|
N-myristoyltransferase 1
Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase 1 also known as myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase 1 (NMT-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NMT1'' gene. It belongs to the protein N-terminal methyltransferase and glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase family of enzymes. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * See also * Myristoylation * NMT2, N-myristoyltransferase 2 External links * EC 2.3.1 Human proteins {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein N-terminal Methyltransferase
Protein N-terminal methyltransferase (, ''NMT1 (gene)'', ''METTL11A (gene)'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''S-adenosyl-L-methionine:N-terminal-(A,P,S)PK-(protein) methyltransferase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction :(1) 3 S-adenosyl-L-methionine + N-terminal-(A,S)PK- rotein\rightleftharpoons 3 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + N-terminal-N,N,N-trimethyl-N-(A,S)PK- rotein(overall reaction) :(1a) S-adenosyl-L-methionine + N-terminal-(A,S)PK- rotein\rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + N-terminal-N-methyl-N-(A,S)PK- rotein:(1b) S-adenosyl-L-methionine + N-terminal-N-methyl-N-(A,S)PK- rotein\rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + N-terminal-N,N-dimethyl-N-(A,S)PK- rotein:(1c) S-adenosyl-L-methionine + N-terminal-N,N-dimethyl-N-(A,S)PK-serine- rotein\rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + N-terminal-N,N,N-trimethyl-N-(A,S)PK- rotein:(2) 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine + N-terminal-PPK- rotein\rightleftharpoons 2 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + N-te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase
In enzymology, a glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :tetradecanoyl-CoA + glycylpeptide \rightleftharpoons CoA + N-tetradecanoylglycylpeptide Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are tetradecanoyl-CoA and glycylpeptide, whereas its two products are CoA and N-tetradecanoylglycylpeptide. It participates in the N-Myristoylation of proteins, and in vertebrates there are two isoenzymes NMT1 and NMT2. Besides tetradecanoyl-CoA, this enzyme is also capable of using modified versions of this substrate. In human retina, an even wider range of fatty acids, including 14:1 n–9, 14:2n–6, and 12:0, are accepted by the enzyme and grafted onto guanylate cyclase activators. This is mainly a result of a special set of fatty-acid-CoA substrates available in the retina. Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those N-acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups (cd04301 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
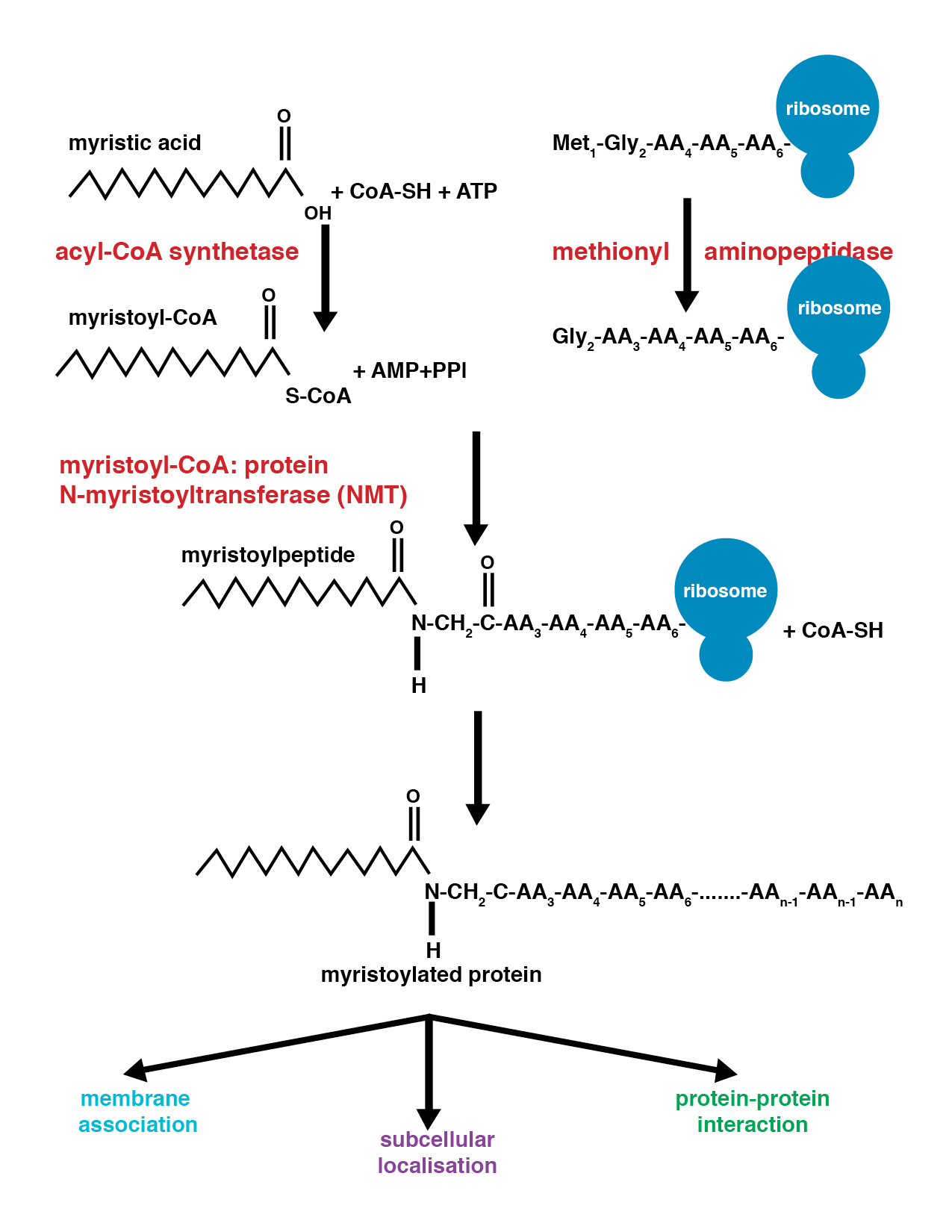
Myristoylation
Myristoylation is a lipidation modification where a myristoyl group, derived from myristic acid, is covalently attached by an amide bond to the alpha-amino group of an N-terminus, N-terminal glycine residue. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid (14:0) with the systematic name of ''n''-Tetradecanoic acid. This modification can be added either co-translationally or Posttranslational modification, post-translationally. N-myristoyltransferase 1, N-myristoyltransferase (NMT) catalyzes the myristic acid addition reaction in the cytoplasm of cells. This lipidation event is the most found type of fatty acylation and is common among many organisms including animals, plants, fungi, protozoans and viruses. Myristoylation allows for weak protein–protein and protein–lipid interactions and plays an essential role in membrane targeting, protein–protein interactions and functions widely in a variety of signal transduction pathways. Discovery In 1982, Koiti Titani's lab id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMT2
Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase 2 known also as N-myristoyltransferase, is an enzyme (EC: 2.3.1.97) that in humans is encoded by the ''NMT2'' gene. Function N-myristoyltransferase (NMT) catalyzes the reaction of N-terminal myristoylation of many signaling proteins. It transfers myristic acid from myristoyl coenzyme A to the amino group of a protein's N-terminal glycine residue. Biochemical evidence indicates the presence of several distinct NMTs, varying in apparent molecular weight and /or subcellular distribution. The 496-amino acid of human NMT2 protein shares 77% and 96% sequence identity with human NMT1 and mouse Nmt2 comprise two distinct families of N-myristoyltransferases. Interactions NMT2 has been shown to interact with: * caspase 3 * MARCKS See also * N-myristoyltransferase 1 Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase 1 also known as myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase 1 (NMT-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NMT1'' gene. It be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |