|
Pakenham Bridge
The Pakenham Bridge is a stone bridge with five arches that crosses the Mississippi River at the town of Pakenham within Mississippi Mills, Ontario, Canada. The bridge measures long, high, and wide. It is the only one of this type in North America. The bridge was built in 1903 by O'Toole & Keating, Scottish masons from Ottawa, for a cost of $14,500. The stones, the largest of which weighs 5 tons, came from a local quarry. As a result of local pressure to preserve it, the bridge was never replaced with a newer one and restored in 1984. At that time, the bridge was also strengthened with reinforced concrete to accommodate car and truck traffic. With a parking lot and rapid Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Rapids are hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''cascade''. ...s right at the bridge, it is a popular picnic spot. Here th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakenham Bridge
The Pakenham Bridge is a stone bridge with five arches that crosses the Mississippi River at the town of Pakenham within Mississippi Mills, Ontario, Canada. The bridge measures long, high, and wide. It is the only one of this type in North America. The bridge was built in 1903 by O'Toole & Keating, Scottish masons from Ottawa, for a cost of $14,500. The stones, the largest of which weighs 5 tons, came from a local quarry. As a result of local pressure to preserve it, the bridge was never replaced with a newer one and restored in 1984. At that time, the bridge was also strengthened with reinforced concrete to accommodate car and truck traffic. With a parking lot and rapid Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Rapids are hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''cascade''. ...s right at the bridge, it is a popular picnic spot. Here th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River (Ontario)
The Mississippi River is a tributary of the Ottawa River in Eastern Ontario, Canada which has no relation with the Mississippi River in the United States. It is in length from its source at Mackavoy Lake, has a drainage area of , and has a mean discharge of . There are more than 250 lakes in the watershed. Communities along the river include the village of Lanark, the towns of Carleton Place, Mississippi Mills (including towns of Almonte and Pakenham), and Galetta. Here it enters the Ottawa River. Etymology The origin of the river's name is something of a mystery; although its current spelling may be derived from that of its much larger American cousin, it is most certainly a corruption of a different indigenous name, as the translation 'great water' would not apply to a relatively minor tributary of the Ottawa, definitely the largest river in the area. Instead, the name may originate from "''Mazinaa ikiniganziibi''", Algonquian for ' aintedimage river', referring to the pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi Mills, Ontario
Mississippi Mills is a town in eastern Ontario, Canada, in Lanark County on the Mississippi River. It is made up of the former Townships of Ramsay and Pakenham, as well as the Town of Almonte. It is partly located within Canada's National Capital Region. History The Town of Mississippi Mills was incorporated on January 1, 1998, by amalgamating the town of Almonte with the townships of Ramsay and Pakenham. Almonte's first settler was David Shepherd, who in 1819 was granted by the Crown to build and operate a mill. The site became known as Shepherd's Falls. That name was never official, however, as Shepherd sold his patent after his mill burned down. The buyer of the patent, Daniel Shipman, rebuilt the mill and the settlement became known as Shipman's Mills in 1820. The majority of Shipman's Mills' early settlers were Scottish. The town grew to encompass thirty stores and forty other businesses. A textile mill town almost from the start, at its peak it boasted seven busy woo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core of the Ottawa–Gatineau census metropolitan area (CMA) and the National Capital Region (NCR). Ottawa had a city population of 1,017,449 and a metropolitan population of 1,488,307, making it the fourth-largest city and fourth-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Ottawa is the political centre of Canada and headquarters to the federal government. The city houses numerous foreign embassies, key buildings, organizations, and institutions of Canada's government, including the Parliament of Canada, the Supreme Court, the residence of Canada's viceroy, and Office of the Prime Minister. Founded in 1826 as Bytown, and incorporated as Ottawa in 1855, its original boundaries were expanded through numerous annexations and were ultimately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their environmental impact. The word ''quarry'' can also include the underground quarrying for stone, such as Bath stone. Types of rock Types of rock extracted from quarries include: *Chalk *China clay *Cinder *Clay *Coal * Construction aggregate (sand and gravel) * Coquina * Diabase *Gabbro *Granite * Gritstone *Gypsum *Limestone *Marble *Ores *Phosphate rock *Quartz *Sandstone * Slate *Travertine Stone quarry Stone quarry is an outdated term for mining construction rocks (limestone, marble, granite, sandstone, etc.). There are open types (called quarries, or open-pit mines) and closed types ( mines and caves). For thousands of years, only hand tools had been used in quarries. In the 18th century, the use of drilling and blasting operatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Rapids are hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''cascade''. Rapids are characterized by the river becoming shallower with some rocks exposed above the flow surface. As flowing water splashes over and around the rocks, air bubbles become mixed in with it and portions of the surface acquire a white color, forming what is called "whitewater". Rapids occur where the bed material is highly resistant to the erosive power of the stream in comparison with the bed downstream of the rapids. Very young streams flowing across solid rock may be rapids for much of their length. Rapids cause water aeration of the stream or river, resulting in better water quality. Rapids are categorized in classes, generally running from I to VI. A Class 5 rapid may be categorized as Class 5.1-5.9. While Class I rapids are eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
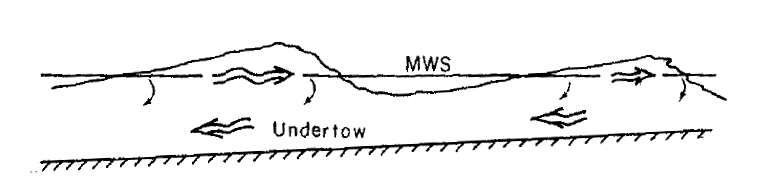
Undertow (water Waves)
In physical oceanography, undertow is the undercurrent that is moving offshore when waves are approaching the shore. Undertow is a natural and universal feature for almost any large body of water: it is a return flow compensating for the onshore-directed average transport of water by the waves in the zone above the wave troughs. The undertow's flow velocities are generally strongest in the surf zone, where the water is shallow and the waves are high due to shoaling. In popular usage, the word "undertow" is often misapplied to rip currents. An undertow occurs everywhere underneath shore-approaching waves, whereas rip currents are localized narrow offshore currents occurring at certain locations along the coast. Oceanography An "undertow" is a steady, offshore-directed compensation flow, which occurs below waves near the shore. Physically, nearshore, the wave-induced mass flux between wave crest and trough is onshore directed. This mass transport is localized in the upper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deck Arch Bridges In Canada
Deck may refer to: A level or platform Buildings and structures * Deck (bridge), the roadway surface of a bridge *Deck (building), an outdoor floor attached to a building made of wood or wood-like material *Another name for a storey *The concrete or tile area surrounding a swimming pool *Deck arch bridge, a type of bridge *Observation deck, a platform situated upon a tall architectural structure or natural feature * Orthotropic deck * Roof deck, the framing and sheathing to which roofing material is applied Transportation *Bus deck, referring to the number of passenger levels on a bus *Cockpit, also called a "flight deck" Maritime *Deck (ship), a floor of a ship * Flight deck of an aircraft carrier Audiovisual equipment * Cassette deck, a type of tape machine for playing and recording compact cassettes * Head unit *Phonograph turntable * Tape deck, a sound recording and playback device People *Deck (surname) * Deck McGuire (born 1989), American baseball player Other uses * Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designated Heritage Properties In Ontario
Designation (from Latin ''designatio'') is the process of determining an incumbent's successor. A candidate that won an election for example, is the ''designated'' holder of the office the candidate has been elected to, up until the candidate's inauguration. Titles typically held by such persons include, amongst others, "President-elect", and "Prime Minister-designate". See also * Acting (law) * -elect * Nominee * President-elect of the United States * Prime Minister-designate A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways ... References International law Legal terminology {{international-law-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario Heritage Trust
The Ontario Heritage Trust (french: link=no, Fiducie du patrimoine ontarien) is a non-profit agency of the Ontario Ministry of Tourism and Culture. It is responsible for protecting, preserving and promoting the built, natural and cultural heritage of Canada's most populous province, Ontario. History It was initially known as the Archaeological and Historic Sites Board during the 1950s. It was incorporated into the Ontario Heritage Foundation in 1968 by the Progressive Conservative government of John Robarts. Its name was changed to the Ontario Heritage Trust in 2005 by an amendment to the ''Ontario Heritage Act''. The Trust's immediate past chair is Harvey McCue. The Trust's most recognizable work is the Provincial Plaque Program. Since 1956 (at Port Carling), it has erected over 1,200 of the now-familiar blue and gold plaques, the vast majority of which are found across Ontario, but also in the United States, France, Germany, Ireland, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |