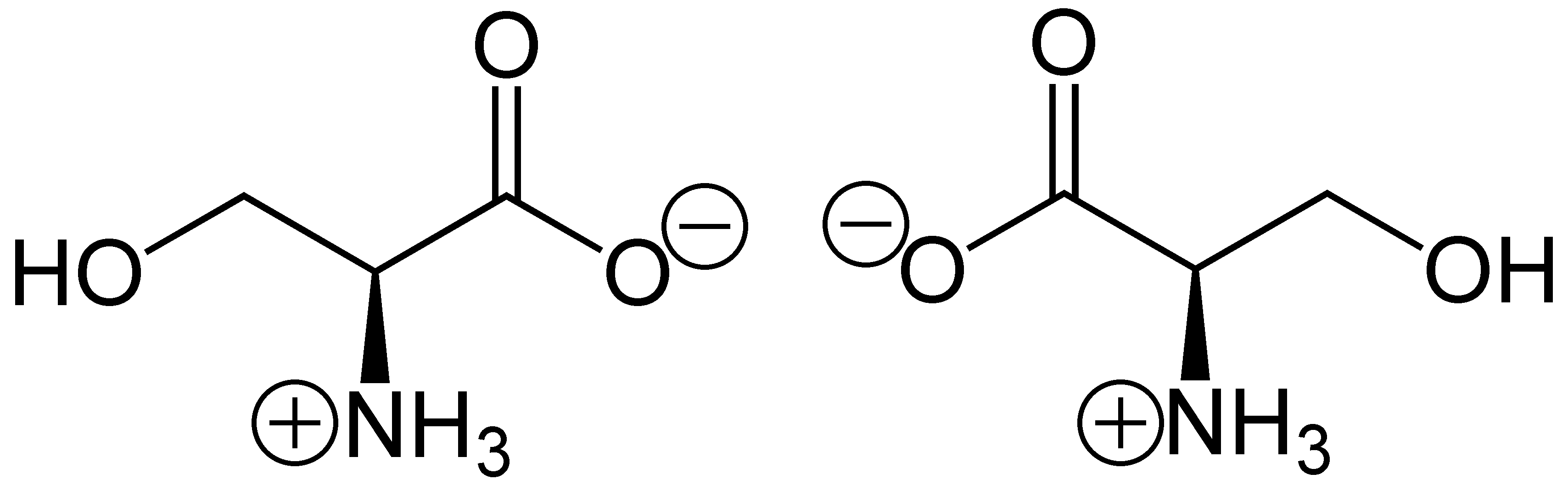|
GYPA
Glycophorin A ( MNS blood group), also known as GYPA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''GYPA'' gene. GYPA has also recently been designated CD235a (cluster of differentiation 235a). Function Glycophorins A (GYPA; this protein) and B ( GYPB) are major sialoglycoproteins of the human erythrocyte membrane which bear the antigenic determinants for the MN and Ss blood groups. In addition to the M or N and S or s antigens, that commonly occur in all populations, about 40 related variant phenotypes have been identified. These variants include all the variants of the Miltenberger complex and several isoforms of Sta; also, Dantu, Sat, He, Mg, and deletion variants Ena, S-s-U- and Mk. Most of the variants are the result of gene recombinations between GYPA and GYPB. Genomics GypA, GypB and GypE are members of the same family and are located on the long arm of chromosome 4 (chromosome 4q31). The family evolved via two separate gene duplication events. The initial duplica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GYPB
Glycophorin B (MNS blood group) (gene designation GYPB) also known as sialoglycoprotein delta and SS-active sialoglycoprotein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''GYPB'' gene. GYPB has also recently been designated CD235b (cluster of differentiation 235b). Function Glycophorin A (GYPA) and B (GYPB; this protein) are major sialoglycoproteins of the human erythrocyte membrane which bear the antigenic determinants for the MN and Ss blood groups respectively. In addition to the M or N and S or s antigens, that commonly occur in all populations, about 40 related variant phenotypes have been identified. These variants include the Miltenberger (Mi) complex and several isoforms of Stones (Sta); also Dantu, Sat, Henshaw (He or MNS6), Mg and deletion variants Ena, S-s-U- and Mk. Most of these are the result of gene recombinations between GYPA and GYPB. Genomics The gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 4 (4q28-q31) and has 5 exons. It was first sequenced in 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MNS Blood Group
The MNS antigen system is a human blood group system based upon two genes ( glycophorin A and glycophorin B) on chromosome 4. There are currently 50 antigens in the system, but the five most important are called M, N, S, s, and U. The system can be thought of as two separate groups: the M and N antigens are at one location on the ECM and S, s, and U are on a closely related location. The two groups are very closely located together on chromosome 4 and are inherited as a haplotype. The MN blood group The MN blood group in humans is under the control of a pair of co-dominant alleles, LM and LN. Most people in the Inuit population are M/M, while this genotype is rare among Aborigines. In fact, they tend to possess the opposite genotype (N/N). The MN blood group system is under the control of an autosomal locus found on chromosome 4, with two alleles designated LM and LN. The blood type is due to a glycoprotein present on the surface of a red blood cell (RBC), which behaves as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natal (region)
South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian Ocean. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment (Great Escarpment) that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is . It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of . The South African central plateau contains only two major rivers: the Limpopo (a stretch of which is shared with Zimbabwe), and the Orange (with its tributary, the Vaal) which runs with a variable flow across the central l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a Unicellular organism, unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female ''Anopheles'' mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. It is responsible for around 50% of all malaria cases. ''P. falciparum'' is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer (Burkitt's lymphoma) and is classified as a List of IARC Group 2A carcinogens, Group 2A (probable) carcinogen. The species originated from the malarial parasite ''Laverania'' found in gorillas, around 10,000 years ago. Alphonse Laveran was the first to identify the parasite in 1880, and named it ''Oscillaria malariae''. Ronald Ross discovered its transmission by mosquito in 1897. Giovanni Battista Grassi elucidated the complete transmission from a female Anopheles, anopheline mosquit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded by the codons GAU and GAC. D-Aspartate is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> In proteins aspartate sidechains are often hydrogen bonded to form asx turns or asx motifs, which frequently occur at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG). Proline is the only proteinogenic secondary amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring. History and etymology Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
) , song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast") , song_type = National and royal anthem , image_map = EU-Denmark.svg , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark , established_title = History of Denmark#Middle ages, Consolidation , established_date = 8th century , established_title2 = Christianization , established_date2 = 965 , established_title3 = , established_date3 = 5 June 1849 , established_title4 = Faroese home rule , established_date4 = 24 March 1948 , established_title5 = European Economic Community, EEC 1973 enlargement of the European Communities, accession , established_date5 = 1 January 1973 , established_title6 = Greenlandic home rule , established_date6 = 1 May 1979 , official_languages = Danish language, Danish , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = German language, GermanGerman is recognised as a protected minority language in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodecyte
A kodecyte (ko•de•cyte) is a living cell that has been modified (koded) by the incorporation of one or more function-spacer-lipid constructs (FSL constructs) to gain a new or novel biological, chemical or technological function. The cell is modified by the lipid tail of the FSL construct incorporating into the bilipid membrane of the cell. All kodecytes retain their normal vitality and functionality while gaining the new function of the inserted FSL constructs. The combination of dispersibility in biocompatible media, spontaneous incorporation into cell membranes, and apparent low toxicity, makes FSL constructs suitable as research tools and for the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic applications. The technology Kode FSL constructs consist of three components; a functional moiety (F), a spacer (S) and a lipid (L). Function groups on FSL constructs that can be used to create kodecytes include saccharides (including ABO blood group-related determinants, siali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bordered to the north by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the extremity of Myanmar. Thailand also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast, and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the nation's capital and largest city. Tai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 11th century. Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon, Khmer Empire and Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states such as the Kingdoms of Ngoenyang, Sukhothai, Lan Na and Ayutthaya, which also rivalled each other. European contact began in 1511 with a Portuguese diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |