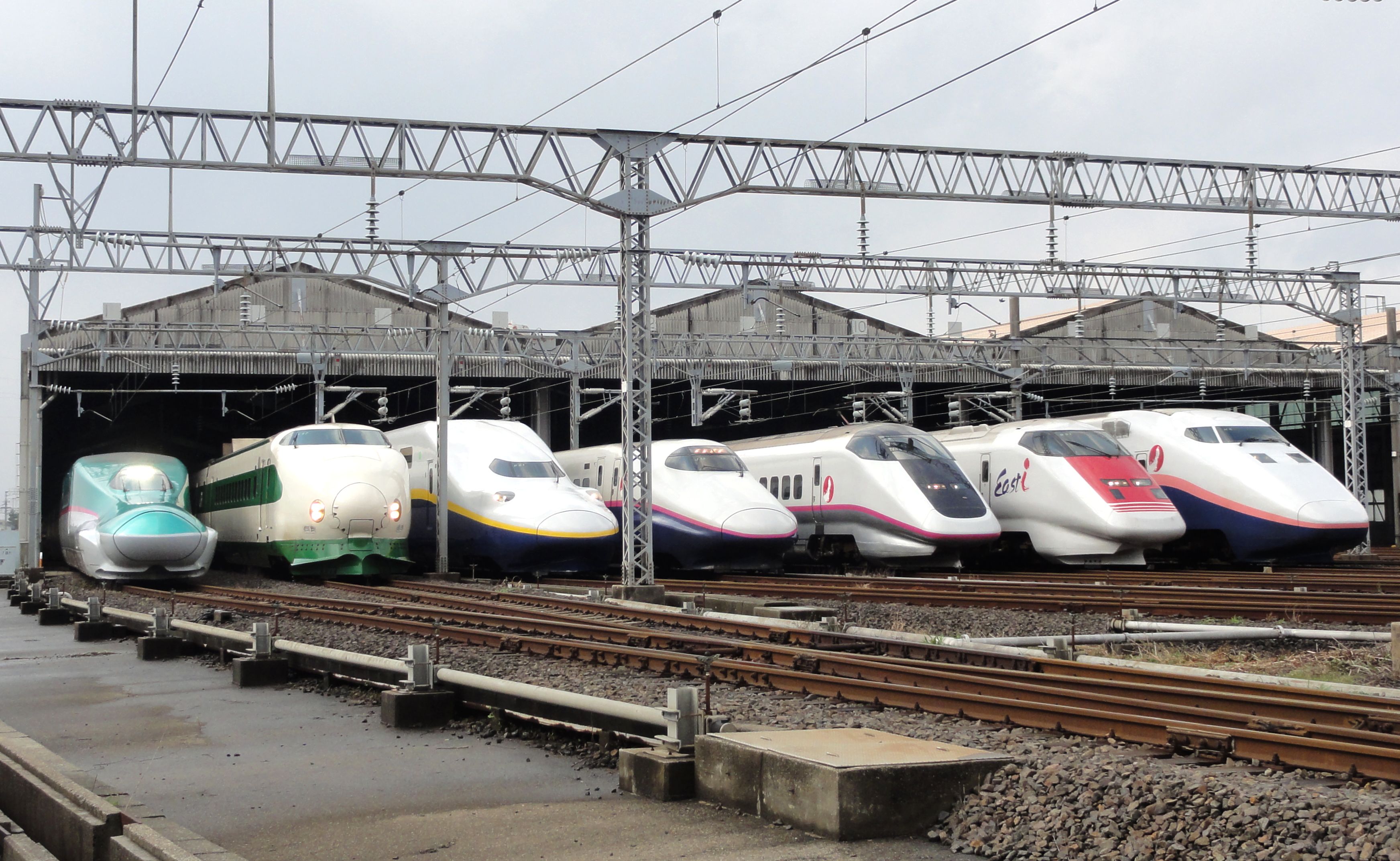
JR East Shinkansen Lineup At Niigata Depot 201210
JR, J. R. or Jr. may refer to: * Jr. or Junior (suffix), a name suffix Arts and entertainment * J.R. (album), ''J.R.'' (album), an album by Jim Bob * ''J R'', a 1975 novel written by William Gaddis * "Jr.", a song by Codeine on the album ''Barely Real'' * J. R. Ewing, a television character from ''Dallas'' * JR Chandler, aka Adam Chandler Jr, a television character from ''All My Children'' * ''Jornal da Record'', a Brazilian news program on RecordTV Businesses and organizations * Aero California, defunct Mexican airline by IATA code * Japan Railways Group or the JR Group, the main operators of the Japanese railway network * Jember railway station * John Radcliffe Hospital * Joy Air, Chinese airline by IATA code People In arts and entertainment * JR (artist) (born 1983), French artist * J.R. (musician) (born 1979), American Christian musician and producer * JR (rapper) (born 1987), South African rapper and entrepreneur * ''J. R.'' a pen-name of writer John Ruskin * ''Jr.'', stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In China
The high-speed rail (HSR) network in the People's Republic of China (PRC) is the world's longest and most extensively used â with a total length of by the end of 2021. The HSR network encompasses newly built rail lines with a design speed of . China's HSR accounts for two-thirds of the world's total high-speed railway networks. Almost all HSR trains, track and service are owned and operated by the China Railway Corporation under the brand China Railway High-speed (CRH). High-speed rail developed rapidly in China since the mid-2000s. China's early high-speed trains were imported or built under technology transfer agreements with foreign train-makers including Alstom, Siemens, Bombardier and Kawasaki Heavy Industries. After the initial technological support, Chinese engineers have since re-designed internal train components and have built and produced indigenous trains manufactured by the state-owned CRRC Corporation, especially on newer lines. CRH was introduced in April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapporo
( ain, ãµãã»ããã»ãã, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous city in Japan. It is the capital city of Hokkaido Prefecture and Ishikari Subprefecture. Sapporo lies in the southwest of Hokkaido, within the alluvial fan of the Toyohira River, which is a tributary stream of the Ishikari. It is considered the cultural, economic, and political center of Hokkaido. As with most of Hokkaido, the Sapporo area was settled by the indigenous Ainu people, beginning over 15,000 years ago. Starting in the late 19th century, Sapporo saw increasing settlement by Yamato migrants. Sapporo hosted the 1972 Winter Olympics, the first Winter Olympics ever held in Asia, and the second Olympic games held in Japan after the 1964 Summer Olympics. Sapporo is currently bidding for the 2030 Winter Olympics. The Sapporo Dome host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
