|
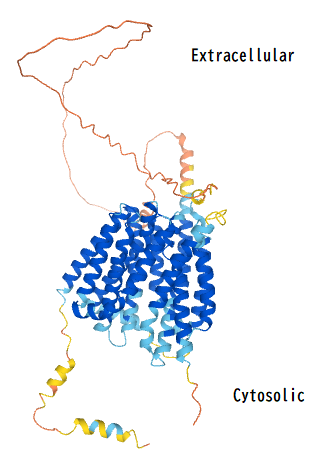
MFSD6L Predicted Tertiary Structure
Major facilitator superfamily domain containing 6 like (MFSD6L) is a protein encoded by the MFSD6L gene in humans. The MFSD6L protein is a transmembrane protein that is part of the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) that uses chemiosmotic gradients to facilitate the transport of small solutes across cell membranes. Gene In the human genome, the MFSD6L gene is located on chromosome 17 (17p13.1). The DNA sequence encoding the polypeptide encompasses 2,256 bases, starting from 8,797,110 bp to 8,799,365 bp. Additionally, the gene sequence resides on the minus strand. The MFSD6L gene has one alias called FLJ35773. The encoding DNA sequence results in only one exon in the translated mRNA sequence. The tumor suppressor gene TP53 was also found within the gene neighborhood of MFSD6L at 17p13.1. mRNA Transcript The MFSD6L gene was not found to have other isoforms due to the presence of only one exon in the MFSD6L encoding sequence. Protein The MFSD6L protein has a precurso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure Of MFSD6L Protein
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene Epoch. The time span covered by the Tertiary has no exact equivalent in the current geologic time system, but it is essentially the merged Paleogene and Neogene periods, which are informally called the Early Tertiary and the Late Tertiary, respectively. The Tertiary established the Antarctic as an icy island continent. Historical use of the term The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in Northern Italy. Later a fourth period, the Quaternary, was applied. In the early dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
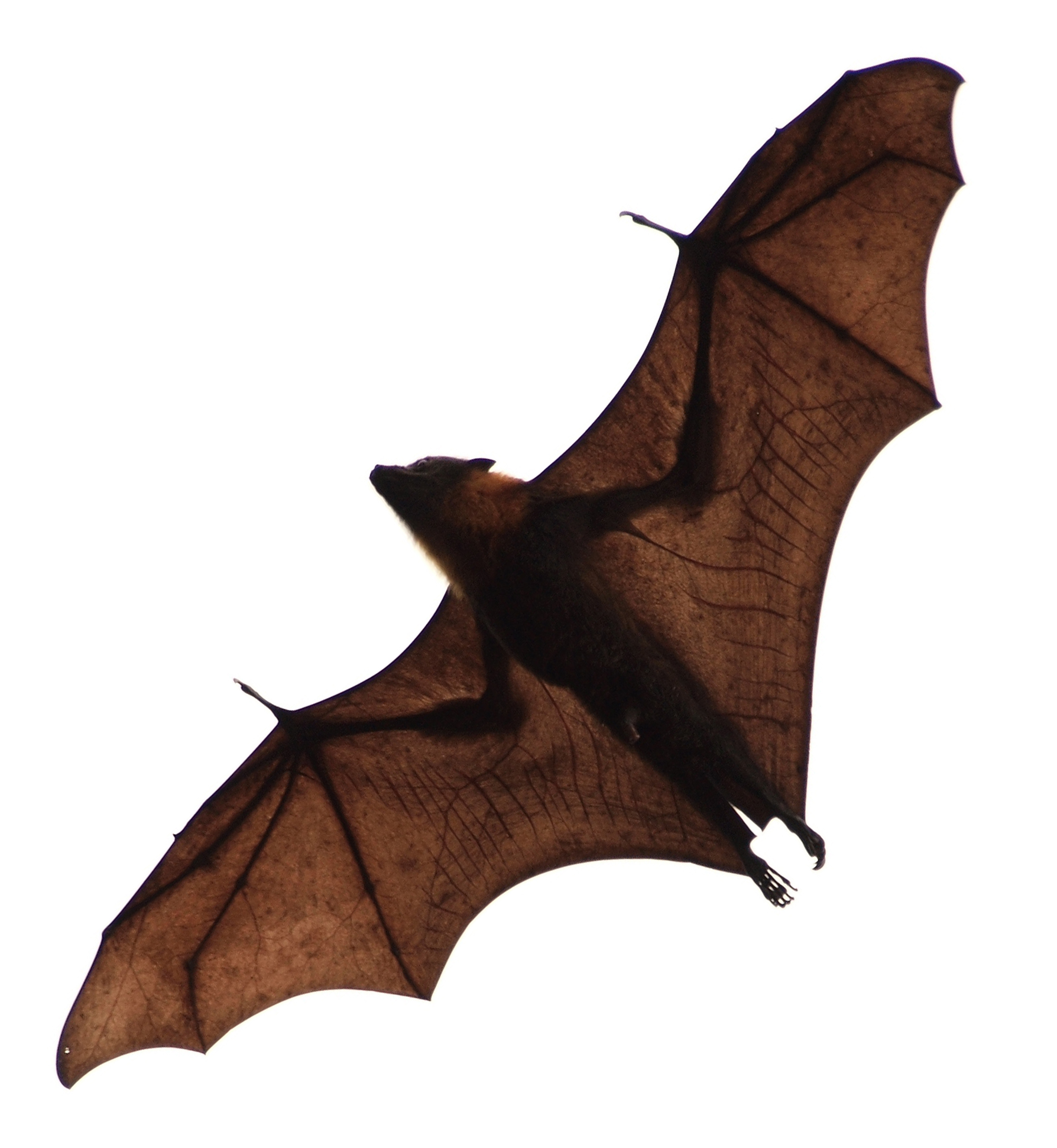
Pteropus
''Pteropus'' (suborder Yinpterochiroptera) is a genus of megabats which are among the largest bats in the world. They are commonly known as fruit bats or flying foxes, among other colloquial names. They live in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia, East Africa, and some oceanic islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. There are at least 60 Extant taxon, extant species in the genus. Flying foxes eat fruit and other plant matter, and occasionally consume insects as well. They locate resources with their keen sense of smell. Most, but not all, are nocturnality, nocturnal. They navigate with keen eyesight, as they cannot Animal echolocation, echolocate. They have R/K selection theory#K-selection, long life spans and low reproductive outputs, with females of most species producing only one offspring per year. Their slow life history makes their populations vulnerable to threats such as Overexploitation, overhunting, culling, and natural disasters. Six flying fox species have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velvety Free-tailed Bat
The velvety free-tailed bat or Pallas's mastiff bat (''Molossus molossus''), is a bat species in the family Molossidae. Description ''M. molossus'' is a medium-sized bat, with a length of and with a wingspan of . This species is brown in color; however, when seen flying around at dusk, it will appear to be black. The tail of ''M. molossus'' is long and extends beyond the tail membrane. Its ears are large and round. Feeding ''M. molossus'' forages in open areas, above tree canopies, around forest edges, and around streams and ponds. Its diet includes moths, beetles, and flying ants. It is commonly seen at dusk, where it will fly solo, catching insects in the air. Distribution and habitat It occurs in the Americas from Argentina north to Cuba and Mexico and also the Florida Keys in the United States. It is very common in the Caribbean. A ''M. molossus'' has been observed being killed by a giant centipede (''Scolopendra viridicornis'') in the Amazon. The lone bat had been roost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narwhal
The narwhal, also known as a narwhale (''Monodon monoceros''), is a medium-sized toothed whale that possesses a large "tusk" from a protruding canine tooth. It lives year-round in the Arctic waters around Greenland, Canada and Russia. It is one of two living species of whale in the family Monodontidae, along with the beluga whale, and the only species in the genus ''Monodon''. The narwhal males are distinguished by a long, straight, helical tusk, which is an elongated upper left canine. The narwhal was one of many species described by Carl Linnaeus in his publication ''Systema Naturae'' in 1758. Like the beluga, narwhals are medium-sized whales. For both sexes, excluding the male's tusk, the total body size can range from ; the males are slightly larger than the females. The average weight of an adult narwhal is . At around 11 to 13 years old, the males become sexually mature; females become sexually mature at about 5 to 8 years old. Narwhals do not have a dorsal fin and thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Mouse
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the order Rodentia, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus '' Mus''. Although a wild animal, the house mouse has benefited significantly from associating with human habitation to the point that truly wild populations are significantly less common than the semi-tame populations near human activity. The house mouse has been domesticated as the pet or fancy mouse, and as the laboratory mouse, which is one of the most important model organisms in biology and medicine. The complete mouse reference genome was sequenced in 2002. Characteristics House mice have an adult body length (nose to base of tail) of and a tail length of . The weight is typically . In the wild they vary in color from grey and light brown to black (individual hairs are actually agouti coloured), but domesticated fancy mice and laboratory mice ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermophile
A thermophile is an organism—a type of extremophile—that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though they can be bacteria or fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earliest bacteria. Thermophiles are found in various geothermally heated regions of the Earth, such as hot springs like those in Yellowstone National Park (see image) and deep sea hydrothermal vents, as well as decaying plant matter, such as peat bogs and compost. Thermophiles can survive at high temperatures, whereas other bacteria or archaea would be damaged and sometimes killed if exposed to the same temperatures. The enzymes in thermophiles function at high temperatures. Some of these enzymes are used in molecular biology, for example the ''Taq'' polymerase used in PCR. "Thermophile" is derived from the el, θερμότητα (''thermotita''), meaning heat, and el, φίλια (''philia''), love. Classification Thermophiles can be c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerolinea
''Anaerolinea'' is a bacteria genus from the family of Anaerolineaceae Anaerolineaceae is a family of bacteria from the order of Anaerolineales. Anaerolineaceae bacteria occur in marine sediments. There are a total of twelve genera in this family, most of which only encompass one species. All known members of the f .... References Further reading * * Chloroflexota Bacteria genera {{bacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Lamprey
The sea lamprey (''Petromyzon marinus'') is a parasitic lamprey native to the Northern Hemisphere. It is sometimes referred to as the "vampire fish". Description The sea lamprey has an eel-like body without paired fins. Its mouth is jawless, round and sucker-like, and as wide or wider than the head; sharp teeth are arranged in many concentric circular rows. There are seven branchial or gill-like openings behind the eye. Sea lampreys are olive or brown-yellow on the dorsal and lateral part of the body, with some black marblings, with lighter coloration on the belly. Adults can reach a length of up to and a body weight up to . Etymology The etymology of the genus name ''Petromyzon'' is from '' petro-'' "stone" and '' myzon'' "sucking"; ''marinus'' is Latin for "of the sea". Distribution and habitat The species is found in the northern and western Atlantic Ocean along the shores of Europe and North America, in the western Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, and as an invasive speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are jawed vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, scales, and a heart with its chambers in series. Extant chondrichthyes range in size from the 10 cm (3.9 in) finless sleeper ray to the 10 m (32 ft) whale shark. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish) and Holocephali ( chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is gradually replaced by a vertebral column during development, except in Holocephali, where the notochord stays intact. In some deepwat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or horny spines (rays), as opposed to the fleshy, lobed fins that characterize the class Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). These actinopterygian fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the link or connection between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). By species count, actinopterygians dominate the vertebrates, and they constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 species of fish. They are ubiquitous throughout freshwater and marine environments from the deep sea to the highest mountain streams. Extant species can range in size from ''Paedocypris'', at , to the massive ocean sunfish, at , and the long-bodied oarfish, at . The vast majority of Actinopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |