|
North Ice
North Ice was a research station of the British North Greenland Expedition (1952 to 1954) on the inland ice of Greenland. The coordinates of the station were , at an altitude of above sea level. The British North Greenland Expedition was led by Commander James Simpson RN. The station recorded a temperature of on 9 January 1954, which made it the lowest temperature ever recorded in North America up until that time. It was superseded by an observation of at the Greenland Ice Sheet on 22 December 1991. The name of the station contrasts to the former British South Ice station in Antarctica. See also *List of research stations in the Arctic *Eismitte *Summit Camp *NEEM Camp NEEM Camp was a small research facility on the northern Greenland Ice Sheet, used as a base for ice core drilling. It was located about 313 km east of the closest coast, Peabody Bay in northern Greenland, 275 km northwest of the histor ... References Research stations in Greenland Arctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of America'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, Glacier, mountain glaciers and the Ice sheet, polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Simpson (explorer)
Commander Cortlandt James Woore Simpson, CBE, DSC, PM (2 September 1911, Westbourne, Sussex – 9 May 2002, South Hams, Devon) was an English polar explorer and naval officer. Personal life Simpson was born into a naval family. His grandfather Vice-Admiral Cortlandt Herbert Simpson was the commander of HMS ''Mullett'' and other vessels, and his father Rear Admiral Cortlandt Herbert Simpson also had a distinguished naval career. His family home for three generations was in Stoke-by-Nayland in Suffolk. Simpson sold it in 1969, building a smaller house for himself in the grounds, before eventually moving to Somerset and then to Devon in later life. Simpson was married four times and had one daughter. His great-grandfather was John Busby, who along with his great-uncle James Busby were the fathers of the Australian wine industry. Naval career He was commissioned into the Royal Navy following graduation from the Royal Naval College, Dartmouth. After service on several vessels, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland Ice Sheet
The Greenland ice sheet ( da, Grønlands indlandsis, kl, Sermersuaq) is a vast body of ice covering , roughly near 80% of the surface of Greenland. It is sometimes referred to as an ice cap, or under the term ''inland ice'', or its Danish equivalent, ''indlandsis''. An acronym, GIS, is frequently used in the scientific literature. It is the second largest ice body in the world, after the Antarctic ice sheet. The ice sheet is almost long in a north–south direction, and its greatest width is at a latitude of 77°N, near its northern margin. The average thickness is about and over at its thickest point. In addition to the large ice sheet, smaller ice caps (such as Maniitsoq and Flade Isblink) as well as glaciers, cover between around the periphery. The Greenland ice sheet is adversely affected by climate change. It is more vulnerable to climate change than the Antarctic ice sheet because of its position in the Arctic, where it is subject to the regional amplification o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a landbridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's third-most-populous island after Java in Indonesia and Honshu in Japan. The term "Great Britain" is often used to refer to England, Scotland and Wales, including their component adjoining islands. Great Britain and Northern Ireland now constitute the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Ice
South Ice was a British support base from the South Pole at 81°57'S, 29°00'W in Edith Ronne Land, Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year, established by Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, where three men overwintered during the Antarctic winter of 1957. In the same winter, men overwintered for the first time at the South Pole. The name of the station contrasts to North Ice which was a British research station in Greenland. See also * List of Antarctic research stations * List of Antarctic field camps Many Antarctic research stations support satellite field camps which are, in general, seasonal camps. The type of field camp can vary – some are permanent structures used during the annual Antarctic summer, whereas others are little more than te ... * Crime in Antarctica References * tp://sidads.colorado.edu/pub/DATASETS/AGDC/antarctic_10m_temps/trans-ant_55.txt Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1957-1958 External links Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1955-1958 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
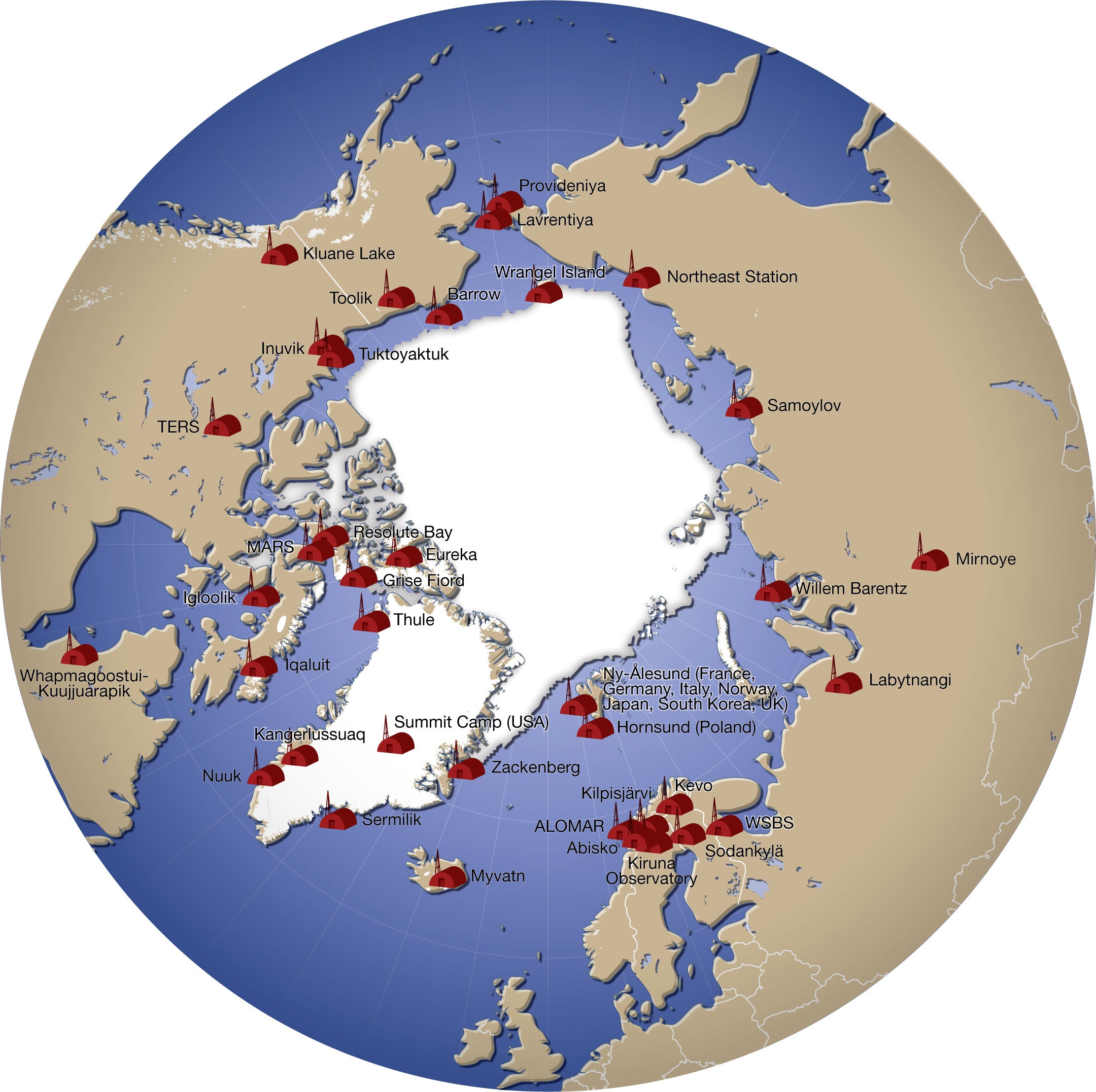
List Of Research Stations In The Arctic
A number of governments maintain permanent research stations in the Arctic. Also known as Arctic bases, polar stations or ice stations, these bases are widely distributed across the northern polar region of Earth. Historically few research stations have been permanent. Most of them were temporary, being abandoned after the completion of the project or owing to lack of funding to continue the research. Some of these were military or intelligence stations (listening posts) created as a result of the proximity of the U.S. and Soviet Union to each other's landmass across the polar region. Ice stations are constructed on land or on ice that rests on land, while others are drifting ice stations built on the sea ice of the high latitudes of the Arctic Ocean. Research stations Drifting ice stations *Fletcher's Ice Island, US (1952 - 1978) In fiction *Ice Station Zebra (novel), by Alistair MacLean **Ice Station Zebra (1968 film) **Ice Station Zebra a song by Jack White on Boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eismitte
Eismitte, in English also called Mid-Ice, was the site of an Arctic expedition in the interior of Greenland that took place from July 1930 through August 1931, and claimed the life of noted German scientist Alfred Wegener. The name "Eismitte" means ''Ice-Middle'' in German, and the campsite was located from the coast at an estimated altitude of 3,010 meters (9,875 feet). The coldest temperature recorded during the expedition was −64.8 °C (−84.6 °F) on March 20, 1931, while the warmest temperature noted was −1.8 °C (28.8 °F) on July 9, 1931. For the 12-month period beginning August 1, 1930 and ending August 5, 1931, the warmest month, July, had a mean monthly temperature of −12.2 °C (10 °F), while the coldest month, February, averaged −47.2 °C (−53 °F). Over the same period a total of 110 millimeters (4.33 inches) of water-equivalent precipitation was recorded, with most of it, rather surprisingly, being received in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit Camp
Summit Camp, also Summit Station, is a year-round staffed research station near the apex of the Greenland ice sheet. The station is located at above sea level. The population of the station is typically five in wintertime and reaches a maximum of 38 in the summer. The station is operated by the United States National Science FoundationArctic Logistics Information And Support (ALIAS) through the logistical-support contractor Battelle Arctic Research Operations (Battelle ARO). A permit from the Danish Polar Center ( da, Dansk Polarcenter) under the auspices of the Home R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEEM Camp
NEEM Camp was a small research facility on the northern Greenland Ice Sheet, used as a base for ice core drilling. It was located about 313 km east of the closest coast, Peabody Bay in northern Greenland, 275 km northwest of the historical ice sheet camp North Ice, and 484 km east-northeast of Siorapaluk, the closest settlement. There was one heavy-duty tent for accommodation of the researchers during summer. Access was by skiway (snow runway). The acronym NEEM stands for North Greenland Eemian Ice Drilling. The ice at the NEEM coring location (77°27'N 51°3.6'W) was predicted to be 2545 m thick. Drilling started at NEEM in June 2009 and drillers expected to hit bedrock in 2010. The drilling progressed well and reached through the brittle zone (~800 m) in mid-July 2009. The plan was to process the ice below the brittle zone, per decision at the steering committee meeting in November 2008 in Copenhagen. By September 1, 2009, the coring had reached 1757.84 m for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |