|
Riyue Mountain
Riyue Mountain (), known in Tibetan as Nyima Dawa La, is actually a mountain pass situated in Huangyuan County, Xining, Qinghai Province, China. The mountain pass is above sea level and separates the Qinghai Lake endorheic basin from the Huangshui River basin, a tributary of the Yellow River. The Daotang River () flows west from the pass into Qinghai Lake. The pass separates Qinghai Province into a pastoral zone in the west and an agricultural zone in the east. The mountain pass is currently crossed by China National Highway 214 that follows the ancient trade route into Tibet.Dorje (1999), pp. 535-536. Legend The Nyima Dawa La (pass) was made famous due to its association with the Han-Chinese Princess Wencheng when she was en route to marry Tibetan King Songtsen Gampo in the 7th century. She is said to have looked in a magic mirror here with a sun-moon design which was supposed to show her family in Chang'an Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riyue Mountain
Riyue Mountain (), known in Tibetan as Nyima Dawa La, is actually a mountain pass situated in Huangyuan County, Xining, Qinghai Province, China. The mountain pass is above sea level and separates the Qinghai Lake endorheic basin from the Huangshui River basin, a tributary of the Yellow River. The Daotang River () flows west from the pass into Qinghai Lake. The pass separates Qinghai Province into a pastoral zone in the west and an agricultural zone in the east. The mountain pass is currently crossed by China National Highway 214 that follows the ancient trade route into Tibet.Dorje (1999), pp. 535-536. Legend The Nyima Dawa La (pass) was made famous due to its association with the Han-Chinese Princess Wencheng when she was en route to marry Tibetan King Songtsen Gampo in the 7th century. She is said to have looked in a magic mirror here with a sun-moon design which was supposed to show her family in Chang'an Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since many of the world's mountain ranges have presented formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human and animal migration throughout history. At lower elevations it may be called a hill pass. A mountain pass is typically formed between two volcanic peaks or created by erosion