|
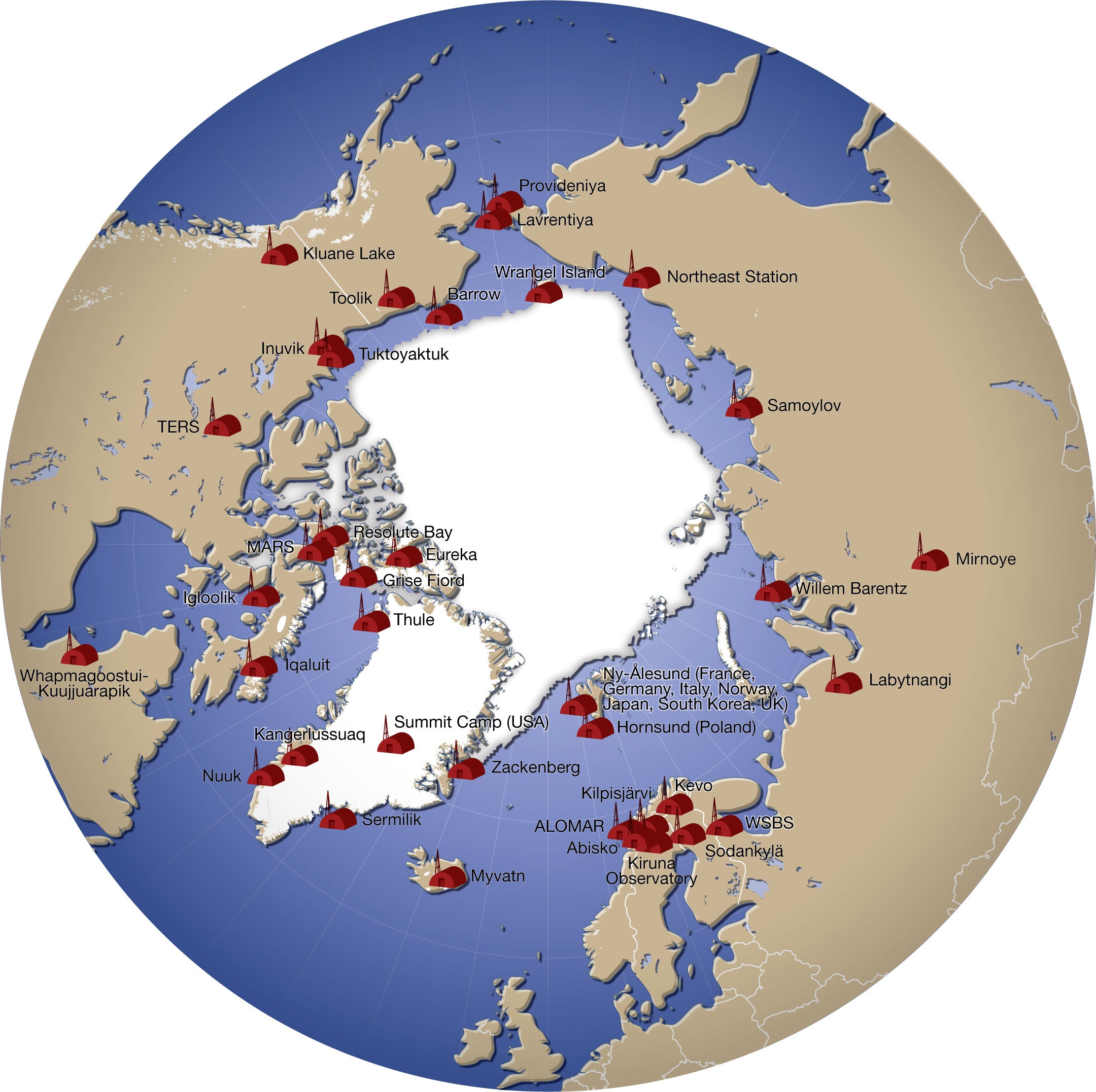
List Of Research Stations In The Arctic
A number of governments maintain permanent research stations in the Arctic. Also known as Arctic bases, polar stations or ice stations, these bases are widely distributed across the northern polar region of Earth. Historically few research stations have been permanent. Most of them were temporary, being abandoned after the completion of the project or owing to lack of funding to continue the research. Some of these were military or intelligence stations (listening posts) created as a result of the proximity of the U.S. and Soviet Union to each other's landmass across the polar region. Ice stations are constructed on land or on ice that rests on land, while others are drifting ice stations built on the sea ice of the high latitudes of the Arctic Ocean. Research stations Drifting ice stations *Fletcher's Ice Island, US (1952 - 1978) In fiction *Ice Station Zebra (novel), by Alistair MacLean **Ice Station Zebra (1968 film) **Ice Station Zebra a song by Jack White on Boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River Station (Arctic)
The Arctic Yellow River Station () was established by the Polar Research Institute of China in Ny-Ålesund, on Svalbard, in 2003. Scientists at the station conducted research into the Aurora Borealis and microbes in the ice-pack, glacier monitoring, atmospheric research. See also *List of research stations in the Arctic *Antarctic Great Wall Station * ''Xuě Lóng'' *Antarctic Zhongshan Station *Arctic policy of China The Arctic Policy of China outlines China's approach to foreign relations with Arctic countries as well as its plans to develop infrastructure, extend military capabilities, conduct research, and excavate resources within the Arctic Circle. A majo ... References Science and technology in the People's Republic of China Research stations in Svalbard Ny-Ålesund 2003 establishments in Norway Polar Research Institute of China {{Svalbard-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peary Land
Peary Land is a peninsula in northern Greenland, extending into the Arctic Ocean. It reaches from Victoria Fjord in the west to Independence Fjord in the south and southeast, and to the Arctic Ocean in the north, with Cape Morris Jesup, the northernmost point of Greenland's mainland, and Cape Bridgman in the northeast. History Ancient settlements Peary Land was historically inhabited by three separate cultures, during which times the climate was milder than presently: *Independence I culture, Paleo-Eskimo (around 2000 BC, oldest remains dating from 2400 BC) *Independence II culture, Paleo-Eskimo (800 BC to 200 BC) *Thule culture (ancestral to the modern Inuit, around AD 1300) Peary's explorations The area is named after Robert E. Peary, who first explored it during his expedition of 1891 to 1892. Originally, Peary Land was believed to be an island, separated from the main island by the so-called Peary Channel, an assumed connection between Nordenskiöld Fjord and Independe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brønlundhus
Brønlundhus, on some maps also Brønlundfjord, is a former research station and radio station located on the western shore of Jørgen Brønlund Fjord in southern Peary Land, in northern Greenland. It is named after Greenlandic Arctic researcher Jørgen Brønlund, or after the namesake fjord on which it is located. It is close to the mouth of Jørgen Brønlund Fjord where it opens into Independence Fjord. History Brønlundhus was built in 1947–48 by the Danish Peary Land Expeditions on initiative of Eigil Knuth, through an air lift by PBY Catalina seaplanes from ''Zackenbergbasen'', a station built for that purpose close to a trapper's hut at the site of present Zackenberg research station area 1000 km farther south. Brønlundhus was the first station in Greenland with all equipment transported by airlift. The seaplanes could land in the fjord only during the ice-free period from mid-July to end of August. Brønlundhus was used as a base for the first expedition 1948&nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakha
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia),, is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far Eastern Federal District, and is the world's largest country subdivision, covering over 3,083,523 square kilometers (1,190,555 sq mi). ''Sakha'' following regular sound changes in the course of development of the Yakut language) as the Evenk and Yukaghir exonyms for the Yakuts. It is pronounced as ''Haka'' by the Dolgans, whose language is either a dialect or a close relative of the Yakut language.Victor P. Krivonogov, "The Dolgans’Ethnic Identity and Language Processes." ''Journal of Siberian Federal University'', Humanities & Social Sciences 6 (2013 6) 870–888. Geography * ''Borders'': ** ''internal'': Chukotka Autonomous Okrug (660 km)(E), Magadan Oblast (1520 km)(E/SE), Khabarovsk Krai (2130 km)(SE), Amur Oblast (S) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island
Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island (russian: Большой Ляховский остров), or Great Lyakhovsky, is the largest of the Lyakhovsky Islands belonging to the New Siberian Islands archipelago between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea in northern Russia. It has an area of , and a maximum altitude of (Emy Tas). The peninsula projecting towards the west of the island is the Kigilyakh Peninsula ''(Poluostrov Kigilyakh)''. Off Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island's southwestern cape lies a small islet called Ostrov Khopto-Terer. The Lyakhovsky Islands are named in honour of Ivan Lyakhov, who explored them in 1773. In 2020, a well preserved ice age cave bear was found on the island. Geology Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island consists of highly folded and faulted Precambrian metamorphic rocks and turbidites; Mesozoic turbidites and igneous rocks; and Cenozoic sediments. Exposed in southeastern part of this island, the older Precambrian. Early Proterozoic, metamorphic rocks consist of schis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Polar Station
Bolshoi (, meaning ''big'', ''large'', ''great'', ''grand'', etc.) may refer to: * Bolshoi Theatre, a ballet and opera theatre in Moscow, Russia ** Bolshoi Ballet, a ballet company at the Bolshoi Theatre *Bolshoi Theatre, Saint Petersburg, a ballet and opera theatre in St. Petersburg, Russia *The Bolshoi, an English post-punk band * 26793 Bolshoi, a main-belt asteroid *Bolshoi Cosmological Simulation, a NASA simulation of the universe *Bolshoi, a bell in Danilov Monastery, Moscow *Command Bolshoi, Japanese professional wrestler See also *Alisher Navoi State Academic Bolshoi Theatre The Navoi Theater ( uz, Alisher Navoiy nomidagi davlat akademik katta teatri, "Alisher Navoi State Academic Big Theatre") is the national opera theater in Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Overview In 1929, amateurs of concert-ethnographic group led by M. ..., Uzbekistan * Bolshoi Drama Theatre, St.Petersburg * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai ( rus, Красноя́рский край, r=Krasnoyarskiy kray, p=krəsnɐˈjarskʲɪj ˈkraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), with its administrative center in the city of Krasnoyarsk, the third-largest city in Siberia (after Novosibirsk and Omsk). Comprising half of the Siberian Federal District, Krasnoyarsk Krai is the largest krai in the Russian Federation, the second largest federal subject (after neighboring Sakha) and the third largest subnational governing body by area in the world, after Sakha and the Australian state of Western Australia. The krai covers an area of , which is nearly one quarter the size of the entire country of Canada (the next-largest country in the world after Russia), constituting roughly 13% of the Russian Federation's total area and containing a population of 2,828,187 (more than a third of them in the city of Krasnoyarsk), or just under 2% of its population, per the 2010 Census. Geography The krai lies in the middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maly Begichev Island
Maly Begichev (russian: Малый Бегичев) is an island in the Laptev Sea, Russia. Its area is 15 km2. This small island (maximum length 5.4 km) is situated within the Khatanga Gulf (Russian: Хатангский залив). Only 8.5 km east of it lies the big island known as Bolshoy Begichev Island. Its size is much larger, with an area of 1764 km sq. The border between administrative divisions of the Russian Federation runs between the two Begichev islands, so that while Maly Begichev is in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Bolshoy Begichev is in the Sakha Republic. Both islands are named after Russian polar explorer Nikifor Begichev. References * William Barr William Pelham Barr (born May 23, 1950) is an American attorney who served as the 77th and 85th United States attorney general in the administrations of Presidents George H. W. Bush and Donald Trump. Born and raised in New York City, Barr ..., ''The First Soviet Convoy to the Mouth of the Lena''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Barrow
Point Barrow or Nuvuk is a headland on the Arctic coast in the U.S. state of Alaska, northeast of Utqiaġvik (formerly Barrow). It is the northernmost point of all the territory of the United States, at , south of the North Pole. (The northernmost point on the North American mainland, Murchison Promontory in Canada, is farther north.) Point Barrow is an important geographical landmark, marking the limit between two marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, the Chukchi Sea to the west and the Beaufort Sea to the east. It was named by English explorer Frederick William Beechey in 1826 for Sir John Barrow, a statesman and geographer of the British Admiralty. The water around it is normally ice-free for two or three months a year, but this was not the experience of the early explorers. Beechey could not reach it by ship and had to send a ship's boat ahead. In 1826 John Franklin tried to reach it from the east and was blocked by ice. In 1837 Thomas Simpson walked 50 miles west to Poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |