|
John Komnenos (governor Of Dyrrhachium)
John Komnenos ( gr, Ἰωάννης Κομνηνός, Iōannēs Komnēnos) was a Byzantine aristocrat, the nephew of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos () and governor ('' doux'') of the strategically important city and theme of Dyrrhachium from 1091 to . Biography Early life John was born in late 1073, the eldest son of the ''sebastokrator'' Isaac Komnenos, older brother of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (), and his Georgian wife, Irene "of Alania".. In 1081, his uncle, Emperor Alexios, proposed to the German emperor Henry IV (), a marriage match between John and a German princess. Alexios recommended his nephew as both handsome and of prudent character, but nothing came of this proposal. Career In early 1091, John was chosen by Alexios to replace John Doukas as the governor ('' doux'') of Dyrrhachium, in modern-day Albania. The city was of great importance to the Byzantine Empire, as the "key of Albania" and the main point of entry from Italy into the Balkans, a fact illustrated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminus Post Quem
''Terminus post quem'' ("limit after which", sometimes abbreviated to TPQ) and ''terminus ante quem'' ("limit before which", abbreviated to TAQ) specify the known limits of dating for events or items.. A ''terminus post quem'' is the earliest date the event may have happened or the item was in existence, and a ''terminus ante quem'' is the latest. An event may well have both a ''terminus post quem'' and a ''terminus ante quem'', in which case the limits of the possible range of dates are known at both ends, but many events have just one or the other. Similarly, ''terminus ad quem'' ("limit to which") is the latest possible date of a non-punctual event (period, era, etc.), while ''terminus a quo'' ("limit from which") is the earliest. The concepts are similar to those of upper and lower bounds in mathematics. These terms are often used in archaeological and historical studies, such as dating layers in excavated sites, coins, historical events, authors, inscriptions or texts wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish Straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, , in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of Southeast Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. The term ''Balkan Peninsula'' was a synonym for Rumelia in the 19th century, the European provinces of the Ottoman Empire. It had a ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
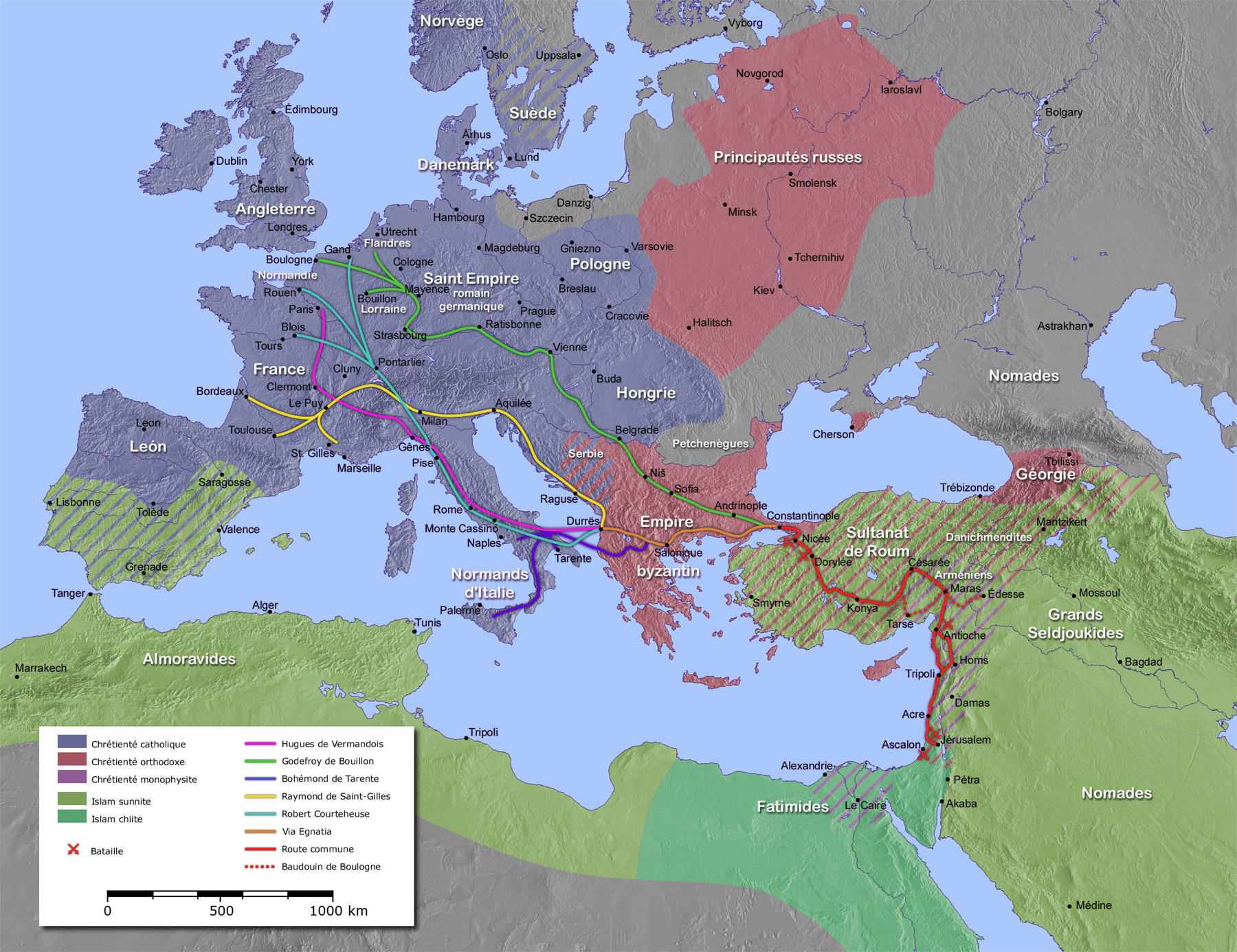
Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene ( gr, Ἄννα Κομνηνή, Ánna Komnēnḗ; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine princess and author of the ''Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, the Byzantine emperor, Alexios I Komnenos. The ''Alexiad'' is the most important primary source of Byzantine history of the late 11th and early 12th centuries. Although she is best known as the author of the ''Alexiad'', Anna played an important part in the politics of the time and attempted to depose her brother, John II Komnenos, as emperor and seize the throne herself.Hanawalt 1982, p. 303. At birth, Anna was betrothed to Constantine Doukas,Hanawalt 1982, p. 303. and she grew up in his mother's household.Neville 2016, p. 2. She was well-educated in "Greek literature and history, philosophy, theology, mathematics, and medicine." Anna and Constantine were next in the line to throne until Anna's younger brother, John II Komnenos, became the heir in 1092. Constan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh I, Count Of Vermandois
Hugh, Count of Vermandois (1057 – October 18, 1101), called the Great (french: Hugues le Grand, la, Hugo Magnus) was the first count of Vermandois from the House of Capet. He is known primarily for being one of the leaders of First Crusade. His nickname ''Magnus'' (greater or elder) is probably a bad translation into medieval Latin of an Old French nickname, ''le Maisné'', meaning "the younger", referring to Hugh as younger brother of King Philip I of France. Early years Hugh was a younger son of King Henry I of France and Anne of Kiev and younger brother of Philip I. He became the first Capetian count of Vermandois after his mentally deficient brother-in-law, Odo, was disinherited. In 1085, Hugh helped William the Conqueror repel a Danish invasion of England. First Crusade In early 1096, Hugh and Philip began discussing the First Crusade after news of the Council of Clermont reached them in Paris. Although Philip could not participate, as he had been excommunicated, Hugh was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis ( Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zvečan
The battle of Zvečan was an 11th-century conflict over land and power between the ruling Byzantine Empire and the Serbians. The borderland town of Zvečan became a central focus for skirmishes, pillow fights, raids, and the eventual decimation and defeat of the Byzantine Empire in Serbia. Background Eighth century Serbian princes In the early 8th century, Serbia had a relationship of entirely nominal suzerainty with the Byzantine Empire. Serbian rulers were crowned as princes and each prince led an independent state with precarious links to Byzantine-ruled Constantinople. The conflict 11th century Serbian enlargement and advancement In the middle of the 11th century, Serbia waged a series of successive wars against the Byzantines. The end result was Serbia's territorial enlargement and its eventual advancement into a kingdom. Serbians Constantine Bodin and Knez Vukan successfully waged war against the Byzantine Empire for many years. The object of Vukan's campaigns wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipljan
Lipjan ( sq-definite, Lipjani) or Lipljan ( sr-Cyrl, Липљан) is a town and municipality located in the Pristina District of Kosovo. According to the 2011 census, the town of Lipjan has 6,870 inhabitants, while the municipality has 57,605 inhabitants. Name The town's name derives from ''Ulpiana'', the Dardanian and Roman era settlement that preceded Lipjan, possibly due to either a ''Ul-'' to ''Li-'' shift seen elsewhere in Roman toponyms. Selami Pulaha states that the shift from ''Ulpiana'' to ''Lipjan'' is in accordance with early Albanian phonetic rules, and must therefore have been inhabited by Albanians to reach its current form. It has also been connected with the Albanian term " ujk" ("wolf") (Old and Dialectal Albanian: "ulk") and the name of the city of Ulqin probably delivers from the same variation. The Roman city of Ulpiana was located near Lipjan and it was named in honor of the Roman Emperor Marcus Ulpius Nerva Traianus. In the early Middle Ages in was par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vukan Of Rascia
Vukan I ( sr, Вукан, gr, Βολκάνος; 1050 – 1112) was the Grand Prince of Serbia from 1083 until his death in 1112. During first years he ruled together with his brother Marko, holding the regions of inner Serbia ( Raška, lat. Rascia). With the death of his cousin, king Constantine Bodin of Duklja in 1101, he became the most powerful ruler among Serbian princes. He defeated the Byzantines several times, conquering parts of northern Macedonia. He is the eponymous founder of the Vukanović dynasty. Biography Vukan was the first-born of Petrislav, the son of King Mihailo I and his second Greek wife.''The early medieval Balkans'', p. 223 He and his brother Marko swore an oath of loyalty to Constantine Bodin and took power as his vassals in Serbia in 1083 or 1084. Marko later disappears from sources. Neither Bosnia, Zachlumia nor Raška were ever permanently integrated into the Kingdom of Duklja. Each region had its own nobility and institutions and acquired a V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language. The majority of Serbs live in their nation state of Serbia, as well as in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro, and Kosovo. They also form significant minorities in North Macedonia and Slovenia. There is a large Serb diaspora in Western Europe, and outside Europe and there are significant communities in North America and Australia. The Serbs share many cultural traits with the rest of the peoples of Southeast Europe. They are predominantly Eastern Orthodox Christians by religion. The Serbian language (a standardized version of Serbo-Croatian) is official in Serbia, co-official in Kosovo and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and is spoken by the plurality in Montenegro. Ethnology The identity of Serbs is rooted in Eastern Orthodoxy and traditions. In the 19th century, the Serbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the cultural capital of Bulgaria and was the European Capital of Culture in 2019. It is an important economic, transport, cultural, and educational center. Plovdiv joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2016. Plovdiv is situated in a fertile region of south-central Bulgaria on the two banks of the Maritsa River. The city has historically developed on seven syenite hills, some of which are high. Because of these hills, Plovdiv is often referred to in Bulgaria as "The City of the Seven Hills". There is evidence of habitation in the area dating back to the 6th millennium BCE, when the first Neolithic settlements were established. The city was subsequently a local Thracians, Thracian settlement, later being conquered and ruled also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophylact Of Bulgaria
Theophylact ( gr, Θεοφύλακτος, bg, Теофилакт; around 1055after 1107) was a Byzantine archbishop of Ohrid and commentator on the Bible. Life Theophylact was born in the mid-11th century at Euripus (Chalcis) in Euboea, at the time part of the Byzantine Empire (now Greece). He became a deacon at Constantinople, attained a high reputation as a scholar, and became the tutor of Constantine Doukas , son of the Emperor Michael VII, for whom he wrote ''The Education of Princes''. In about 1078 he moved to the Province of Bulgaria where he became the archbishop of Achrida (modern Ohrid). Ohrid was one of the capital cities of Bulgaria that had been re-conquered by the Byzantines sixty years earlier. In this demanding position in a conquered territory on the outskirts of the Byzantine Empire, he conscientiously and energetically carried out his pastoral duties over the course of the next twenty years. Although a Byzantine by upbringing and outlook, he was a diligent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Ohrid
The Archbishop of Ohrid is a historic title given to the primate of the Archbishopric of Ohrid. The whole original title of the primate was Archbishop of Justiniana Prima and all Bulgaria ( gr, ἀρχιεπίσκοπὴ τῆς Πρώτης Ἰουστινιανῆς καὶ πάσης Βουλγαρίας). The archbishopric was established in 1018 by lowering of the rank of the autocephalous Bulgarian Patriarchate to the rank of archbishopric. The autocephaly of the Ohrid Archbishopric remained respected during the periods of Byzantine, Bulgarian, Serbian and Ottoman rule and continued to exist until its abolition in 1767. Today, the primates of the Macedonian Orthodox Church and Orthodox Ohrid Archbishopric are both claimants to the title of Archbishop of Ohrid. According to the statutes of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church, the current Bulgarian Patriarchate is the successor of the Ohrid Archbishopric. Archbishopric of Ohrid, 1018–1767 Macedonian Orthodox Church Macedonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)