from water or wind. Overview Mountain passes make use of a gap (landform), gap, saddle (landform), saddle, col or notch (landform), notch. A topographic saddle is analogous to the mathematical concept of a saddle surface, with a saddle point marking the highest point between two valleys and the lowest point along a ridge. On a topographic map, passes are characterized by contour lines with an hourglass shape, which indicates a low spot between two higher points. In the high mountains, a difference of between the summit and the mountain is defined as a mountain pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huangyuan County
Huangyuan County () is a county of Qinghai Province, China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Xining, the capital of Qinghai. It is under the administration of Xining city. The county seat is Chengguan Town, known in Mongolian as Dan Gar and in Tibetan as Tongkor. The remains of Ladrolne Gompa and Rali Hermitage may be seen between Haiyan and Tongkor. A branch of Tongkor Monastery, known as Ganden Tengyeling (Ch. Cinghosi), just to the northwest of the Chengguan is also in ruins.Dorje (1999), p. 536. Climate Tourist sites *Dan Gar Ancient Town, the historic core of Chengguan Town, a historic trading town. *Riyue Mountain and the remains of Tongkor Monastery, a mountain pass where Princess Wencheng supposedly traveled through in the 7th century CE. See also * List of administrative divisions of Qinghai Qinghai, a province of the People's Republic of China, is made up of the following administrative divisions. Administrative divisions All o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
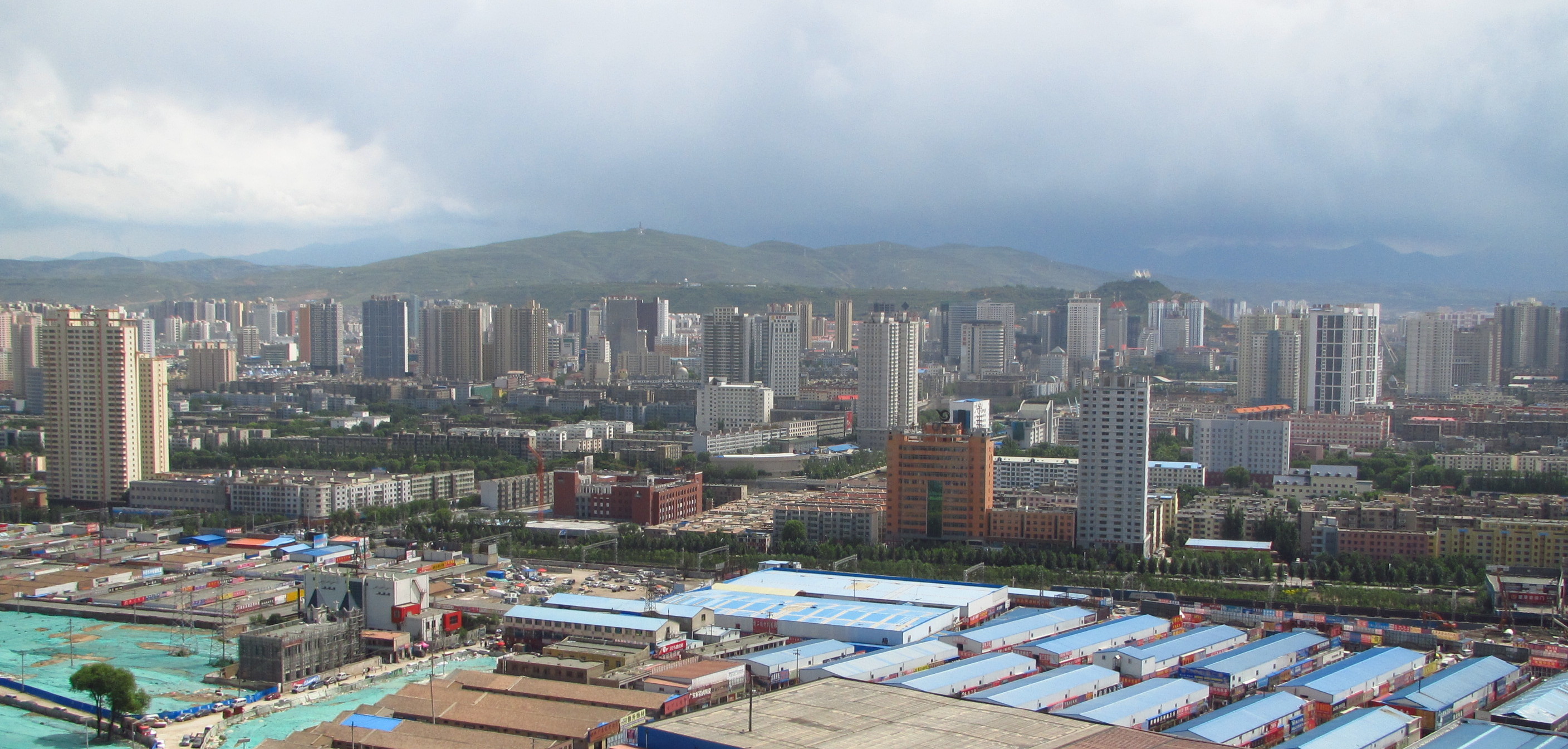
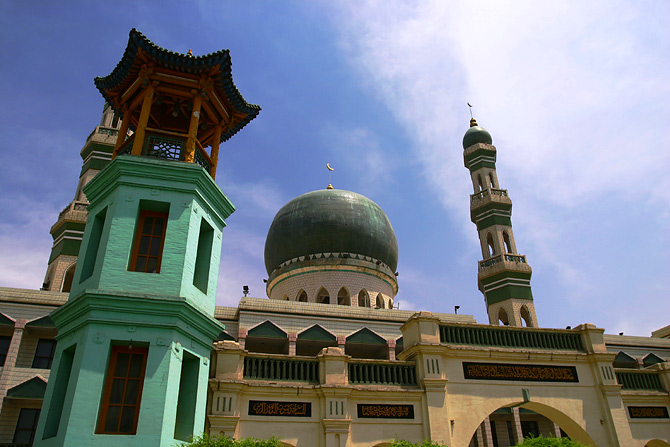
Xining
Xining (; ), alternatively known as Sining, is the capital of Qinghai province in western China and the largest city on the Tibetan Plateau. The city was a commercial hub along the Northern Silk Road's Hexi Corridor for over 2000 years, and was a stronghold of the Han, Sui, Tang dynasty, Tang, and Song dynasty, Song dynasties' resistance against nomadic attacks from the west. Although long a part of Gansu province, Xining was added to Qinghai in 1928. Xining holds sites of religious significance to Muslims and Buddhists, including the Dongguan Mosque and Ta'er Monastery. The city lies in the Huangshui River valley, and owing to its high altitude, has a cool climate on the borderline between Semi-arid climate#Cold semi-arid climates, cool semi-arid and dry winter humid continental climate, humid continental. It is Qinghai–Tibet railway, connected by rail to Lhasa, Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet and Lanzhou-Xinjiang High-Speed Railway, connected by high-speed rail to Lanzhou, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Manchu Relations in Five Phases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai Lake
Qinghai Lake or Ch'inghai Lake, also known by other names, is the largest lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline salt lake. The lake has fluctuated in size, shrinking over much of the 20th century but increasing since 2004. It had a surface area of , an average depth of , and a maximum depth of in 2008. Names Qinghai is the romanized Standard Chinese pinyin pronunciation of the name Although modern Chinese distinguishes between the colors blue and green, this distinction did not exist in classical Chinese. The color (''qīng'') was a "single" color inclusive of both blue and green as separate shades. (English for ''qīng'' is cyan or turquoise, also linguists have coined the portmanteau "grue" to discuss its existence in Chinese and other languages.) The name is thus variously translated as "Blue Sea", "Green Sea", "Blue-Green Sea", "Blue/Green Sea", etc. For a time after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorheic Basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. They are also called closed or terminal basins, internal drainage systems, or simply basins. Endorheic regions contrast with exorheic regions. Endorheic water bodies include some of the largest lakes in the world, such as the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water. Basins with subsurface outflows which eventually lead to the ocean are generally not considered endorheic; they are cryptorheic. Endorheic basins constitute local base levels, defining a limit of erosion and deposition processes of nearby areas. Etymology The term was borrowed from French ''endor(rh)éisme'', coined from the combining form ''endo-'' (from grc, ἔνδον ''éndon'' 'wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
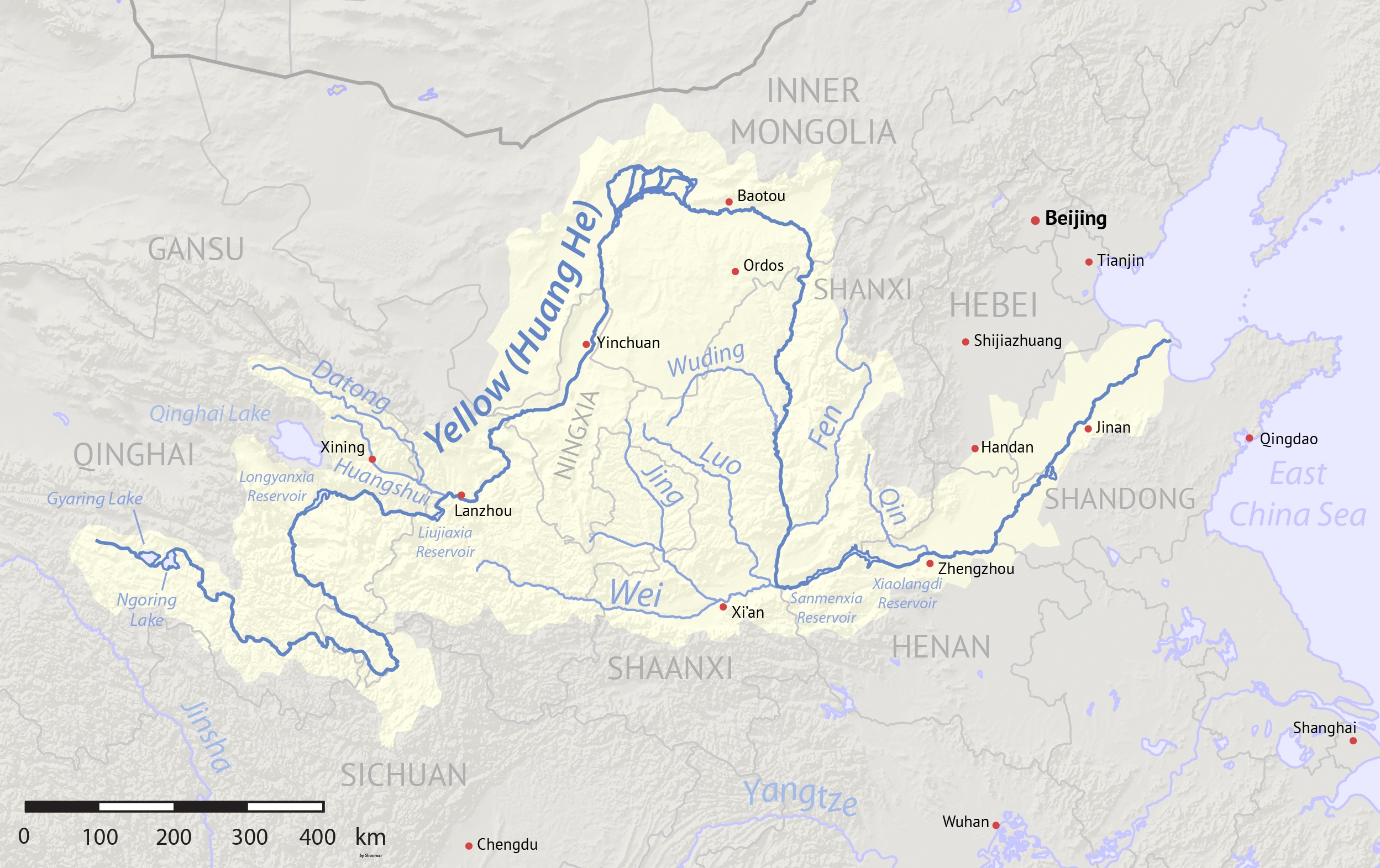
Huangshui River
The Huangshui River or Huang Shui is a river in Qinghai and Gansu, China. The river is a left tributary of the Yellow River and its total length is with a basin area of . Etymology The Huangshui River () is also referred to simply as Huang River () in China. The river was formerly romanized as the Hwong-Choui. In Amdo Tibetan, the Huangshui is known as the Tsong Chu. History The Huangshui River valley has long been important as a route between Chinese, Tibetan, and Mongolian cultures. As one of the few fertile valleys on the northeast edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the river's basin has supported agriculture for various Neolithic and Bronze Age civilizations including the Majiayao culture, Qijia culture, Xindian culture, and Kayue culture. Huangshui's valley was also one of the routes utilized by travelers on the Northern Silk Road. The city of Xining formed on the Huangshui due to its strategic importance. Geography The Huangshui River, in name, is a short river th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Standard Beijing Mandarin, Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the Yellow River civilization, birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far East, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating natural disasters in China, floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Highway 214
China National Highway 214 (G214) runs from Xining, Qinghai to Jinghong, Yunnan. It is 3,256 kilometres in length and runs south from Xining towards Tibet, and ends in Yunnan Province. Route and distance See also * China National Highways The China National Highways (CNH/Guodao) () is a network of trunk roads across mainland China. Apart from the expressways of China that are planned and constructed later, most of the CNH are not controlled-access highways. History The bui ... External linksOfficial website of Ministry of Transport of PRC 214 Transport in Qinghai Roads in Tibet Transport in Yunnan {{PRChina-road-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui settlers. Since Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |