Narwhal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The narwhal, also known as a narwhale (''Monodon monoceros''), is a medium-sized toothed whale that possesses a large " tusk" from a protruding
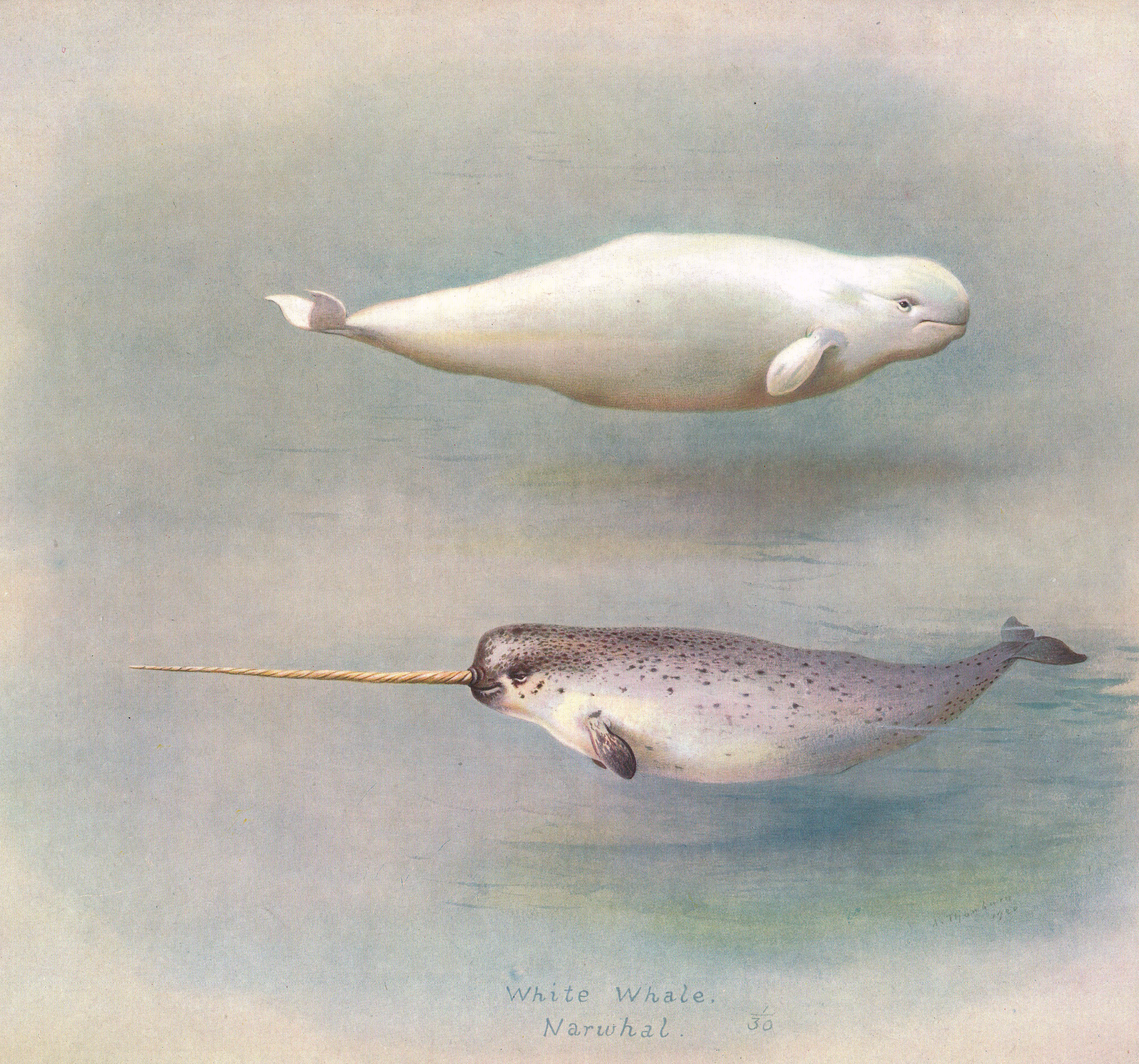 The narwhal was one of many species originally described by
The narwhal was one of many species originally described by
in ''Nature''; Mikkel Skovrind, Jose Alfredo Samaniego Castruita, James Haile, Eve C. Treadaway, Shyam Gopalakrishnan, Michael V. Westbury, Mads Peter Heide-Jørgensen, Paul Szpak & Eline D. Lorenzen; Scientific Reports; volume 9, Article number: 7729 (2019) The white whales,
canine tooth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened however ...
. It lives year-round in the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada ( Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm ( Greenland), Finland, Iceland ...
waters around Greenland, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
. It is one of two living species of whale in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Monodontidae, along with the beluga whale
The beluga whale () (''Delphinapterus leucas'') is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus ''Delphinapterus''. It is also known as the whi ...
, and the only species in the genus ''Monodon''. The narwhal males are distinguished by a long, straight, helical tusk, which is an elongated upper left canine. The narwhal was one of many species described by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
in his publication ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
'' in 1758.
Like the beluga, narwhals are medium-sized whales. For both sexes, excluding the male's tusk, the total body size can range from ; the males are slightly larger than the females. The average weight of an adult narwhal is . At around 11 to 13 years old, the males become sexually mature; females become sexually mature at about 5 to 8 years old. Narwhals do not have a dorsal fin and their neck vertebrae are jointed like those of most other mammals, not fused as in dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s and most whales.
Found primarily in Canadian Arctic and Greenlandic and Russian waters, the narwhal is a uniquely specialised Arctic predator. In winter, it feeds on benthic prey, mostly flatfish, under dense pack ice. During the summer, narwhals eat mostly Arctic cod and Greenland halibut, with other fish such as polar cod making up the remainder of their diet. Each year, they migrate from bays into the ocean as summer comes. In the winter, the male narwhals occasionally dive up to in depth, with dives lasting up to 25 minutes. Narwhals, like most toothed whales, communicate with "clicks", "whistles" and "knocks".
Narwhals can live up to 50 years and are often killed by suffocation after being trapped due to the formation of sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
. Other causes of death, specifically among young whales, are starvation and predation by orcas. As previous estimates of the world narwhal population were below 50,000, narwhals are categorised by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as "nearly threatened". More recent estimates list higher populations (upwards of 170,000), thus lowering the status to "least concern". Narwhals have been harvested for hundreds of years by Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, ...
in northern Canada and Greenland for meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
and ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
and a regulated subsistence hunt continues.
Taxonomy and etymology
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
in his landmark 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. Its name is derived from the Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and t ...
word ''nár'', meaning "corpse", in reference to the animal's greyish, mottled pigmentation, like that of a drowned sailor and its summertime habit of lying still at or near the surface of the sea (called "logging"). The scientific name, ''Monodon monoceros'', is derived from Greek: "one-tooth one-horn".
The narwhal is most closely related to the beluga whale. Together, these two species comprise the only extant members of the family Monodontidae, sometimes referred to as the "white whales". The Monodontidae are distinguished by their medium size (at around in length), pronounced melons (round sensory organs), short snouts and the absence of a true dorsal fin.
Although the narwhal and the beluga are classified as separate genera, with one species each, there is some evidence that they may, very rarely, interbreed. The complete skull of an anomalous whale was discovered in West Greenland circa 1990. It was described by marine zoologists as unlike any known species, but with features midway between a narwhal and a beluga, consistent with the hypothesis that the anomalous whale was a narwhal-beluga hybrid; in 2019, this was confirmed by DNA and isotopic analysis.Hybridization between two high Arctic cetaceans confirmed by genomic analysisin ''Nature''; Mikkel Skovrind, Jose Alfredo Samaniego Castruita, James Haile, Eve C. Treadaway, Shyam Gopalakrishnan, Michael V. Westbury, Mads Peter Heide-Jørgensen, Paul Szpak & Eline D. Lorenzen; Scientific Reports; volume 9, Article number: 7729 (2019) The white whales,
dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (t ...
s (Delphinidae) and porpoise
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals an ...
s (Phocoenidae) together comprise the superfamily Delphinoidea, which are of likely monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
origin. Genetic evidence suggests the porpoises are more closely related to the white whales and that these two families constitute a separate clade which diverged from the rest of Delphinoidea within the past 11 million years. Fossil evidence shows that ancient white whales lived in tropical waters. They may have migrated to Arctic and sub-Arctic waters in response to changes in the marine food chain during the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58 Narwhals do not have a dorsal fin, possibly an evolutionary adaptation to swimming easily under ice, to facilitate rolling, or to reduce surface area and heat loss. Instead narwhals possess a shallower dorsal ridge. Their neck vertebrae are jointed, like those of land mammals, instead of being fused together as in most whales, allowing a great range of neck flexibility. Both these characteristics are shared by the fellow
 The most conspicuous characteristic of the male narwhal is a single long tusk, which is in fact a
The most conspicuous characteristic of the male narwhal is a single long tusk, which is in fact a
 The narwhal is found predominantly in the Atlantic and Russian areas of the
The narwhal is found predominantly in the Atlantic and Russian areas of the
 Narwhals can live an average of 50 years, however research using aspartic acid racemization from the lens of the eyes suggests that narwhals can live to be as old as 115 ± 10 years and 84 ± 9 years for females and males, respectively Mortality often occurs when the narwhals suffocate after they fail to leave before the surface of the Arctic waters freeze over in the late autumn. As narwhals need to breathe, they drown if open water is no longer accessible and the ice is too thick for them to break through. Maximum aerobic swimming distance between breathing holes in ice is less than which limits the use of foraging grounds and these holes must be at least wide to allow an adult whale to breathe. The last major entrapment events occurred when there was little to no wind. Entrapment can affect as many as 600 individuals, most occurring in narwhal wintering areas such as Disko Bay. In the largest entrapment in 1915 in West Greenland, over 1,000 narwhals were trapped under the ice.
Despite the decreases in sea ice cover, there were several large cases of sea ice entrapment in 2008–2010 in the winter close to known summering grounds, two of which were locations where there had been no previous cases documented. This suggests later departure dates from summering grounds. Sites surrounding Greenland experience advection (moving) of sea ice from surrounding regions by wind and currents, increasing the variability of sea ice concentration. Due to strong site fidelity, changes in weather and ice conditions are not always associated with narwhal movement toward open water. More information is needed to determine the vulnerability of narwhals to sea ice changes. Narwhals can also die of starvation.
Narwhals can live an average of 50 years, however research using aspartic acid racemization from the lens of the eyes suggests that narwhals can live to be as old as 115 ± 10 years and 84 ± 9 years for females and males, respectively Mortality often occurs when the narwhals suffocate after they fail to leave before the surface of the Arctic waters freeze over in the late autumn. As narwhals need to breathe, they drown if open water is no longer accessible and the ice is too thick for them to break through. Maximum aerobic swimming distance between breathing holes in ice is less than which limits the use of foraging grounds and these holes must be at least wide to allow an adult whale to breathe. The last major entrapment events occurred when there was little to no wind. Entrapment can affect as many as 600 individuals, most occurring in narwhal wintering areas such as Disko Bay. In the largest entrapment in 1915 in West Greenland, over 1,000 narwhals were trapped under the ice.
Despite the decreases in sea ice cover, there were several large cases of sea ice entrapment in 2008–2010 in the winter close to known summering grounds, two of which were locations where there had been no previous cases documented. This suggests later departure dates from summering grounds. Sites surrounding Greenland experience advection (moving) of sea ice from surrounding regions by wind and currents, increasing the variability of sea ice concentration. Due to strong site fidelity, changes in weather and ice conditions are not always associated with narwhal movement toward open water. More information is needed to determine the vulnerability of narwhals to sea ice changes. Narwhals can also die of starvation.
 Humans hunt narwhals, often selling commercially the skin, carved vertebrae, teeth and tusk, while eating the meat, or feeding it to dogs. About 1,000 narwhals per year are killed, 600 in Canada and 400 in Greenland. Canadian harvests were steady at this level in the 1970s, dropped to 300–400 per year in the late 1980s and 1990s and rose again since 1999. Greenland harvested more, 700–900 per year, in the 1980s and 1990s.
Tusks are sold with or without carving in Canada and Greenland. An average of one or two vertebrae and one or two teeth per narwhal are carved and sold. In Greenland the skin ( muktuk) is sold commercially to fish factories, and in Canada to other communities. One estimate of the annual gross value received from narwhal hunts in
Humans hunt narwhals, often selling commercially the skin, carved vertebrae, teeth and tusk, while eating the meat, or feeding it to dogs. About 1,000 narwhals per year are killed, 600 in Canada and 400 in Greenland. Canadian harvests were steady at this level in the 1970s, dropped to 300–400 per year in the late 1980s and 1990s and rose again since 1999. Greenland harvested more, 700–900 per year, in the 1980s and 1990s.
Tusks are sold with or without carving in Canada and Greenland. An average of one or two vertebrae and one or two teeth per narwhal are carved and sold. In Greenland the skin ( muktuk) is sold commercially to fish factories, and in Canada to other communities. One estimate of the annual gross value received from narwhal hunts in
 In Inuit legend, the narwhal's tusk was created when a woman with a harpoon rope tied around her waist was dragged into the ocean after the harpoon had struck a large narwhal. She was transformed into a narwhal and her hair, which she was wearing in a twisted knot, became the characteristic spiral narwhal tusk.
Some
In Inuit legend, the narwhal's tusk was created when a woman with a harpoon rope tied around her waist was dragged into the ocean after the harpoon had struck a large narwhal. She was transformed into a narwhal and her hair, which she was wearing in a twisted knot, became the characteristic spiral narwhal tusk.
Some
 The narwhal was one of two possible explanations of the giant sea phenomenon written by
The narwhal was one of two possible explanations of the giant sea phenomenon written by
Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals
', Perrin, Wursig and Thewissen eds. * Groc, Isabelle. "Hunt for the sea unicorn", ''New Scientist'' feature article, Issue 2956, 15 February 201
Narwhal Discoveries
{{Authority control Mammals described in 1758 Cetaceans of the Arctic Ocean Mammals of Canada Mammals of Greenland Mammals of Russia Monodontidae Articles containing video clips Unicorns Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Holarctic fauna
beluga whale
The beluga whale () (''Delphinapterus leucas'') is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus ''Delphinapterus''. It is also known as the whi ...
. The tail flukes of female narwhals have front edges that are swept back and those of males have front edges that are more concave and lack a sweep-back. This is thought to be an adaptation for reducing drag
Drag or The Drag may refer to:
Places
* Drag, Norway, a village in Tysfjord municipality, Nordland, Norway
* ''Drág'', the Hungarian name for Dragu Commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Drag (Austin, Texas), the portion of Guadalupe Street adj ...
caused by the tusk.
Tusk
 The most conspicuous characteristic of the male narwhal is a single long tusk, which is in fact a
The most conspicuous characteristic of the male narwhal is a single long tusk, which is in fact a canine tooth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened however ...
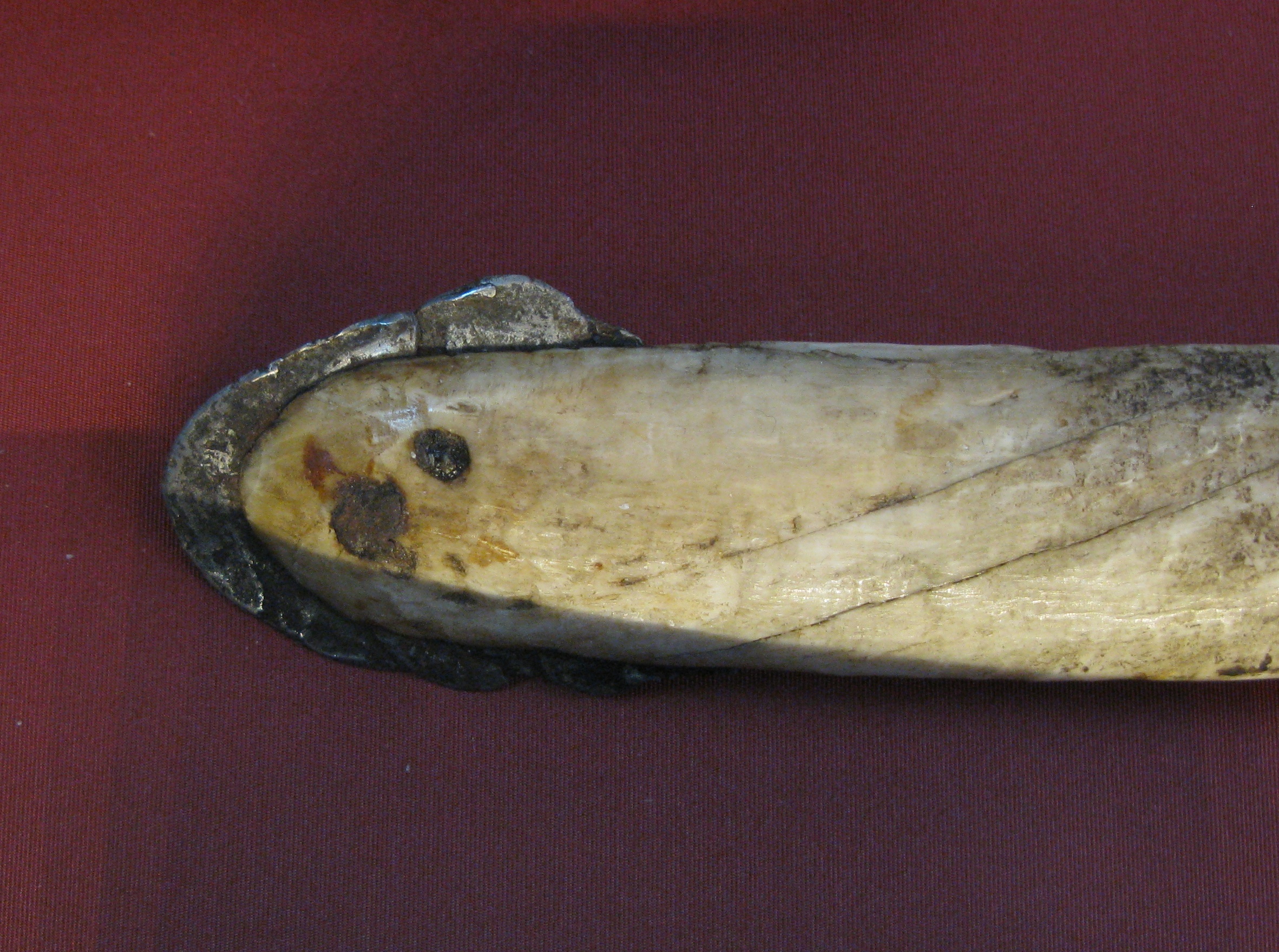
that projects from the left side of the upper jaw, through the lip and forms a left-handed helical spiral. The tusk grows throughout life, reaching a length of about . It is hollow and weighs around . About one in 500 males has two tusks, occurring when the right canine also grows out through the lip. Only about 15 percent of females grow a tusk, which typically is smaller than a male tusk, with a less noticeable spiral. Collected in 1684, there is only one known case of a female growing a second tusk (image).
Scientists have long speculated on the biological function of the tusk. Proposed functions include use of the tusk as a weapon, for opening breathing holes in sea ice, in feeding, as an acoustic organ and as a secondary sex character. The leading theory has long been that the narwhal tusk serves as a secondary sex character of males, for nonviolent assessment of hierarchical status on the basis of relative tusk size. However, detailed analysis reveals that the tusk is a highly innervate
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
d sensory organ
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system r ...
with millions of nerve endings connecting seawater stimuli in the external ocean environment with the brain. The rubbing of tusks together by male narwhals is thought to be a method of communicating information about characteristics of the water each has travelled through, rather than the previously assumed posturing display of aggressive male-to-male rivalry. In August 2016, drone
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
videos of narwhals surface-feeding in Tremblay Sound, Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' ...
showed that the tusk was used to tap and stun small Arctic cod, making them easier to catch for feeding. The tusk cannot serve a critical function for the animal's survival, as females — which generally do not have tusks — typically live longer than males. Therefore, the general scientific consensus is that the narwhal tusk is a sexual trait, much like the antlers of a stag, the mane of a lion, or the feathers of a peacock.
Vestigial teeth
The tusks are surrounded posteriorly, ventrally and laterally by several small vestigial teeth which vary in morphology and histology. These teeth can sometimes be extruded from the bone, but mainly reside inside open tooth sockets in the narwhal's snout alongside the tusks. The varied morphology and anatomy of small teeth indicate a path of evolutionary obsolescence, leaving the narwhal's mouth toothless.Genome
A 2.3 GB genome sequence has been assembled from multiple Illumina libraries. The genome consists of 37.9% repetitive elements and encodes 21,785protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
-coding gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s (similar to many other mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a ...
s). The genome will help to place the narwhal both into the evolutionary context of other whales but also will help to understand the evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
and embryonic development of features such as the striking tusk and its sexual dimorphism.
Distribution
 The narwhal is found predominantly in the Atlantic and Russian areas of the
The narwhal is found predominantly in the Atlantic and Russian areas of the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
. Individuals are commonly recorded in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, such as in the northern part of Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
, Hudson Strait, Baffin Bay; off the east coast of Greenland; and in a strip running east from the northern end of Greenland round to eastern Russia ( 170° East). Land in this strip includes Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norway, Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of continental Europe, mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The ...
, Franz Joseph Land and Severnaya Zemlya. The northernmost sightings of narwhal have occurred north of Franz Joseph Land, at about 85° North latitude.
Behaviour
Social
Narwhals normally congregate in groups of about five to ten and sometimes up to 20 individuals outside the summer. Groups may be "nurseries" with only females and young, or can contain only post-dispersal juveniles or adult males ("bulls"), but mixed groups can occur at any time of year. In the summer, several groups come together, forming larger aggregations which can contain from 500 to over 1000 individuals. At times, a bull narwhal may rub its tusk with another bull, a display known as "tusking" and thought to maintain social dominance hierarchies. However, this behaviour may exhibit tusk use as a sensory and communication organ for sharing information about water chemistry sensed in tusk microchannels.Migration
Narwhals exhibit seasonal migrations, with a high fidelity of return to preferred, ice-free summering grounds, usually in shallow waters. In summer months, they move closer to coasts, often in pods of 10–100. In the winter, they move to offshore, deeper waters under thick pack ice, surfacing in narrow fissures in the sea ice, or leads. As spring comes, these leads open up into channels and the narwhals return to the coastalbay
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a Gulf (geography), gulf, sea, sound (geography), sound, or bight (geogra ...
s. Narwhals from Canada and West Greenland winter regularly in the pack ice of Davis Strait and Baffin Bay along the continental slope with less than 5% open water and high densities of Greenland halibut. Feeding in the winter accounts for a much larger portion of narwhal energy intake than in the summer.
Diet
Narwhals have a relatively restricted and specialized diet. Their prey is predominantly composed of Greenland halibut, polar and Arctic cod, cuttlefish,shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
and armhook squid
The Gonatidae, also known as armhook squid, are a family of moderately sized squid. The family contains about 19 species in three genera, widely distributed and plentiful in cold boreal waters of the Pacific Ocean. At least one species is known f ...
. Additional items found in stomachs have included wolffish, capelin, skate eggs and sometimes rocks, accidentally ingested when whales feed near the bottom. Due to the lack of well-developed dentition in the mouth, narwhals are believed to feed by swimming towards prey until it is within close range and then sucking it with considerable force into the mouth. It is thought that the beaked whale
Beaked whales ( systematic name Ziphiidae) are a family of cetaceans noted as being one of the least known groups of mammals because of their deep-sea habitat and apparent low abundance. Only three or four of the 24 species are reasonably well- ...
s, which have similarly reduced dentition, also suck up their prey. The distinctive tusk is used to tap and stun small prey, facilitating a catch.
Narwhals have a very intense summer feeding society. One study published in the Canadian Journal of Zoology tested 73 narwhals of different age and gender to see what they ate. The individuals were from the Pond Inlet and had their stomach contents tested from June 1978 until September 1979. The study found in 1978 that the Arctic cod ('' Boreogadus saida'') made up about 51% of the diet of the narwhals, with the next most common animal being the Greenland halibut (''Reinhardtius hippoglossoides
The Greenland halibut or Greenland turbot (''Reinhardtius hippoglossoides'') belongs to the family Pleuronectidae (the right-eye flounders), and is the only species of the genus ''Reinhardtius''. It is a predatory fish that mostly ranges at dept ...
''), consisting of 37% of the weight of their diet. A year later, the percentages of both animals in the diet of narwhals had changed. Arctic cod represented 57% and Greenland halibut 29% in 1979. The deep-water fish – halibut, redfish (''Sebastes marinus
''Sebastes norvegicus'', the rose fish, ocean perch, Atlantic redfish, Norway haddock, golden redfish or pinkbelly rosefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorp ...
'') and polar cod ('' Arctogadus glacialis'') – were found primarily in the diet of the males, which means that the narwhals can dive deeper than below sea level. The study found that the dietary needs of the narwhal did not differ among genders or ages.
Diving
When in their wintering waters, narwhals make some of the deepest dives recorded for a marine mammal, diving to at least over 15 times per day, with many dives reaching . Dives to these depths last around 25 minutes, including the time spent at the bottom and the transit down and back from the surface. Dive times can also vary in time and depth, based on local variation between environments, as well as seasonality. For example, in the Baffin Bay wintering grounds, narwhals farther south appear to be spending most of their time diving to deeper depths along the steep slopes of Baffin Bay, suggesting differences in habitat structure, prey availability, or innate adaptations between subpopulations. Curiously, whales in the deeper northern wintering ground have access to deeper depths, yet make shallower dives. Because vertical distribution of narwhal prey in the water column influences feeding behaviour and dive tactics, regional differences in the spatial and temporal patterns of prey density, as well as differences in prey assemblage, may be shaping winter foraging behaviour of narwhals.Communication
As in most toothed whales, narwhals use sound to navigate and hunt for food. Narwhals primarily vocalise through "clicks", "whistles" and "knocks", created by air movement between chambers near the blow-hole. These sounds are reflected off the sloping front of the skull and focused by the animal's melon, which can be controlled by musculature. Echolocation clicks are primarily produced for prey detection and for locating obstacles at short distances. It is possible that individual "bangs" are capable of disorienting or incapacitating prey, making them easier to hunt, but this has not been verified. They also emit tonal signals, such as whistles and pulsed calls, that are believed to have a communication function. The calls recorded from the same herd are more similar than calls from different herds, suggesting the possibility of group or individual-specific calls in narwhals. Narwhals may also adjust the duration and the pitch of their pulsed calls to maximise sound propagation in varying acoustic environments Other sounds produced by narwhals include trumpeting and squeaking door sounds. The narwhal vocal repertoire is similar to that of the closely related beluga, with comparable whistle frequency ranges, whistle duration and repetition rates of pulse calls, however beluga whistles may have a higher frequency range and more diversified whistle contours.Breeding and early life
Females start bearing calves when six to eight years old. Adult narwhals mate in April or May when they are in the offshore pack ice.Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
lasts for 14 months and calves are born between June and August the following year. As with most marine mammals, only a single young is born, averaging in length and white or light grey in colour. During summer population counts along different coastal inlets of Baffin Island, calf numbers varied from 0.05% to 5% of the total numbering from 10,000 to 35,000 narwhals, indicating that higher calf counts may reflect calving and nursery habitats in favourable inlets. Hybrids have been documented between the narwhal and beluga (specifically a beluga male and a narwhal female), as one, perhaps even as many as three, were killed and harvested during a sustenance hunt. Whether or not these hybrids could breed remains unknown. The unusual dentition seen in the single remaining skull indicates the hybrid hunted on the seabed, much as walruses do, indicating feeding habits different from those of either parent species.
Newborn calves begin their lives with a thin layer of blubber which thickens as they nurse their mother's milk which is rich in fat. Calves are dependent on milk for around 20 months. This long lactation period gives calves time to learn skills needed for survival during maturation when they stay within two body lengths of the mother.
Lifespan and mortality
 Narwhals can live an average of 50 years, however research using aspartic acid racemization from the lens of the eyes suggests that narwhals can live to be as old as 115 ± 10 years and 84 ± 9 years for females and males, respectively Mortality often occurs when the narwhals suffocate after they fail to leave before the surface of the Arctic waters freeze over in the late autumn. As narwhals need to breathe, they drown if open water is no longer accessible and the ice is too thick for them to break through. Maximum aerobic swimming distance between breathing holes in ice is less than which limits the use of foraging grounds and these holes must be at least wide to allow an adult whale to breathe. The last major entrapment events occurred when there was little to no wind. Entrapment can affect as many as 600 individuals, most occurring in narwhal wintering areas such as Disko Bay. In the largest entrapment in 1915 in West Greenland, over 1,000 narwhals were trapped under the ice.
Despite the decreases in sea ice cover, there were several large cases of sea ice entrapment in 2008–2010 in the winter close to known summering grounds, two of which were locations where there had been no previous cases documented. This suggests later departure dates from summering grounds. Sites surrounding Greenland experience advection (moving) of sea ice from surrounding regions by wind and currents, increasing the variability of sea ice concentration. Due to strong site fidelity, changes in weather and ice conditions are not always associated with narwhal movement toward open water. More information is needed to determine the vulnerability of narwhals to sea ice changes. Narwhals can also die of starvation.
Narwhals can live an average of 50 years, however research using aspartic acid racemization from the lens of the eyes suggests that narwhals can live to be as old as 115 ± 10 years and 84 ± 9 years for females and males, respectively Mortality often occurs when the narwhals suffocate after they fail to leave before the surface of the Arctic waters freeze over in the late autumn. As narwhals need to breathe, they drown if open water is no longer accessible and the ice is too thick for them to break through. Maximum aerobic swimming distance between breathing holes in ice is less than which limits the use of foraging grounds and these holes must be at least wide to allow an adult whale to breathe. The last major entrapment events occurred when there was little to no wind. Entrapment can affect as many as 600 individuals, most occurring in narwhal wintering areas such as Disko Bay. In the largest entrapment in 1915 in West Greenland, over 1,000 narwhals were trapped under the ice.
Despite the decreases in sea ice cover, there were several large cases of sea ice entrapment in 2008–2010 in the winter close to known summering grounds, two of which were locations where there had been no previous cases documented. This suggests later departure dates from summering grounds. Sites surrounding Greenland experience advection (moving) of sea ice from surrounding regions by wind and currents, increasing the variability of sea ice concentration. Due to strong site fidelity, changes in weather and ice conditions are not always associated with narwhal movement toward open water. More information is needed to determine the vulnerability of narwhals to sea ice changes. Narwhals can also die of starvation.
Predation and hunting
Major predators are polar bears, which attack at breathing holes mainly for young narwhals and Greenland sharks.Killer whale
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
s (orcas) group together to overwhelm narwhal pods in the shallow water of enclosed bays, in one case killing dozens of narwhals in a single attack. To escape predators such as orcas, narwhals may use prolonged submergence to hide under ice floes rather than relying on speed.
 Humans hunt narwhals, often selling commercially the skin, carved vertebrae, teeth and tusk, while eating the meat, or feeding it to dogs. About 1,000 narwhals per year are killed, 600 in Canada and 400 in Greenland. Canadian harvests were steady at this level in the 1970s, dropped to 300–400 per year in the late 1980s and 1990s and rose again since 1999. Greenland harvested more, 700–900 per year, in the 1980s and 1990s.
Tusks are sold with or without carving in Canada and Greenland. An average of one or two vertebrae and one or two teeth per narwhal are carved and sold. In Greenland the skin ( muktuk) is sold commercially to fish factories, and in Canada to other communities. One estimate of the annual gross value received from narwhal hunts in
Humans hunt narwhals, often selling commercially the skin, carved vertebrae, teeth and tusk, while eating the meat, or feeding it to dogs. About 1,000 narwhals per year are killed, 600 in Canada and 400 in Greenland. Canadian harvests were steady at this level in the 1970s, dropped to 300–400 per year in the late 1980s and 1990s and rose again since 1999. Greenland harvested more, 700–900 per year, in the 1980s and 1990s.
Tusks are sold with or without carving in Canada and Greenland. An average of one or two vertebrae and one or two teeth per narwhal are carved and sold. In Greenland the skin ( muktuk) is sold commercially to fish factories, and in Canada to other communities. One estimate of the annual gross value received from narwhal hunts in Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
in 2013 was for 81 narwhals, or per narwhal. However the net income, after subtracting costs in time and equipment, was a loss of per person. Hunts receive subsidies, but they continue as a tradition, rather than for the money and the economic analysis noted that whale watching may be an alternate revenue source. Of the gross income, was for skin and meat, to replace beef, pork and chickens which would otherwise be bought, was received for tusks and carved vertebrae and teeth of males and was received for carved vertebrae and teeth of females.
Conservation issues
Narwhals are one of many mammals that are being threatened by human actions. Estimates of the world population of narwhals range from around 50,000 (from 1996) to around 170,000 (compilation of various sub-population estimates from the years 2000–2017). They are considered to be near threatened and several sub-populations have evidence of decline. In an effort to support conservation, the European Union established an import ban on tusks in 2004 and lifted it in 2010. The United States has forbidden imports since 1972 under the Marine Mammal Protection Act. Narwhals are difficult to keep in captivity.
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, ...
are able to hunt this whale species legally, as discussed above in Predation and hunting. Narwhals have been extensively hunted the same way as other sea mammals, such as seals and whales, for their large quantities of fat. Almost all parts of the narwhal, meat, skin, blubber and organs are consumed. '' Muktuk'', the name for raw skin and blubber, is considered a delicacy. One or two vertebrae per animal are used for tools and art. The skin is an important source of vitamin C which is otherwise difficult to obtain. In some places in Greenland, such as Qaanaaq, traditional hunting methods are used and whales are harpooned from handmade kayaks. In other parts of Greenland and Northern Canada, high-speed boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically found on i ...
s and hunting rifles are used.
During growth, the narwhal accumulates metals in its internal organs. One study found that many metals are low in concentration in the blubber of narwhals and high in the liver and the kidney. Zinc and cadmium are found in higher densities in the kidney than the liver and lead, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
and mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
were found to be the opposite. Certain metals were correlated with size and sex. During growth, it was found that mercury accumulated in the liver, kidney, muscle and blubber and that cadmium settled in the blubber.
Narwhals are one of the most vulnerable Arctic marine mammals to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
due to altering sea ice coverage in their environment, especially in their northern wintering grounds such as the Baffin Bay and Davis Strait regions. Satellite data collected from these areas shows the amount of sea ice has been markedly reduced. Narwhals' ranges for foraging are believed to be patterns developed early in their life which increase their ability to gain necessary food resources during winter. This strategy focuses on strong site fidelity
Philopatry is the tendency of an organism to stay in or habitually return to a particular area. The causes of philopatry are numerous, but natal philopatry, where animals return to their birthplace to breed, may be the most common. The term derives ...
rather than individual level responses to local prey distribution and this results in focal foraging areas during the winter. As such, despite changing conditions, narwhals will continue returning to the same areas during migration. Despite its vulnerability to sea ice change, the narwhal has some flexibility when it comes to sea ice and habitat selection. It evolved in the late Pliocene and so is moderately accustomed to periods of glaciation and environmental variability.
An indirect danger for narwhals associated with changes in sea ice is the increased exposure in open water. In 2002 there was an increase in narwhal catches by hunters in Siorapaluk that did not appear to be associated with increased effort, implying that climate change may be making the narwhal more vulnerable to harvesting. Scientists urge assessment of population numbers with the assignment of sustainable quotas for stocks and the collaboration of management agreements to ensure local acceptance. Seismic surveys associated with oil exploration have also disrupted normal migration patterns which may also be associated with increased sea ice entrapment.
Cultural depictions
In legend
 In Inuit legend, the narwhal's tusk was created when a woman with a harpoon rope tied around her waist was dragged into the ocean after the harpoon had struck a large narwhal. She was transformed into a narwhal and her hair, which she was wearing in a twisted knot, became the characteristic spiral narwhal tusk.
Some
In Inuit legend, the narwhal's tusk was created when a woman with a harpoon rope tied around her waist was dragged into the ocean after the harpoon had struck a large narwhal. She was transformed into a narwhal and her hair, which she was wearing in a twisted knot, became the characteristic spiral narwhal tusk.
Some medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
Europeans believed narwhal tusks to be the horns from the legendary unicorn.Daston, Lorraine and Park, Katharine (2001). ''Wonders and the Order of Nature, 1150–1750''. New York: Zone Books, . As these horns were considered to have magic powers, such as neutralising poison and curing melancholia, Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
and other northern traders were able to sell them for many times their weight in gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
. The tusks were used to make cups that were thought to negate any poison that may have been slipped into the drink. A narwhal tusk exhibited at Warwick Castle is according to legend the rib of the mythical Dun Cow. In 1555, Olaus Magnus published a drawing of a fish-like creature with a horn on its forehead, correctly identifying it as a "Narwal". During the 16th century, Queen Elizabeth I received a narwhal tusk worth 10,000 pounds sterling—the 16th-century equivalent cost of a castle (approximately £1.5–2.5 million in 2007, using the retail price index)–from Sir Humphrey Gilbert, who proposed that the tusk was from a "sea-unicorne". The tusks were staples of the cabinet of curiosities.
In literature and art
 The narwhal was one of two possible explanations of the giant sea phenomenon written by
The narwhal was one of two possible explanations of the giant sea phenomenon written by Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the ''Voyages extraor ...
in his 1870 novel '' Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea''. Verne thought that it would be unlikely that there was such a gigantic narwhal in existence. The size of the narwhal, or "unicorn of the sea", as found by Verne, would have been . For the narwhal to have caused the phenomenon, Verne stated that its size and strength would have to increase by five or ten times.
Herman Melville wrote a section on the narwhal (written as "narwhale") in his 1851 novel '' Moby-Dick'', in which he claims a narwhal tusk hung for "a long period" in Windsor Castle after Sir Martin Frobisher
Sir Martin Frobisher (; c. 1535 – 22 November 1594) was an English seaman and privateer who made three voyages to the New World looking for the North-west Passage. He probably sighted Resolution Island near Labrador in north-eastern Canada ...
had given it to Queen Elizabeth
Queen Elizabeth, Queen Elisabeth or Elizabeth the Queen may refer to:
Queens regnant
* Elizabeth I (1533–1603; ), Queen of England and Ireland
* Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022 ...
. Another claim he made was that the Danish kings made their thrones from narwhal tusks.
See also
* List of cetaceansReferences
Further reading
* * M. P. Heide-Jorgensen. "Narwhal", inEncyclopedia of Marine Mammals
', Perrin, Wursig and Thewissen eds. * Groc, Isabelle. "Hunt for the sea unicorn", ''New Scientist'' feature article, Issue 2956, 15 February 201
External links
*Narwhal Discoveries
{{Authority control Mammals described in 1758 Cetaceans of the Arctic Ocean Mammals of Canada Mammals of Greenland Mammals of Russia Monodontidae Articles containing video clips Unicorns Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Holarctic fauna