|
Beta-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcription. In humans, the CTNNB1 protein is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. In ''Drosophila'', the homologous protein is called ''armadillo''. β-catenin is a subunit of the cadherin protein complex and acts as an intracellular signal transducer in the Wnt signaling pathway. It is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to γ-catenin, also known as plakoglobin. Beta-catenin is widely expressed in many tissues. In cardiac muscle, beta-catenin localizes to adherens junctions in intercalated disc structures, which are critical for electrical and mechanical coupling between adjacent cardiomyocytes. Mutations and overexpression of β-catenin are associated with many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, lun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenomatous Polyposis Coli
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 (DP2.5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APC'' gene. The APC protein is a negative regulator that controls beta-catenin concentrations and interacts with E-cadherin, which are involved in cell adhesion. Mutations in the ''APC'' gene may result in colorectal cancer. ''APC'' is classified as a tumor suppressor gene. Tumor suppressor genes prevent the uncontrolled growth of cells that may result in cancerous tumors. The protein made by the ''APC'' gene plays a critical role in several cellular processes that determine whether a cell may develop into a tumor. The APC protein helps control how often a cell divides, how it attaches to other cells within a tissue, how the cell polarizes and the morphogenesis of the 3D structures, or whether a cell moves within or away from tissue. This protein also helps ensure that the chromosome number in cells produced through cell division is correct. The APC pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APC Gene
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 (DP2.5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APC'' gene. The APC protein is a negative regulator that controls beta-catenin concentrations and interacts with E-cadherin, which are involved in cell adhesion. Mutations in the ''APC'' gene may result in colorectal cancer. ''APC'' is classified as a tumor suppressor gene. Tumor suppressor genes prevent the uncontrolled growth of cells that may result in cancerous tumors. The protein made by the ''APC'' gene plays a critical role in several cellular processes that determine whether a cell may develop into a tumor. The APC protein helps control how often a cell divides, how it attaches to other cells within a tissue, how the cell polarizes and the morphogenesis of the 3D structures, or whether a cell moves within or away from tissue. This protein also helps ensure that the chromosome number in cells produced through cell division is correct. The APC pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plakoglobin
Plakoglobin, also known as junction plakoglobin or gamma-catenin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUP'' gene. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to β-catenin. Plakoglobin is a cytoplasmic component of desmosomes and adherens junctions structures located within intercalated discs of cardiac muscle that function to anchor sarcomeres and join adjacent cells in cardiac muscle. Mutations in plakoglobin are associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Structure Human plakoglobin is 81.7 kDa in molecular weight and 745 amino acids long. The ''JUP'' gene contains 13 exons spanning 17 kb on chromosome 17q21. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin family, since it contains a distinct repeating amino acid motif called the armadillo repeat. Plakoglobin is highly similar to β-catenin; both have 12 armadillo repeats as well as N-terminal and C-terminal globular domains of unknown structure. Plakoglobin was originally identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part by the SPATS1 gene. The noncanonical plana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catenin
Catenins are a family of proteins found in complexes with cadherin cell adhesion molecules of animal cells. The first two catenins that were identified became known as α-catenin and β-catenin. α-Catenin can bind to β-catenin and can also bind filamentous actin (F-actin). β-Catenin binds directly to the cytoplasmic tail of classical cadherins. Additional catenins such as γ-catenin and δ-catenin have been identified. The name "catenin" was originally selected ('catena' means 'chain' in Latin) because it was suspected that catenins might link cadherins to the cytoskeleton. Types * α-catenin * β-catenin *γ-catenin * δ-catenin All but α-catenin contain armadillo repeats. They exhibit a high degree of protein dynamics, alone or in complex. Function Several types of catenins work with N-cadherins to play an important role in learning and memory. Cell-cell adhesion complexes are required for simple epithelia in higher organisms to maintain structure, function and pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium (the lining of the uterus or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first sign is most often vaginal bleeding not associated with a menstrual period. Other symptoms include pain with urination, pain during sexual intercourse, or pelvic pain. Endometrial cancer occurs most commonly after menopause. Approximately 40% of cases are related to obesity. Endometrial cancer is also associated with excessive estrogen exposure, high blood pressure and diabetes. Whereas taking estrogen alone increases the risk of endometrial cancer, taking both estrogen and a progestogen in combination, as in most birth control pills, decreases the risk. Between two and five percent of cases are related to genes inherited from the parents. Endometrial cancer is sometimes loosely referred to as "uterine cancer", although it is distinct from other fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plakoglobin
Plakoglobin, also known as junction plakoglobin or gamma-catenin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUP'' gene. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to β-catenin. Plakoglobin is a cytoplasmic component of desmosomes and adherens junctions structures located within intercalated discs of cardiac muscle that function to anchor sarcomeres and join adjacent cells in cardiac muscle. Mutations in plakoglobin are associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Structure Human plakoglobin is 81.7 kDa in molecular weight and 745 amino acids long. The ''JUP'' gene contains 13 exons spanning 17 kb on chromosome 17q21. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin family, since it contains a distinct repeating amino acid motif called the armadillo repeat. Plakoglobin is highly similar to β-catenin; both have 12 armadillo repeats as well as N-terminal and C-terminal globular domains of unknown structure. Plakoglobin was originally identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous Adenomatous polyps, adenomatous Colorectal polyp, polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the colon (anatomy), large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colorectal cancer, colon cancer occurs when they are left untreated. Three variants are known to exist, FAP and attenuated FAP (originally called hereditary flat adenoma syndrome) are caused by APC gene defects on chromosome 5 while autosomal recessive FAP (or MUTYH-associated polyposis) is caused by defects in the ''MUTYH'' gene on chromosome 1. Of the three, FAP itself is the most severe and most common; although for all three, the resulting colonic polyps and cancers are initially confined to the colon wall. Detection and removal before metastasis outside the colon can greatly reduce and in many cases eliminate the spread of cancer. The root cause of FAP is understood to be a genetic mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
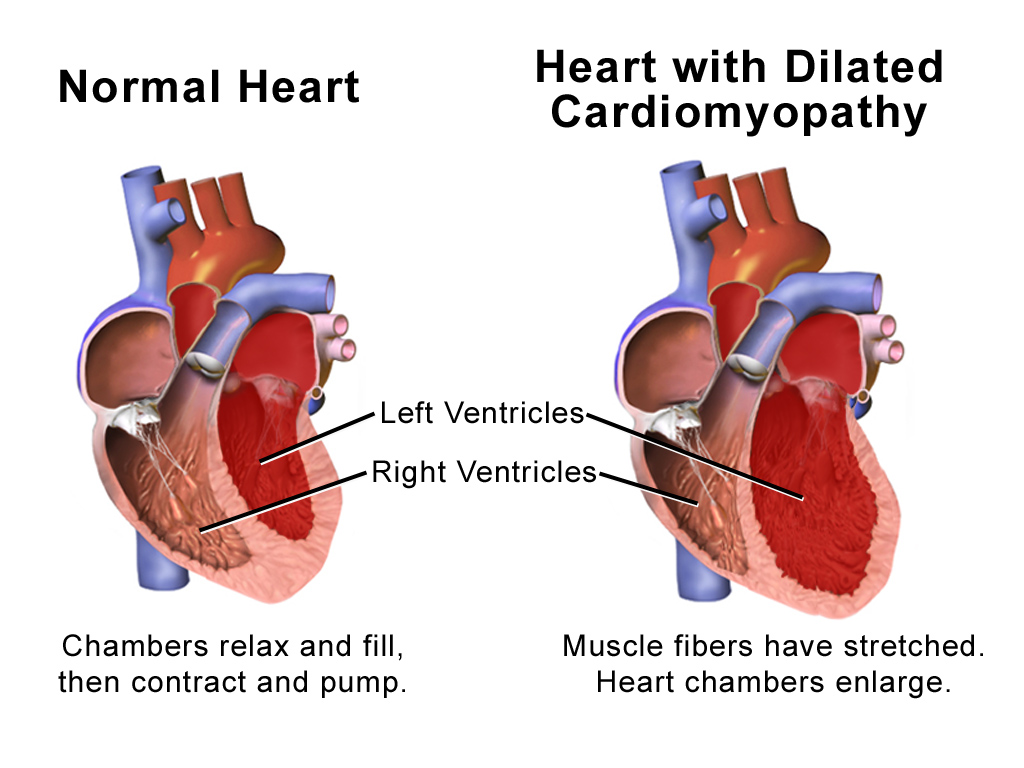
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinners or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
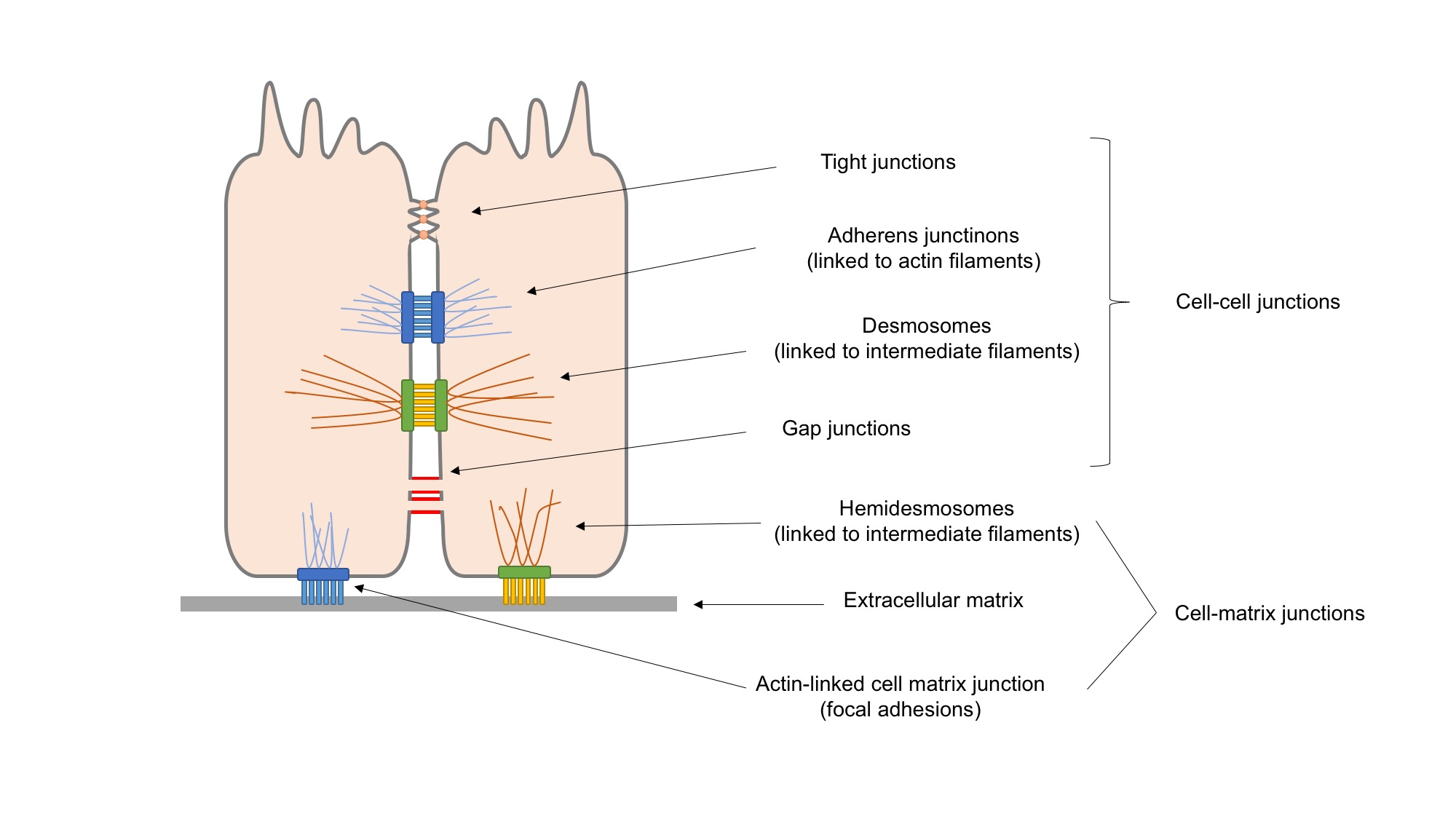
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |