|
NMT2
Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase 2 known also as N-myristoyltransferase, is an enzyme (EC: 2.3.1.97) that in humans is encoded by the ''NMT2'' gene. Function N-myristoyltransferase (NMT) catalyzes the reaction of N-terminal myristoylation of many signaling proteins. It transfers myristic acid from myristoyl coenzyme A to the amino group of a protein's N-terminal glycine residue. Biochemical evidence indicates the presence of several distinct NMTs, varying in apparent molecular weight and /or subcellular distribution. The 496-amino acid of human NMT2 protein shares 77% and 96% sequence identity with human NMT1 and mouse Nmt2 comprise two distinct families of N-myristoyltransferases. Interactions NMT2 has been shown to interact with: * caspase 3 * MARCKS See also * N-myristoyltransferase 1 Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase 1 also known as myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase 1 (NMT-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NMT1'' gene. It be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myristoylation
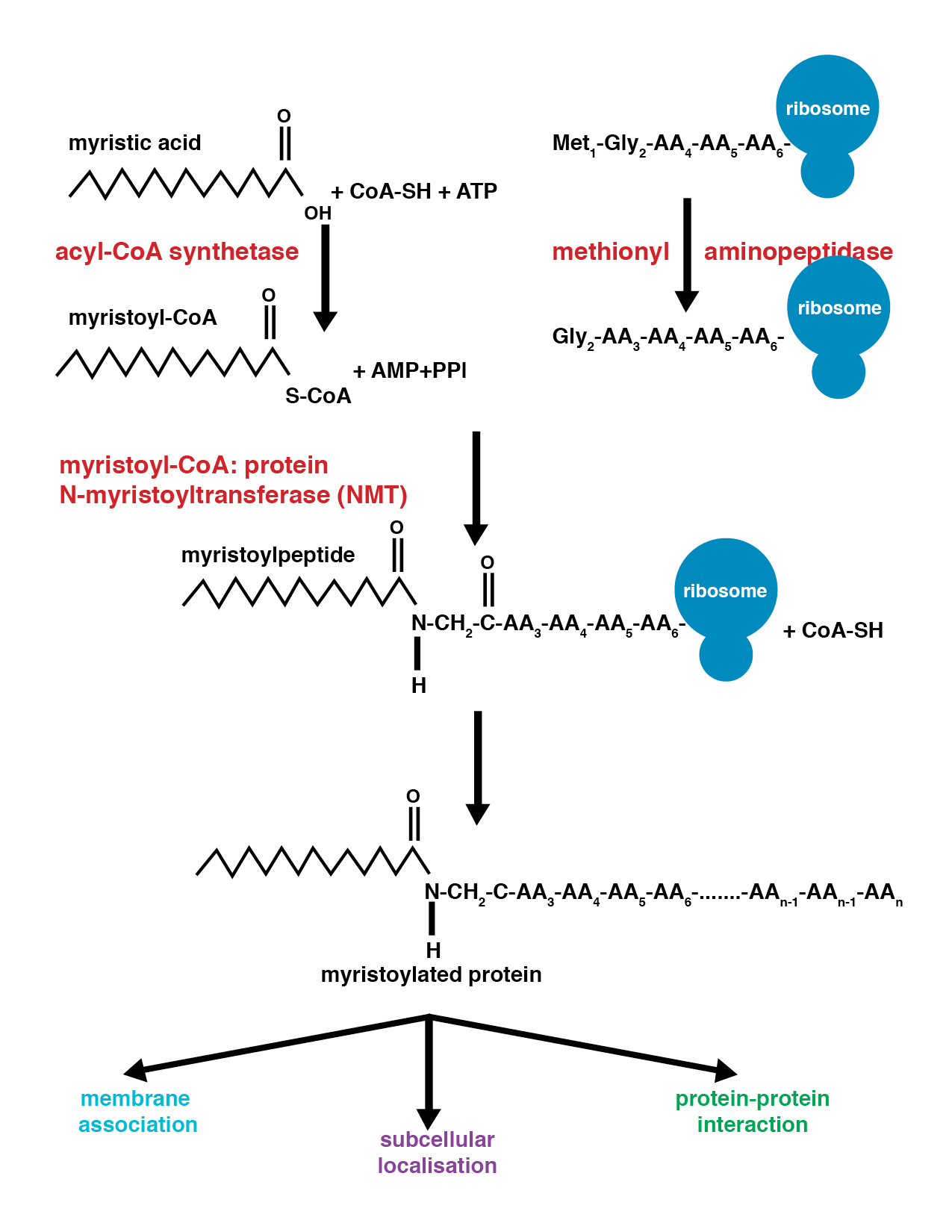
Myristoylation is a lipidation modification where a myristoyl group, derived from myristic acid, is covalently attached by an amide bond to the alpha-amino group of an N-terminus, N-terminal glycine residue. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid (14:0) with the systematic name of ''n''-Tetradecanoic acid. This modification can be added either co-translationally or Posttranslational modification, post-translationally. N-myristoyltransferase 1, N-myristoyltransferase (NMT) catalyzes the myristic acid addition reaction in the cytoplasm of cells. This lipidation event is the most found type of fatty acylation and is common among many organisms including animals, plants, fungi, protozoans and viruses. Myristoylation allows for weak protein–protein and protein–lipid interactions and plays an essential role in membrane targeting, protein–protein interactions and functions widely in a variety of signal transduction pathways. Discovery In 1982, Koiti Titani's lab id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase 3
Caspase-3 is a caspase protein that interacts with caspase-8 and caspase-9. It is encoded by the ''CASP3'' gene. ''CASP3'' orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. The CASP3 protein is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein cleaves and activates caspases 6 and 7; and the protein itself is processed and activated by caspases 8, 9, and 10. It is the predominant caspase involved in the cleavage of amyloid-beta 4A precursor protein, which is associated with neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease. Alternative splicing of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MARCKS
Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MARCKS'' gene. It plays important roles in cell shape, cell motility, secretion, transmembrane transport, regulation of the cell cycle, and neural development. Recently, MARCKS has been implicated in the exocytosis of a number of vesicles and granules such as mucin and chromaffin. It is also the name of a protein family, of which MARCKS is the most studied member. They are intrinsically disordered proteins, with an acidic pH, with high proportions of alanine, glycine, proline, and glutamic acid. They are membrane-bound through a lipid anchor at the N-terminus, and a polybasic domain in the middle. They are regulated by Ca2+/calmodulin and protein kinase C. In their unphosphorylated form, they bind to actin filaments, causing them to crosslink, and sequester acidic membrane phospholipids such as PIP2. The protein encoded by this gene is a substrate for protein kinase C. It is localized to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signaling Protein
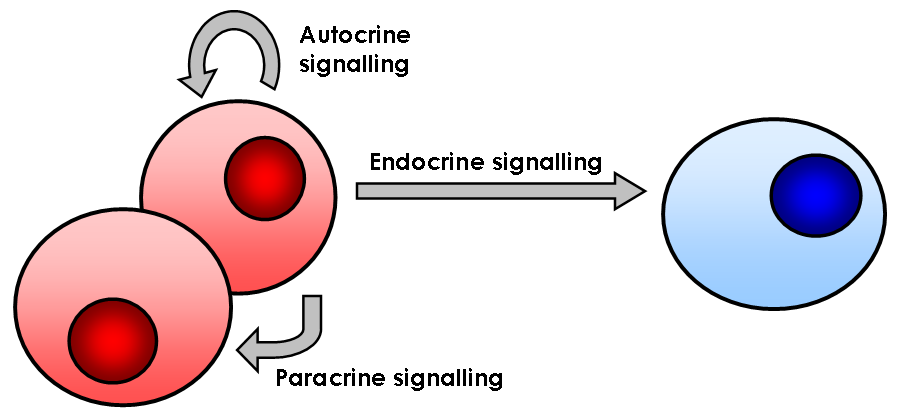
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the interio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myristic Acid
Myristic acid (IUPAC name: tetradecanoic acid) is a common saturated fatty acid with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)12COOH. Its salts and esters are commonly referred to as myristates or tetradecanoates. It is named after the binomial name for nutmeg (''Myristica fragrans''), from which it was first isolated in 1841 by Lyon Playfair, 1st Baron Playfair, Lyon Playfair. Occurrence Nutmeg#Nutmeg butter, Nutmeg butter has 75% trimyristin, the triglyceride of myristic acid. Besides nutmeg, myristic acid is found in palm kernel oil, coconut oil, butterfat, 8–14% of bovine milk, and 8.6% of breast milk as well as being a minor component of many other animal fats. It is found in spermaceti, the crystallized fraction of oil from the sperm whale. It is also found in the rhizomes of the Iris (plant), Iris, including Orris root. Chemical behaviour Myristic acid acts as a Lipid-anchored protein, lipid anchor in biomembranes. Reduction (chemistry), Reduction of myristic acid yields myristy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenic acid, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In acetyl-CoA, its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the Anabolism, anabolic and Catabolism, catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of Pyruvic acid, pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946, who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |