|
PMS2
Mismatch repair endonuclease PMS2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PMS2'' gene. Function This gene is one of the PMS2 gene family members which are found in clusters on chromosome 7. Human PMS2 related genes are located at bands 7p12, 7p13, 7q11, and 7q22. Exons 1 through 5 of these homologues share high degree of identity to human PMS2 The product of this gene is involved in DNA mismatch repair. The protein forms a heterodimer with MLH1 and this complex interacts with MSH2 bound to mismatched bases. Defects in this gene are associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer, with Turcot syndrome, and are a cause of supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed. Mismatch repair and endonuclease activity PMS2 is involved in mismatch repair and is known to have latent endonuclease activity that depends on the integrity of the meta-binding motif in MutL homologs. As an endonuclease, PMS2 int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ERCC4
ERCC4 is a protein designated as DNA repair endonuclease XPF that in humans is encoded by the ''ERCC4'' gene. Together with ERCC1, ERCC4 forms the ERCC1-XPF enzyme complex that participates in DNA repair and DNA recombination. The nuclease enzyme ERCC1-XPF cuts specific structures of DNA. Many aspects of these two gene products are described together here because they are partners during DNA repair. The ERCC1-XPF nuclease is an essential activity in the pathway of DNA nucleotide excision repair (NER). The ERCC1-XPF nuclease also functions in pathways to repair double-strand breaks in DNA, and in the repair of "crosslink" damage that harmfully links the two DNA strands. Cells with disabling mutations in ''ERCC4'' are more sensitive than normal to particular DNA damaging agents, including ultraviolet radiation and to chemicals that cause crosslinking between DNA strands. Genetically engineered mice with disabling mutations in ''ERCC4'' also have defects in DNA repair, accompani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MLH1
DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 or MutL protein homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MLH1 gene located on chromosome 3. It is a gene commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Orthologs of human MLH1 have also been studied in other organisms including mouse and the budding yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. Function This gene was identified as a locus frequently mutated in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. It is a human homolog of the ''E. coli'' DNA mismatch repair gene, mutL, which mediates protein-protein interactions during mismatch recognition, strand discrimination, and strand removal. Defects in MLH1 are associated with the microsatellite instability observed in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described, but their full-length natures have not been determined. Role in DNA mismatch repair MLH1 protein is one component of a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
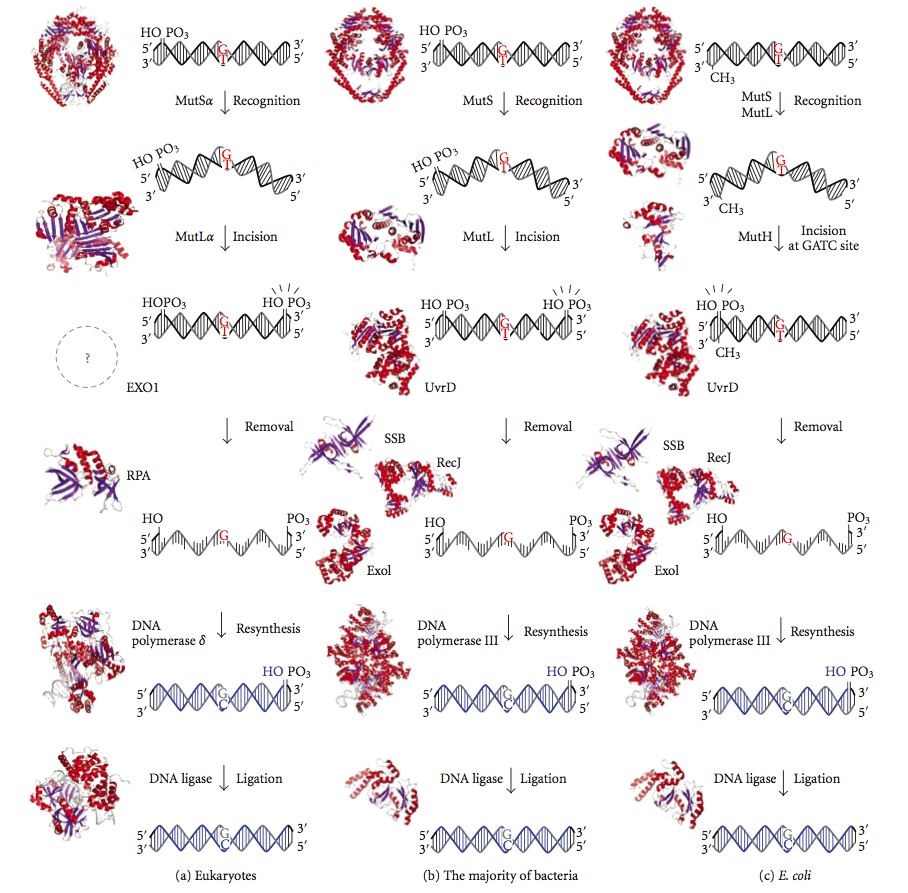
DNA Mismatch Repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage. Mismatch repair is strand-specific. During DNA synthesis the newly synthesised (daughter) strand will commonly include errors. In order to begin repair, the mismatch repair machinery distinguishes the newly synthesised strand from the template (parental). In gram-negative bacteria, transient hemimethylation distinguishes the strands (the parental is methylated and daughter is not). However, in other prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the exact mechanism is not clear. It is suspected that, in eukaryotes, newly synthesized lagging-strand DNA transiently contains nicks (before being sealed by DNA ligase) and provides a signal that directs mismatch proofreading systems to the appropriate strand. This implies that these nicks must be present in the leading s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) or Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition that is associated with a high risk of colon cancer as well as other cancers including endometrial cancer (second most common), ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin. The increased risk for these cancers is due to inherited mutations that impair DNA mismatch repair. It is a type of cancer syndrome. Because patients with Lynch syndrome can have polyps, the term HNPCC has fallen out of favor. Signs and symptoms Risk of cancer ''Lifetime risk and mean age at diagnosis for Lynch syndrome associated cancers'' In addition to the types of cancer found in the chart above, it is understood that Lynch syndrome also contributes to an increased risk of small bowel cancer, pancreatic cancer, ureter/renal pelvis cancer, biliary tract cancer, brain cancer, and sebaceous neoplasms. Increased risk of prostate cancer and breast cance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mismatch Repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage. Mismatch repair is strand-specific. During DNA synthesis the newly synthesised (daughter) strand will commonly include errors. In order to begin repair, the mismatch repair machinery distinguishes the newly synthesised strand from the template (parental). In gram-negative bacteria, transient hemimethylation distinguishes the strands (the parental is methylated and daughter is not). However, in other prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the exact mechanism is not clear. It is suspected that, in eukaryotes, newly synthesized lagging-strand DNA transiently contains nicks (before being sealed by DNA ligase) and provides a signal that directs mismatch proofreading systems to the appropriate strand. This implies that these nicks must be present in the leading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turcot Syndrome
Mismatch repair cancer syndrome (MMRCS) is a cancer syndrome associated with biallelic DNA mismatch repair mutations. It is also known as Turcot syndrome (after Jacques Turcot, who described the condition in 1959) and by several other names. In MMRCS, neoplasia typically occurs in both the gut and the central nervous system (CNS). In the large intestine, multiple colonic polyps develop; in the CNS, brain tumors. Genetics Under the name constitutional mismatch repair-deficiency, (CMMR-D), it has been mapped to MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 or PMS2. Monoallelic mutations of these genes are observed in the condition known as Lynch syndrome or hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer, while biallelic mutations are observed in CMMR-D. People expressing the HNPCC (which itself is considered autosomal dominant) trait are considered carriers of CMMR-D, thus CMMR-D is classified as autosomal recessive. The term "childhood cancer syndrome" has also been proposed. Café-au-lait macules have been obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSH2
DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 also known as MutS homolog 2 or MSH2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSH2'' gene, which is located on chromosome 2. MSH2 is a tumor suppressor gene and more specifically a caretaker gene that codes for a DNA mismatch repair (MMR) protein, MSH2, which forms a heterodimer with MSH6 to make the human MutSα mismatch repair complex. It also dimerizes with MSH3 to form the MutSβ DNA repair complex. MSH2 is involved in many different forms of DNA repair, including transcription-coupled repair, homologous recombination, and base excision repair. Mutations in the MSH2 gene are associated with microsatellite instability and some cancers, especially with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). At least 114 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Clinical significance Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), sometimes referred to as Lynch syndrome, is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematoxylin
Haematoxylin or hematoxylin (), also called natural black 1 or C.I. 75290, is a compound extracted from heartwood of the logwood tree ('' Haematoxylum campechianum'') with a chemical formula of . This naturally derived dye has been used as a histologic stain, ink and as a dye in the textile and leather industry. As a dye, haematoxylin has been called Palo de Campeche, logwood extract, bluewood and blackwood. In histology, haematoxylin staining is commonly followed ( counterstained), with eosin, when paired, this staining procedure is known as H&E staining, and is one of the most commonly used combinations in histology. In addition to its use in the H&E stain, haematoxylin is also a component of the Papanicolaou stain (or PAP stain) which is widely used in the study of cytology specimens. Although the stain is commonly called ''haematoxylin'', the active colourant is the oxidized form haematein, which forms strongly coloured complexes with certain metal ions (commonly F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. '' In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
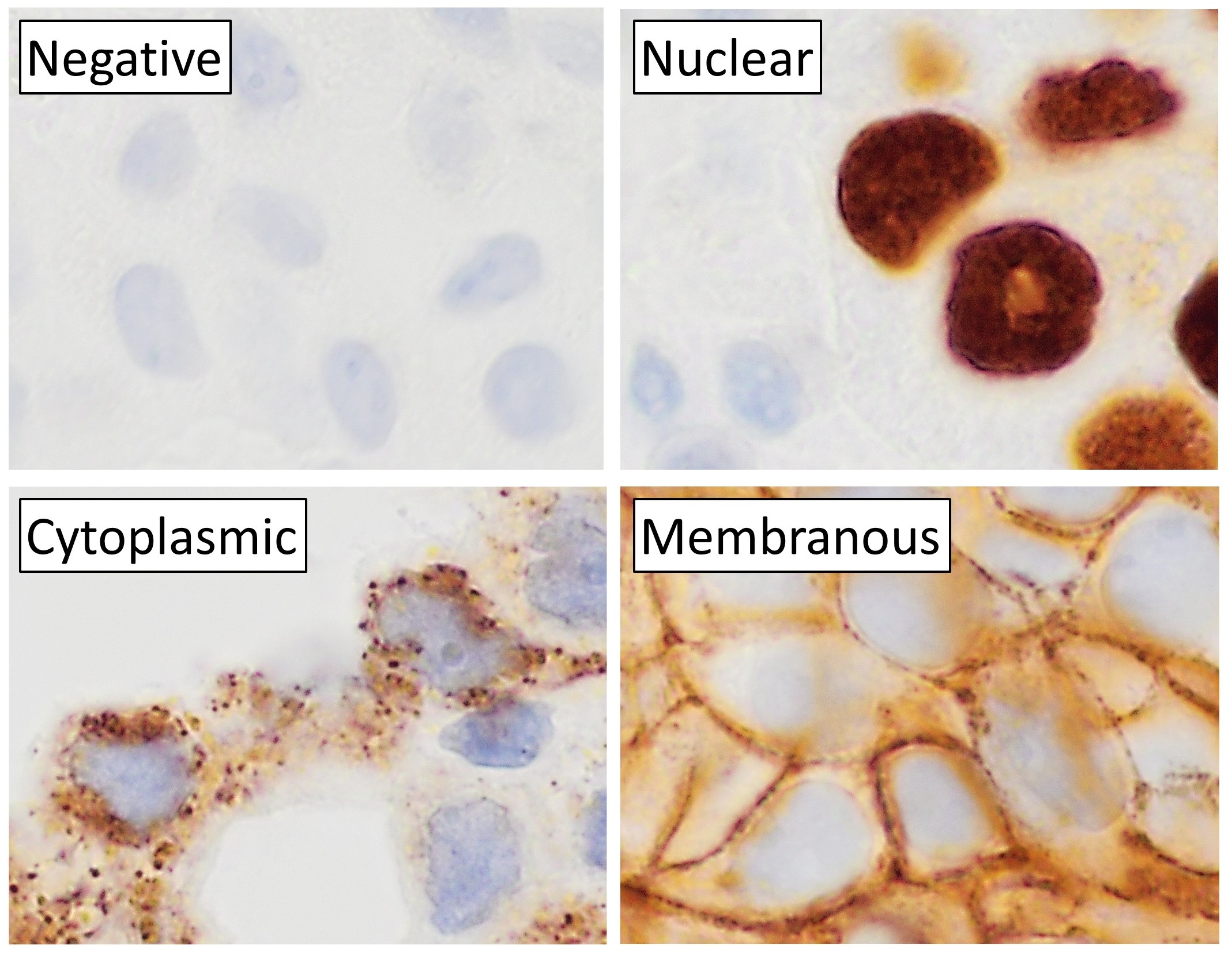
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * '' Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |