|
Li Ke(Zhengzhou CPC Party Chief)
Li Ke ( ; 619 вҖ“ 10 March 653), posthumously known as the Prince of YГ№lГӯn (й¬ұжһ—зҺӢ), often known by his greater title as the Prince of WГә (еҗізҺӢ), was an imperial prince of the Tang Dynasty. As a highly honored son of Emperor Taizong, he was one time considered a possible candidate as crown prince after both his older brother Li Chengqian and younger brother Li Tai were both deposed in 643, but eventually, his younger brother Li Zhi, as a son of Emperor Taizong's wife Empress Zhangsun, was created crown prince and inherited the throne after Emperor Taizong's death in 649 (as Emperor Gaozong), under the insistence of Li Zhi's uncle and Emperor Taizong's brother-in-law Zhangsun Wuji. Zhangsun, however, detested Li Ke, and in 653, he implicated Li Ke in a plot by the official Fang Yi'ai (жҲҝйҒәж„ӣ) and had Emperor Gaozong order Li Ke to commit suicide. Early life It is not known exactly when Li Ke was born, but he was likely born around 619,This is based on the historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Ke (Jin)
Li Ke ( ; 619 вҖ“ 10 March 653), posthumously known as the Prince of YГ№lГӯn (й¬ұжһ—зҺӢ), often known by his greater title as the Prince of WГә (еҗізҺӢ), was an imperial prince of the Tang Dynasty. As a highly honored son of Emperor Taizong, he was one time considered a possible candidate as crown prince after both his older brother Li Chengqian and younger brother Li Tai were both deposed in 643, but eventually, his younger brother Li Zhi, as a son of Emperor Taizong's wife Empress Zhangsun, was created crown prince and inherited the throne after Emperor Taizong's death in 649 (as Emperor Gaozong), under the insistence of Li Zhi's uncle and Emperor Taizong's brother-in-law Zhangsun Wuji. Zhangsun, however, detested Li Ke, and in 653, he implicated Li Ke in a plot by the official Fang Yi'ai (жҲҝйҒәж„ӣ) and had Emperor Gaozong order Li Ke to commit suicide. Early life It is not known exactly when Li Ke was born, but he was likely born around 619,This is based on the historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the wife of the person styled crown prince. ''Crown prince'' as a descriptive term has been used throughout history for the prince who is first-in-line to a throne and is expected to succeed (i.e. the heir apparent), barring any unforeseen future event preventing this. In certain monarchies, a more specific substantive title A substantive title is a title of nobility or royalty acquired either by individual grant or inheritance. It is to be distinguished from a title shared among cadets, borne as a courtesy title by a peer's relatives, or acquired through marriage. ... may be accorded and become associated with the position of '' heir apparent'' (e.g. Prince of Wales in the United Kingdom or Prince of Asturias in the Spain, Kingdom of Spain) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bazhong
Bazhong () is a prefecture-level city in north-eastern Sichuan province, China. Its population was 2,712,894 at the 2020 census whom 1,064,766 lived in Bazhou and Enyang urban districts. History Bazhong became a prefecture-level city in 1993. Its history goes back further; during the Xia and Shang dynasties, it was purportedly a vassal territory of Liang State. In the Spring and Autumn period, it was called Bazi (). In the Qin and Western Han dynasties it was called Ba County (). In the Eastern Han Dynasty, around the year 100 CE, this was changed to Hanchang County (). One hundred years later it reverted to Baxi County (). Since then it has usually either been called Liang County () or Yi County (). In ancient times, it was the land of the Ba Kingdom, and after the Qin Kingdom destroyed the Ba Kingdom, the Ba County was established. The Western Han Dynasty belongs to Dangqu County, Ba County. In the third year of Yongyuan in the Eastern Han Dynasty (91 years), Hanchang County was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cui Dunli
Cui Dunli (еҙ”ж•ҰзҰ®) (596 вҖ“ August 29, 656 ), nГ© Cui Yuanli (еҙ”е…ғзҰ®), courtesy name Anshang (е®үдёҠ), formally Duke Zhao of Gu'an (еӣәе®үжҳӯе…¬), was an official, general, and diplomat of the Chinese Tang Dynasty, serving as chancellor during the reign of Emperor Gaozong. Background Cui Dunli was born in 596, originally named Cui Yuanli, His family was from "the second house of Boling" of the prominent Cui clan of Boling, although by the end of Northern Wei it had already relocated to Yong Prefecture (йӣҚе·һ, roughly modern Xi'an, Shaanxi). Cui Dunli's grandfather Cui Zhongfang (еҙ”д»Іж–№) served as the minister of ceremonies during Sui Dynasty. It was said that Cui studied biographies and had sought to keep himself faithful and righteous. During Emperor Gaozu's reign During the reign of Tang's founder Emperor Gaozu, Cui Dunli served as a mid-low-level official at the legislative bureau of government (дёӯжӣёзңҒ, ''Zhongshu Sheng''). It was said that he was skillful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fang Xuanling
Fang Qiao (; 579 вҖ“ 18 August 648), courtesy name Xuanling, better known as Fang Xuanling, posthumously known as Duke Wenzhao of Liang, was a Chinese statesman and writer who served as a chancellor under Emperor Taizong in the early Tang dynasty. He was the lead editor of the historical record ''Book of Jin'' (covering the history of the Jin dynasty (266вҖ“420)) and one of the most celebrated Tang dynasty chancellors. He and his colleague, Du Ruhui, were often described as role models for chancellors in imperial China. During the Sui dynasty Fang Xuanling was born in 579, shortly before the founding of the Sui dynasty in 581, during Sui's predecessor state, Northern Zhou. His great-grandfather Fang Yi (жҲҝзҝј) was a general, official, and hereditary count under the Northern Wei dynasty, and his grandfather Fang Xiong (жҲҝзҶҠ) was also an official. His father Fang Yanqian (жҲҝеҪҘи¬ҷ) was a county magistrate during the Sui dynasty. Fang Xuanling was said to be intelligent and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor Of Tang Dynasty
The chancellor () was a semi-formally designated office position for a number of high-level officials at one time during the Tang dynasty of China. This list also includes chancellors of the short-lived Wu Zhou dynasty, which is typically treated as an interregnum of the Tang dynasty by historians. Origins Ouyang Xiu, the author of the ''New Book of Tang'', asserts that the Tang dynasty inherited its bureaucracy from its dynastic predecessor, the Sui dynasty, under which the founder Emperor Wen of Sui divided his government into five main bureaus: * ''ShГ ngshЕ«shДӣng'' (е°ҡжӣёзңҒ) вҖ“ The Department of State Affairs * ''MГ©nxiГ shДӣng'' (й–ҖдёӢзңҒ) вҖ“ The Chancellery * ''NГЁishЗҗshДӣng'' (е…§еҸІзңҒ) вҖ“ The Legislative Bureau (note different tone than the eunuch bureau below) * ''MГ¬shЕ«shДӣng'' (з§ҳжӣёзңҒ) вҖ“ The Palace Library * ''NГЁishГ¬shДӣng'' (е…§дҫҚзңҒ) вҖ“ The Eunuch bureau (note different tone than the legislative bureau above), later changed by Emperor Wen's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, В§ Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), Ningxia (NW) and Inner Mongolia (N). Shaanxi covers an area of over with about 37 million people, the 16th highest in China. Xi'an – which includes the sites of the former Capitals of China, Chinese capitals Fenghao and Chang'an – is the Xi'an, provincial capital as well as the largest city in Northwest China and also one of the oldest cities in China and the oldest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals, being the capital for the Western Zhou, Western Han, Sima Jin, Jin, Sui dynasty, Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang List of Chinese dynasties, dynasties. Xianyang, which served as the Qin dynasty capital, is just north across Wei River. The other Prefectures of China, prefecture-level pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanzhong
Hanzhong (; abbreviation: Han) is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering the provinces of Sichuan to the south and Gansu to the west. The founder of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang, was once enfeoffed as the king of the Hanzhong region after overthrowing the Qin dynasty. During the Chu-Han contention, Liu Bang shortened his title to the King of Han (), and later used it as the name of his imperial dynasty. In this way, Hanzhong was responsible for the naming of the Han dynasty, which was later hailed as the first golden age in imperial Chinese history and lends its name to the principal ethnic group in China. Hanzhong is located at the modern headwater of the Han River, the largest tributary of the Yangtze River. Hanzhong city covers and is centered around the Hantai District. The prefecture-level city consists of two urban district and nine rural counties. As of the 2020 census, its population was 3,211,462, of whom 1,084,448 lived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital, Wuhan, serves as a major transportation hub and the political, cultural, and economic hub of central China. Hubei's name is officially abbreviated to "" (), an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the State of E of the Western Zhou dynasty of вҖ“771 BCE; a popular name for Hubei is "" () (suggested by that of the powerful State of Chu, which existed in the area during the Eastern Zhou dynasty of 770 вҖ“ 256 BCE). Hubei borders the provinces of Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxi to the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province. Hubei is the 7th-largest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
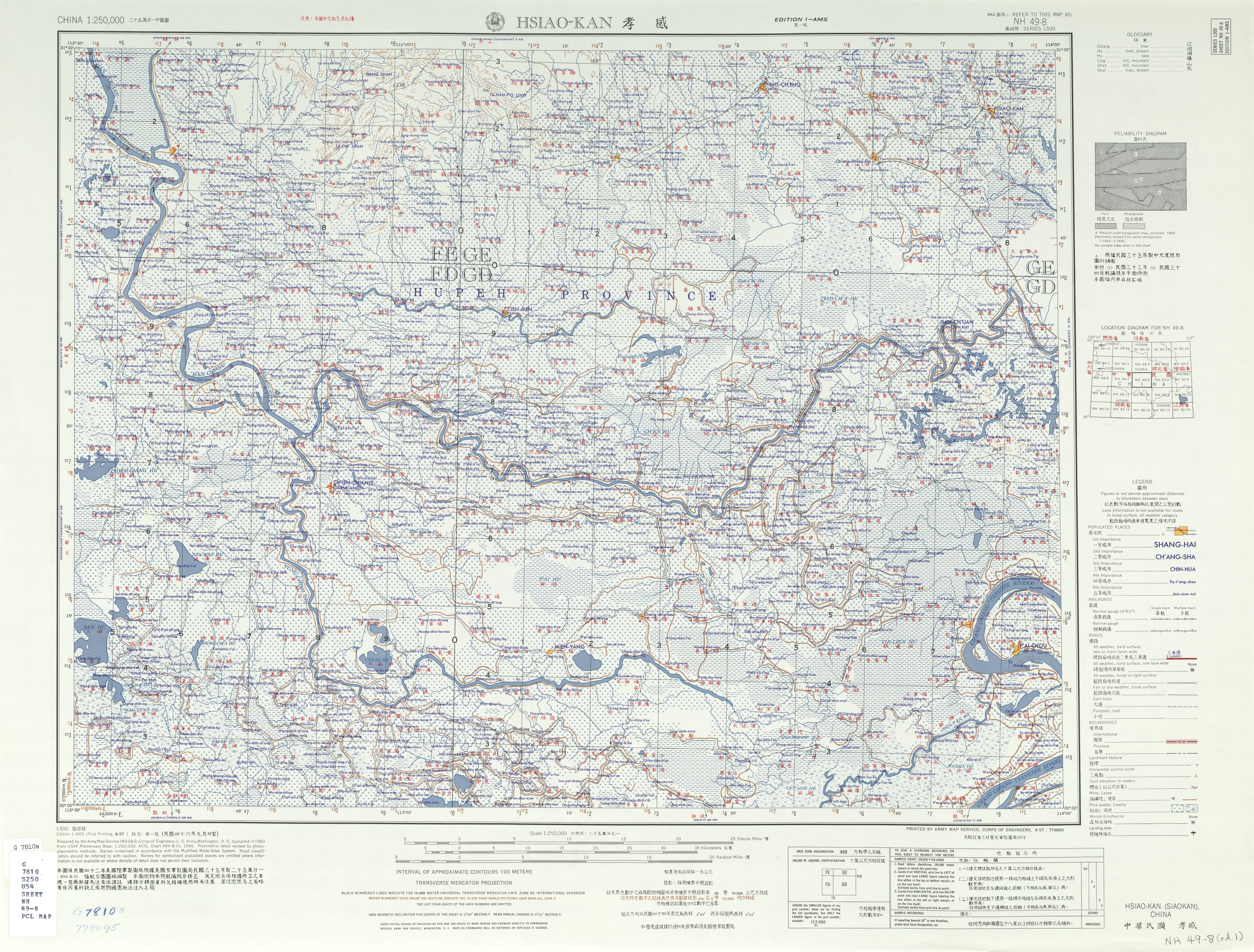
Xiaogan
Xiaogan () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Hubei province, People's Republic of China, some northwest of the provincial capital of Wuhan. According to the 2020 census, its population totaled 4,270,371, of whom 988,479 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area of Xiaonan District. The city name Xiaogan, meaning ''Filial Piety Moves Tian'' (), is from the story of Dong Yong (), who sold himself for his father's funeral, in ''The Twenty-four Filial Exemplars''. The Sheshui River originates in Xiaogan's Dawu County. On the third day of the third month of the lunar calendar, many in Wuhan eat 'di cai zhu ji dan' () which is supposed to prevent illness in the coming year. This practice is related to a story involving Shennong in Xiaogan. Administrative divisions Since 2000, Xiaogan has been divided into 1 district, 3 county-level cities and 3 counties: *Xiaonan District () *Yingcheng City () *Anlu City () *Hanchuan City () *Xiaochang County () * Dawu County () *Yunmeng Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains to the south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu is the birthplace of Confucius and was later established as the center of Confucianism. Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinan
Jinan (), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanization of Chinese, romanized as Tsinan, is the Capital (political), capital of Shandong province in East China, Eastern China. With a population of 9.2 million, it is the second-largest city in Shandong. The area of present-day Jinan has played an important role in the history of the region from the earliest beginnings of civilization and has evolved into a major national administrative, economic, and transportation hub. The city has held Sub-provincial city, sub-provincial administrative status since 1994. Jinan is often called the "City of Springs" for its famous 72 Artesian aquifer, artesian springs. Jinan is one of the top List of cities by scientific output, 40 cities in the world for scientific research as tracked by the Nature Index according to the Nature Index 2022 Science Cities. The city is home to List of universities and colleges in Shandong, several major universities, including Shandong University, Shangdong, Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)