|
Philochortus
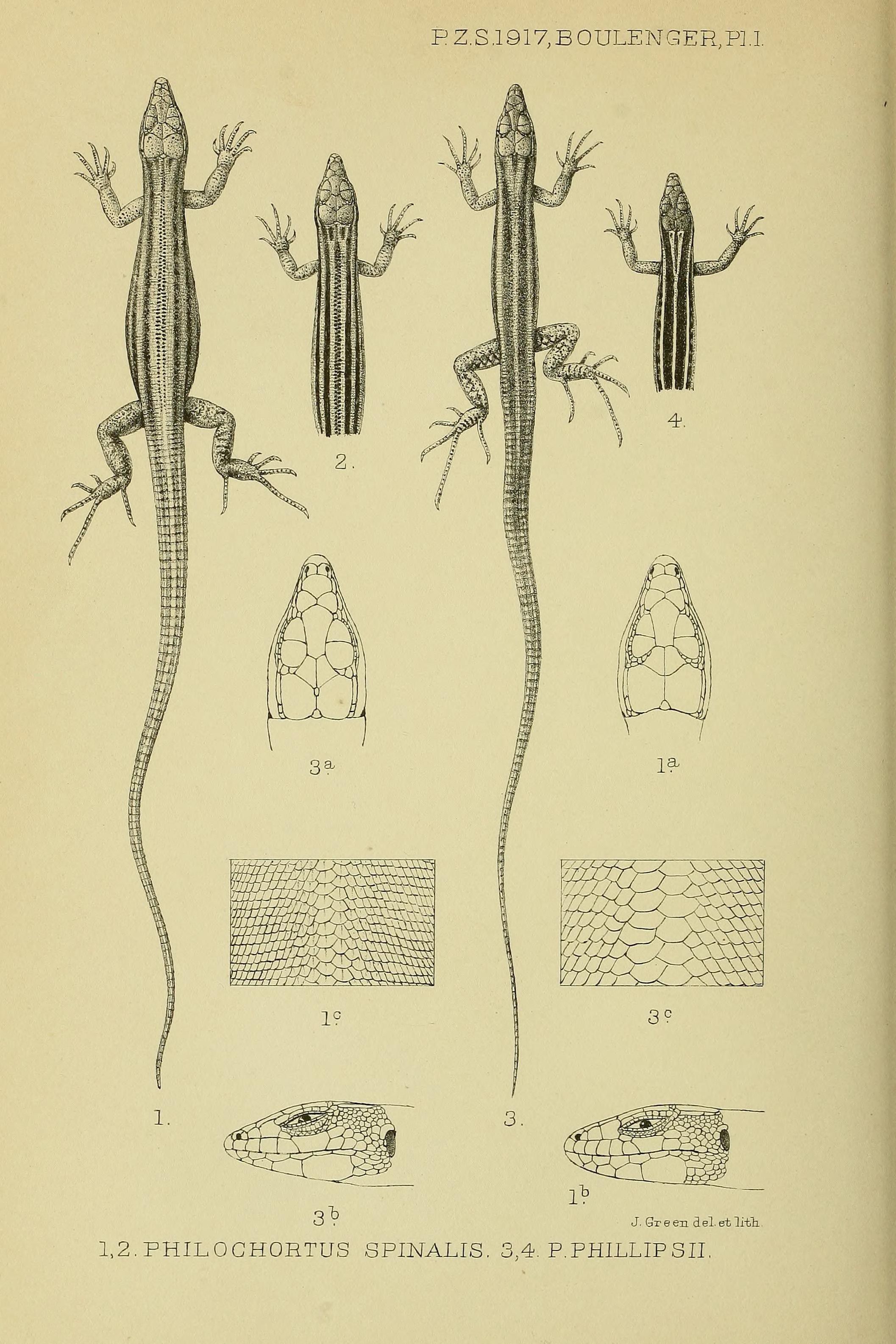
''Philochortus'' is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. Species of this genus are distributed in Egypt, Algeria, Libya, Mali, Niger, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Eritrea, Somalia, Kenya, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia. Etymology ''Philochortus'' means grass-loving (Greek: ''philos'' = friend, ''chortos'' = grass). The common name of ''Philochortus'' species is therefore grass-loving lizards, or shield-backed ground lizards because of their typical back scalation and terrestrial habitat. Diagnosis Species of ''Philochortus'' are medium to large-sized lacertids with long cylindrical tails. The unregenerated tail is up to 3.25 times longer than head and body. Eyes with movable lids. The nostril is pierced between two shields and usually bordered by the first supralabial or narrowly separated from it. The collar is well marked. The ventral plates are smooth, feebly imbricate and arranged in 6 longitudinal series. The dorsal scales are smooth or keeled. Back with 2 to 6 longitudinal series o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philochortus 1
''Philochortus'' is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. Species of this genus are distributed in Egypt, Algeria, Libya, Mali, Niger, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Eritrea, Somalia, Kenya, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia. Etymology ''Philochortus'' means grass-loving (Greek: ''philos'' = friend, ''chortos'' = grass). The common name of ''Philochortus'' species is therefore grass-loving lizards, or shield-backed ground lizards because of their typical back scalation and terrestrial habitat. Diagnosis Species of ''Philochortus'' are medium to large-sized lacertids with long cylindrical tails. The unregenerated tail is up to 3.25 times longer than head and body. Eyes with movable lids. The nostril is pierced between two shields and usually bordered by the first supralabial or narrowly separated from it. The collar is well marked. The ventral plates are smooth, feebly imbricate and arranged in 6 longitudinal series. The dorsal scales are smooth or keeled. Back with 2 to 6 longitudinal series o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philochortus Hardeggeri
''Philochortus hardeggeri'', also known commonly as Hardegger's orangetail lizard and Hardegger's shield-backed lizard, is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is native to the Horn of Africa. Etymology The specific name, ''hardeggeri'', is in honor of Austrian physician Dominik Kammel von Hardegger (1844–1915), who explored in Ethiopia and Somalia. Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Philochortus hardeggeri'', p. 116). Geographic range ''P. hardeggeri'' is found in Djibouti, Ethiopia, and Somalia. Habitat The preferred natural habitats of ''P. hardeggeri'' are desert and savanna, at altitudes below . Reproduction ''P. hardeggeri'' is oviparous. Taxonomy ''Philochortus hardeggeri'' was originally described as ''Latastia hardeggeri'', a species new to science, by Austrian herpetologist Franz Steindachner in 1891. In 1917 the specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacertidae
The Lacertidae are the family (biology), family of the wall lizards, true lizards, or sometimes simply lacertas, which are native to Afro-Eurasia. It is a diverse family with at least 300 species in 39 genera. They represent the dominant group of reptiles found in Europe. The group includes the genus ''Lacerta (genus), Lacerta'', which contains some of the most commonly seen lizard (thus "true" lizard) species in Europe. Habitat The European and Mediterranean species of lacertids live mainly in forest and scrubland, scrub habitats. ''Eremias'' and ''Ophisops'' species replace these in the grassland and desert habitats of Asia. African species usually live in rocky, arid areas. ''Holaspis'' species are among the few arboreal lacertids, and its two species, ''Holaspis guentheri'' and ''Holaspis laevis'', are gliders (although apparently poor ones), using their broad tail and flattened body as an aerofoil. Description Lacertids are small or medium-sized lizards. Most species are le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
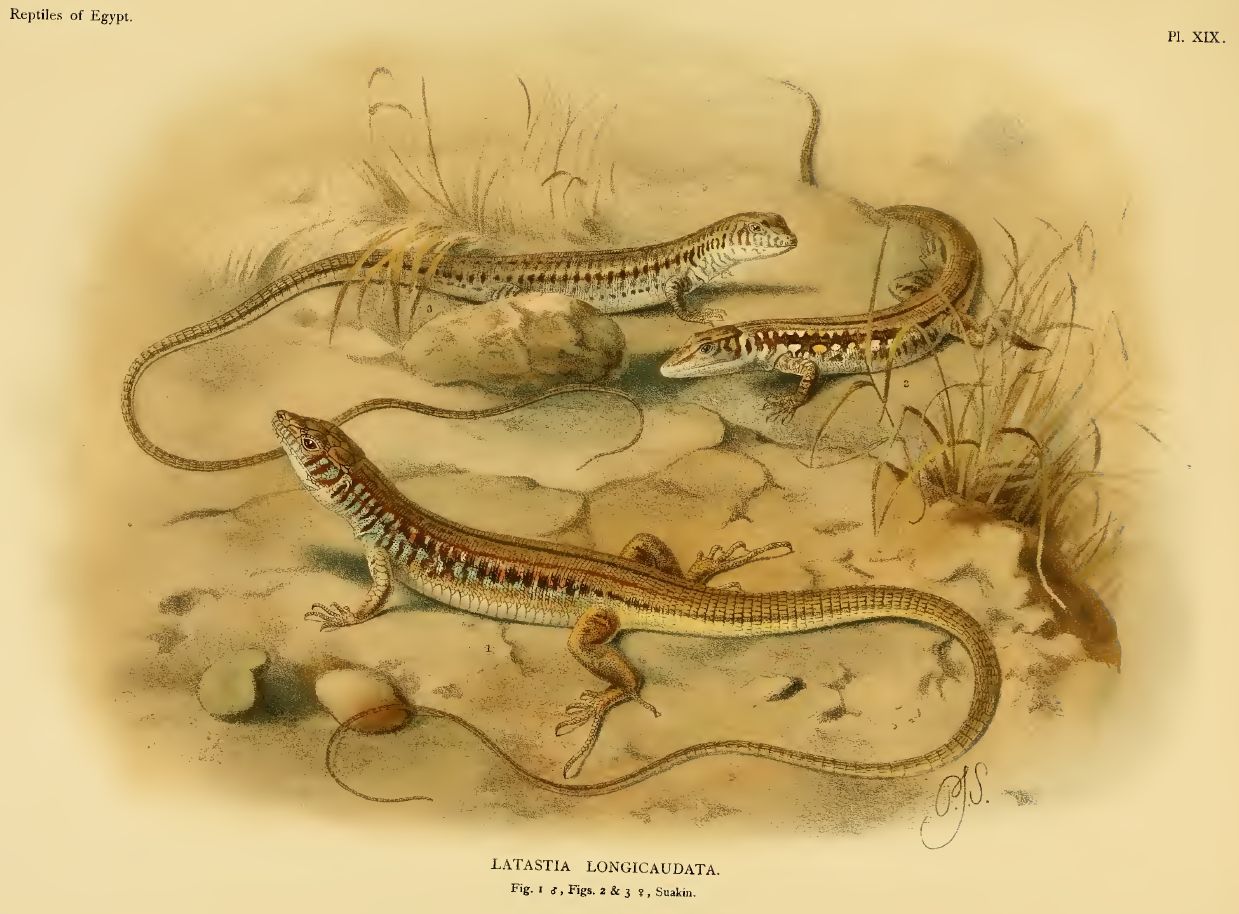
Latastia
''Latastia'' is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. Species of this genus are distributed in Africa (Egypt, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Eritrea, Guinea-Bissau, Cameroon, Kenya, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Zambia, Senegal, Zimbabwe, Somalia, Sudan, South Sudan, Tanzania) but one subspecies (''Latastia longicaudata andersonii'') lives in Yemen.The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org. Collectively, they are known as long-tailed lizards. Etymology Jacques von Bedriaga named this genus in honor of French herpetologist Fernand Lataste. Diagnosis Species of ''Latastia'' are medium to large-sized lacertids with long cylindrical tails. The unregenerated tail is up to 3.2 times longer than head and body. Eyes with movable lids. The nostril is surrounded by 3-5 scales and usually reaches the first supralabial. The collar is well marked. Ventral plates smooth and in 6 longitudinal series (sometimes 8-10 with outer plates small). The dorsal scales are homogenous, small an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmostachya Bipinnata
''Desmostachya bipinnata'', commonly known as halfa grass, big cordgrass, and salt reed-grass, is an Old World perennial grass, long known and used in human history. The grass is tall, tufted, leafy, perennial grass, branching from the base, erect from a stout creeping rootstock. Distribution ''Desmostachya bipinnata'' is native to northeast and west tropical, and northern Africa (in Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Libya, Mauritania, Somalia, Sudan, Tunisia); and countries in the Middle East, and temperate and tropical Asia (in Afghanistan, China, India, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Thailand). In agriculture, ''Desmostachya bipinnata'' is a weed commonly found in wheat crops. Taxonomy On the basis of distinct morphological and reproductive characters, four new subspecies of ''D. bipinnata'' have been described by Pandeya and Pandeya (2002). However, it is uncertain whether these subspecies represent actual genetic differences, the author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semidesert
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commiphora
The genus of the myrrhs, ''Commiphora'', is the most species-rich genus of flowering plants in the frankincense and myrrh family, Burseraceae. The genus contains approximately 190 species of shrubs and trees, which are distributed throughout the (sub-) tropical regions of Africa, the western Indian Ocean islands, the Arabian Peninsula, India, and South America.Weeks, A. and Simpson, B.B. 2007. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Commiphora (Burseraceae) yields insight on the evolution and historical biogeography of an “impossible” genus. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 42:62–79. The genus is drought-tolerant and common throughout the xerophytic scrub, seasonally dry tropical forests, and woodlands of these regions. The common name myrrh refers to several species of the genus, from which aromatic resins are derived for various fragrance and medicinal uses by humans. Description Leaves in ''Commiphora'' are pinnately compound (or very rarely unifoliolate). Many spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia. The genus name is New Latin, borrowed from the Greek (), a term used by Dioscorides for a preparation extracted from the leaves and fruit pods of ''Vachellia nilotica'', the original type of the genus. In his ''Pinax'' (1623), Gaspard Bauhin mentioned the Greek from Dioscorides as the origin of the Latin name. In the early 2000s it had become evident that the genus as it stood was not monophyletic and that several divergent lineages needed to be placed in separate genera. It turned out that one lineage comprising over 900 species mainly native to Australia, New Guinea, and Indonesia was not closely related to the much smaller group of African lineage that contained ''A. nilotica''—the type species. This meant that the Australasian lineage (by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperarid
An aridity index (AI) is a numerical indicator of the degree of dryness of the climate at a given location. A number of aridity indices have been proposed (see below); these indicators serve to identify, locate or delimit regions that suffer from a deficit of available water, a condition that can severely affect the effective use of the land for such activities as agriculture or stock-farming. Historical background and indices Köppen At the turn of the 20th century, Wladimir Köppen and Rudolf Geiger developed the concept of a climate classification where arid regions were defined as those places where the annual rainfall accumulation (in centimetres) is less than R/2, where: * R=2\times T if rainfall occurs mainly in the cold season, * R=2\times T+14 if rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year, and * R=2\times T+28 if rainfall occurs mainly in the hot season. where T is the mean annual temperature in Celsius. This was one of the first attempts at defining an arid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most arid climates straddle the Equator; these regions include parts of Africa, Asia, South America, North America, and Australia. Change over time The distribution of aridity at any time is largely the result of the general circulation of the atmosphere. The latter does change significantly over time through climate change. For example, temperature increase by 1.5–2.1 percent across the Nile Basin over the next 30–40 years could change the region from semi-arid to arid, significantly reducing the land usable for agriculture. In addition, changes in land use can increase demands on soil water and thereby increase aridity. See also * Arid Forest Research Institute * Aridity index * Desert climate * Desiccation tolerance * Drought * Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)






