|
Midway, Georgia
Midway is a city in Liberty County, Georgia, Liberty County, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, United States. It is a part of the Hinesville, Georgia, Hinesville-Fort Stewart, Georgia, Fort Stewart Hinesville-Fort Stewart metropolitan area, metropolitan statistical area. The population was 2,121 as of the 2010 census, up from 1,100 at the 2000 census. Midway has several museums, including the Midway Museum and Cemetery and the Dorchester Academy, Dorchester Academy Museum. The Midway Historic District (Midway, Georgia), Midway Historic District is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. History Midway's history dates back to the 18th century. Puritans migrated to St. John's Parish, Georgia, from Dorchester, South Carolina, in 1752 and established several settlements, including what became the Midway community. The Council of Georgia granted them , as colonial officials wanted a large number of settlers in the area to help protect them from the Muscogee, Creek Indians. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorchester Academy
Dorchester Academy was a school for African-Americans located just outside Midway, Georgia. Operating from 1869 to 1940, its campus, of which only the 1935 Dorchester Academy Boys' Dormitory survives, was the primary site of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference's Citizen Education Program. This program, ran here from 1961 to 1970, worked toward attaining equality for blacks in the American South by teaching them their rights and helping them acquire the knowledge necessary to become registered voters by passing the required test. The dormitory building was designated a U.S. National Historic Landmark in 2006 for its later role in the American civil rights movement, and for its association with activist Septima Poinsette Clark, who oversaw the education program. The campus, which includes several later buildings, is now a museum and research center. Description and history The former Dorchester Academy campus is located at the corner of Lewis Fraser Road and East Ogletho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
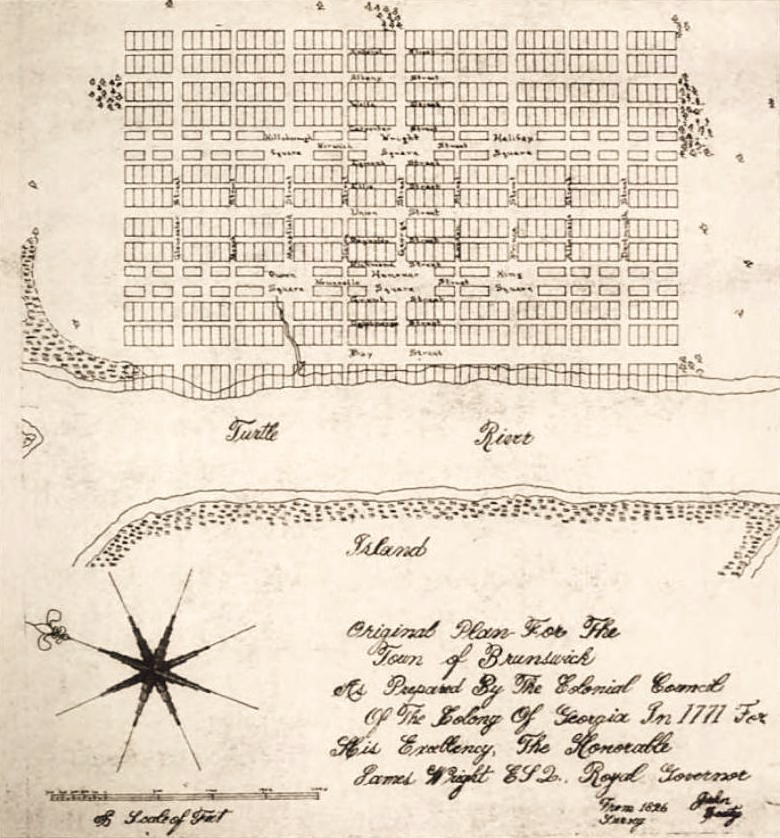
Brunswick, Georgia
Brunswick () is a city in and the county seat of Glynn County, Georgia, Glynn County in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. As the primary urban and economic center of the lower southeast portion of Georgia, it is the second-largest urban area on the Georgia coastline after Savannah, Georgia, Savannah and contains the Brunswick Old Town Historic District. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, the population of the city proper was 15,210; Brunswick metropolitan area, the Brunswick metropolitan area's population as of 2020 was 113,495. Established as "Brunswick" after the German duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Duchy of Brunswick–Lüneburg, the ancestral home of the House of Hanover, the municipal community was incorporated as a city in 1856. Throughout its history, Brunswick has served as an important port city; in World War II, for example, it served as a strategic military location with an operational base for escort blimps and a shipbuilding facility fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia and is the county seat of Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the British colonial capital of the Province of Georgia and later the first state capital of Georgia. A strategic port city in the American Revolution and during the American Civil War, Savannah is today an industrial center and an important Atlantic seaport. It is Georgia's fifth-largest city, with a 2020 U.S. Census population of 147,780. The Savannah metropolitan area, Georgia's third-largest, had a 2020 population of 404,798. Each year, Savannah attracts millions of visitors to its cobblestone streets, parks, and notable historic buildings. These buildings include the birthplace of Juliette Gordon Low (founder of the Girl Scouts of the USA), the Georgia Historical Society (the oldest continually operating historical society in the South), the Telfair Academy of Arts and Sciences (one of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate 95
Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from US Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Florida, to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between Maine and the Canadian province of New Brunswick. The highway largely parallels the Atlantic coast and US 1, except for the portion between Savannah, Georgia, and Washington DC and the portion between Portland and Houlton in Maine, both of which follow a more direct inland route. I-95 serves as the principal road link between the major cities of the Eastern Seaboard. Major metropolitan areas along its route include Miami, Jacksonville, Savannah, Florence, Fayetteville, and Richmond in the Southeast; Washington, Baltimore, Wilmington and Philadelphia, Newark, and New York City in the Mid-Atlantic; and New Haven, Providence, Boston, Portsmouth, and Portland in New England. The Charleston, Wilmington, and Norfolk–Virginia Beach metropolitan a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Slavery In Georgia (U
Slavery in Georgia is known to have been practiced by European colonists. During the colonial era, the practice of slavery in Georgia soon became surpassed by industrial-scale plantation slavery. The colony of the Province of Georgia under James Oglethorpe banned slavery in 1735, the only one of the thirteen colonies to have done so. However, it was legalized by royal decree in 1751, in part due to George Whitefield's support for the institution of slavery. Pre-colonial period Native Americans did not commonly enslave members of their own and other tribes before Europeans arrived but this practice became common after European intrusion, continuing into the 1800s; slaves might or might not be adopted eventually, especially if enslaved as children; and the enslavement was rarely if ever hereditary. Native American slaves were most often captives from wars; captives bartered from other tribes, sometimes at great distances; or children sold by their parents during famines. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantations In The American South
A plantation complex in the Southern United States is the built environment (or complex) that was common on agricultural plantations in the American South from the 17th into the 20th century. The complex included everything from the main residence down to the pens for livestock. Until the abolition of slavery, such plantations were generally self-sufficient settlements that relied on the forced labor of enslaved people. Plantations are an important aspect of the history of the Southern United States, particularly the antebellum era (pre-American Civil War). The mild temperate climate, plentiful rainfall, and fertile soils of the southeastern United States allowed the flourishing of large plantations, where large numbers of enslaved Africans or African Americans were held captive and forced to produce crops to create wealth for a white elite. Today, as was also true in the past, there is a wide range of opinion as to what differentiated a plantation from a farm. Typically, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly '' Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of '' Oryza''. As a cereal grain, domesticated rice is the most widely consumed staple food for over half of the world's human population,Abstract, "Rice feeds more than half the world's population." especially in Asia and Africa. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production, after sugarcane and maize. Since sizable portions of sugarcane and maize crops are used for purposes other than human consumption, rice is the most important food crop with regard to human nutrition and caloric intake, providing more than one-fifth of the calories consumed worldwide by humans. There are many varieties of rice and culinary preferences t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscogee
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsTranscribed documents Sequoyah Research Center and the American Native Press Archives in the United States, United States of America. Their original homelands are in what now comprises southern Tennessee, much of Alabama, western Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and parts of northern Florida. Most of the Muscogee people were forcibly Indian Removal, removed to Indian Territory (now Oklahoma) by the federal government in the 1830s during the Trail of Tears. A small group of the Muscogee Creek Confederacy remained in Alabama, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorchester, South Carolina
Dorchester was a town in the Province of South Carolina. Situated on the Ashley River about from Charleston, it was founded in February 1696 by followers of Reverend Joseph Lord from Dorchester, Massachusetts. They named it after their home town, which had been named by earlier immigrants after the English town Dorchester). Dorchester was abandoned in 1751. History The town was developed near the mouths of Dorchester Creek and Eagle's Creek, where they flowed into the Ashley. Both had been named by English colonists. The local Native Americans, of this region, referred to the land between the two mouths, as ''Boo-shoo-ee''. The meaning of this name is not known, although the ''-ee'' suffix probably referred to water, given that nearly all other names ending in ''-ee'' referred to a water feature. John Smith In 1675, a wealthy Englishman named John Smith arrived in South Carolina with his wife Mary. As a personal friend of the influential Earl of Shaftesbury, he was given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Catholic Church, Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. Puritanism played a significant role in English history, especially during the Protectorate. Puritans were dissatisfied with the limited extent of the English Reformation and with the Church of England's toleration of certain practices associated with the Roman Catholic Church. They formed and identified with various religious groups advocating greater purity of worship and doctrine, as well as personal and corporate piety. Puritans adopted a Reformed theology, and in that sense they were Calvinists (as were many of their earlier opponents). In church polity, some advocated separation from all other established Christian denominations in favour of autonomous gathered churches. These English Dissenters, Separatist and Indepe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |