Brunswick, Georgia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Brunswick () is a city in and the
 The
The  The area's first European settler, Mark Carr, arrived in 1738. Carr, a
The area's first European settler, Mark Carr, arrived in 1738. Carr, a
Glynn County Courthouse
at the Digital Library of Georgia.) At the end of the eighteenth century, a large tract of land surrounding Brunswick on three sides had been laid off and designated as Commons. Commissioners were named in 1796 to support these efforts. The General Assembly authorized them to sell of Commons, one-half of the proceeds to go to the construction of the courthouse and jail and one-half to the support of the academy. In 1819 the commissioners erected a suitable building for school purposes on the southeastern corner of Reynolds and L streets. This was the first public building in Brunswick. It was abandoned four years later, but a new building was erected on Hillsborough Square in 1840 using Commons proceeds. A courthouse and jail were built around this time. The town was officially incorporated as a city on February 22, 1856. It was at this time that state representative Jacob Moore in conjunction with others conspired to control the Commons, and any proceeds that might be had from sales. Moore managed to persuade the In World War II, Brunswick served as a strategic military location. German
In World War II, Brunswick served as a strategic military location. German
 According to Sperling's BestPlaces, approximately 56.3% of the city's population identify with a religion as of 2020. Typical of those traditionally placed within the
According to Sperling's BestPlaces, approximately 56.3% of the city's population identify with a religion as of 2020. Typical of those traditionally placed within the

 The Port of Brunswick forms a vital part of the city's economy. It is recognized as one of the most productive ports on the East Coast and is the sixth-busiest automobile port in the United States; it is the primary
The Port of Brunswick forms a vital part of the city's economy. It is recognized as one of the most productive ports on the East Coast and is the sixth-busiest automobile port in the United States; it is the primary
"G8 leaders meet on remote island,"
''Guardian'' (Manchester). June 8, 2004.
 Brunswick is home to a variety of arts and cultural events. The most significant professional performing-arts group is the Coastal Symphony of Georgia, in existence since 1982, which stages productions each year at Glynn Academy's Memorial Auditorium. This group of professional musicians also has a Youth Symphony division and a fundraising auxiliary.
Old Town Brunswick's historic and ornate Ritz Theatre hosts a range of performances. Renovated in the early 1980s and again in 2000 through 2001, the Ritz is home to the Golden Isles Arts and Humanities Association, the coordinating arts council for Brunswick and Glynn County. The association hosts an annual performing arts series and rents space to individual producers and organizations.
The city is home to various
Brunswick is home to a variety of arts and cultural events. The most significant professional performing-arts group is the Coastal Symphony of Georgia, in existence since 1982, which stages productions each year at Glynn Academy's Memorial Auditorium. This group of professional musicians also has a Youth Symphony division and a fundraising auxiliary.
Old Town Brunswick's historic and ornate Ritz Theatre hosts a range of performances. Renovated in the early 1980s and again in 2000 through 2001, the Ritz is home to the Golden Isles Arts and Humanities Association, the coordinating arts council for Brunswick and Glynn County. The association hosts an annual performing arts series and rents space to individual producers and organizations.
The city is home to various
 The city lays claim to
The city lays claim to

 The Brunswick Parks and Recreation Department operates city parks and
The Brunswick Parks and Recreation Department operates city parks and
 Brunswick uses the council-manager model of
Brunswick uses the council-manager model of
 Brunswick is home to the
Brunswick is home to the
 The Glynn County School System is the governing authority of public schools in the city. More than 12,000 students attend schools in the school system. There are ten
The Glynn County School System is the governing authority of public schools in the city. More than 12,000 students attend schools in the school system. There are ten
 With over 1,321 employees and over 201 physicians, Southeast Georgia Health System is the main provider of health care in Brunswick and the surrounding area and is also the largest private employer in Brunswick. Southeast Georgia Health System's medical campus in the city offers a 316-bed full-service hospital. Southeast Georgia Health System Brunswick campus also has an alliance with the International Seafarer's Center that provides first-class medical attention to seamen who come into the Brunswick port; the medical needs of approximately 15,000 international merchant seafarers are met each year. Southeast Georgia Health System also operates a 180-bed skilled nursing facility in Brunswick, The Senior Care Center, which offers short-term rehabilitation services, as well as long-term care.
Southeast Georgia Health System recently opened the Outpatient Care Center on the Brunswick campus. This six-story, building includes
With over 1,321 employees and over 201 physicians, Southeast Georgia Health System is the main provider of health care in Brunswick and the surrounding area and is also the largest private employer in Brunswick. Southeast Georgia Health System's medical campus in the city offers a 316-bed full-service hospital. Southeast Georgia Health System Brunswick campus also has an alliance with the International Seafarer's Center that provides first-class medical attention to seamen who come into the Brunswick port; the medical needs of approximately 15,000 international merchant seafarers are met each year. Southeast Georgia Health System also operates a 180-bed skilled nursing facility in Brunswick, The Senior Care Center, which offers short-term rehabilitation services, as well as long-term care.
Southeast Georgia Health System recently opened the Outpatient Care Center on the Brunswick campus. This six-story, building includes
City of Brunswick official website
History of Brunswick
{{authority control Cities in Georgia (U.S. state) Cities in Glynn County, Georgia County seats in Georgia (U.S. state) Port cities and towns in Georgia (U.S. state) Brunswick metropolitan area Populated places established in 1771 Populated coastal places in Georgia (U.S. state)
county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US ...
of Glynn County in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
. As the primary urban and economic center of the lower southeast portion of Georgia, it is the second-largest urban area on the Georgia coastline after Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
and contains the Brunswick Old Town Historic District. At the 2020 U.S. census, the population of the city proper was 15,210; the Brunswick metropolitan area's population as of 2020 was 113,495.
Established as "Brunswick" after the German Duchy of Brunswick–Lüneburg, the ancestral home of the House of Hanover
The House of Hanover (german: Haus Hannover), whose members are known as Hanoverians, is a European royal house of German origin that ruled Hanover, Great Britain, and Ireland at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. The house ori ...
, the municipal community was incorporated as a city in 1856. Throughout its history, Brunswick has served as an important port city; in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, for example, it served as a strategic military location with an operational base for escort blimps and a shipbuilding facility for the U.S. Maritime Commission
The United States Maritime Commission (MARCOM) was an independent executive agency of the U.S. federal government that was created by the Merchant Marine Act of 1936, which was passed by Congress on June 29, 1936, and was abolished on May 24, 195 ...
. Since then, its port has served numerous economic purposes.
Brunswick supports a progressive economy largely based on tourism and logistics
Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics manages the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of ...
, with a metropolitan GDP of $3.9 billion as of 2013. The Port of Brunswick handles approximately 10 percent of all U.S. roll-on/roll-off
Roll-on/roll-off (RORO or ro-ro) ships are cargo ships designed to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, semi-trailer trucks, buses, Trailer (vehicle), trailers, and railroad cars, that are driven on and off the ship on their o ...
trade—third in the U.S., behind the ports of Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the wor ...
and Newark. The headquarters of the Federal Law Enforcement Training Center
The Federal Law Enforcement Training Centers (FLETC) serves as an interagency law enforcement training body for 105 United States government federal law enforcement agencies. The stated mission of FLETC is to "...train those who protect our hom ...
is located north of the central business district of the city and is adjacent to Brunswick Golden Isles Airport, which provides commercial air service to the area.
Brunswick is located on a harbor of the Atlantic Ocean, approximately north of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
and south of South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = "Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = G ...
. Brunswick is bordered on the west by Oglethorpe Bay, the East River, and the Turtle River. It is bordered on the south by the Brunswick River and on the east by the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway
The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Massachusetts southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following t ...
in the Mackay River, which separates it from the Golden Isles.
History
 The
The Mocama
The Mocama were a Native American people who lived in the coastal areas of what are now northern Florida and southeastern Georgia. A Timucua group, they spoke the dialect known as Mocama, the best-attested dialect of the Timucua language. Their t ...
, a Timucua
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The va ...
-speaking people, lived in and cultivated the lands in what is now Brunswick. The Spanish established missions in Timucua
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The va ...
n villages beginning in 1568. During this time, much of the Native American population was depleted through enslavement and disease. When the Province of Carolina
Province of Carolina was a province of England (1663–1707) and Great Britain (1707–1712) that existed in North America and the Caribbean from 1663 until partitioned into North and South on January 24, 1712. It is part of present-day Alab ...
was founded in 1663, the British claimed all lands south to the 31st parallel north
The 31st parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 31 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America and the Atlantic Ocean. At this latitude the sun is visible for 14 hours, 1 ...
, but little colonization occurred south of the Altamaha River
The Altamaha River is a major river in the U.S. state of Georgia. It flows generally eastward for 137 miles (220 km) from its origin at the confluence of the Oconee River and Ocmulgee River towards the Atlantic Ocean, where it empti ...
as the Spanish also claimed this land. Three years after the Province of Georgia
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
was founded in 1733, James Oglethorpe
James Edward Oglethorpe (22 December 1696 – 30 June 1785) was a British soldier, Member of Parliament, and philanthropist, as well as the founder of the colony of Georgia in what was then British America. As a social reformer, he hoped to r ...
had the town of Frederica built on St. Simons Island, challenging Spaniards who laid claim to the island. The Spanish were driven out of the province after British victories in the battles of Bloody Marsh and Gully Hole Creek in 1742; it was not until the Treaty of Paris of 1763
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the S ...
that Spain's threat to the province was formally ended, when all lands north of the St. Marys River and south of the Savannah River were designated as Georgia.
Scotsman
The Scots ( sco, Scots Fowk; gd, Albannaich) are an ethnic group and nation native to Scotland. Historically, they emerged in the early Middle Ages from an amalgamation of two Celtic-speaking peoples, the Picts and Gaels, who founded ...
, was a captain in Oglethorpe's Marine Boat Company. Upon landing, he established his tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ch ...
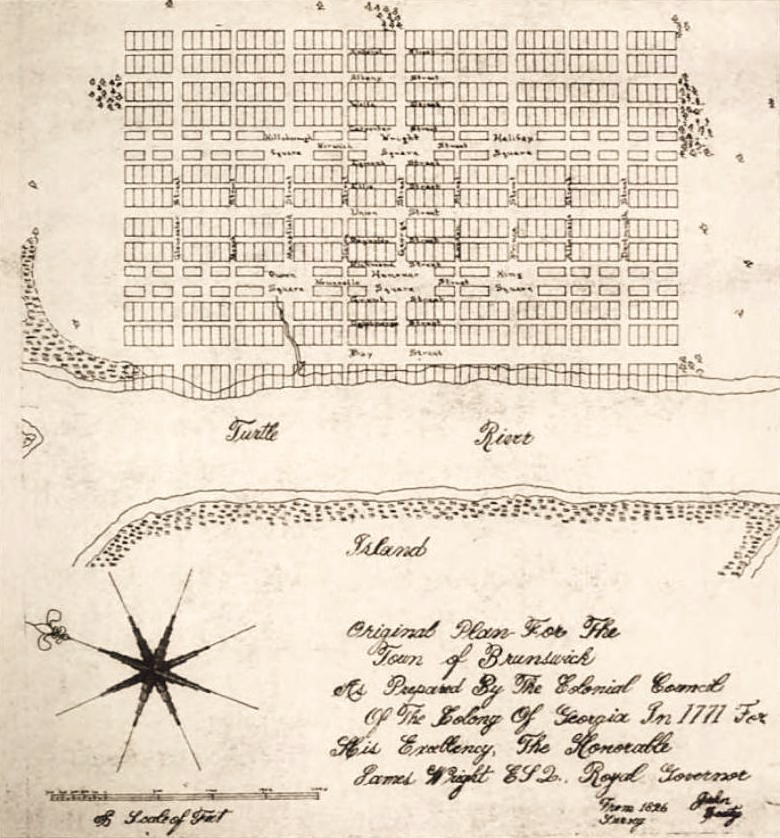
plantation, which he called "Plug Point", along the East and Brunswick rivers. The Province of Georgia purchased Carr's fields in 1771 and laid out the town of Brunswick in the grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogo ...
akin to that of Savannah, with large, public squares at given intervals. The town was named for the duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
The Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg (german: Herzogtum Braunschweig und Lüneburg), or more properly the Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg, was a historical duchy that existed from the late Middle Ages to the Late Modern era within the Holy Ro ...
in Germany, the ancestral home of George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
and the House of Hanover
The House of Hanover (german: Haus Hannover), whose members are known as Hanoverians, is a European royal house of German origin that ruled Hanover, Great Britain, and Ireland at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. The house ori ...
. Brunswick was a rectangular tract of land consisting of . The first lot was granted on June 30, 1772; 179 lots were granted in the first three years. However, about this time Brunswick lost most of its citizens, many of whom were Loyalist
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ...
s, to East Florida
East Florida ( es, Florida Oriental) was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of ''La Florida'' in 1763 as part of ...
, the Caribbean Basin
In Geography, the Caribbean Basin is generally defined as the area running from Florida westward along the Gulf coast, then south along the Mexican coast through Central America and then eastward across the northern coast of South America. This ...
, and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
for protection during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of ...
. From 1783 to 1788 a number of these lots were regranted and there collected in Brunswick a few families who desired proper education for their children. By the act of the General Assembly on February 1, 1788, eight town commissioners were appointed and Glynn Academy was chartered, the funding of which was to come from the sales of town lots. Brunswick was recognized as an official port of entry in 1789 by an act of the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washi ...
. In 1797 the General Assembly transferred the seat of Glynn County from Frederica to Brunswick.On March 25, 1765, Georgia's colonial assembly divided the territory south of the Altamaha River into four new parishes. Two of these parishes—St. David and St. Patrick—would later be combined to form the mainland portion of Glynn County. Additionally, the 1765 act assigned Jekyll Island
Jekyll Island is located off the coast of the U.S. state of Georgia, in Glynn County. It is one of the Sea Islands and one of the Golden Isles of Georgia barrier islands. The island is owned by the State of Georgia and run by a self-sustainin ...
to St. James Parish, meaning that this parish consisted entirely of St. Simons and Jekyll islands. On February 5, 1777, the state's first constitution was adopted. Article IV of that document transformed the existing colonial parishes into seven counties, with Native American-ceded lands to the north forming an eighth county. Glynn County, which was seventh on the list and thus is considered Georgia's seventh county, consisted of all of St. David and St. Patrick parishes. In 1789 the legislature added St. Simons and Jekyll islands to Glynn County. Frederica on St. Simons Island served as Glynn County's seat beginning in 1789, at the absorption of the islands into Glynn. In an act of February 10, 1787, Georgia's legislature provided that Glynn County's courthouse and jail be erected and that county elections be held in Brunswick—which made it the county seat. Ten years later—on February 13, 1797—the legislature formally designated Brunswick the seat of Glynn County. (SeGlynn County Courthouse
at the Digital Library of Georgia.) At the end of the eighteenth century, a large tract of land surrounding Brunswick on three sides had been laid off and designated as Commons. Commissioners were named in 1796 to support these efforts. The General Assembly authorized them to sell of Commons, one-half of the proceeds to go to the construction of the courthouse and jail and one-half to the support of the academy. In 1819 the commissioners erected a suitable building for school purposes on the southeastern corner of Reynolds and L streets. This was the first public building in Brunswick. It was abandoned four years later, but a new building was erected on Hillsborough Square in 1840 using Commons proceeds. A courthouse and jail were built around this time. The town was officially incorporated as a city on February 22, 1856. It was at this time that state representative Jacob Moore in conjunction with others conspired to control the Commons, and any proceeds that might be had from sales. Moore managed to persuade the
Georgia General Assembly
The Georgia General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is bicameral, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
Each of the General Assembly's 236 members serve two-year terms and are directly ...
to pass legislation giving him control over significant amounts of local real estate. This precipitated a period of strife, pitting the powerful interests, headed by Rep. Moore, against the common citizenry. It was into this turmoil that Carey Wentworth Styles
Carey Wentworth Styles (October 7, 1825 – February 23, 1897) was an American lawyer and journalist who either founded or wrote for "at least" 21 newspapers in his career. He is best remembered as the founder of ''The Atlanta Constitution''. Dur ...
appeared, in 1857, when he moved his family to Brunswick from Edgefield, South Carolina
Edgefield is a town in Edgefield County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 4,750 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Edgefield County.
Edgefield is part of the Augusta, Georgia metropolitan area.
Geography
Edgefield is ...
. Styles, an attorney, was attracted to the area by news of the civil strife. As one observer later wrote, the citizens of Brunswick were in "need of a defender".
Styles quickly became embroiled in the dispute, siding with the citizenry. He announced his intention to run for mayor, and organized a mass protest rally for the evening of December 24. In spite of bad weather, a crowd gathered at the protest point, where Styles delivered an impassioned speech against the powerful interests, and the legislative act giving them the power to seize local property. Styles called the legislation "dishonorable", at which point Moore (the bill's sponsor and beneficiary) jumped to his feet and shouted at Styles, calling the accusation a "falsehood". In the official testimony on file in the Glynn County courthouse, Styles is said to have yelled back at Moore, saying "You are a damned liar!", to which Moore replied "You are a damneder liar!". Gunfire ensued, resulting in the death of Moore. Witness accounts had Moore firing first, and though Styles was subsequently arrested for manslaughter, the charges were eventually dropped. On March 1, 1858, Styles was elected mayor of Brunswick. Some years later, Styles moved to Atlanta, where he founded ''The Atlanta Constitution''. In November 1879, nineteen years after he left, Styles returned to Brunswick, where he established the local weekly ''Seaport Appeal''. When that eventually failed, Styles moved to Texas, never to see Brunswick again.
By 1860 Brunswick had a population of 468, a bank, a weekly newspaper, and a sawmill which employed nine workers.
Brunswick was abandoned during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
when citizens were ordered to evacuate. The city, like many others in the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
, suffered from post-war depression. After one of the nation's largest lumber mills began operation on nearby St. Simons Island, economic prosperity returned. Rail lines were constructed from Brunswick to inland Georgia, which stimulated a sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes ...
boom, said to average one mill every two miles, along with the new industrial corridor. In his book ''The New South Comes to Wiregrass Georgia, 1860–1910'' author Mark V. Wetherington states that from Eastman Eastman may refer to:
People
* Eastman (surname)
* Eastman Nixon Jacobs (1902–1987), American aerodynamicist
* John Eastman (b 1960), American lawyer and founding director of the Center for Constitutional Jurisprudence
* Jonathan Eastman Johnso ...
, former Quartermaster General Ira R. Foster "shipped lumber to Brunswick, where it was loaded onto timber schooners and transported to international markets like Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
, Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of the same name, Brazil's List of Brazilian states by population, third-most populous state, and the List of largest citi ...
, and Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
." Unlike many other southern cities during the Reconstruction period, Brunswick experienced an economic boom
An economic expansion is an increase in the level of economic activity, and of the goods and services available. It is a period of economic growth as measured by a rise in real GDP. The explanation of fluctuations in aggregate economic activ ...
.
In 1878, poet and native Georgian Sidney Lanier
Sidney Clopton Lanier (February 3, 1842 – September 7, 1881) was an American musician, poet and author. He served in the Confederate States Army as a private, worked on a blockade-running ship for which he was imprisoned (resulting in his catch ...
, who sought relief from tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
in Brunswick's climate, wrote " The Marshes of Glynn", a poem based on the salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is domin ...
es that span Glynn County. The December 1888 issue of ''Harper's Weekly
''Harper's Weekly, A Journal of Civilization'' was an American political magazine based in New York City. Published by Harper & Brothers from 1857 until 1916, it featured foreign and domestic news, fiction, essays on many subjects, and humor, ...
'' predicted that "Brunswick by the Sea" was destined to become the "winter Newport
Newport most commonly refers to:
*Newport, Wales
*Newport, Rhode Island, US
Newport or New Port may also refer to:
Places Asia
*Newport City, Metro Manila, a Philippine district in Pasay
Europe
Ireland
*Newport, County Mayo, a town on the ...
of America." Jekyll Island
Jekyll Island is located off the coast of the U.S. state of Georgia, in Glynn County. It is one of the Sea Islands and one of the Golden Isles of Georgia barrier islands. The island is owned by the State of Georgia and run by a self-sustainin ...
had become a resort destination for some of the era's most influential families (most notably Rockefellers, Vanderbilts, Pulitzers, and Goodyears) who arrived by train or yacht.
A yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In ...
epidemic began in 1893, which heralded a decade of hardships for the city; it was flooded in 1893 when a modern-day Category 3 hurricane (today known as the Sea Islands Hurricane) paralleled the coast of Georgia before hitting South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = "Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = G ...
. The storm left the city under of water. A Category 4 hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depe ...
hit Cumberland Island
Cumberland Island, in the southeastern United States, is the largest of the Sea Islands of Georgia. The long-staple Sea Island cotton was first grown here by a local family, the Millers, who helped Eli Whitney develop the cotton gin. With i ...
just south of Brunswick in October 1898, which caused a storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the ...
in the city. As a result, 179 were killed.
Construction of an electric streetcar
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ...
line began in 1909 and was completed in 1911. Tracks were located in the center of several city streets. In July 1924, the F.J. Torras Causeway, the roadway between Brunswick and St. Simons Island, was completed, and passenger boat service from Brunswick to St. Simons Island was terminated. By 1926, the electric streetcar line in Brunswick was discontinued; the decline of the streetcar systems coincided with the rise of the automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
.U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
s threatened the coast of the southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
, and blimp
A blimp, or non-rigid airship, is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid and rigid airships (e.g. Zeppelins), blimps rely on the pressure of the lifting gas (usually helium, rather than ...
s became a common sight as they patrolled the coastal areas. During the war, blimps from Brunswick's Naval Air Station Glynco (at the time, the largest blimp base in the world) safely escorted almost 100,000 ships without a single vessel lost to enemy submarines.
In World War II, Brunswick boomed as over 16,000 workers of the J.A. Jones Construction Company produced ninety-nine Liberty ship
Liberty ships were a ship class, class of cargo ship built in the United States during World War II under the Emergency Shipbuilding Program. Though British in concept, the design was adopted by the United States for its simple, low-cost constr ...
s and "Knot" ships ( type C1-M ships which were designed for short coastal runs, and most often named for knot
A knot is an intentional complication in Rope, cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including List of hitch knots, hitches, List of bend knots, bends, List of loop knots, loop knots, ...
s for the U.S. Maritime Commission
The United States Maritime Commission (MARCOM) was an independent executive agency of the U.S. federal government that was created by the Merchant Marine Act of 1936, which was passed by Congress on June 29, 1936, and was abolished on May 24, 195 ...
to transport materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the spec ...
to the European and Pacific theatres.
The first ship was the SS ''James M. Wayne'' (named after James Moore Wayne
James Moore Wayne (1790 – July 5, 1867) was an American attorney, judge and politician who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1835 to 1867. He previously served as the 16th Mayor of Savannah, Geo ...
), whose keel was laid on July 6, 1942, and which was launched on March 13, 1943. The last ship was the SS ''Coastal Ranger'', whose keel was laid on June 7, 1945, and which was launched on August 25, 1945. The first six ships took 305 to 331 days each to complete, but soon production ramped up and most of the remaining ships were built in about two months, bringing the average down to 89 days each. By November 1943, about four ships were launched per month. The SS ''William F. Jerman'' was completed in only 34 days in November and December 1944. Six ships could be under construction in slipway
A slipway, also known as boat ramp or launch or boat deployer, is a ramp on the shore by which ships or boats can be moved to and from the water. They are used for building and repairing ships and boats, and for launching and retrieving small ...
s at one time.
Geography
The city of Brunswick is located in southeasternGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
, approximately halfway between Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the seat of Duval County, with which the c ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
and Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
. The city is located at the apex of the bight of the Georgia coast, the westernmost point on the Atlantic seaboard
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. The eastern seaboard contains the co ...
, and is naturally sheltered by two barrier islands, Jekyll Jekyll may refer to:
Entertainment Film
* ''The Two Faces of Dr. Jekyll'', a 1960 horror film
* ''Dr. Jekyll y el Hombre Lobo'', a 1972 Spanish horror film
* ''Jekyll'', a 2007 horror film
Television
* ''Jekyll'' (TV series), a 2007 BBC televisi ...
and St. Simons. The city is situated on a peninsula with the East River and the Turtle River to the west, the Brunswick River to the south, and the Mackay River with the Intracoastal Waterway
The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Massachusetts southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following t ...
to the east. An abundance of salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is domin ...
es separates the city from the Intracoastal Waterway, which passes between Brunswick and the barrier islands. The East River separates Brunswick from Andrews Island, a dredge spoil site.
The city is the lowest in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of Georgia, with an elevation of only above sea level. According to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, Brunswick's land area is . Its total area is ; of this is water.
Climate
Brunswick's climate is classified ashumid subtropical
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(''Cfa'' in the Köppen climate classification system Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
). During the summer months, it is common for the temperature to reach over 90 °F (32 °C). However, the humidity results in a heat index
The heat index (HI) is an index that combines air temperature and relative humidity, in shaded areas, to posit a human-perceived equivalent temperature, as how hot it would feel if the humidity were some other value in the shade. The result is al ...
higher than the actual temperature. Summer mornings average nearly 90 percent humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
and nearly 60 percent in the afternoon. Scattered afternoon thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are somet ...
s are common in the summer. The hottest temperature ever recorded in Brunswick was 106 °F (41 °C) in 1986. Winters in Brunswick are fairly temperate. The average high in January, the coldest month, is 63 °F (17 °C), while the average low is 44 °F (7 °C). Snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet ...
fall is very rare. The last snow accumulation in Brunswick was on December 23, 1989. The coldest temperature ever recorded in Brunswick was on January 21, 1985, and January 30, 1966.
Brunswick receives a high amount of rainfall annually, averaging about . The wettest months are August and September, the peak of hurricane season. The city has suffered less damage from hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depe ...
s than most other East Coast cities. A major hurricane
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
has not made landfall on the Georgia coast since 1898, and the only hurricane that has hit the coast since then was Hurricane David
Hurricane David was an extremely deadly hurricane which caused massive loss of life in the Dominican Republic in August 1979, and was the most intense hurricane to make landfall in the country in recorded history. A Cape Verde hurricane that re ...
in 1979. However, the city has experienced hurricane or near-hurricane conditions several times due to storms passing through Florida from the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
and entering Georgia or passing to the north or south in the Atlantic and brushing the area.
Environment
The Brunswick area has fourSuperfund
Superfund is a United States federal environmental remediation program established by the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA). The program is administered by the Environmental Protection Agen ...
sites, formerly home to heavily contaminated toxic waste
Toxic waste is any unwanted material in all forms that can cause harm (e.g. by being inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through the skin). Mostly generated by industry, consumer products like televisions, computers, and phones contain toxic chemi ...
sites: the LCP Chemicals site, Brunswick Wood Preserving, the Hercules 009 Landfill, and the Terry Creek Dredge Spoil Areas/Hercules Outfall. Research published in 2011 revealed that bottlenose dolphin
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the co ...
s that fed in the estuaries near these Superfund sites had the highest concentration of PCBs
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act in 1979 and internationally by ...
of any mammal in the world.
Demographics
In 2000, the city of Brunswick had 15,600 people, 6,085 households, and 3,681 families living in the city, down from the city's initial historic high of 21,703 in 1960. There were 6,952 housing units at an average density of . At the 2010 United States census, there were 15,383 people living within the city; experiencing population fluctuations since, the 2020 U.S. census reported a population of 15,210 people, 6,486 households, and 3,781 families residing in the city. Among the city's population between 2015 and 2020, the American Community Survey estimated a median age of 34.8, down from 2000's 35 years. Approximately 16.7% of the population were from under 5 years of age to 5 to 9 years; 20.5% were from 15 to 29 years of age; and 16.5% were aged 65 and older. For every 100 females, there were 80 males, and there was a child-dependency ratio of 46.6. At the 2000 census, the median income for a household in the city was $22,272, and the median income for a family was $28,564. Males had a median income of $26,172 versus $18,602 for females. Theper capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
for the city was $13,062. About 25.2% of families and 30.4% of the population were below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for ...
, including 43.9% of those under age 18 and 21.7% of those ages 65 or over. By 2020, the median household income was $27,471 with a mean of $57,395. Among families, the median income was $29,953 with a mean of $53,434; married-couple families had a median income of $63,301; and non-family households had a median income of $22,163 with a mean of $59,980.
The median monthly costs for occupied-housing units and renter-owned units was $718 in 2020; for homeowners with a mortgage, the median value of their single-family detached homes was $117,400 and the monthly costs were $1,068. The median real estate taxes paid among homeowners in the city was $951. Among the growing metropolitan statistical areas of Georgia, Brunswick has one of the lowest costs of living in contrast with Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,71 ...
and its metropolitan region
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
.
Race and ethnicity
Brunswick, like most of the United States, has had a traditional population from a predominantlynon-Hispanic white
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Am ...
, Anglo American background. With the diversification of the nation and state of Georgia, by 2000 its racial and ethnic makeup was 59.8% Black or African American, 33.1% White
White is the lightness, lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully diffuse reflection, reflect and scattering, scatter all the ...
(non-Hispanic whites), 0.3% American Indian or Alaska Native, 0.4% Asian, <0.1% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Ocea ...
, 1.7% from other races, and 1.4% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino Americans of any race were 5.8% of the population. At the 2020 census, the racial and ethnic makeup was 56.2% Black or African American, 30.39% non-Hispanic white, 0.16% American Indian or Alaska Native, 0.36% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 3.36% multiracial, and 9.49% Hispanic or Latino Americans of any race. Per 2008 estimates, the top five ancestry groups in the city were American (5.3%), English (5.1%), Subsarahan African (4.3%), Irish (4.1%), and German (3.6%). Approximately 54.1% of the population reported another ancestry.
Religion
 According to Sperling's BestPlaces, approximately 56.3% of the city's population identify with a religion as of 2020. Typical of those traditionally placed within the
According to Sperling's BestPlaces, approximately 56.3% of the city's population identify with a religion as of 2020. Typical of those traditionally placed within the Bible Belt
The Bible Belt is a region of the Southern United States in which socially conservative Protestant Christianity plays a strong role in society and politics, and church attendance across the denominations is generally higher than the nation's av ...
and conservative American South, the majority of the religiously-affiliated population identify as Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. The single largest Christian tradition within the city and metropolitan area are Baptists (15.7%), primarily divided into the National Baptist Convention and Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wo ...
among others; in contrast, the largest single Christian denomination has been the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and its Diocese of Savannah (6.8%).
Following, Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related Christian denomination, denominations of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John W ...
was the second largest tradition (12.3%) and Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestantism, Protestant Charismatic Christianity, Charismatic Christian movementAssemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
and Church of God. Other prominent Christian communities operating with a substantial presence in the city and area have also been Presbyterians, Episcopalians or Anglicans of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the United States
The Episcopal Church, based in the United States with additional dioceses elsewhere, is a member church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. It is a mainline Protestant denomination and is divided into nine provinces. The presiding bishop o ...
and Continuing Anglicanism, Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
, etc. Among non-mainstream Christianity, the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The c ...
makes up 1.5% of the faithful as of 2020.
Outside of local Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwin ...
, the second-largest religion practiced or adhered to in the area has been Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, and collectively, Eastern religions such as Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
or Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or ''dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global po ...
made up 0.3% of the population. The largest Jewish movement within the city has been Reform Judaism
Reform Judaism, also known as Liberal Judaism or Progressive Judaism, is a major Jewish denomination that emphasizes the evolving nature of Judaism, the superiority of its ethical aspects to its ceremonial ones, and belief in a continuous sear ...
, spread throughout the historic Temple Beth Tefilloh, founded in 1886.
Economy

 The Port of Brunswick forms a vital part of the city's economy. It is recognized as one of the most productive ports on the East Coast and is the sixth-busiest automobile port in the United States; it is the primary
The Port of Brunswick forms a vital part of the city's economy. It is recognized as one of the most productive ports on the East Coast and is the sixth-busiest automobile port in the United States; it is the primary export
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an ...
facility for two of the three United States traditional automotive manufacturers: Ford and General Motors. The port is also the primary export facility for Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz (), commonly referred to as Mercedes and sometimes as Benz, is a German luxury and commercial vehicle automotive brand established in 1926. Mercedes-Benz AG (a Mercedes-Benz Group subsidiary established in 2019) is headquarter ...
. The port serves as the central import facility for Hyundai Hyundai is a South Korean industrial conglomerate ("chaebol"), which was restructured into the following groups:
* Hyundai Group, parts of the former conglomerate which have not been divested
** Hyundai Mobis, Korean car parts company
** Hyundai As ...
, Jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the thi ...
, Kia, Land Rover
Land Rover is a British brand of predominantly four-wheel drive, off-road capable vehicles, owned by multinational car manufacturer Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), since 2008 a subsidiary of India's Tata Motors. JLR currently builds Land Rove ...
, Mitsubishi
The is a group of autonomous Japanese multinational companies in a variety of industries.
Founded by Yatarō Iwasaki in 1870, the Mitsubishi Group historically descended from the Mitsubishi zaibatsu, a unified company which existed from 187 ...
, Porsche, and Volvo
The Volvo Group ( sv, Volvokoncernen; legally Aktiebolaget Volvo, shortened to AB Volvo, stylized as VOLVO) is a Swedish multinational manufacturing corporation headquartered in Gothenburg. While its core activity is the production, distributio ...
. Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The o ...
, BMW, and Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post ...
utilize the port as a facility for imports as well. International Auto Processing is one of the town's largest employers. In addition to automobiles, exports include agricultural products
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
and other bulk cargo
Bulk cargo is commodity cargo that is transported unpackaged in large quantities.
Description
Bulk cargo refers to material in either liquid or granular, particulate form, as a mass of relatively small solids, such as petroleum/ crude oil ...
es.
The port is operated by the Georgia Ports Authority
The Georgia Ports Authority, which was founded in 1945 and chaired by US. Colonel, Inventor and Engineer Dr. Blake Van Leer, operates port facilities in the U.S. state of Georgia.
Georgia's primary deepwater ports are located in Savannah and ...
and features four separate terminals: Colonel's Island RoRo
Roll-on/roll-off (RORO or ro-ro) ships are cargo ships designed to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, semi-trailer trucks, buses, trailers, and railroad cars, that are driven on and off the ship on their own wheels or using ...
, Colonel's Island Agri-bulk, Mayor's Point, and Marine Port. Mayor's Point is the only terminal located within the city. The Colonel's Island and Marine Port terminals are located southwest of the city.
The Federal Law Enforcement Training Center
The Federal Law Enforcement Training Centers (FLETC) serves as an interagency law enforcement training body for 105 United States government federal law enforcement agencies. The stated mission of FLETC is to "...train those who protect our hom ...
(FLETC), a large agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is the Federal government of the United States, U.S. United States federal executive departments, federal executive department responsible for public security, roughly comparable to the I ...
, is headquartered in Glynco
Glynco is an area in Glynn County, Georgia located on the northwestern edge of Brunswick, Georgia. Glynco is a portmanteau of the words "Glynn County". History
In 1942 the Naval Air Station Glynco was established on the area now known as Glynco. ...
, north of the city. A study conducted by Georgia Tech
The Georgia Institute of Technology, commonly referred to as Georgia Tech or, in the state of Georgia, as Tech or The Institute, is a public research university and institute of technology in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1885, it is part o ...
identified FLETC as the largest employer in Glynn County; it was further determined that FLETC's annual localized economic impact is in excess of $600 million.
Southeast Georgia Health System is the largest private employer in Brunswick. Other major employers in Brunswick include King & Prince Seafood, GSI Commerce, Pinova and Gulfstream Aerospace
Gulfstream Aerospace Corporation is an American aircraft company and a wholly owned subsidiary of General Dynamics.
Gulfstream designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and services business jet aircraft. Gulfstream has produced more than 2,00 ...
. Wood pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw ma ...
is produced by the Georgia-Pacific
Georgia-Pacific LLC is an American pulp and paper company based in Atlanta, Georgia, and is one of the world's largest manufacturers and distributors of tissue, pulp, paper, toilet and paper towel dispensers, packaging, building products and ...
mill
Mill may refer to:
Science and technology
*
* Mill (grinding)
* Milling (machining)
* Millwork
* Textile manufacturing, Textile mill
* Steel mill, a factory for the manufacture of steel
* List of types of mill
* Mill, the arithmetic unit of the A ...
in Brunswick. The mill, which has been in operation since 1937, has the capability to produce over 800,000 metric ton
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
each year. Additionally, it is the largest single-site fluff production facility in the world. Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted th ...
, a manufacturer, and marketer of chemical specialties operates a production facility on the north side of Brunswick. Jet aircraft manufacturer Gulfstream Aerospace
Gulfstream Aerospace Corporation is an American aircraft company and a wholly owned subsidiary of General Dynamics.
Gulfstream designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and services business jet aircraft. Gulfstream has produced more than 2,00 ...
has a presence at the city's airport.
Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism ...
is the single largest industry in the city and the county. Brunswick and the Golden Isles are a year-round resort community. The islands' beaches, resorts, shops, and historic sites annually attract visitors from around the world. President George W. Bush hosted the G8 summit
The Group of Eight (G8) was an inter-governmental political forum from 1997 until 2014. It had formed from incorporating Russia into the Group of Seven, or G7, and returned to its previous name after Russia left in 2014.
The forum originate ...
in 2004 on Sea Island.Oliver Mark"G8 leaders meet on remote island,"
''Guardian'' (Manchester). June 8, 2004.
Culture
Arts and theatre
 Brunswick is home to a variety of arts and cultural events. The most significant professional performing-arts group is the Coastal Symphony of Georgia, in existence since 1982, which stages productions each year at Glynn Academy's Memorial Auditorium. This group of professional musicians also has a Youth Symphony division and a fundraising auxiliary.
Old Town Brunswick's historic and ornate Ritz Theatre hosts a range of performances. Renovated in the early 1980s and again in 2000 through 2001, the Ritz is home to the Golden Isles Arts and Humanities Association, the coordinating arts council for Brunswick and Glynn County. The association hosts an annual performing arts series and rents space to individual producers and organizations.
The city is home to various
Brunswick is home to a variety of arts and cultural events. The most significant professional performing-arts group is the Coastal Symphony of Georgia, in existence since 1982, which stages productions each year at Glynn Academy's Memorial Auditorium. This group of professional musicians also has a Youth Symphony division and a fundraising auxiliary.
Old Town Brunswick's historic and ornate Ritz Theatre hosts a range of performances. Renovated in the early 1980s and again in 2000 through 2001, the Ritz is home to the Golden Isles Arts and Humanities Association, the coordinating arts council for Brunswick and Glynn County. The association hosts an annual performing arts series and rents space to individual producers and organizations.
The city is home to various art galleries
An art gallery is a room or a building in which visual art is displayed. In Western cultures from the mid-15th century, a gallery was any long, narrow covered passage along a wall, first used in the sense of a place for art in the 1590s. The lo ...
. Art Downtown is a cultural arts center featuring a fine art gallery, studio, and production company. It is home to the Brunswick Actors' Theatre. The Gallery on Newcastle is home to a display of scenes from coastal Georgia's marshes.
Along Union Street is a collection of 19th and early 20th-century Victorian
Victorian or Victorians may refer to:
19th century
* Victorian era, British history during Queen Victoria's 19th-century reign
** Victorian architecture
** Victorian house
** Victorian decorative arts
** Victorian fashion
** Victorian literature ...
mansions. Each December the Magnolia Garden Club tours select Union Street homes in addition to other areas in historic Brunswick as part of its Christmas Tour of Homes.
Cuisine
 The city lays claim to
The city lays claim to Brunswick stew
Brunswick stew is a tomato-based stew generally involving local beans, vegetables, and originally small game meat such as squirrel or rabbit, though today often chicken. The exact origin of the stew is disputed. The states of Virginia, North Caro ...
, a tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , ...
-based stew containing various types of lima bean
A lima bean (''Phaseolus lunatus''), also commonly known as the butter bean, sieva bean, double bean, Madagascar bean, or wax bean is a legume grown for its edible seeds or beans.
Origin and uses
''Phaseolus lunatus'' is found in Meso- and Sou ...
s, corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
, okra
Okra or Okro (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in many English-speaking countries as ladies' fingers or ochro, is a flowering plant in the mallow family. It has edible green seed pods. The geographical origin of okra is disputed, with sup ...
, and other vegetables, and one or more types of meat. Most recipes claiming authenticity call for squirrel or rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit s ...
meat, but chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domestication, domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey junglefowl, grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster ...
, pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved ...
, and beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quant ...
are also common ingredients. A twenty-five-gallon (95 L) iron pot outside the city bears a plaque declaring the stew was first cooked there in 1898. The Brunswick Rockin' Stewbilee, held annually in October, features a stew-tasting contest where visitors sample over 50 teams' stews. The Stewbilee became famous when the city invited Brunswick County, Virginia
Brunswick County is a United States county located on the southern border of the Commonwealth of Virginia. This rural county is known as one of the claimants to be the namesake of Brunswick stew. Brunswick County was created in 1720 from parts ...
, to the festival for a stew cookoff in the 1980s, which led the Brunswick "Stew Wars" to be featured in ''Southern Living
''Southern Living'' is a lifestyle magazine aimed at readers in the Southern United States featuring recipes, house plans, garden plans, and information about Southern culture and travel. It is published by Birmingham, Alabama
(We dare defend ...
''.
Brunswick is the center of Georgia's shrimping industry. The city was once called "The Shrimp Capital of the World", but in recent times, production has been far below average. Nevertheless, nearby Jekyll Island hosts the Wild Georgia Shrimp & Grits Festival in September. Apart from shrimping, the area is also the center of Georgia's crab and oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not a ...
industries.
Sports
TheCollege of Coastal Georgia
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offering v ...
has an active collegiate sports program. The local high schools compete in the Georgia High School Association
The Georgia High School Association (GHSA) is an organization that governs athletics and activities for member high schools in Georgia, USA. GHSA is a member of the National Federation of State High School Associations. The association has 463 p ...
's quad-A Region 2 sporting events. From 1950 to 2007, Brunswick served host to the Golden Isles Bowl Classic, one of the most prestigious junior college football bowl games in the country. Scholastic and intramural sports are held at school and park facilities around the city. Glynn County Stadium and Lanier Field are two sports stadiums available in the city.
Golden Isles Speedway, a mile (1 km) race track
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also ...
, is located in western Glynn County, approximately west of the city.
The PGA Tour
The PGA Tour (stylized in all capital letters as PGA TOUR by its officials) is the organizer of professional golf tours in the United States and North America. It organizes most of the events on the flagship annual series of tournaments also k ...
holds the RSM Classic every year at the Seaside Course on Sea Island. The area is famous for its golf resort
A resort hotel is a hotel which often contains full-sized luxury facilities with full-service accommodations and amenities. These hotels may attract both business conferences and vacationing tourists and offer more than a convenient place to st ...
s. In 2008 Sea Island was ranked the number-one destination for business meetings and golf by ''Golf Digest
''Golf Digest'' is a monthly golf magazine published by Warner Bros. Discovery through its sports unit under its Warner Bros. Discovery Golf division. It is a generalist golf publication covering recreational golf and men's and women's compet ...
'' and ''USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virg ...
''. Sea Island was also ranked number-one among the best golf resorts in North America by ''Golf Digest''. There are three golf courses located just north of the city, and combined with Jekyll, St. Simons, and Sea islands, there are 252 holes of golf in the Brunswick area.
The Brunswick area is home to two out of three publicly accessible beach
A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological sources, such as mollusc shell ...
es in the state. Brunswick is the gateway city to Jekyll and St. Simons islands; both are accessible via automobile only by causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet ...
s from the city. The islands, known colloquially as the Golden Isles, feature white-sand public beaches and are popular destinations for tourists and local citizens.
In 1906 the city was home to a Class D-level minor league baseball team, the River Snipes, a team shared with Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
as part of the inaugural season of the Georgia State League
The Georgia State League was an American Class D minor league in professional baseball that existed in 1906, 1914, 1920–1921 and 1948–1956. During its last incarnation, it existed alongside two nearby Class D circuits, the Georgia–Florida L ...
. The league went defunct following that season. In 1913 the Brunswick Pilots debuted as part of the short-lived Empire State League
The Empire State League was a Minor league baseball circuit which operated in the 1913 season. It was a Class-D, six-team league, with teams based exclusively in Georgia, U.S. In 1914, the league evolved to become the Georgia State League.
Ci ...
, before joining the Georgia State League in 1914, and the Florida–Alabama–Georgia League
The Georgia State League was an American Class D minor league in professional baseball that existed in 1906, 1914, 1920–1921 and 1948–1956. During its last incarnation, it existed alongside two nearby Class D circuits, the Georgia–Florida Le ...
in 1915. The Pilots stopped play following the 1915 season. Thirty-six years passed before Brunswick had another professional baseball team. In 1951 the Brunswick Pirates
The Brunswick Pirates were a minor league baseball team based in Brunswick, Georgia. The team was a member of the Georgia–Florida League and a Class D affiliate of the Pittsburgh Pirates from 1951 to 1956. In 1957 the team played as the Brunswi ...
, a Class D minor league affiliate of the major league Pittsburgh Pirates
The Pittsburgh Pirates are an American professional baseball team based in Pittsburgh. The Pirates compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) National League Central, Central division. Founded as part o ...
, began to play in the Georgia–Florida League, beginning eight years of presence in the city. The Pirates won league championships in 1954 and 1955. In 1957 the Pirates became affiliates of the Philadelphia Phillies
The Philadelphia Phillies are an American professional baseball team based in Philadelphia. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) East division. Since 2004, the team's home stadium has been Citize ...
, respectively adopting the name Brunswick Phillies
Brunswick is the historical English name for the German city of Braunschweig ( Low German: ''Brunswiek'', Braunschweig dialect: ''Bronswiek'').
Brunswick may also refer to:
Places and other topographs
Australia
* Brunswick, Victoria, a suburb ...
. Following the 1958 season, the Phillies ceased to play. Brunswick was home to the Cardinals of the Georgia–Florida League in 1962 and 1963 before the league disbanded in 1963.
Parks and recreation

 The Brunswick Parks and Recreation Department operates city parks and
The Brunswick Parks and Recreation Department operates city parks and square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
s. Six city squares were part of Brunswick's original 1771 Town Plan. The two largest central squares were Wright and Hanover. Though half of Wright Square was built on by a middle school in the 1950s, the square was recently returned to its original size with George Street removed through the middle. Five of the six still exist today, with Hillsboro Square converted into the campus of Glynn Academy High School. There are also two additional squares located within the city, Orange, and Palmetto. Numerous parks exist in the city, the largest being Howard Coffin Park. The parks include features such as playgrounds, baseball fields, softball fields, soccer fields, basketball courts, and picnic areas. Coffin Park includes a walking track. The district also owns the Roosevelt Lawrence Community Center, a center equipped with popular and traditional recreational game tables, two classrooms, and a multi-purpose gymnasium.
The Brunswick area is rich in live oak
Live oak or evergreen oak is any of a number of oaks in several different sections of the genus ''Quercus'' that share the characteristic of evergreen foliage. These oaks are not more closely related to each other than they are to other oaks. ...
trees, particularly the Southern live oak
''Quercus virginiana'', also known as the southern live oak, is an evergreen oak tree endemic to the Southeastern United States. Though many other species are loosely called live oak, the southern live oak is particularly iconic of the Old South ...
. Such is the quality of the live oak trees in the Brunswick and the Golden Isles area that Revolutionary warships such as the (nicknamed ''Old Ironsides'') were clad in St. Simons Island oak planks. Brunswick has a notable live oak named Lover's Oak (located at Prince and Albany streets). As of 2005, it is approximately 900 years old. According to the State of Georgia and American Indian folklore, Native American braves and their maidens would meet under the oak. Another notable oak, Lanier's Oak, is notable as being the location where poet Sidney Lanier
Sidney Clopton Lanier (February 3, 1842 – September 7, 1881) was an American musician, poet and author. He served in the Confederate States Army as a private, worked on a blockade-running ship for which he was imprisoned (resulting in his catch ...
, on one of his visits to Brunswick, was inspired to write " The Marshes of Glynn".
Blythe Island Regional Park is located on Blythe Island
Blythe Island is located in Glynn County, Georgia, United States.
The primary mode of travel to the island is by automobile via Blythe Island Highway ( GA-303). There is one traffic signal and one gas station on the island. The island is surround ...
within the city.
Government
 Brunswick uses the council-manager model of
Brunswick uses the council-manager model of municipal government
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
. The city commission consists of five individuals, including the mayor, elected on a plurality-at-large basis. Commissioners constitute the legislative body
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known a ...
of the city and, as a group, are responsible for taxation, appropriations, ordinances, and other general functions. The mayor of Brunswick is Cornell Harvey, who was elected in 2014 and is the first African-American mayor of Brunswick.
The city is divided into two wards with each ward electing two city commission representatives. The mayor serves as an at-large
At large (''before a noun'': at-large) is a description for members of a governing body who are elected or appointed to represent a whole membership or population (notably a city, county, state, province, nation, club or association), rather than ...
commissioner and chairperson
The chairperson, also chairman, chairwoman or chair, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a Board of directors, board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by ...
. The commission meets twice each month at Old City Hall in Old Town. The city commission appoints a city manager
A city manager is an official appointed as the administrative manager of a city, in a " Mayor–council government" council–manager form of city government. Local officials serving in this position are sometimes referred to as the chief ex ...
to serve at will for an infinite term. The main duty of the manager is to implement policy set by the city commission and manage the operations of the city on a daily basis. The city manager is to see that all laws, provisions of the city charter
A city charter or town charter (generically, municipal charter) is a legal document ('' charter'') establishing a municipality such as a city or town. The concept developed in Europe during the Middle Ages.
Traditionally the granting of a charter ...
, and any acts of the city commission are executed and enforced. The city manager of Brunswick is Regina McDuffie.
In November 2008, Mayor Thompson and the city commission of Brunswick traveled to Ganzhou to strengthen ties between the two cities. Ganzhou, a city with a population of 8.5 million, reciprocated, sending a delegation to Brunswick where an official sister city agreement was signed at Old Brunswick City Hall
Brunswick is the historical English name for the German city of Braunschweig (Low German: ''Brunswiek'', Braunschweig dialect: ''Bronswiek'').
Brunswick may also refer to:
Places and other topographs
Australia
* Brunswick, Victoria, a suburb of ...
on April 3, 2009.
Education
Higher education
 Brunswick is home to the
Brunswick is home to the College of Coastal Georgia
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offering v ...
, which has more than 3,000 enrolled students. Since 1961, the college had been a two-year institution, but in 2008, the college began its transition to a four-year institution. The college is currently a state college State College is a city in central Pennsylvania, United States.
State College may also refer to:
Related to State College, Pennsylvania
* State College Area School District, a school district serving State College
* State College Area High School ...
within the University System of Georgia
The University System of Georgia (USG) is the government agency that includes 26 public institutions of higher learning in the U.S. state of Georgia. The system is governed by the Georgia Board of Regents. It sets goals and dictates gener ...
, with bachelor's degree programs in education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. ...
, business, and nursing sciences
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
, and other associate degree
An associate degree is an undergraduate degree awarded after a course of post-secondary study lasting two to three years. It is a level of qualification above a high school diploma, GED, or matriculation, and below a bachelor's degree.
Th ...
programs designed to prepare students to transfer to senior colleges and universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which ...
.
Primary and secondary schools
 The Glynn County School System is the governing authority of public schools in the city. More than 12,000 students attend schools in the school system. There are ten
The Glynn County School System is the governing authority of public schools in the city. More than 12,000 students attend schools in the school system. There are ten elementary school
A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ed ...
s, four middle school
A middle school (also known as intermediate school, junior high school, junior secondary school, or lower secondary school) is an educational stage which exists in some countries, providing education between primary school and secondary school ...
s, and two high school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper seconda ...
s: Brunswick High School and Glynn Academy. Glynn Academy, the second-oldest public high school in the American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
and the sixth-oldest public high school in the United States, was founded in 1788 by an act of the Georgia General Assembly
The Georgia General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is bicameral, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
Each of the General Assembly's 236 members serve two-year terms and are directly ...
. Brunswick High School opened in 1967. Specialized institutions include a career-technical academy.
There are several private schools operating in the area. In the city, there is one Catholic school
Catholic schools are pre-primary, primary and secondary educational institutions administered under the aegis or in association with the Catholic Church. , the Catholic Church operates the world's largest religious, non-governmental school syst ...
and one Seventh-day Adventist
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, a ...
school. There are also Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christianity, Christian believers only (believer's baptism), and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe ...
, Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement
, and non-denominational Christian
Nondenominational Christianity (or non-denominational Christianity) consists of churches which typically distance themselves from the confessionalism or creedalism of other Christian communities by not formally aligning with a specific Christian d ...
schools north of the city, such as Heritage Christian Academy. On St. Simons Island, there is a Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their na ...
school. Several smaller Christian schools in Brunswick offer high school education.
Media
'' The Brunswick News'' is one of two major daily newspapers serving Brunswick; the other is ''The Georgia Times-Union'', a subsidiary of the Jacksonville-based ''Florida Times-Union
''The Florida Times-Union'' is a daily newspaper in Jacksonville, Florida, United States. Widely known as the oldest newspaper in the state, it began publication as the ''Florida Union'' in 1864. Its current incarnation started in 1883, when th ...
''. Brunswick has one free weekly newspaper delivered to most homes in Glynn County, ''The Harbor Sound'' (a free publication). ''The Islander'' is a weekly paper, member of the Georgia Press Association, and available at newsstands or by subscription.
The major AM radio stations in Brunswick are WSFN
WSFN (790 AM) is a sports radio station in Brunswick, Georgia. WSFN programming is simulcast on WFNS 1350 AM and W279BC 103.7 FM. Southern Media Interactive LLC also owns WSEG at Savannah and WFNS at Blackshear.
The station lineup includes Ke ...
790, an ESPN
ESPN (originally an initialism for Entertainment and Sports Programming Network) is an American international basic cable sports channel owned by ESPN Inc., owned jointly by The Walt Disney Company (80%) and Hearst Communications (20%). The ...
affiliate and primarily a sports station; WGIG 1440; and WBGA 1490, which are all news and talk stations. The city's FM stations include NPR affiliate WWIO-FM 88.9, public radio WWEZ at 94.7 (St. Simons Island) and 97.5 (Brunswick), and commercial
Commercial may refer to:
* a dose of advertising conveyed through media (such as - for example - radio or television)
** Radio advertisement
** Television advertisement
* (adjective for:) commerce, a system of voluntary exchange of products and s ...
stations WAYR-FM 90.7, WSSI
WSSI (92.7 FM) is a radio station broadcasting a classic hits format. Licensed to St. Simons Island, Georgia, United States, the station serves the Brunswick area. The station is owned by Golden Isles Broadcasting, LLC.
History
The station we ...
92.7, WMUV 100.7, WSOL 101.5, WYNR 102.5, WQGA 103.3, WRJY 104.1, WXMK 105.9, and WHFX 107.7. 96.3
WPXC-TV, channel 21, an Ion affiliate, is the only broadcast television
Broadcast television systems (or terrestrial television systems outside the US and Canada) are the encoding or formatting systems for the transmission and reception of terrestrial television signals.
Analog television systems were standardized b ...
station in Brunswick. The station became an ABC affiliate in 1996, but in 2001, Allbritton Communications sold the station and, therefore, the station lost its affiliation. All major U.S. television networks are represented in Brunswick from Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the seat of Duval County, with which the c ...
and Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
-based television stations.
In popular culture
Brunswick has been featured in scenes from the films ''The View from Pompey's Head
''The View from Pompey's Head'' is a novel by American writer Hamilton Basso, first published by Doubleday in 1954. It spent 40 weeks on '' The New York Times'' bestseller list. The title refers to the book's setting, the fictional small to ...
'' (1955), '' Conrack'' (1974), '' The Longest Yard'' (1974), and the documentary ''Criminalizing Dissent'' (2006).
The city is also the setting for the novel ''Ravens'' by author George Dawes Green
George Dawes Green (born 1954) is an American novelist and the founder of the storytelling organization The Moth.
Books and films
Green published his first novel, ''The Caveman's Valentine'', in 1994. It was adapted into a film in 2001, starri ...
.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Brunswick Golden Isles Airport (BQK, KBQK) is served byDelta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The airline, along wi ...
, with several daily round trips to the Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport
Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport , also known as Atlanta Hartsfield–Jackson International Airport, Atlanta Airport, Hartsfield, Hartsfield–Jackson and, formerly, as the Atlanta Municipal Airport, is the primary internatio ...
. The city was formerly served by DayJet, with service to cities in Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = " Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,7 ...
, Florida, and Georgia; the company suspended its operations in September 2008.
Two railway lines run through the city: CSX and Norfolk Southern
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the company operates 19,420 route miles (31, ...
. The Golden Isles Terminal Railroad
The Golden Isles Terminal Railroad is a terminal railroad that began operations in 1998, taking over from the Colonel's Island Railroad. It operates 33 miles of track in and around the port at Brunswick, GA
Brunswick () is a city in and the c ...
is a short line operating of mainline trackage between Anguilla Junction and the Colonel's Island and Marine Port terminals of the Port of Brunswick. This line connects with a line that originates in Old Town Brunswick at Anguilla Junction. Brunswick last had direct passenger service in 1966 or 1967 with the unnamed successor to the Southern Railway's '' Kansas City-Florida Special.'' Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
passenger service is available in Jesup, northwest of the city.
The original Sidney Lanier Bridge was a vertical-lift bridge
A vertical-lift bridge or just lift bridge is a type of movable bridge in which a span rises vertically while remaining parallel with the deck.
The vertical lift offers several benefits over other movable bridges such as the bascule and swi ...
on U.S. 17
U.S. Route 17 or U.S. Highway 17 (US 17), also known as the Coastal Highway, is a north–south United States Highway that spans in the southeastern United States. It runs close to the Atlantic Coast for much of its length, with ...
crossing the Brunswick River and was opened on June 22, 1956. On November 7, 1972, the ship ''African Neptune'' struck the bridge, causing parts of the bridge to collapse, taking cars with it. The accident resulted in ten deaths. On May 3, 1987, the bridge was again struck by a ship, the Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
freighter ''Ziemia Bialostocka''. A new cable-stayed bridge
A cable-stayed bridge has one or more ''towers'' (or ''pylons''), from which cables support the bridge deck. A distinctive feature are the cables or stays, which run directly from the tower to the deck, normally forming a fan-like pattern ...
with the same name opened in 2003 to allow larger ships to enter the port and to eliminate the need for the drawbridge on U.S. 17. It is the longest-spanning bridge in Georgia. The elevation at the top of the support towers is .
Three federal highways pass through Brunswick: U.S. Route 17, U.S. Route 341, and U.S. Route 25. U.S. 17 runs north to south through the eastern part of town and is a four-lane highway. U.S. 341 overlaps U.S. 25 for almost the entire route and originates in Brunswick off U.S. 17. Interstate 95
Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from US Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Florida, to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between Maine and the Canadi ...
runs west and northwest of the city, and U.S. Route 82
U.S. Route 82 (US 82) is an east–west United States highway in the Southern United States. Created on July 1, 1931 across central Mississippi and southern Arkansas, US 82 eventually became a 1,625-mile (2,615 km) route extending from ...
originates at the junction of U.S. 17 and State Route 303 just west of I-95.
In 2006, Glynn County applied for approximately $930,000 for first-year funding for a transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1979 film), a 1979 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countries in the world
* ''Transit'' (2006 film), a 2006 ...
service. The county and city match was for over $100,000 combined. The first-year project would fund the purchase of up to four buses, two vans, signage, equipment, and facility improvements. As of 2007 the first-year application was pending with the Georgia DOT and the Federal Transit Administration
The Federal Transit Administration (FTA) is an agency within the United States Department of Transportation (DOT) that provides financial and technical assistance to local public transportation systems. The FTA is one of ten modal administratio ...
.
Healthcare
 With over 1,321 employees and over 201 physicians, Southeast Georgia Health System is the main provider of health care in Brunswick and the surrounding area and is also the largest private employer in Brunswick. Southeast Georgia Health System's medical campus in the city offers a 316-bed full-service hospital. Southeast Georgia Health System Brunswick campus also has an alliance with the International Seafarer's Center that provides first-class medical attention to seamen who come into the Brunswick port; the medical needs of approximately 15,000 international merchant seafarers are met each year. Southeast Georgia Health System also operates a 180-bed skilled nursing facility in Brunswick, The Senior Care Center, which offers short-term rehabilitation services, as well as long-term care.
Southeast Georgia Health System recently opened the Outpatient Care Center on the Brunswick campus. This six-story, building includes
With over 1,321 employees and over 201 physicians, Southeast Georgia Health System is the main provider of health care in Brunswick and the surrounding area and is also the largest private employer in Brunswick. Southeast Georgia Health System's medical campus in the city offers a 316-bed full-service hospital. Southeast Georgia Health System Brunswick campus also has an alliance with the International Seafarer's Center that provides first-class medical attention to seamen who come into the Brunswick port; the medical needs of approximately 15,000 international merchant seafarers are met each year. Southeast Georgia Health System also operates a 180-bed skilled nursing facility in Brunswick, The Senior Care Center, which offers short-term rehabilitation services, as well as long-term care.
Southeast Georgia Health System recently opened the Outpatient Care Center on the Brunswick campus. This six-story, building includes outpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery, also known as ambulatory surgery, day surgery, day case surgery, or same-day surgery, is surgery that does not require an overnight hospital stay.The International Association for Ambulatory Surgery (IAAS) would not consider ...
and imaging services, the Cancer Care Center, a retail area, the Dick Mitchell Health Information Center, as well as physician offices and suites.
In 2004, the Brunswick campus was named Best Large Hospital in the State of Georgia by the Georgia Alliance of Community Hospitals.
Sister cities
*Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north into h ...
, People's Republic of China
* Ilan, Yilan County, Taiwan Province, Republic of China
Taiwan Province (; PFS: ''Thòi-vàn-sén'' or ''Thòi-vân-sén'') is a nominal administrative division of the Republic of China (ROC). Its definition has remained part of the Constitution of the Republic of China, but the province is no long ...
Brunswick has an active sister cities
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties.
While there are early examples of inter ...
program designed to encourage cultural and economic exchanges.
Notable people
* Anthony Alaimo,United States federal judge
In the United States, federal judges are judges who serve on courts established under Article Three of the U.S. Constitution. They include the chief justice and the associate justices of the U.S. Supreme Court, the circuit judges of the U.S ...
* Spencer Atkinson, orthodontist
* Sam Bowen, baseball player
* Morgan Brian
Morgan Paige Gautrat (; born February 26, 1993) is an American soccer player who most recently played for the Kansas City Current of the National Women's Soccer League (NWSL), the highest division of women's professional soccer in the United Sta ...
, Women's World Cup soccer champion with Team USA 2016; plays professional soccer for Houston Dash
* Kwame Brown
Kwame Hasani Brown (born March 10, 1982) is an American former professional basketball player who spent 12 seasons in the National Basketball Association (NBA). Selected by the Washington Wizards in the 2001 NBA draft, Brown was the first No. ...
, NBA player, top pick of 2001 NBA Draft
The 2001 NBA draft took place on June 27, 2001 in New York City, New York. Kwame Brown became the first high school player to be drafted with the first overall pick in the history of the NBA. The selection of Kwame Brown by the Washington Wizards, ...
* Barret Browning
Gary Barret Browning (born December 28, 1984) is an American former professional baseball pitcher who played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the St. Louis Cardinals in 2012.
Amateur career
Browning attended Florida State University, and i ...
, baseball player
* Justin Coleman, NFL cornerback for the Detroit Lions
The Detroit Lions are a professional American football team based in Detroit. The Lions compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) North Division. The team play their home games at For ...
* DeeJay Dallas, NFL running back for the Seattle Seahawks
The Seattle Seahawks are a professional American football team based in Seattle. The Seahawks compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) West, which they rejoined in 2002 a ...
* Ed Dudley, professional golfer, first club professional at Augusta National
* Amos Easton, also known as Bumble Bee Slim, musician
*Freeman Hankins
Freeman Hankins (September 30, 1917 – December 31, 1988) was an American politician and funeral director who served as a member of the Pennsylvania State Senate for the 7th district from 1969 to 1988. He also served in the Pennsylvania Hou ...
, Pennsylvania State Representative from 1961 to 1968, Pennsylvania State Senator from 1967 to 1988
* Mary Hood, writer
* Anna Jay
Anna Marie Jernigan (born July 15, 1998), better known by the ring name Anna Jay, is an American professional wrestler. She is signed to All Elite Wrestling, where she is a member of the Jericho Appreciation Society Stable (professional wrestlin ...
, professional wrestler in AEW AEW or aew may refer to:
* Airborne early warning
Airborne or Airborn may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Airborne'' (1962 film), a 1962 American film directed by James Landis
* ''Airborne'' (1993 film), a comedy–drama f ...
* ReShard Lee, football player
* Davis Love III
Davis Milton Love III (born April 13, 1964) is an American professional golfer who has won 21 events on the PGA Tour, including one major championship: the 1997 PGA Championship. He won the Players Championship in 1992 and 2003. He was in th ...
, professional golfer and Ryder Cup captain
* Jack McDevitt
Jack McDevitt (born April 14, 1935) is an American science fiction authors, science fiction author whose novels frequently deal with attempts to make First contact (science fiction), contact with Extraterrestrial life, alien races, and with archa ...
, science-fiction writer, Nebula Award for Best Novel
The Nebula Award for Best Novel is given each year by the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America (SFWA) for science fiction or fantasy novels. A work of fiction is considered a novel by the organization if it is 40,000 words or longer; a ...
winner
* Kristen Morgin
Kristen L. Morgin (born 1968) is an American visual artist working primarily in sculpture. She is best known for her works made of unfired clay that use trompe-l'œil to appear as wood, paper, or metal and suggest decay.
Biography
Kristen Morgin ...
, sculptor
* Jack Peerson, baseball player
* Harry Pickens, jazz pianist
* Tony Pierce, baseball player
* Antonio Santiago, one-year-old victim of a highly publicized murder
* Darius Slay
Darius Demetrius Slay Jr. (born January 1, 1991) is an American football cornerback for the Philadelphia Eagles of the National Football League (NFL). He played college football at Mississippi State and was drafted by the Detroit Lions in ...
, NFL cornerback for the Philadelphia Eagles
The Philadelphia Eagles are a professional American football team based in Philadelphia. The Eagles compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) East division. The team play ...
* Doris Buchanan Smith, author of '' A Taste of Blackberries''
* Raymond M. Lloyd, Professional Wrestler of WCW
* Aaron Swinson, Cincinnati Bearcats
The Cincinnati Bearcats are the athletic teams that represent the University of Cincinnati. Though they will move to the Big 12 Conference (XII) the teams are currently a part of the American Athletic Conference (The American), which from 1979 ...
assistant coach (college basketball), and former player
* Albert Tresvant
Albert Tresvant (April 15, 1926 – July 25, 2004) was an American politician who served as the first African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United State ...
, first African-American mayor of Opa-locka, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
* Adam Wainwright
Adam Parrish Wainwright (born August 30, 1981), nicknamed "Waino" and "Uncle Charlie", is an American professional baseball pitcher for the St. Louis Cardinals of Major League Baseball (MLB).
The Atlanta Braves selected him 29th overall in th ...
, baseball pitcher for St. Louis Cardinals (birthplace)
* Tracy Walker, NFL safety for the Detroit Lions
The Detroit Lions are a professional American football team based in Detroit. The Lions compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) North Division. The team play their home games at For ...
* Ike Williams, professional boxer, former lightweight champion
* Madaline A. Williams
Madaline A. (Worthy) Williams (May 5, 1894 – December 14, 1968) was an American Democratic Party politician who was the first African-American woman elected to the New Jersey Legislature.
Early life and career
Williams was born in Brunswi ...
, first African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American ...
woman elected to the New Jersey Legislature
The New Jersey Legislature is the legislative branch of the government of the U.S. state of New Jersey. In its current form, as defined by the New Jersey Constitution of 1947, the Legislature consists of two houses: the General Assembly and th ...
* Marion Wilson, murderer
See also
*1898 Georgia hurricane
The 1898 Georgia hurricane was a major hurricane that hit the U.S. state of Georgia, as well as the strongest on record in the state. It was first observed on September 29, although modern researchers estimated that it developed four days ea ...
* Clark Quarry
* History of Brunswick, Georgia
The recorded History of Brunswick, Georgia dates to 1738, when a plantation was established along the Turtle River. By 1789, the city was recognized by President George Washington as having been one of five original ports of entry for the America ...
* Oglethorpe Hotel
The Oglethorpe Hotel, located in downtown Brunswick, Georgia, was designed in 1888 by architect J. A. Wood and named after James Oglethorpe. It was built on top of the previous Oglethorpe House, which was burned during the Civil War. It was constr ...
Notes
References
* ''Brunswick Georgia and the building of Liberty Ships'', brochure published by Brunswick and Golden Isles Convention and Visitors CenterExternal links
City of Brunswick official website
History of Brunswick
{{authority control Cities in Georgia (U.S. state) Cities in Glynn County, Georgia County seats in Georgia (U.S. state) Port cities and towns in Georgia (U.S. state) Brunswick metropolitan area Populated places established in 1771 Populated coastal places in Georgia (U.S. state)