|
Sag Aloo
Saag (), also spelled sag or saga, is an Indian leaf vegetable dish eaten with bread such as roti or naan, or in some regions with rice. Saag can be made from spinach, mustard greens, collard greens, basella, finely chopped broccoli or other greens, along with added spices and sometimes other ingredients such as chhena. Saag is common in the state of Odisha, where it is eaten with pakhala. In the Shree Jagannath Temple of Puri, saag is one of the dishes offered to Jagannath as part of Mahaprasad. Saag is also common in West Bengal and other regions of North India, where the most common preparation is sarson ka saag (mustard plant leaves), which may be eaten with makki ki roti, a yellow roti made with maize flour. ''Saag gosht'' or ''hariyali maans'' (spinach and mutton) is a common dish in the North Indian state of Haryana. Etymology The word ''saag'' is derived from the Sanskrit word ''shaak'' (''śāka'') meaning leafy green vegetables. Variations Odisha In Odia cuisine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarson Ka Saag
Sarson ka saag (as it is known in Hindi/Haryanvi or Sarson da saag in Punjabi or Sareyan Da Saag in Dogri) is a popular vegetarian dish from the northern region of the Indian subcontinent. It is made from mustard greens (sarson) and spices such as ginger and garlic. It is often served with Makki ki roti. Sarson ka Saag and Makki ki Roti is closely associated with Jammu, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and Punjab and is considered a special dish in entire North India. It is eaten especially in the winter season. Etymology ''Sarson Ka Saag'' literally translates to leafy vegetable preparation of mustard. The word ''Sarson'' is derived from Sanskrit word ''Sarśapa'', the Sanskrit word for mustard. The Dogri word ''Sareyan'' is derived from the same Sanskrit root, and the word ''Saag'' is derived from Sanskrit word ''Śāka'' ''(Shaak)'' meaning greens or leafy vegetable. Mode of serving The dish is regarded as the traditional way to prepare saag and is usually served with ''Makki ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagannath Temple, Puri
The Jagannath Temple is an important Hindu temple dedicated to Jagannath, a form of Vishnu - one of the Trimurti, trinity of supreme divinity in Hinduism. Puri is in the state of Odisha, on the eastern coast of India. The present temple was rebuilt from the tenth century onwards, on the site of pre existing temples in the compound but not the main Jagannatha temple, and begun by Anantavarman Chodaganga, the first king of the Eastern Ganga dynasty. The Puri temple is famous for its annual Ratha Yatra, or chariot festival, in which the three principal murti, deities are pulled on huge and elaborately decorated temple cars. Unlike the stone and metal icons found in most Hindu temples, the image of Jagannath (which gave its name to the English term 'juggernaut') is made of wood and is ceremoniously replaced every twelve or 19 years by an exact replica. It is one of the Char Dham pilgrimage sites. The temple is sacred to all Hindus, and especially in those of the Vaishnavism, Vai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaranthus Viridis
''Amaranthus viridis'' is a cosmopolitan species in the botanical family Amaranthaceae and is commonly known as slender amaranth or green amaranth. Description ''Amaranthus viridis'' is an annual herb with an upright, light green stem that grows to about 60–80 cm in height. Numerous branches emerge from the base, and the leaves are ovate, 3–6 cm long, 2–4 cm wide, with long petioles of about 5 cm. The plant has terminal panicles with few branches, and small green flowers with 3 stamens. Uses ''Amaranthus viridis'' is eaten as a boiled green or as a vegetable in many parts of the world. In the Northeastern Indian state of Manipur, it is known as ''cheng-kruk''; it is also eaten as a vegetable in South India, especially in Kerala, where it is known as ''kuppacheera'' കുപ്പച്ചീര. It is a common vegetable in Bengali cuisine, where it is called ''note shak'' ("shak" means leafy vegetable). It a very common vegetable used in Odia Cuisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaranthus Dubius
''Amaranthus dubius'', the red spinach, Chinese spinach, (), spleen amaranth, hon-toi-moi, yin choy, hsien tsai, or Arai keerai () is a plant species. It belongs to the economically important family Amaranthaceae. This plant is native to South America, Mexico, and the West Indies, however; it is widely introduced throughout the world. The species occurs locally in France and Germany and is naturalized or invasive in tropical and subtropical regions of the United States (Florida and Hawaii), Africa, Asia, Australia and the Pacific. Description Usually it grows to a size of . It has both green and red varieties, as well as some with mixed colors. The green variety is practically indistinguishable from ''Amaranthus viridis''. It flowers from summer to fall in the tropics, but can flower throughout the year in subtropical conditions. It is a ruderal species, usually found in waste places or disturbed habitats. ''Amaranthus dubius'' is considered to be a morphologically deviant all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaranth
''Amaranthus'' is a cosmopolitan genus of annual or short-lived perennial plants collectively known as amaranths. Some amaranth species are cultivated as leaf vegetables, pseudocereals, and ornamental plants. Catkin-like cymes of densely packed flowers grow in summer or autumn. Amaranth varies in flower, leaf, and stem color with a range of striking pigments from the spectrum of maroon to crimson and can grow longitudinally from tall with a cylindrical, succulent, fibrous stem that is hollow with grooves and bracteoles when mature. There are approximately 75 species in the genus, 10 of which are dioecious and native to North America with the remaining 65 monoecious species endemic to every continent (except Antarctica) from tropical lowlands to the Himalayas. Members of this genus share many characteristics and uses with members of the closely related genus ''Celosia''. Amaranth grain is collected from the genus. The leaves of some species are also eaten. Description Amar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipomoea Aquatica
''Ipomoea aquatica'', widely known as water spinach, is a semi- aquatic, tropical plant grown as a vegetable for its tender shoots. ''I. aquatica'' is generally believed to have been first domesticated in Southeast Asia. It is widely cultivated in Southeast Asia, East Asia, and South Asia. It grows abundantly near waterways and requires little to no care. Description ''Ipomoea aquatica'' grows in water or on moist soil. Its stems are or longer, rooting at the nodes, and they are hollow and can float. The leaves vary from typically sagittate (arrow head-shaped) to lanceolate, long and broad. The flowers are trumpet-shaped, in diameter, and usually white in colour with a mauve centre. Propagation is either by planting cuttings of the stem shoots, which will root along nodes, or by planting the seeds from flowers that produce seed pods. Names ''Ipomoea aquatica'' is widely known as kangkong (also spelled kangkung), its common name in Maritime Southeast Asia, which possibly or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land area. The state capital is Chandigarh, which it shares with the neighboring state of Punjab, and the most populous city is Faridabad, which is a part of the National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region. The city of Gurugram is among India's largest financial and technology hubs. Haryana has 6 Divisions of Haryana, administrative divisions, 22 List of districts of Haryana, districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 tehsil, revenue tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 Community development block in India, community development blocks, 154 List of cities in Haryana by population, cities and towns, 7,356 villages, and 6,222 Gram panchayat, villages panchayats. Haryana contains 32 special economic zones (SEZs), mainly located within the industrial corri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The leafy stalk of the plant produces pollen inflorescences (or "tassels") and separate ovuliferous inflorescences called ears that when fertilized yield kernels or seeds, which are fruits. The term ''maize'' is preferred in formal, scientific, and international usage as a common name because it refers specifically to this one grain, unlike ''corn'', which has a complex variety of meanings that vary by context and geographic region. Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat or rice. In addition to being consumed directly by humans (often in the form of masa), maize is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarson Ka Saag
Sarson ka saag (as it is known in Hindi/Haryanvi or Sarson da saag in Punjabi or Sareyan Da Saag in Dogri) is a popular vegetarian dish from the northern region of the Indian subcontinent. It is made from mustard greens (sarson) and spices such as ginger and garlic. It is often served with Makki ki roti. Sarson ka Saag and Makki ki Roti is closely associated with Jammu, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and Punjab and is considered a special dish in entire North India. It is eaten especially in the winter season. Etymology ''Sarson Ka Saag'' literally translates to leafy vegetable preparation of mustard. The word ''Sarson'' is derived from Sanskrit word ''Sarśapa'', the Sanskrit word for mustard. The Dogri word ''Sareyan'' is derived from the same Sanskrit root, and the word ''Saag'' is derived from Sanskrit word ''Śāka'' ''(Shaak)'' meaning greens or leafy vegetable. Mode of serving The dish is regarded as the traditional way to prepare saag and is usually served with ''Makki ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
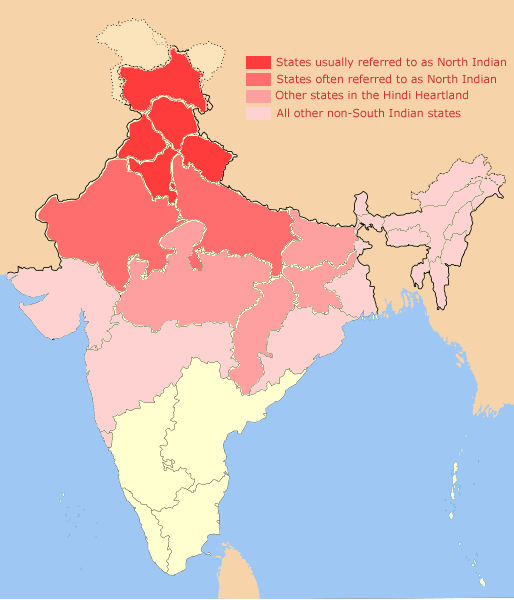
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourth-most populous and thirteenth-largest state by area in India, as well as the eighth-most populous country subdivision of the world. As a part of the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, it borders Bangladesh in the east, and Nepal and Bhutan in the north. It also borders the Indian states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Sikkim and Assam. The state capital is Kolkata, the third-largest metropolis, and seventh largest city by population in India. West Bengal includes the Darjeeling Himalayan hill region, the Ganges delta, the Rarh region, the coastal Sundarbans and the Bay of Bengal. The state's main ethnic group are the Bengalis, with the Bengali Hindus forming the demographic majority. The area's early history featured a succession ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |