endometrial cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Endometrial cancer is a

 PTEN and p27 loss of function mutations are associated with a good prognosis, particularly in obese women. The
PTEN and p27 loss of function mutations are associated with a good prognosis, particularly in obese women. The
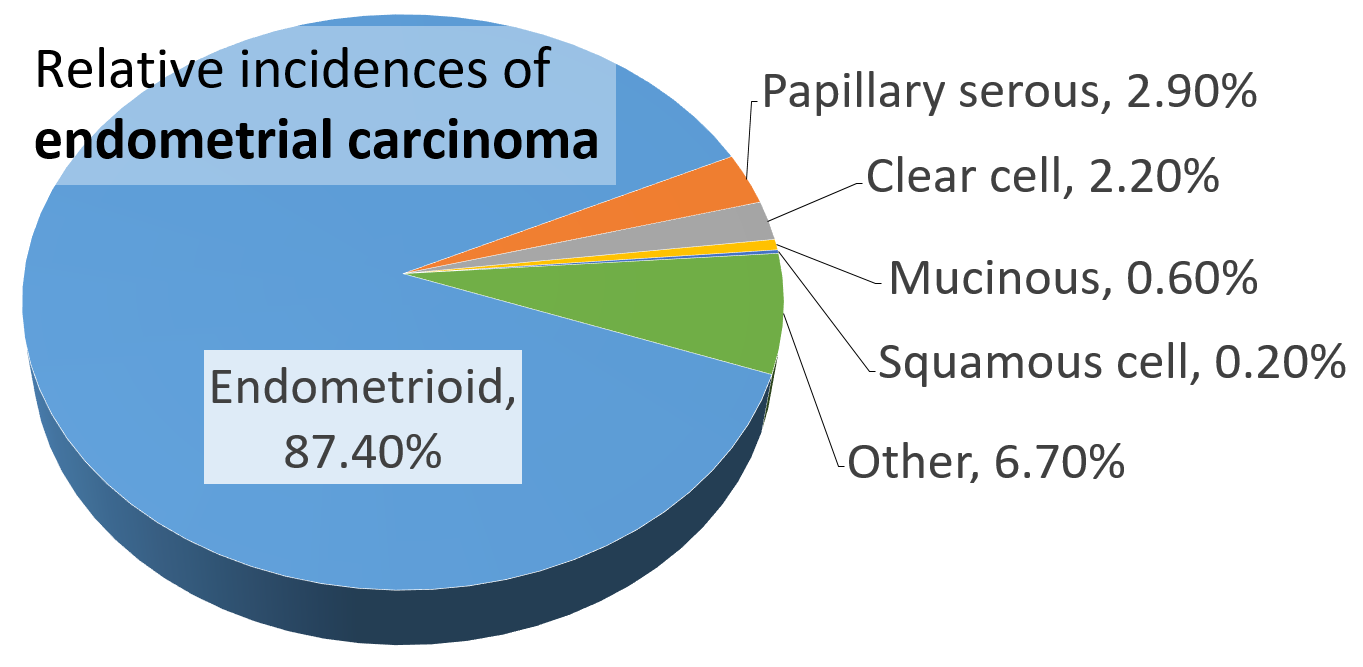 Traditional classification of endometrial carcinomas is based either on clinical and endocrine features (Type I and Type II) or histopathological characteristics (endometrioid, serous, and clear-cell). Some tumors are difficult to classify and have features overlapping more than one category. High-grade endometrioid tumors, in particular, tend to have both type I and type II features.
Traditional classification of endometrial carcinomas is based either on clinical and endocrine features (Type I and Type II) or histopathological characteristics (endometrioid, serous, and clear-cell). Some tumors are difficult to classify and have features overlapping more than one category. High-grade endometrioid tumors, in particular, tend to have both type I and type II features.
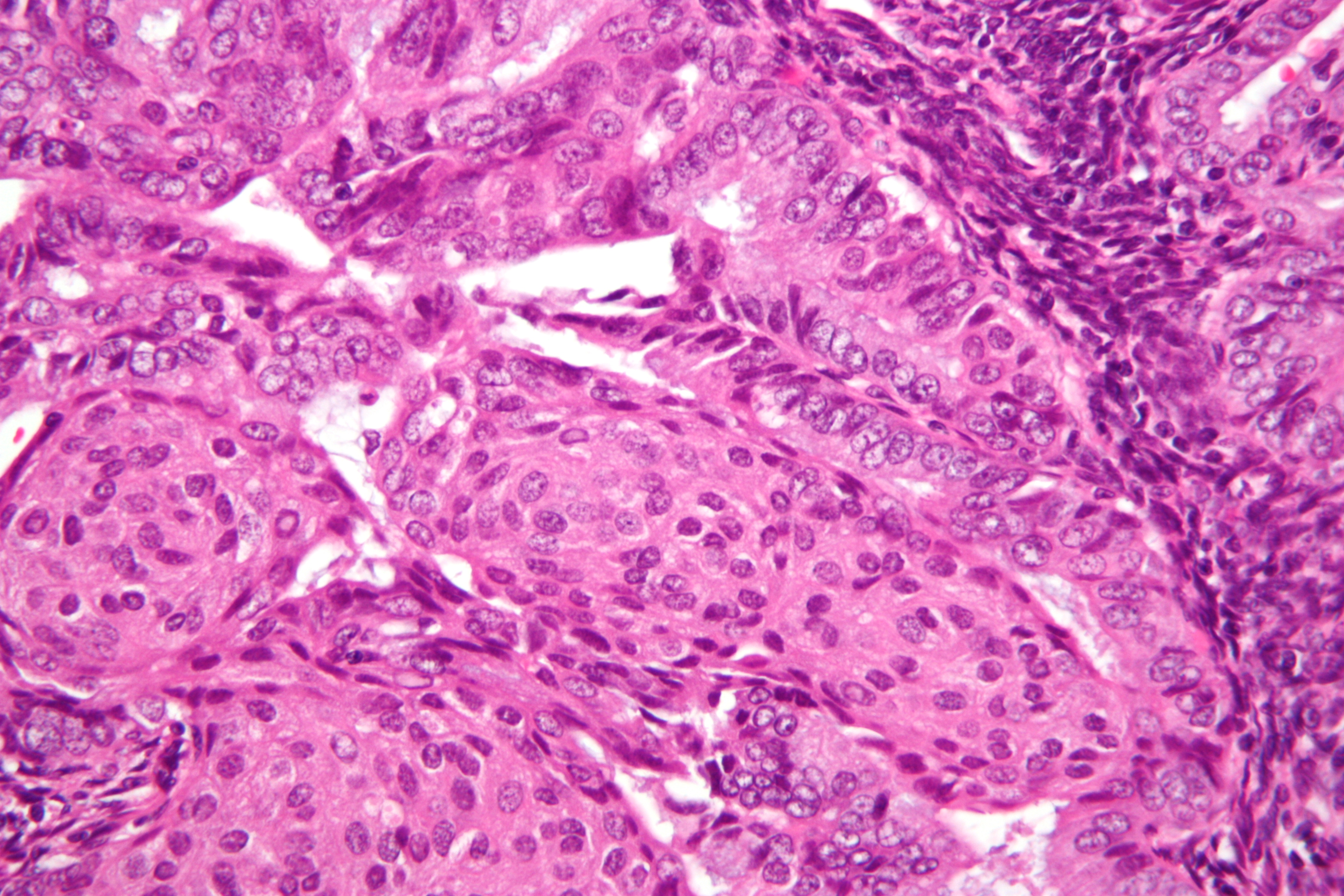 In contrast to endometrial carcinomas, the uncommon endometrial stromal sarcomas are cancers that originate in the non-glandular
In contrast to endometrial carcinomas, the uncommon endometrial stromal sarcomas are cancers that originate in the non-glandular
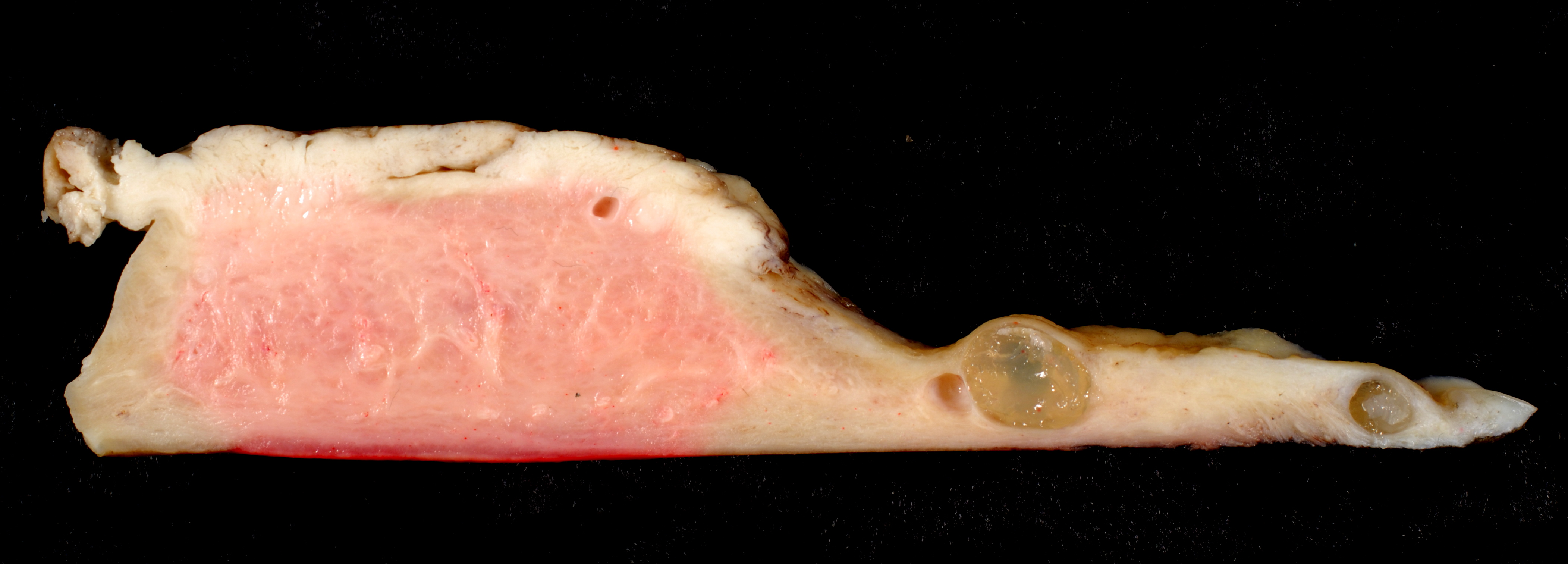 There is a three-tiered system for histologically classifying endometrial cancers, ranging from cancers with well-differentiated cells (grade I), to very poorly-differentiated cells (grade III). Grade I cancers are the least aggressive and have the best prognosis, while grade III tumors are the most aggressive and likely to recur. Grade II cancers are intermediate between grades I and III in terms of cell differentiation and aggressiveness of disease. There is also a separate "nuclear grade" system, where grade 1 tumors have inconspicuous
There is a three-tiered system for histologically classifying endometrial cancers, ranging from cancers with well-differentiated cells (grade I), to very poorly-differentiated cells (grade III). Grade I cancers are the least aggressive and have the best prognosis, while grade III tumors are the most aggressive and likely to recur. Grade II cancers are intermediate between grades I and III in terms of cell differentiation and aggressiveness of disease. There is also a separate "nuclear grade" system, where grade 1 tumors have inconspicuous
File:Endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterus FIGO grade III.jpg, A stage III endometrioid adenocarcinoma that has invaded the myometrium
File:Metastatic endometrial carcinoma (3944215367).jpg, Metastatic endometrial cancer seen in a removed lung
File:Histopathology of FIGO (architectural) grade 1 endometrial adenocarcinoma.png, Grade 1: ≤5% solid non-glandular, non-squamous growth.Images by Mikael Häggström, MD. Source for grading criteria:
- File:FIGO grade 2 endometrial adenocarcinoma.jpg, Grade 2: >5% and ≤50% solid non-glandular, non-squamous growth. File:FIGO grade 3 endometrial adenocarcinoma.jpg, Grade 3: >50% solid non-glandular, non-squamous growth. File:Histopathology of endometrioid cancer, grade 1, nuclear grade 1.jpg, Nuclear grade 1: Oval, mildly enlarged nucleus with evenly distributed chromatin.Images by Mikael Häggström, MD. Source for criteria:
- File:Histopathology of endometrioid cancer, grade 1, nuclear grade 2.jpg, Nuclear grade 2: Intermediate features. File:Endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma, nuclear and architectural grade 3.jpg, Nuclear grade 3: Markedly enlarged and pleomorphic nuclei, with coarse chromatin and distinct nucleoli. File:Endometrial endometrioid carcinoma with squamous differentiation and keratin granulomas, high magnification.jpg, Squamous growth seen as necrotic “ghost cells” of keratinocytes at right in image, leaving pink keratin.
 Myometrial invasion and involvement of the pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes are the most commonly seen patterns of spread. A Stage 0 is sometimes included; in this case, it is referred to as "
Myometrial invasion and involvement of the pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes are the most commonly seen patterns of spread. A Stage 0 is sometimes included; in this case, it is referred to as "
File:Diagram showing stage 1A and 1B cancer of the womb CRUK 196.svg, alt=A diagram of stage IA and IB endometrial cancer, Stage IA and IB endometrial cancer
File:Diagram showing stage 2 cancer of the womb CRUK 206.svg, alt=A diagram of stage II endometrial cancer, Stage II endometrial cancer
File:Diagram showing stage 3A to 3C cancer of the womb CRUK 224.svg, alt=A diagram of stage III endometrial cancer, Stage III endometrial cancer
File:Diagram showing stage 4A and 4B cancer of the womb CRUK 234.svg, alt=A diagram of stage IV endometrial cancer, Stage IV endometrial cancer
 The initial treatment for endometrial cancer is surgery; 90% of women with endometrial cancer are treated with some form of surgery. Surgical treatment typically consists of
The initial treatment for endometrial cancer is surgery; 90% of women with endometrial cancer are treated with some form of surgery. Surgical treatment typically consists of
American Cancer Society's Detailed Guide: Endometrial Cancer
U.S. National Cancer Institute: Uterine cancer
Anatomical pathology images
{{DEFAULTSORT:Endometrial Cancer Articles containing video clips Gynaecological cancer Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Women's health
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
that arises from the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The funct ...
(the lining of the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first sign is most often vaginal bleeding not associated with a menstrual period
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eg ...
. Other symptoms include pain with urination, pain during sexual intercourse, or pelvic pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the area of the pelvis. Acute (medicine), Acute pain is more common than chronic pain. If the pain lasts for more than six months, it is deemed to be chronic pelvic pain. It can affect both the male and female pelvis.
Common ...
. Endometrial cancer occurs most commonly after menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
.
Approximately 40% of cases are related to obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
. Endometrial cancer is also associated with excessive estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
exposure, high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
and diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
. Whereas taking estrogen alone increases the risk of endometrial cancer, taking both estrogen and a progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestins, progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestoge ...
in combination, as in most birth control pills Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control. The introduction of the birth control pill ("the Pill") in 1960 revolutionized the options for contraception, ...
, decreases the risk. Between two and five percent of cases are related to genes inherited from the parents. Endometrial cancer is sometimes called " uterine cancer", although it is distinct from other forms of cancer of the uterus such as cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later sympt ...
, uterine sarcoma, and trophoblastic disease. The most frequent type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* ...
of endometrial cancer is endometrioid carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoder ...
, which accounts for more than 80% of cases. Endometrial cancer is commonly diagnosed by endometrial biopsy or by taking samples during a procedure known as dilation and curettage
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to:
Physiology or medicine
* Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc.
* Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex
* Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and s ...
. A pap smear is not typically sufficient to show endometrial cancer. Regular screening in those at normal risk is not called for.
The leading treatment option for endometrial cancer is abdominal hysterectomy (the total removal by surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
of the uterus), together with removal of the Fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the Ovary, ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproduct ...
s and ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
on both sides, called a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. In more advanced cases, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
or hormone therapy
Hormone therapy or hormonal therapy is the use of hormones in medical treatment. Treatment with hormone antagonists may also be referred to as hormonal therapy or antihormone therapy. The most general classes of hormone therapy are hormonal therap ...
may also be recommended. If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, the outcome is favorable, and the overall five-year survival rate
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year surv ...
in the United States is greater than 80%.
In 2012, endometrial cancers newly occurred in 320,000 women and caused 76,000 deaths. This makes it the third most common cause of death in cancers which only affect women, behind ovarian and cervical cancer. It is more common in the developed world and is the most common cancer of the female reproductive tract in developed countries. Rates of endometrial cancer have risen in several countries between the 1980s and 2010. This is believed to be due to the increasing number of elderly people and rising obesity rates.
Signs and symptoms
Vaginal bleeding or spotting in women aftermenopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
occurs in 90% of endometrial cancer. Bleeding is quite common with adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ; AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
, occurring in two-thirds of all cases. Abnormal menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eg ...
s or extremely long, heavy, or frequent episodes of bleeding in women before menopause may also be a sign of endometrial cancer.
Symptoms other than bleeding are not common. Other symptoms include thin white or clear vaginal discharge in postmenopausal women. More advanced disease shows more obvious symptoms or signs that can be detected on a physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
. The uterus may become enlarged or the cancer may spread, causing lower abdominal pain or pelvic cramping. Painful sexual intercourse or painful or difficult urination are less common signs of endometrial cancer. The uterus may also fill with pus ( pyometrea). Of women with these less common symptoms (vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, and pus), 10–15% have cancer.
Risk factors
Risk factors for endometrial cancer includeobesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
, breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
, use of tamoxifen
Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has been used for Albright syndrome ...
, never having had a child, late menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
, high levels of estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
, and increasing age. Immigration studies (migration studies), which examine the change in cancer risk in populations moving between countries with different rates of cancer, show that there is some environmental component to endometrial cancer. These environmental risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
s are not well characterized. It is found that adiposity is associated with the earlier diagnosis of EC, particularly the endometrioid subtype.
Hormones
Most of the risk factors for endometrial cancer involve high levels of estrogens. An estimated 40% of cases are thought to be related to obesity. In obesity, the excess ofadipose tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
increases conversion of androstenedione
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione (abbreviated as A4 or Δ4-dione), also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of estrone and of testosterone from dehydroe ...
into estrone
Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized ...
, an estrogen. Higher levels of estrone in the blood causes less
Less or LESS may refer to:
Computing
* less (Unix), a Unix utility program
* Less (style sheet language), a dynamic style sheet language
* Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS), a product development framework that extends Scrum
Other uses
* -less, a priv ...
or no ovulation and exposes the endometrium continuously to high levels of estrogens. Obesity also causes less estrogen to be removed from the blood. Polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovarian syndrome, (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The name is a misnomer, as not all women with this condition develop cysts on their ovaries. The name origin ...
(PCOS), which also causes irregular or no ovulation, is associated with higher rates of endometrial cancer for the same reasons as obesity. Specifically, obesity, type II diabetes, and insulin resistance are risk factors for Type I endometrial cancer. Obesity increases the risk for endometrial cancer by 300–400%.
Estrogen replacement therapy during menopause when not balanced (or "opposed") with progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a '' synthetic'' progestogen. ...
is another risk factor. Higher doses or longer periods of estrogen therapy have higher risks of endometrial cancer. Women of lower weight are at greater risk from unopposed estrogen. A longer period of fertility—either from an early first menstrual period or late menopause—is also a risk factor. Unopposed estrogen raises an individual's risk of endometrial cancer by 2–10 fold, depending on weight and length of therapy. In trans men
A trans man or transgender man is a man who was assigned female at birth. Trans men have a male gender identity, and many trans men undergo Gender transition, medical and social transition to alter their appearance in a way that aligns with th ...
who take testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
and have not had a hysterectomy, the conversion of testosterone into estrogen via androstenedione may lead to a higher risk of endometrial cancer. Higher circulating testosterone levels in women have also been identified as an independent endometrial cancer risk factor.
Genetics
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
s can also cause endometrial cancer. Overall, hereditary causes contribute to 2–10% of endometrial cancer cases. Lynch syndrome, an autosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The firs ...
genetic disorder that mainly causes colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the Colon (anatomy), colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include Lower gastrointestinal ...
, also causes endometrial cancer, especially before menopause. Women with Lynch syndrome have a 40–60% risk of developing endometrial cancer, higher than their risk of developing colorectal (bowel) or ovarian cancer. Ovarian and endometrial cancer develop simultaneously in 20% of people. Endometrial cancer nearly always develops before colon cancer, on average, 11 years before. Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cell (biology), cells are malignant transformation, transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, G ...
in Lynch syndrome comes from a mutation in MLH1
DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 or MutL protein homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MLH1'' gene located on chromosome 3. The gene is commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Orthologs of human ...
or MLH2: genes that participate in the process of mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of nucleobase, bases that can arise during DNA replication and Genetic recombination, recombination, as well as DNA repair, ...
, which allows a cell to correct mistakes in the DNA. Other genes mutated in Lynch syndrome include MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2, which are also mismatch repair genes. Women with Lynch syndrome represent 2–3% of endometrial cancer cases; some sources place this as high as 5%. Depending on the gene mutation, women with Lynch syndrome have different risks of endometrial cancer. With MLH1 mutations, the risk is 54%; with MSH2, 21%; and with MSH6, 16%.
Women with a family history of endometrial cancer are at higher risk. Two genes most commonly associated with some other women's cancers, BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a ...
and BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are human genes and their protein products, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associate ...
, do not cause endometrial cancer. There is an apparent link with these genes. It is attributable to the use of tamoxifen, a drug that itself can cause endometrial cancer, in breast and ovarian cancers. The inherited genetic condition Cowden syndrome can also cause endometrial cancer. Women with this disorder have a 5–10% lifetime risk of developing endometrial cancer, compared to the 2–3% risk for unaffected women.
Common genetic variation has also been found to affect endometrial cancer risk in large-scale genome-wide association studies. Sixteen genomic regions have been associated with endometrial cancer and the common variants explain up to 7% of the familial relative risk.
Other health problems
Some therapies for other forms of cancer increase the lifetime risk of endometrial cancer, which is a baseline 2–3%. Tamoxifen, a drug used to treat estrogen-positive breast cancers, has been associated with endometrial cancer in approximately 0.1% of users, particularly older women. The benefits for survival from tamoxifen generally outweigh the risk of endometrial cancer. A one to two-year course of tamoxifen approximately doubles the risk of endometrial cancer, and a five-year course of therapy quadruples that risk. Raloxifene, a similar drug, did not raise the risk of endometrial cancer. Previously havingovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different ...
is a risk factor for endometrial cancer, as is having had previous radiotherapy to the pelvis. Specifically, ovarian granulosa cell tumors and thecoma
Thecomas or theca cell tumors are benign Ovarian cancer, ovarian neoplasms composed only of theca cells. Histogenetically they are classified as sex cord-stromal tumours.
They are typically estrogen-producing and they occur in older women (mean a ...
s are tumors associated with endometrial cancer.
Low immune function has also been implicated in endometrial cancer. High blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
is also a risk factor, but this may be because of its association with obesity. Sitting
Sitting is a basic action and resting position in which the body weight is supported primarily by the bony ischial tuberosities with the buttocks in contact with the ground or a horizontal surface such as a chair seat, instead of by the low ...
regularly for prolonged periods is associated with higher mortality from endometrial cancer. The risk is not negated by regular exercise, though it is lowered.
Protective factors
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
and the use of progestin are both protective against endometrial cancer. Smoking protects by altering the metabolism of estrogen and promoting weight loss and early menopause. This protective effect lasts long after smoking is stopped. Progestin is present in the combined oral contraceptive pill and the hormonal intrauterine device
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are a form of long-acting rever ...
(IUD). Combined oral contraceptives reduce risk more the longer they are taken: by 56% after four years, 67% after eight years, and 72% after twelve years. This risk reduction continues for at least fifteen years after contraceptive use has been stopped. Obese women may need higher doses of progestin to be protected. Having had more than five infants (grand multiparity) is also a protective factor, and having at least one child reduces the risk by 35%. Breastfeeding for more than 18 months reduces risk by 23%. Increased physical activity reduces an individual's risk by 38–46%. There is preliminary evidence that consumption of soy
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source of f ...
is protective. Mendelian randomization analyses have established potential protective factors such as LDL cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall dens ...
, later age of menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fe ...
and sex hormone binding globulin.
Pathophysiology
Endometrial cancer forms when there are errors in normal endometrialcell growth
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
. Usually, when cells grow old or get damaged, they die, and new cells take their place. Cancer starts when new cells form unneeded, and old or damaged cells do not die as they should. The buildup of extra cells often forms a mass of tissue called a growth or tumor. These abnormal cancer cells have many genetic abnormalities that cause them to grow excessively.
In 10–20% of endometrial cancers, mostly Grade 3 (the highest histologic grade), mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
s are found in a tumor suppressor
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results ...
gene, commonly p53 or PTEN. In 20% of endometrial hyperplasias and 50% of endometrioid cancers, PTEN has a loss-of-function mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis ...
or a null mutation
A null allele is a nonfunctional allele (a variant of a gene) caused by a genetic mutation. Such mutations can cause a complete lack of production of the associated gene product or a product that does not function properly; in either case, the al ...
, making it less effective or completely ineffective. Loss of PTEN function leads to up-regulation of the PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway, which causes cell growth. The p53 pathway can either be suppressed or highly activated in endometrial cancer. When a mutant version of p53 is overexpressed, the cancer tends to be particularly aggressive. P53 mutations and chromosome instability
Chromosomal instability (CIN) is a type of genome instability, genomic instability in which chromosomes are unstable, such that either whole chromosomes or parts of chromosomes are duplicated or deleted. More specifically, CIN refers to the increa ...
are associated with serous carcinomas, which tend to resemble ovarian and Fallopian carcinomas. Serous carcinomas are thought to develop from endometrial intraepithelial carcinoma.
 PTEN and p27 loss of function mutations are associated with a good prognosis, particularly in obese women. The
PTEN and p27 loss of function mutations are associated with a good prognosis, particularly in obese women. The Her2/neu
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that normally resides in the membranes of cells and is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The ...
oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
, which indicates a poor prognosis, is expressed in 20% of endometrioid and serous carcinomas. CTNNB1
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (''beta''-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
β-Catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcr ...
(beta-catenin; a transcription gene) mutations are found in 14–44% of endometrial cancers and may indicate a good prognosis, but the data is unclear. Beta-catenin mutations are commonly found in endometrial cancers with squamous cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of Cell (biology), cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial (Mesothelium, mesothelial) tissues line ...
s. FGFR2
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR-2) also known as CD332 (cluster of differentiation 332) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGFR2'' gene residing on chromosome 10. FGFR2 is a receptor for fibroblast growth factor.
FGFR-2 is ...
mutations are found in approximately 10% of endometrial cancers, and their prognostic significance is unclear. SPOP is another tumor suppressor gene found to be mutated in some cases of endometrial cancer: 9% of clear cell endometrial carcinomas and 8% of serous endometrial carcinomas have mutations in this gene.
Type I and Type II cancers (explained below) tend to have different mutations involved. ARID1A, which often carries a point mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences ...
in Type I endometrial cancer, is also mutated in 26% of clear cell carcinomas of the endometrium and 18% of serous carcinomas. Epigenetic silencing and point mutations of several genes are commonly found in Type I endometrial cancer. Mutations in tumor suppressor genes are common in Type II endometrial cancer. PIK3CA is commonly mutated in both Type I and Type II cancers. In women with Lynch syndrome-associated endometrial cancer, microsatellite instability is common.
Development of an endometrial hyperplasia (overgrowth of endometrial cells) is a significant risk factor because hyperplasias can and often do develop into adenocarcinoma, though cancer can develop without the presence of a hyperplasia. Within ten years, 8–30% of atypical endometrial hyperplasias develop into cancer, whereas 1–3% of non-atypical hyperplasias do so. An atypical hyperplasia is one with visible abnormalities in the nuclei. Pre-cancerous endometrial hyperplasias are also referred to as endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia
Endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN) is a premalignant lesion of the uterine lining that predisposes to endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma. It is composed of a collection of abnormal endometrial cells, arising from the glands that li ...
. Mutations in the KRAS
''KRAS'' ( Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, a part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell's nucleus. These signals instruct the ce ...
gene can cause endometrial hyperplasia and therefore Type I endometrial cancer. Endometrial hyperplasia typically occurs after the age of 40. Endometrial glandular dysplasia occurs with an overexpression of p53, and develops into a serous carcinoma.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of endometrial cancer is made first by a physical examination, endometrial biopsy, ordilation and curettage
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to:
Physiology or medicine
* Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc.
* Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex
* Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and s ...
(removal of endometrial tissue; D&C). This tissue is then examined histologically for characteristics of cancer. If cancer is found, medical imaging may be done to see whether the cancer has spread or invaded tissues like the myometrium (the muscular wall of the womb) or the uterine cervix. A study from 2024 indicates that transvaginal ultrasound provides diagnostic performance comparable to magnetic resonance imaging regarding the myometrial infiltration assessment. However, magnetic resonance imaging showed significantly better specificity in low-grade endometrial cancer.
Examination
Routine screening of asymptomatic people is not indicated since the disease is highly curable in its early, symptomatic stages. Instead, women, particularly menopausal women, should be aware of the symptoms and risk factors of endometrial cancer. A cervical screening test, such as a Pap smear, is not a useful diagnostic tool for endometrial cancer because the smear will be normal 50% of the time. A Pap smear can detect disease that has spread to the cervix. Results from apelvic examination
A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, ...
are frequently normal, especially in the early stages of disease. Changes in the size, shape, or consistency of the uterus or its surrounding, supporting structures may exist when the disease is more advanced. Cervical stenosis, the narrowing of the cervical opening, is a sign of endometrial cancer when pus or blood is found collected in the uterus (pyometra or hematometra).
Women with Lynch syndrome should begin to have annual biopsy screening at the age of 35. Some women with Lynch syndrome elect to have a prophylactic hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy to greatly reduce the risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer.
Transvaginal ultrasound
Vaginal ultrasonography is a medical ultrasonography that applies an ultrasound transducer (or "probe") in the vagina to visualize organs within the pelvic cavity. It is also called transvaginal ultrasonography because the ultrasound waves go ''a ...
to examine the endometrial thickness in women with postmenopausal bleeding is increasingly being used to aid in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer in the United States. In the United Kingdom, both an endometrial biopsy and a transvaginal ultrasound used in conjunction are the standard of care for diagnosing endometrial cancer. The homogeneity of the tissue visible on transvaginal ultrasound can help to indicate whether the thickness is cancerous. Ultrasound findings alone are not conclusive in cases of endometrial cancer, so another screening method (for example, endometrial biopsy) must be used in conjunction. Other imaging studies are of limited use. CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
s are used for preoperative imaging of tumors that appear advanced on physical exam or have a high-risk subtype (at high risk of metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
). They can also be used to investigate extrapelvic disease. An MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
can be of some use in determining if the cancer has spread to the cervix or if it is an endocervical adenocarcinoma. MRI is also useful for examining the nearby lymph nodes.
Dilation and curettage or an endometrial biopsy are used to obtain a tissue sample for histological examination. Endometrial biopsy is the less invasive option, but it may not give conclusive results every time. Hysteroscopy only shows the gross anatomy of the endometrium, which is often not indicative of cancer and is, therefore, not used unless in conjunction with a biopsy. Hysteroscopy can be used to confirm a diagnosis of cancer. New evidence shows that D&C has a higher false negative rate than endometrial biopsy.
Before treatment is begun, several other investigations are recommended. These include a chest x-ray, liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel or liver panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial ...
, kidney function tests, and a test for levels of CA-125, a tumor marker
A tumor marker is a biomarker that can be used to indicate the presence of cancer or the behavior of cancers (measure progression or response to therapy). They can be found in bodily fluids or tissue. Markers can help with assessing prognosis, s ...
that can be elevated in endometrial cancer.
Classification
Endometrial cancers may be tumors derived from epithelial cells (carcinomas), mixed epithelial and mesenchymal tumors (carcinosarcomas), or mesenchymal tumors. Traditional classification of endometrial carcinomas is based either on clinical and endocrine features (Type I and Type II) or histopathological characteristics (endometrioid, serous, and clear-cell). Some tumors are difficult to classify and have features overlapping more than one category. High-grade endometrioid tumors, in particular, tend to have both type I and type II features.
Traditional classification of endometrial carcinomas is based either on clinical and endocrine features (Type I and Type II) or histopathological characteristics (endometrioid, serous, and clear-cell). Some tumors are difficult to classify and have features overlapping more than one category. High-grade endometrioid tumors, in particular, tend to have both type I and type II features.
Carcinoma
The vast majority of endometrial cancers are carcinomas (usually adenocarcinomas), meaning that they originate from the single layer ofepithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
cells that line the endometrium and form the endometrial glands. There are many microscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale betwe ...
subtypes of endometrial carcinoma, but they are broadly organized into two categories, Type I and Type II, based on clinical features and pathogenesis. The two subtypes are genetically distinct.
Type I endometrial carcinomas occur most commonly before and around the time of menopause. In the United States, they are more common in white women, particularly those with a history of endometrial hyperplasia. Type I endometrial cancers are often low-grade, minimally invasive into the underlying uterine wall (myometrium
The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes) but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions.
Stru ...
), estrogen-dependent, and have a good outcome with treatment. Type I carcinomas represent 75–90% of endometrial cancer.
Type II endometrial carcinomas usually occur in older, post-menopausal people. In the United States, they are more common in black women
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
and are not associated with increased exposure to estrogen or a history of endometrial hyperplasia. Type II endometrial cancers are often high-grade, with deep invasion into the underlying uterine wall (myometrium), are of the serous
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The fl ...
or clear cell type, and carry a poorer prognosis. They can appear to be epithelial ovarian cancer on evaluation of symptoms. They tend to present later than Type I tumors and are more aggressive, with a greater risk of relapse and/or metastasis.
=Endometrioid adenocarcinoma
= In endometrioid adenocarcinoma, the cancer cells grow in patterns reminiscent of normal endometrium, with many new glands formed from columnar epithelium with some abnormal nuclei. Low-grade endometrioid adenocarcinomas have well-differentiated cells, have not invaded the myometrium, and are seen alongside endometrial hyperplasia. The tumor's glands form very close together, without the stromal tissue that normally separates them. Higher-grade endometrioid adenocarcinomas have less well-differentiated cells, have more solid sheets of tumor cells no longer organized into glands, and are associated with an atrophied endometrium. There are several subtypes of endometrioid adenocarcinoma with similar prognoses, including villoglandular, secretory, and ciliated cell variants. There is also a subtype characterized bysquamous
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
differentiation. Some endometrioid adenocarcinomas have foci of mucinous carcinoma.
The genetic mutations most commonly associated with endometrioid adenocarcinoma are in the genes PTEN, a tumor suppressor; PIK3CA, a kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
; KRAS, a GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a ...
that functions in signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
; and CTNNB1, involved in adhesion and cell signaling. The CTNNB1 (beta-catenin) gene is most commonly mutated in the squamous subtype of endometrioid adenocarcinoma.
=Serous carcinoma
= Serous carcinoma is a Type II endometrial tumor that makes up 5–10% of diagnosed endometrial cancer and is common in postmenopausal women with atrophied endometrium and black women. Serous endometrial carcinoma is aggressive and often invades the myometrium and metastasizes within the peritoneum (seen as omental caking) or the lymphatic system. Histologically, it appears with many atypical nuclei, papillary structures, and, in contrast to endometrioid adenocarcinomas, rounded cells instead of columnar cells. Roughly 30% of endometrial serous carcinomas also have psammoma bodies. Serous carcinomas spread differently than most other endometrial cancers; they can spread outside the uterus without invading the myometrium. The genetic mutations seen in serous carcinoma arechromosomal instability
Chromosomal instability (CIN) is a type of genomic instability in which chromosomes are unstable, such that either whole chromosomes or parts of chromosomes are duplicated or deleted. More specifically, CIN refers to the increase in rate of addi ...
and mutations in TP53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
, an important tumor suppressor gene.
=Clear cell carcinoma
= Clear cell carcinoma is a Type II endometrial tumor that makes up less than 5% of diagnosed endometrial cancer. Like serous cell carcinoma, it is usually aggressive and carries a poor prognosis. Histologically, it is characterized by the features common to all clear cells: the eponymous clear cytoplasm whenH&E stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin–eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diag ...
ed and visible, distinct cell membranes. The p53 cell signaling system is not active in endometrial clear cell carcinoma. This form of endometrial cancer is more common in postmenopausal women.
=Mucinous carcinoma
= Mucinous carcinomas are a rare form of endometrial cancer, making up less than 1–2% of all diagnosed endometrial cancers. Mucinous endometrial carcinomas are most often stage I and grade I, giving them a good prognosis. They typically have well-differentiated columnar cells organized into glands with the characteristicmucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins ( glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in ...
in the cytoplasm. Mucinous carcinomas must be differentiated from cervical adenocarcinoma.
=Mixed or undifferentiated carcinoma
= Mixed carcinomas are those that have both Type I and Type II cells, with one making up at least 10% of the tumor. These include the malignant mixed Müllerian tumor, which derives from endometrial epithelium and has a poor prognosis. Undifferentiated endometrial carcinomas make up less than 1–2% of diagnosed endometrial cancers. They have a worse prognosis than grade III tumors. Histologically, these tumors show sheets of identical epithelial cells with no identifiable pattern.=Other carcinomas
= Non-metastaticsquamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, comprises a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
and transitional cell carcinoma
Transitional cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from the transitional epithelium, a tissue lining the inner surface of these hollow organs. It typically occurs in the urothelium of the urinary system; in that case, it is also called ...
are very rare in the endometrium. Squamous cell carcinoma of the endometrium has a poor prognosis. It has been reported fewer than 100 times in the medical literature since its characterization in 1892. For primary squamous cell carcinoma of the endometrium (PSCCE) to be diagnosed, there must be no other primary cancer in the endometrium or cervix, and it must not be connected to the cervical epithelium. Because of the rarity of this cancer, there are no guidelines for how it should be treated, nor any typical treatment. The common genetic causes remain uncharacterized. Primary transitional cell carcinomas of the endometrium are even more rare; 16 cases had been reported . Its pathophysiology and treatments have not been characterized. Histologically, TCCE resembles endometrioid carcinoma and is distinct from other transitional cell carcinomas.
Sarcoma
 In contrast to endometrial carcinomas, the uncommon endometrial stromal sarcomas are cancers that originate in the non-glandular
In contrast to endometrial carcinomas, the uncommon endometrial stromal sarcomas are cancers that originate in the non-glandular connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
of the endometrium. They are generally non-aggressive and, if they recur, can take decades. Metastases to the lungs and pelvic or peritoneal cavities are the most frequent. They typically have estrogen and/or progesterone receptors. The prognosis for low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma is good, with 60–90% five-year survival. High-grade undifferentiated endometrial sarcoma (HGUS) has a worse prognosis, with high rates of recurrence and 25% five-year survival. HGUS prognosis is dictated by whether or not the cancer has invaded the arteries and veins. Without vascular invasion, the five-year survival is 83%; it drops to 17% when vascular invasion is observed. Stage I ESS has the best prognosis, with a five-year survival rate of 98% and a ten-year survival rate of 89%. ESS makes up 0.2% of uterine cancers.
Metastasis
Endometrial cancer frequently metastasizes to the ovaries and Fallopian tubes when the cancer is located in the upper part of the uterus, and the cervix when the cancer is in the lower part of the uterus. The cancer usually first spreads into the myometrium and theserosa
The serous membrane (or serosa) is a smooth epithelial membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces. The serous mem ...
, then into other reproductive and pelvic structures. When the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lympha ...
is involved, the pelvic
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton).
...
and para-aortic nodes are usually first to become involved, but in no specific pattern, unlike cervical cancer. More distant metastases are spread by the blood and often occur in the lungs, as well as the liver, brain, and bone. Endometrial cancer metastasizes to the lungs 20–25% of the time, more than any other gynecologic cancer
Gynecologic cancer is a type of cancer that affects the female reproductive system, including ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and vulvar cancer.
Gynecological cancers comprise 10-15% of women's cancers, mainly a ...
.
Histopathology
 There is a three-tiered system for histologically classifying endometrial cancers, ranging from cancers with well-differentiated cells (grade I), to very poorly-differentiated cells (grade III). Grade I cancers are the least aggressive and have the best prognosis, while grade III tumors are the most aggressive and likely to recur. Grade II cancers are intermediate between grades I and III in terms of cell differentiation and aggressiveness of disease. There is also a separate "nuclear grade" system, where grade 1 tumors have inconspicuous
There is a three-tiered system for histologically classifying endometrial cancers, ranging from cancers with well-differentiated cells (grade I), to very poorly-differentiated cells (grade III). Grade I cancers are the least aggressive and have the best prognosis, while grade III tumors are the most aggressive and likely to recur. Grade II cancers are intermediate between grades I and III in terms of cell differentiation and aggressiveness of disease. There is also a separate "nuclear grade" system, where grade 1 tumors have inconspicuous cell nuclei
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoc ...
, whereas grade 3 tumors have highly atypical nuclei.
The histopathology of endometrial cancers is highly diverse. The most common finding is a well-differentiated endometrioid adenocarcinoma, which is composed of numerous, small, crowded glands with varying degrees of nuclear atypia, mitotic activity, and stratification. This often appears on a background of endometrial hyperplasia. Frank adenocarcinoma may be distinguished from atypical hyperplasia by the finding of clear stromal invasion, or "back-to-back" glands, which represent nondestructive replacement of the endometrial stroma by the cancer. With progression of the disease, the myometrium is infiltrated.
- File:FIGO grade 2 endometrial adenocarcinoma.jpg, Grade 2: >5% and ≤50% solid non-glandular, non-squamous growth. File:FIGO grade 3 endometrial adenocarcinoma.jpg, Grade 3: >50% solid non-glandular, non-squamous growth. File:Histopathology of endometrioid cancer, grade 1, nuclear grade 1.jpg, Nuclear grade 1: Oval, mildly enlarged nucleus with evenly distributed chromatin.Images by Mikael Häggström, MD. Source for criteria:
- File:Histopathology of endometrioid cancer, grade 1, nuclear grade 2.jpg, Nuclear grade 2: Intermediate features. File:Endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma, nuclear and architectural grade 3.jpg, Nuclear grade 3: Markedly enlarged and pleomorphic nuclei, with coarse chromatin and distinct nucleoli. File:Endometrial endometrioid carcinoma with squamous differentiation and keratin granulomas, high magnification.jpg, Squamous growth seen as necrotic “ghost cells” of keratinocytes at right in image, leaving pink keratin.
Staging
Endometrial carcinoma is surgically staged using the FIGO cancer staging system. The 2009 FIGO staging system is commonly used. There is an updated 2023 FIGO staging system, but it is not yet universally adopted. The 2009 FIGO staging system is as follows: Myometrial invasion and involvement of the pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes are the most commonly seen patterns of spread. A Stage 0 is sometimes included; in this case, it is referred to as "
Myometrial invasion and involvement of the pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes are the most commonly seen patterns of spread. A Stage 0 is sometimes included; in this case, it is referred to as "carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma ''in situ'' (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells. While they are a form of neoplasm, there is disagreement over whether CIS should be classified as cancer. This controversy also depends on the exact CIS in question (e.g., cervical, skin, b ...
". In 26% of presumably early-stage cancers, intraoperative staging revealed pelvic and distant metastases, making comprehensive surgical staging necessary.
Management
Surgery
hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes ( salpi ...
including a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, which is the removal of the uterus, both ovaries, and the Fallopian tubes. Lymphadenectomy
Lymphadenectomy, or lymph node dissection, is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in ...
, or removal of pelvic and para-aortic lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s, is performed for tumors of histologic grade II or above. Lymphadenectomy is routinely performed for all stages of endometrial cancer in the United States, but in the United Kingdom, the lymph nodes are typically only removed with disease of stage II or greater. The topic of lymphadenectomy and what survival benefit it offers in stage I disease is still being debated. In women with presumed stage I disease, a 2017 systematic review found no evidence that lymphadenectomy reduces the risk of death or relapse of cancer when compared with no lymphadenectomy. Women who undergo lymphadenectomy are more likely to experience systemic morbidity related to surgery or lymphoedema/lymphocyst formation. In stage III and IV cancers, cytoreductive surgery is the norm, and a biopsy of the omentum may also be included. In stage IV disease, where there are distant metastases, surgery can be used as part of palliative therapy. Laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy.
Origins and history
The first successful laparotomy was performed without ...
, an open-abdomen procedure, is the traditional surgical procedure; however, in those with presumed early stage primary endometrial cancer, laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.Medli ...
(keyhole surgery) is associated with reduced operative morbidity and similar overall and disease free survival. Removal of the uterus via the abdomen is recommended over removal of the uterus via the vagina because it allows examining and obtaining washings of the abdominal cavity to detect any further evidence of cancer. Staging of the cancer is done during the surgery.
The few contraindications to surgery include inoperable tumor, massive obesity, a particularly high-risk operation, or a desire to preserve fertility. These contraindications happen in about 5–10% of cases. Women who wish to preserve their fertility and have low-grade stage I cancer can be treated with progestins, with or without concurrent tamoxifen therapy. This therapy can be continued until the cancer does not respond to treatment or until childbearing is done. Uterine perforation
Uterine perforation is a potential complication of any intrauterine procedure. It may be associated with injury to surrounding blood vessels or viscera such as the bladder or intestine. If not diagnosed at the time of the procedure it can occasi ...
may occur during a D&C or an endometrial biopsy. Side effects of surgery to remove endometrial cancer can specifically include sexual dysfunction, temporary incontinence, and lymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized edema, swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns inters ...
, along with more common side effects of any surgery, including constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The Human feces, stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the ...
.
Add-on therapy
There are many possible additional therapies. Surgery can be followed byradiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
and/or chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
in cases of high-risk or high-grade cancers. This is called adjuvant therapy
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in ...
.
Chemotherapy
Adjuvant chemotherapy
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in ...
is a recent innovation, consisting of some combination of paclitaxel
Paclitaxel, sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer. It is administered b ...
(or other taxane
Taxanes are a class of diterpenes. They were originally identified from plants of the genus ''Taxus'' (yews), and feature a taxadiene core. Paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere) are widely used as chemotherapy agents. Cabazitaxel was FDA app ...
s like docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cel ...
), doxorubicin (and other anthracyclines
Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from '' Streptomyces peucetius'' bacterium. These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, b ...
), and platins (particularly cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemical compound with chemical formula, formula ''cis''-. It is a coordination complex of platinum that is used as a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, c ...
and carboplatin
Carboplatin, sold under the brand name Paraplatin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of forms of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, brain cancer, and neuroblastoma. It is a ...
). Adjuvant chemotherapy has been found to increase survival in stage III and IV cancer more than added radiotherapy. Mutations in mismatch repair genes, like those found in Lynch syndrome, can lead to resistance against platins, meaning that chemotherapy with platins is ineffective in people with these mutations. Side effects of chemotherapy are common. These include hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
, low neutrophil levels in the blood, and gastrointestinal problems.
In cases where surgery is not indicated, palliative chemotherapy is an option; higher-dose chemotherapy is associated with longer survival. Palliative chemotherapy, particularly using capecitabine
Capecitabine, sold under the brand name Xeloda among others, is a anticancer medication used to treat breast cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. For breast cancer it is often used together with docetaxel. It is taken by mouth.
...
and gemcitabine, is also often used to treat recurrent endometrial cancer.
Low-certainty evidence suggests that in women with recurrent endometrial cancer who have had chemotherapy, receiving drugs that inhibit the mTOR pathway may reduce the risk of disease worsening compared to having more chemotherapy or hormonal therapy. However, mTOR inhibitors may increase the chance of experiencing digestive tract ulcers.
Radiotherapy
Adjuvant radiotherapy is commonly used in early-stage (stage I or II) endometrial cancer. It can be delivered through vaginal brachytherapy (VBT), which is becoming the preferred route due to its reduced toxicity, or external beam radiotherapy (EBRT).Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation, radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. The word "brachytherapy" comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek word , meaning "short-distance" or "s ...
involves placing a radiation source in the organ affected; in the case of endometrial cancer a radiation source is placed directly in the vagina. External beam radiotherapy involves a beam of radiation aimed at the affected area from outside the body. VBT is used to treat any remaining cancer solely in the vagina, whereas EBRT can be used to treat remaining cancer elsewhere in the pelvis following surgery. However, the benefits of adjuvant radiotherapy are controversial. Though EBRT significantly reduces the rate of relapse in the pelvis, overall survival and metastasis rates are not improved. VBT provides a better quality of life than EBRT.
Radiotherapy can also be used before surgery in certain cases. When pre-operative imaging or clinical evaluation shows tumor invading the cervix, radiation can be given before a total hysterectomy is performed. Brachytherapy and EBRT can also be used, singly or in combination, when there is a contraindication for hysterectomy. Both delivery methods of radiotherapy are associated with side effects, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
.
Hormonal therapy
Hormonal therapy is only beneficial in certain types of endometrial cancer. It was once thought to be beneficial in most cases. If a tumor is well-differentiated and known to have progesterone and estrogen receptors, progestins may be used in treatment. There is no evidence to support the use of progestagen in addition to surgery for newly diagnosed endometrial cancer. About 25% of metastatic endometrioid cancers show a response to progestins. Also, endometrial stromal sarcomas can be treated with hormonal agents, including tamoxifen,hydroxyprogesterone caproate
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate, sold under the brand name Delalutin among others, is a medication used to reduce the risk of preterm birth in women pregnant with one baby who have a history of spontaneous preterm birth. In March 2023, the manuf ...
, letrozole
Letrozole, sold under the brand name Femara among others, is an aromatase inhibitor medication that is used in the treatment of breast cancer for post-menopausal women.
It was patented in 1986 and approved for medical use in 1996. In 2021, ...
, megestrol acetate, and medroxyprogesterone
Medroxyprogesterone (MP), is a progestin which is not used medically. A derivative, medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), is used as a medication in humans, and is far more widely known in comparison. ''Medroxyprogesterone'' is sometimes used as a ...
. This treatment is effective in endometrial stromal sarcomas because they typically have estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
and/or progestin receptors. Progestin receptors function as tumor suppressor
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results ...
s in endometrial cancer cells. Preliminary research and clinical trials have shown these treatments to have a high rate of response even in metastatic disease.
In 2010, hormonal therapy was of unclear effect in those with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. There is insufficient evidence to inform women considering hormone replacement therapy after treatment for endometrial cancer.
Targeted therapy
Dostarlimab has been approved by the FDA for therapy of endometrial cancer with specific biomarkerMonitoring
The tumor marker CA-125 is frequently elevated in endometrial cancer and can be used to monitor response to treatment, particularly in serous cell cancer or advanced disease. Periodic MRIs or CT scans may be recommended in advanced disease and women with a history of endometrial cancer should receive more frequent pelvic examinations for the five years following treatment. Examinations conducted every three to four months are recommended for the first two years following treatment, and every six months for the next three years. Women with endometrial cancer should not have routine surveillance imaging to monitor the cancer unless new symptoms appear ortumor markers
A tumor marker is a Biomarker (medicine), biomarker that can be used to indicate the presence of cancer or the behavior of cancers (measure progression or response to therapy). They can be found in Body fluid, bodily fluids or Tissue (biology), ti ...
begin rising. Imaging without these indications is discouraged because it is unlikely to detect a recurrence or improve survival and because it has its costs and side effects.
If a recurrence is suspected, PET/CT scanning is recommended.
Prognosis
Survival rates
The five-year survival rate for endometrial adenocarcinoma following appropriate treatment is 80%. More than 70% of women diagnosed have FIGO stage I cancer, which has the best prognosis. Stage III and especially Stage IV cancers have a worse prognosis, but these are relatively rare, occurring in only 13% of cases. The median survival time for stage III–IV endometrial cancer is nine to ten months. Older age indicates a worse prognosis. In the United States, white women have a higher survival rate than black women, who tend to develop more aggressive forms of the disease by the time of their diagnosis. Tumors with highprogesterone receptor
The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone.
In humans, PR is encoded by a single ''PGR'' gene resi ...
expression have a good prognosis compared to tumors with low progesterone receptor expression; 93% of women with high progesterone receptor disease survived to three years, compared with 36% of women with low progesterone receptor disease. Heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
is the most common cause of death among those who survive endometrial cancer, with other obesity-related health problems also being common. Following diagnosis, quality of life is also positively associated with a healthy lifestyle (no obesity, high-quality diet, physical activity).
Recurrence rates
Recurrence of early-stage endometrial cancer ranges from 3% to 17%, depending on primary and adjuvant treatment. Most recurrences (75–80%) occur outside of the pelvis, and most occur within two to three years of treatment—64% within two years and 87% within three years. Higher-staged cancers are more likely to recur, as are those that have invaded the myometrium or cervix or that have metastasized into the lymphatic system. Papillary serous carcinoma, clear cell carcinoma, and endometrioid carcinoma are the subtypes at the highest risk of recurrence. High-grade histological subtypes are also at elevated risk for recurrence. The most common site of recurrence is in thevagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
; vaginal relapses of endometrial cancer have the best prognosis. If relapse occurs from a cancer that has not been treated with radiation, EBRT is the first-line treatment and is often successful. If a cancer treated with radiation recurs, pelvic exenteration
Pelvic exenteration (or pelvic evisceration) is a radical surgical treatment that removes all organs from a person's pelvic cavity. It is used to treat certain advanced or recurrent cancers. The urinary bladder, urethra, rectum, and anus are rem ...
is the only option for curative treatment. Palliative chemotherapy, cytoreductive surgery, and radiation are also performed. Radiation therapy (VBT and EBRT) for a local vaginal recurrence has a 50% five-year survival rate. Pelvic recurrences are treated with surgery and radiation, and abdominal recurrences are treated with radiation and, if possible, chemotherapy. Other common recurrence sites are the pelvic lymph nodes, para-aortic lymph nodes, peritoneum (28% of recurrences), and lungs, though recurrences can also occur in the brain (<1%), liver (7%), adrenal glands (1%), bones (4–7%; typically the axial skeleton
The axial skeleton is the core part of the endoskeleton made of the bones of the head and trunk of vertebrates. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of the skull (28 bones, including the cranium, mandible and the midd ...
), lymph nodes outside the abdomen (0.4–1%), spleen, and muscle/soft tissue (2–6%).
Epidemiology
, approximately 320,000 women are diagnosed with endometrial cancer worldwide each year and 76,000 die, making it the sixth most common cancer in women. It is more common in developed countries, where the lifetime risk of endometrial cancer in women is 1.6%, compared to 0.6% in developing countries. It occurs in 12.9 out of 100,000 women annually in developed countries. In the United States, endometrial cancer is the most frequently diagnosed gynecologic cancer and, in women, the fourth mostcommon
Common may refer to:
As an Irish surname, it is anglicised from Irish Gaelic surname Ó Comáin.
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Com ...
cancer overall, representing 6% of all cancer cases in women. In that country, it was estimated that 52,630 women were diagnosed yearly and 8,590 would die from the disease. Northern Europe, Eastern Europe, and North America have the highest rates of endometrial cancer, whereas Africa and West Asia have the lowest rates. Asia saw 41% of the world's endometrial cancer diagnoses in 2012, whereas Northern Europe, Eastern Europe, and North America together comprised 48% of diagnoses. Unlike most cancers, the number of new cases has risen in recent years, including an increase of over 40% in the United Kingdom between 1993 and 2013. Some of this rise may be due to the increase in obesity rates in developed countries, increasing life expectancies, and lower birth rates. The average lifetime risk for endometrial cancer is approximately 2–3% in people with uteruses. In the UK, approximately 7,400 cases are diagnosed annually, and in the EU, approximately 88,000.
Endometrial cancer appears most frequently during perimenopause (the period just before, just after, and during menopause), between the ages of 50 and 65; overall, 75% of endometrial cancer occurs after menopause. Women younger than 40 make up 5% of endometrial cancer cases and 10–15% of cases occur in women under 50 years of age. This age group is at risk for developing ovarian cancer at the same time. The worldwide median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “ ...
age of diagnosis is 63 years of age; in the United States, the average
In colloquial, ordinary language, an average is a single number or value that best represents a set of data. The type of average taken as most typically representative of a list of numbers is the arithmetic mean the sum of the numbers divided by ...
age of diagnosis is 60 years of age. White American women are at higher risk for endometrial cancer than black American women, with a 2.88% and 1.69% lifetime risk, respectively. Japanese-American women and American Latina women have lower rates, and Native Hawaiian women have higher rates.
Research
There are several experimental therapies for endometrial cancer under research, including immunologic, hormonal, and chemotherapeutic treatments.Trastuzumab
Trastuzumab, sold under the brand name Herceptin among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat breast cancer and stomach cancer. It is specifically used for cancer that is HER2 receptor positive. It may be used by itself or together ...
(Herceptin), an antibody
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
against the Her2 protein, has been used in cancers known to be positive for the Her2/neu oncogene, but research is still underway. Immunologic therapies are also under investigation, particularly in uterine papillary serous carcinoma.
Cancers can be analyzed using genetic techniques (including DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
and immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Alber ...
) to determine if certain therapies specific to mutated genes can be used to treat it. PARP inhibitors are used to treat endometrial cancer with PTEN mutations, specifically, mutations that lower the expression of PTEN. The PARP inhibitor shown to be active against endometrial cancer is olaparib. Research has been ongoing in this area as of the 2010s.
Research is ongoing on the use of metformin
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, ...
, a diabetes medication, in obese women with endometrial cancer before surgery. Early research has shown it to be effective in slowing the rate of cancer cell proliferation. Preliminary research has shown that preoperative metformin administration can reduce the expression of tumor markers. Long-term use of metformin has not been shown to have a preventative effect against developing cancer, but it may improve overall survival.
Temsirolimus
Temsirolimus, sold under the brand name Torisel, is an intravenous drug for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), developed by Wyeth Pharmaceuticals and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2007, and was also app ...
, an mTOR inhibitor, is under investigation as a potential treatment. Research shows that mTOR inhibitors may be particularly effective for cancers with mutations in PTEN. Ridaforolimus (deforolimus) is also being researched as a treatment for people who have previously had chemotherapy. Preliminary research has been promising, and a stage II trial for ridaforolimus was completed by 2013. There has also been research on combined ridaforolimus/progestin treatments for recurrent endometrial cancer. Bevacizumab and tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which inhibit angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and ...
, are being researched as potential treatments for endometrial cancers with high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, ), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors ...
. Ixabepilone
Ixabepilone ( INN; also known as azaepothilone B, codenamed BMS-247550) is a pharmaceutical drug developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb as a chemotherapeutic medication for cancer.
History
Ixabepilone is a semi-synthetic analog of epothilone B, a ...
is being researched as a possible chemotherapy for advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. Treatments for rare high-grade undifferentiated endometrial sarcoma are being researched, as there is no established standard of care yet for this disease. Chemotherapies being researched include doxorubicin and ifosfamide.
There is also research in progress on more genes and biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s that may be linked to endometrial cancer. The protective effect of combined oral contraceptives and the IUD is being investigated. Preliminary research has shown that the levonorgestrel
Levonorgestrel is a hormonal medication used in a number of birth control methods. It is combined with an estrogen to make combination birth control pills. As an emergency birth control, sold under the brand names Plan B One-Step and Julie, ...
IUD placed for a year, combined with six monthly injections of gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and rele ...
, can stop or reverse the progress of endometrial cancer in young women, specifically complex atypical hyperplasia; however, the results have been inconclusive. An experimental drug that combines a hormone with doxorubicin is also under investigation for greater efficacy in cancers with hormone receptors. Hormone therapy that is effective in treating breast cancer, including the use of aromatase inhibitor
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are a class of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women and in men, and gynecomastia in men. They may also be used off-label to reduce estrogen conversion when supplementing testosterone exo ...
s, is also being investigated for use in endometrial cancer. One such drug is anastrozole
Anastrozole, sold under the brand name Arimidex among others, is an antiestrogenic medication used in addition to other treatments for breast cancer. Specifically it is used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. It has also been used t ...
, which is currently being researched in hormone-positive recurrences after chemotherapy. Research into hormonal treatments for endometrial stromal sarcomas is ongoing as well. It includes trials of drugs like mifepristone
Mifepristone, and also known by its developmental code name RU-486, is a drug typically used in combination with misoprostol to bring about a medical abortion during pregnancy. This combination is 97% effective during the first 63 days (9 wee ...
, a progestin antagonist, and aminoglutethimide
Aminoglutethimide (AG), sold under the brand names Elipten, Cytadren, and Orimeten among others, is a medication which has been used in the treatment of seizures, Cushing's syndrome, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, among other indications. ...
and letrozole, two aromatase inhibitors.
Research continues into the best imaging method for detecting and staging endometrial cancer. As current diagnostic methods are invasive and inaccurate, researchers are looking into new ways to catch endometrial cancer, especially in its early stages. A study found that using a technique involving infrared light
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those o ...
on simple blood test samples detected uterine cancer with high accuracy (87%) and could detect precancerous growths in all cases. In surgery, research has shown that complete pelvic lymphadenectomy along with hysterectomy in stage 1 endometrial cancer does not improve survival and increases the risk of negative side effects, including lymphedema. Other research is exploring the potential of identifying the sentinel lymph node
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph nodes are the target organs primarily reached by metastasiz ...
s for biopsy by injecting the tumor with dye that shines under infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
light. Intensity modulated radiation therapy is currently under investigation and already used in some centers for application in endometrial cancer to reduce side effects from traditional radiotherapy. Its risk of recurrence has not yet been quantified. Research on hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an increase in barometric pressure of typically air or oxygen is used. The immediate effects include reducing the size of gas emboli and raising the partial pressures of the gases present. Initial ...
to reduce side effects is also ongoing. The results of the PORTEC 3 trial assessing combining adjuvant radiotherapy with chemotherapy were awaited in late 2014.
There is not enough evidence to determine if people with endometrial cancer benefit from additional behavioural and lifestyle interventions that are aimed at losing excess weight.
History and culture
Endometrial cancer is not widely known by the general populace despite its frequency. There is low awareness of the symptoms, which can lead to later diagnosis and worse survival.References
External links
American Cancer Society's Detailed Guide: Endometrial Cancer
U.S. National Cancer Institute: Uterine cancer
Anatomical pathology images
{{DEFAULTSORT:Endometrial Cancer Articles containing video clips Gynaecological cancer Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Women's health