|
Nicholas Dyson
Nicholas Dyson is Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, the James and Shirley Curvey MGH Research Scholar and Scientific Director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center. Research The Dyson Lab studies the retinoblastoma protein. Working as a post-doctoral fellow in the laboratory of Dr. Ed Harlow, Dyson demonstrated that the retinoblastoma protein can form complexes ''in vitro'' with the E7 oncoprotein of Human papilloma virus type-16. This result implicated pRB binding to E7 as a step in human papilloma virus-associated carcinogenesis. More recently, Dyson's group has shown that the transcription factor E2F1 Transcription factor E2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''E2F1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the E2F family of transcription factors. The E2F family plays a crucial role in the control of cell ... is a potent and specific inhibitor of beta-catenin/T-cell factor (TCF)-dependent transcripti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the third oldest general hospital in the United States and has a capacity of 999 beds. With Brigham and Women's Hospital, it is one of the two founding members of Mass General Brigham (formerly known as Partners HealthCare), the largest healthcare provider in Massachusetts. Massachusetts General Hospital houses the largest hospital-based research program in the world, the Mass General Research Institute, with an annual research budget of more than $1 billion in 2019. It is currently ranked as the #8 best hospital in the United States by '' U.S. News & World Report''. In , ''The Boston Globe'' ranked MGH the fifth best place to work out of Massachusetts companies with over 1,000 employees. History Founded in 1811, the original hospital was designed by the famous American architect Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ed Harlow
Ed Harlow (born 1952) is an American molecular biologist. Harlow received the Ph.D. degree from the Imperial Cancer Research Fund Laboratories in London. Harlow is professor of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology at Harvard Medical School. He has been associate director of the Dana–Farber Cancer Institute as well as research director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center and the National Cancer Institute. From 2009 to 2011 he was Chief Scientific Officer at Constellation Pharmaceuticals. Among Harlow's discoveries was the demonstration that the retinoblastoma protein interacts with viral transforming proteins, thereby linking tumor viruses with the cell cycle. He is also the author, with David Lane, of "Using antibodies: a laboratory manual." (1999). Dr. Harlow has trained scientists in the field of molecular biology and oncology, including Nicholas Dyson (Professor at Harvard Medical School and Scientific Director of the Massachusetts General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Boulton
Simon Joseph Boulton is a British scientist who has made important contributions to the understanding of DNA repair and the treatment of cancer resulting from DNA damage. He currently occupies the position of Senior Scientist and group leader of the DSB Repair Metabolism Laboratory at the Francis Crick Institute, London. He is also an honorary Professor at University College London. Early life and education Boulton studied Molecular Biology at the University of Edinburgh, then studied for a Ph.D. at the University of Cambridge under Professor Steve Jackson of the Gurdon Institute from 1994 to 1998. It was at Cambridge that Boulton began researching mechanisms of DNA. He has described his first exposure to the research environment at Cambridge as "extremely influential." Research The website of Cancer Research UK explains Boulton's work in this way: human DNA "is constantly under assault from chemical reactions taking place in our bodies and from things we're exposed to in ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Brook
Adam Brook is an American thoracic surgeon who is a surgical attending at St. Joseph's Medical Center in New York. Biography Dr. Brook received the A.B. degree in biology from Harvard University and the M.D. from Harvard Medical School. He also received the Ph.D. in genetics from the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. Brook completed his doctoral research in the laboratory of Professor Nicholas Dyson of the Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center. Brook subsequently completed thoracic surgical training at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center and then served as Specialist Registrar in Cardiothoracic Surgery at Barts Health NHS Trust in London, under Mr. Alan Wood. Brook is currently an attending thoracic surgeon at St. Joseph's Medical Center and the Northport Veterans Administration Medical Center in New York. Academic work Dr. Brook is a specialist in the treatment of lung cancer. His research has focused on molecular mechanisms of carcinogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoblastoma Protein
The retinoblastoma protein (protein name abbreviated pRb; gene name abbreviated ''Rb'', ''RB'' or ''RB1'') is a proto-oncogenic tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in several major cancers. One function of pRb is to prevent excessive cell growth by inhibiting cell cycle progression until a cell is ready to divide. When the cell is ready to divide, pRb is phosphorylated, inactivating it, and the cell cycle is allowed to progress. It is also a recruiter of several chromatin remodeling enzymes such as methylases and acetylases. pRb belongs to the pocket protein family, whose members have a pocket for the functional binding of other proteins. Should an oncogenic protein, such as those produced by cells infected by high-risk types of human papillomavirus, bind and inactivate pRb, this can lead to cancer. The ''RB'' gene may have been responsible for the evolution of multicellularity in several lineages of life including animals. Name and genetics In humans, the prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School (HMS) is the graduate medical school of Harvard University and is located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. Founded in 1782, HMS is one of the oldest medical schools in the United States and is consistently ranked first for research among medical schools by '' U.S. News & World Report''. Unlike most other leading medical schools, HMS does not operate in conjunction with a single hospital but is directly affiliated with several teaching hospitals in the Boston area. Affiliated teaching hospitals and research institutes include Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston Children's Hospital, McLean Hospital, Cambridge Health Alliance, The Baker Center for Children and Families, and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital. History Harvard Medical School was founded on September 19, 1782, after President Joseph Willard presented a report with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoblastoma Protein
The retinoblastoma protein (protein name abbreviated pRb; gene name abbreviated ''Rb'', ''RB'' or ''RB1'') is a proto-oncogenic tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in several major cancers. One function of pRb is to prevent excessive cell growth by inhibiting cell cycle progression until a cell is ready to divide. When the cell is ready to divide, pRb is phosphorylated, inactivating it, and the cell cycle is allowed to progress. It is also a recruiter of several chromatin remodeling enzymes such as methylases and acetylases. pRb belongs to the pocket protein family, whose members have a pocket for the functional binding of other proteins. Should an oncogenic protein, such as those produced by cells infected by high-risk types of human papillomavirus, bind and inactivate pRb, this can lead to cancer. The ''RB'' gene may have been responsible for the evolution of multicellularity in several lineages of life including animals. Name and genetics In humans, the prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E7 Papillomavirus Protein
''Papillomaviridae'' is a family of non- enveloped DNA viruses whose members are known as papillomaviruses. Several hundred species of papillomaviruses, traditionally referred to as "types", have been identified infecting all carefully inspected mammals, but also other vertebrates such as birds, snakes, turtles and fish. Infection by most papillomavirus types, depending on the type, is either asymptomatic (e.g. most Beta-PVs) or causes small benign tumors, known as papillomas or warts (e.g. human papillomavirus 1, HPV6 or HPV11). Papillomas caused by some types, however, such as human papillomaviruses 16 and 18, carry a risk of becoming cancerous. Papillomaviruses are usually considered as highly host- and tissue-tropic, and are thought to rarely be transmitted between species. Papillomaviruses replicate exclusively in the basal layer of the body surface tissues. All known papillomavirus types infect a particular body surface, typically the skin or mucosal epithelium of the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
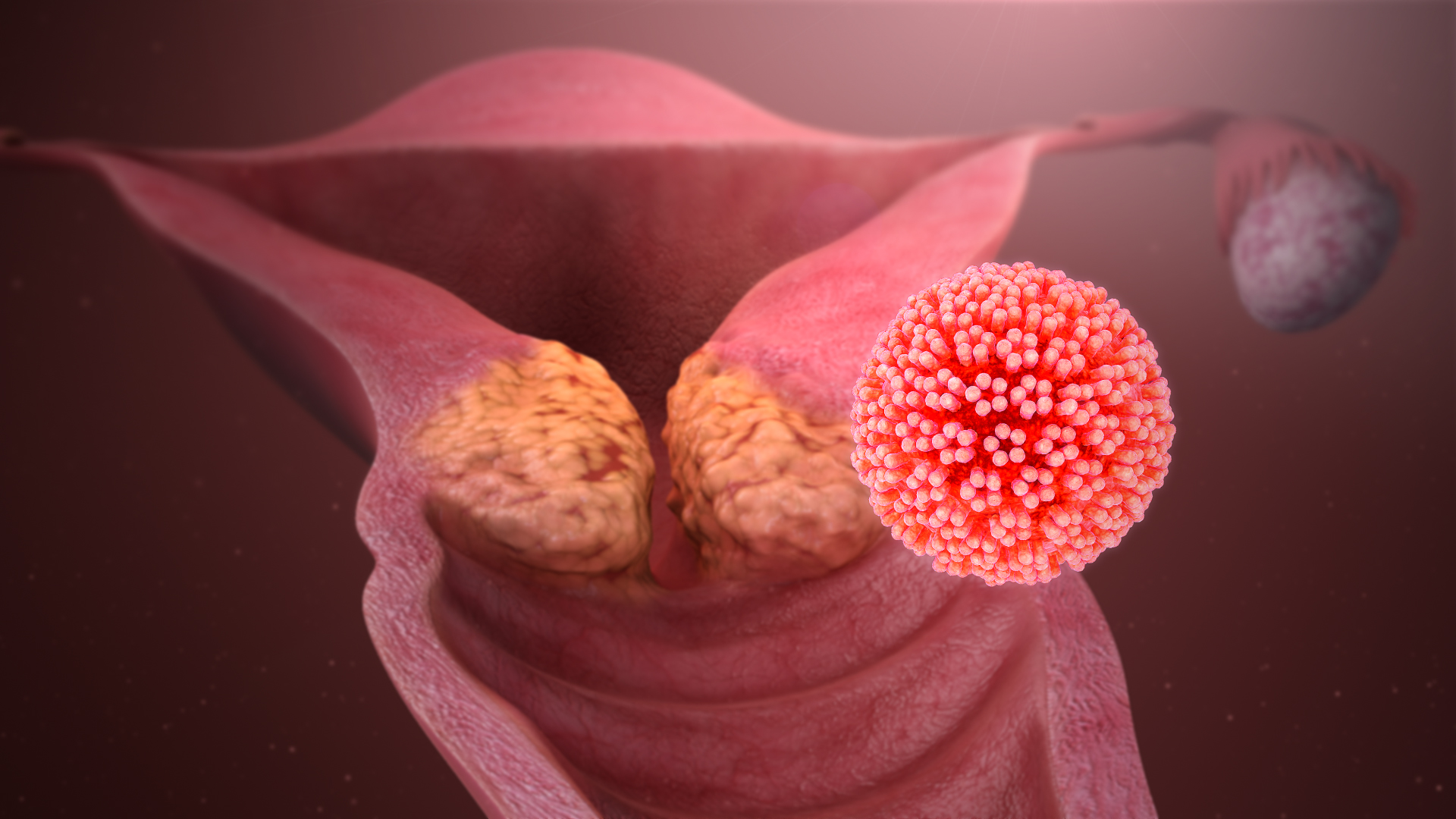
Human Papilloma Virus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E2F1
Transcription factor E2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''E2F1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the E2F family of transcription factors. The E2F family plays a crucial role in the control of cell cycle and action of tumor suppressor proteins and is also a target of the transforming proteins of small DNA tumor viruses. The E2F proteins contain several evolutionarily conserved domains found in most members of the family. These domains include a DNA binding domain, a dimerization domain which determines interaction with the differentiation regulated transcription factor proteins (DP), a transactivation domain enriched in acidic amino acids, and a tumor suppressor protein association domain which is embedded within the transactivation domain. This protein and another 2 members, E2F2 and E2F3, have an additional cyclin binding domain. This protein binds preferentially to retinoblastoma protein pRB in a cell-cycle dependent manner. It ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcription. In humans, the CTNNB1 protein is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. In ''Drosophila'', the homologous protein is called ''armadillo''. β-catenin is a subunit of the cadherin protein complex and acts as an intracellular signal transducer in the Wnt signaling pathway. It is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to γ-catenin, also known as plakoglobin. Beta-catenin is widely expressed in many tissues. In cardiac muscle, beta-catenin localizes to adherens junctions in intercalated disc structures, which are critical for electrical and mechanical coupling between adjacent cardiomyocytes. Mutations and overexpression of β-catenin are associated with many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, lun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |