|
Eiswoog
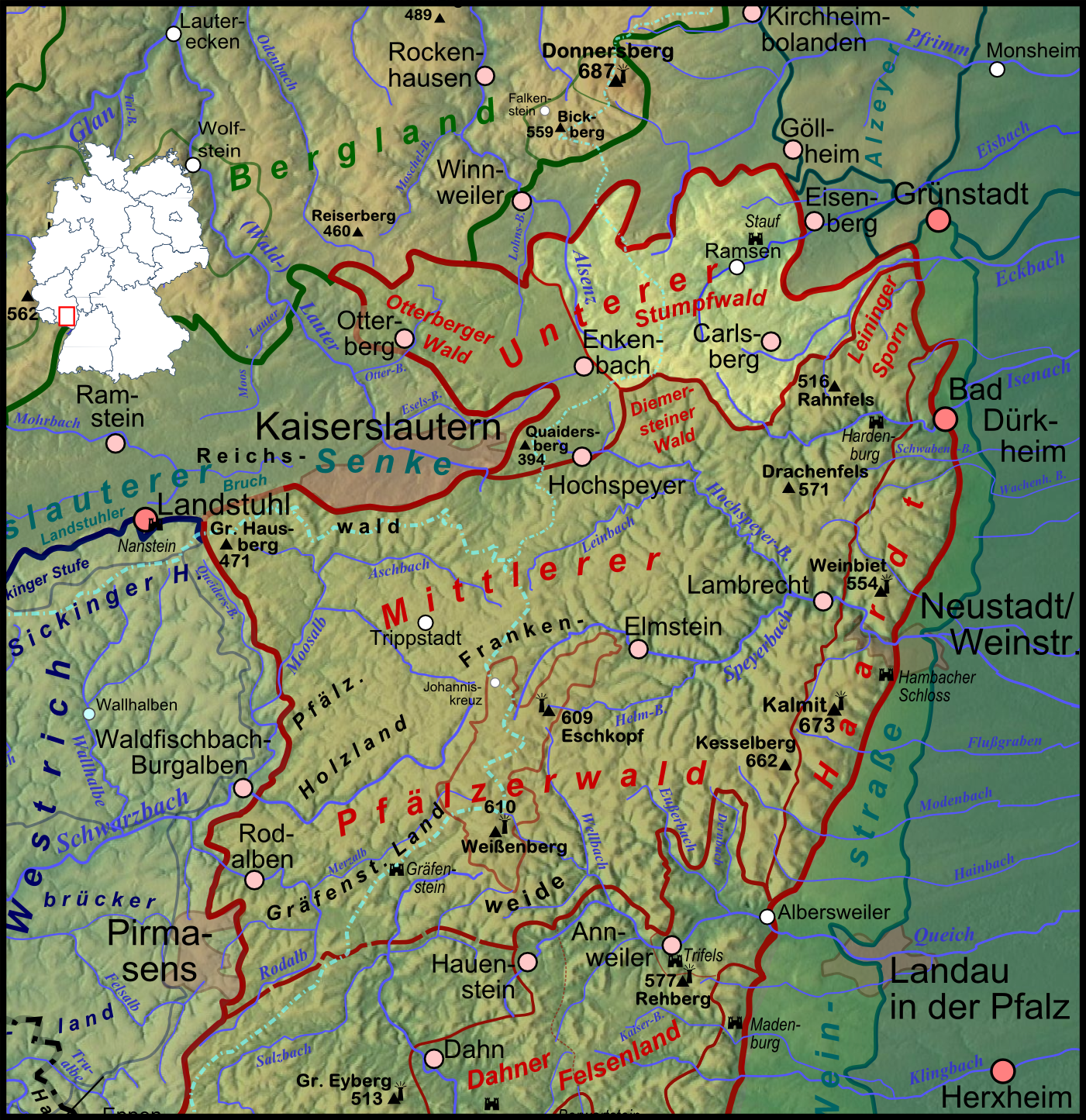
The Eiswoog is a reservoir, roughly six hectares in area, on the Eisbach stream, locally also called ''die Eis'', in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It is oriented from south to north in the water meadows near the source of the stream in part of the northern Palatinate Forest known as the Stumpfwald. Geography The Eisbach, a left tributary of the Rhine, is impounded southwest of the village of Ramsen near its seven sources, to form a '' woog''. A ''woog'' is the local German name given to natural or artificial lakes in this part of the world that used to act as storage reservoirs for watermills and hammer mills or as assembly points for the rafts of firewood or sawn timber. The ''Barbarossa Cycleway'' and ''Landesstraße 395'' state road, which links Eisenberg in the east with Enkenbach-Alsenborn in the west, run past above the lake to the north. The ''L 395'' goes to the city of Kaiserslautern to the southwest and the town of Grünstadt to the north, about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisbach (Rhine)
The Eisbach, locally known as , is a long river and left or western tributary of the Rhine in the northeastern Palatinate and southeastern Rhenish Hesse, in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Course The largest of the seven springs of the Eisbach is at an elevation of about above sea level on the northern slope of the Hohe Bühl mountain, , in the northern Palatinate Forest, southwest of Ramsen. After about two kilometres, the seven streams unite in the Eiswoog reservoir. At the hamlet of ''Kleehof'', the long Bockbach flows in from the right. Here, the direction of the river changes from straight north to northeast. The direction remains northeast until the confluence with the Rhine. The river then flows past Ramsen and Eisenberg. Below Ebertsheim, it receives the long Seltenbach from the right and a few metres further, its largest tributary, the Rodenbach from the left. At Asselheim, a ward of Grünstadt, the Eisbach reaches the Upper Rhine Valley. It then fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woog
A ''woog'' (from ''wâc'', a Middle High German hydronym) is the local name for a body of still water in parts of southwest Germany. A ''woog'' may be of natural origin or manmade. Distribution of the name The name is used for waterbodies in the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate (being especially common in the Palatine Forest), the Saarland, in South Hesse (commonly in the Odenwald) and in the state of Baden-Württemberg ( Nordbaden); even the names of roads or settlements are derived from such bodies of water. Examples are: Baden-Württemberg * Woogsee, natural lake near Rastatt in the basin of the Kinzig-Murg-Rinne Hesse * Großer Woog, reservoir on the Darmbach Rhineland-Palatinate * Biedenbacher Woog, reservoir on the Leinbach * Büttelwoog, campsite near Dahn * Dämmelswoog, reservoir near Fischbach * Eiswoog, reservoir on the Eisbach * Finsterthaler Woog, reservoir on the Leinbach * Franzosenwoog, former reservoir on the Hochspeyerbach * Gelter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stumpfwald
The Stumpfwald is part of the northern Palatine Forest and is located in the south of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It covers an area of about 150 km², most of which is part of North Palatinate and runs from west to east on the territories of Enkenbach-Alsenborn ( county of Kaiserslautern) and Ramsen (county of Donnersbergkreis). It has given its name to the '' Stumpfwaldgericht'', an old thingstead, and the heritage line of the Stumpfwald Railway. Geography and geology The hills and woods of the Stumpfwald, bisected by valleys in all directions, have an average height of just under . The stream with the greatest volumetric flow in the Stumpfwald is the upper Eisbach and its headstream, the Bockbach. Geologically, the Stumpfwald - like most of the Palatine uplands - is predominantly made of bunter sandstone, which was formed from wind-blown desert sand about 250 million years ago (during the Permian / Triassic transition) in what was then the Germanic Basin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grünstadt
Grünstadt ( pfl, Grinnschdadt) is a town in the Bad Dürkheim district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany with roughly 13,200 inhabitants. It does not belong to any ''Verbandsgemeinde'' – a kind of collective municipality – but is nonetheless the administrative seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Leiningerland. Geography Location The town lies in the Leiningerland (the lands once held by the Counts of Leiningen) on the northern border of the Palatinate Forest about 10 km north of Bad Dürkheim, 15 km southwest of Worms and 20 km northwest of Ludwigshafen at the point where the German Wine Route crosses the Autobahn A 6. Grünstadt belongs to the “Unterhaardt” a landscape with submediterranean character as the geographer Christophe Neff wrote in his paysages blog. The town's landmark mountain is the so-called Grünstadter Berg. Climate Yearly precipitation in Grünstadt amounts to 529 mm, which is very low, falling into the lowest tenth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the form of magnetite (, 72.4% Fe), hematite (, 69.9% Fe), goethite (, 62.9% Fe), limonite (, 55% Fe) or siderite (, 48.2% Fe). Ores containing very high quantities of hematite or magnetite (greater than about 60% iron) are known as "natural ore" or "direct shipping ore", meaning they can be fed directly into iron-making blast furnaces. Iron ore is the raw material used to make pig iron, which is one of the main raw materials to make steel—98% of the mined iron ore is used to make steel. In 2011 the ''Financial Times'' quoted Christopher LaFemina, mining analyst at Barclays Capital, saying that iron ore is "more integral to the global economy than any other commodity, except perhaps oil". Sources Metallic iron is virtually unknown on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Von Linde
Carl Paul Gottfried von Linde (11 June 1842 – 16 November 1934) was a German scientist, engineer, and businessman. He discovered a refrigeration cycle and invented the first industrial-scale air separation and gas liquefaction processes, which led to the first reliable and efficient compressed-ammonia refrigerator in 1876. These breakthroughs laid the backbone for the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics that was awarded to Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Linde was a member of scientific and engineering associations, including being on the board of trustees of the Physikalisch-Technische Reichsanstalt and the Bavarian Academy of Sciences and Humanities. Linde was also the founder of what is now known as Linde plc but formerly known (variously) as the Linde division of Union Carbide, Linde, Linde Air Products, Praxair, and others. Linde is the world's largest producer of industrial gases and ushered in the creation of the global supply chain for industrial gases. He was knighted in 1897 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement
A basement or cellar is one or more floors of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, car park, and air-conditioning system are located; so also are amenities such as the electrical system and cable television distribution point. In cities with high property prices, such as London, basements are often fitted out to a high standard and used as living space. In British English, the word ''basement'' is usually used for underground floors of, for example, department stores. The word is usually used with houses when the space below the ground floor is habitable, with windows and (usually) its own access. The word ''cellar'' applies to the whole underground level or to any large underground room. A ''subcellar'' is a cellar that lies further underneath. Purpose, geography, and history A basement can be used in almost exactly th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice House (building)
An ice house, or icehouse, is a building used to store ice throughout the year, commonly used prior to the invention of the refrigerator. Some were underground chambers, usually man-made, close to natural sources of winter ice such as freshwater lakes, but many were buildings with various types of insulation. During the winter, ice and snow would be cut from lakes or rivers, taken into the ice house, and packed with insulation (often straw or sawdust). It would remain frozen for many months, often until the following winter, and could be used as a source of ice during the summer months. The main application of the ice was the storage of foods, but it could also be used simply to cool drinks, or in the preparation of ice-cream and sorbet desserts. During the heyday of the ice trade, a typical commercial ice house would store of ice in a and building. History A cuneiform tablet from c. 1780 BC records the construction of an icehouse by Zimri-Lim, the King of Mari, in the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramsen Abbey
Ramsen may refer to: * Ramsen, Rhineland-Palatinate, a village in Donnersbergkreis, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany * Ramsen, Schaffhausen, village in Schaffhausen, Switzerland * Ramsen (card game) Ramsen or Ramsch is a traditional Bavarian plain-trick, card game for three to five players that is played with a 32-card German-suited pack and is suitable both for adults and for children. It is one of the Rams group of card games that are disti ..., a traditional Bavarian card game See also * Remsen (other) * Rumsen (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eis Valley Viaduct
Eis or EIS may refer to: Education * Eastern Independent Schools of Melbourne, in Australia * Educational Institute of Scotland, a trade union * Ekamai International School, in Bangkok, Thailand * English for Integrated Studies, a program in Thailand * English International School Moscow, a school network in Moscow, Russia * Era International School, in Andhra Pradesh, India * Escuela Internacional Sampedrana, a school in San Pedro Sula, Honduras * Essence International School, in Kaduna, Nigeria * European International School, in Parañaque City, Philippines * European International School Ho Chi Minh City, in Vietnam Government * Enhanced Imaging System, an American satellite program * Enterprise Investment Scheme, series of UK Tax reliefs * Epidemic Intelligence Service, a program of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Health and medicine * Emergency Infant Services, an American charity * Estrogen insensitivity syndrome People * Egon Eis (1910–199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedictine Nun
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG , caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal , abbreviation = OSB , formation = , motto = (English: 'Pray and Work') , founder = Benedict of Nursia , founding_location = Subiaco Abbey , type = Catholic religious order , headquarters = Sant'Anselmo all'Aventino , num_members = 6,802 (3,419 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Abbot Primate , leader_name = Gregory Polan, OSB , main_organ = Benedictine Confederation , parent_organization = Catholic Church , website = The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict ( la, Ordo Sancti Benedicti, abbreviated as OSB), are a monastic religious order of the Catholic Church following the Rule of Saint Benedict. They are also sometimes called the Black Monks, in reference to the colour of their religious habits. They were f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiserslautern
Kaiserslautern (; Palatinate German: ''Lautre'') is a city in southwest Germany, located in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate at the edge of the Palatinate Forest. The historic centre dates to the 9th century. It is from Paris, from Frankfurt am Main, 666 kilometers (414 miles) from Berlin, and from Luxembourg. Kaiserslautern is home to about 100,000 people. Additionally, approximately 45,000 NATO military personnel are based in the city and its surrounding district ('' Landkreis Kaiserslautern''), contributing approximately US$1 billion annually to the local economy. History and demographics Prehistoric settlement in the area of what is now Kaiserslautern has been traced to at least 800 BC. Some 2,500-year-old Celtic tombs were uncovered at Miesau, a town about west of Kaiserslautern. The recovered relics are now in the Museum for Palatinate History at Speyer. Medieval period Kaiserslautern received its name from the favourite hunting retreat of Holy Roman Emperor F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)