|
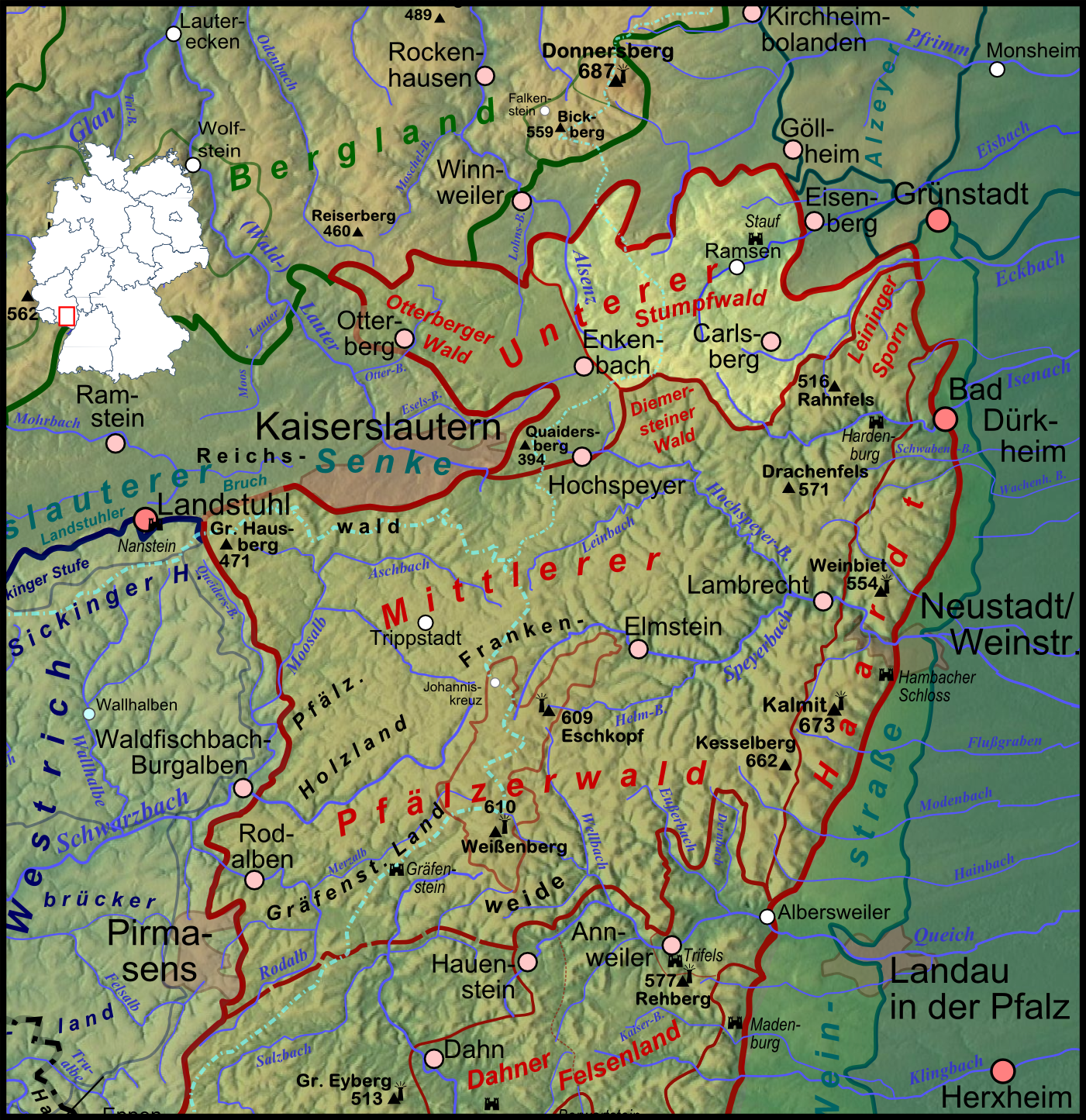
Stumpfwald
The Stumpfwald is part of the northern Palatine Forest and is located in the south of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It covers an area of about 150 km², most of which is part of North Palatinate and runs from west to east on the territories of Enkenbach-Alsenborn ( county of Kaiserslautern) and Ramsen (county of Donnersbergkreis). It has given its name to the '' Stumpfwaldgericht'', an old thingstead, and the heritage line of the Stumpfwald Railway. Geography and geology The hills and woods of the Stumpfwald, bisected by valleys in all directions, have an average height of just under . The stream with the greatest volumetric flow in the Stumpfwald is the upper Eisbach and its headstream, the Bockbach. Geologically, the Stumpfwald - like most of the Palatine uplands - is predominantly made of bunter sandstone, which was formed from wind-blown desert sand about 250 million years ago (during the Permian / Triassic transition) in what was then the Germanic Basin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stumpfwald Railway
The Stumpfwald Railway (german: Stumpfwaldbahn) is a narrow gauge heritage railway that has operated since 1996 in the Stumpfwald, a woodland area in the north of the Palatine Forest in the municipality of Ramsen. Course The western end of the Stumpfwald Railway starts at Eiswoog railway station Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ..., next to the Eiswoog, eponymous lake. Some years after the line opened, a railway halt was built on the nearby (standard gauge) Eis Valley Railway, which also bears the name ''Eiswoog''. This halt is served by most of the trains on the Eis Valley Railway on Sundays and holidays. On weekdays, however, services on the Eis Valley line ends in Ramsen. The original eastern operating point of the Stumpfwald Railway was ''Bockbachtal'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisbach (Rhine)
The Eisbach, locally known as , is a long river and left or western tributary of the Rhine in the northeastern Palatinate and southeastern Rhenish Hesse, in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Course The largest of the seven springs of the Eisbach is at an elevation of about above sea level on the northern slope of the Hohe Bühl mountain, , in the northern Palatinate Forest, southwest of Ramsen. After about two kilometres, the seven streams unite in the Eiswoog reservoir. At the hamlet of ''Kleehof'', the long Bockbach flows in from the right. Here, the direction of the river changes from straight north to northeast. The direction remains northeast until the confluence with the Rhine. The river then flows past Ramsen and Eisenberg. Below Ebertsheim, it receives the long Seltenbach from the right and a few metres further, its largest tributary, the Rodenbach from the left. At Asselheim, a ward of Grünstadt, the Eisbach reaches the Upper Rhine Valley. It then fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eis Valley Railway
The Eis Valley Railway (german: Eistalbahn) is a branch line in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, that runs through the Palatine Forest. It runs from Grünstadt in a southwesterly direction through the valley of the Eisbach (or "Eis") to Enkenbach. The section from Grünstadt to Eisenberg was opened as early as 1876 by the Palatine Northern Railway Company. The iron ore industry in and around Eisenberg gave the line considerable importance for the transport of goods, whilst passenger services played a rather secondary role. The remaining stretch of line to Enkenbach was not completed until 1932 under the direction of the Deutsche Reichsbahn. After passenger services had been withdrawn in 1976, strategic considerations during the Cold War prevented its complete closure. Goods traffic between Eisenberg and Enkenbach ended in 1988. In the period from 1994 to 2001 the line between Grünstadt and the Eiswoog reservoir was re-opened; the remaining section, however, stayed clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leininger Sporn
The Leininger Sporn is a highly prominent ridge in the northeast of the Palatinate Forest in western Germany, mainly composed of the rock formations of the Middle and Upper Bunter. It forms the western edge of Upper Rhine Plain between Grünstadt in the north and Leistadt, a village in the county of Bad Dürkheim, in the southeast.Landscape information system of the Rhineland-Palatine Nature Conservation AdministratioLeininger Sporn landscape fact file Retrieved 10 November 2012 In the natural region system of the German Central Uplands it is considered one of the four sub-units of the Middle Palatinate Forest. Geography Location The Leininger Sporn lies between the valleys of the river Isenach in the south and the Eckbach stream in the north, and has an area of around 44.8 km². From north to south it is about 10 kilometres long, and from east to west it is about 4 to 5, and at its northern tip, only about 2 to 3 kilometres wide.The outer boundary of this hill ridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsenz
Alsenz () is a municipality in the Donnersbergkreis district, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Alsenz has an area of 12.88 km2 and a population of 1,647 (as of December 31, 2020). Culture and sights In the centre of the village is the Renaissance village hall (''Rathaus''), built in 1578. The building consists of a bricked lower storey with round arches and timber-framed upper storey. The Palatine Stonemason Museum, (''Pfälzische Steinhauermuseum'') the Museum of Local History (''Museum für Heimatgeschichte'') and the North Palatinate Gallery (''Nordpfalzgalerie'') also use rooms in the village hall. The Nassau-Weilburg district headquarters (''Amtshof''), built around 1780, the 1756 former synagogue and the 18th century Protestant church characterise the village scene. Notable residents * Wilhelm Frick Wilhelm Frick (12 March 1877 – 16 October 1946) was a prominent German politician of the Nazi Party (NSDAP), who served as Reich Minister of the Interior in A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Mainz on the left bank, and Wiesbaden, the capital of the neighbouring state Hesse, on the right bank. Mainz is an independent city with a population of 218,578 (as of 2019) and forms part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region. Mainz was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans in the 1st century BC as a military fortress on the northernmost frontier of the empire and provincial capital of Germania Superior. Mainz became an important city in the 8th century AD as part of the Holy Roman Empire, capital of the Electorate of Mainz and seat of the Elector of Mainz, Archbishop-Elector of Mainz, the Primate (bishop), Primate of Germany. Mainz is famous as the birthplace of Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiserslautern
Kaiserslautern (; Palatinate German: ''Lautre'') is a city in southwest Germany, located in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate at the edge of the Palatinate Forest. The historic centre dates to the 9th century. It is from Paris, from Frankfurt am Main, 666 kilometers (414 miles) from Berlin, and from Luxembourg. Kaiserslautern is home to about 100,000 people. Additionally, approximately 45,000 NATO military personnel are based in the city and its surrounding district ('' Landkreis Kaiserslautern''), contributing approximately US$1 billion annually to the local economy. History and demographics Prehistoric settlement in the area of what is now Kaiserslautern has been traced to at least 800 BC. Some 2,500-year-old Celtic tombs were uncovered at Miesau, a town about west of Kaiserslautern. The recovered relics are now in the Museum for Palatinate History at Speyer. Medieval period Kaiserslautern received its name from the favourite hunting retreat of Holy Roman Emperor F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saarbrücken
Saarbrücken (; french: link=no, Sarrebruck ; Rhine Franconian: ''Saarbrigge'' ; lb, Saarbrécken ; lat, Saravipons, lit=The Bridge(s) across the Saar river) is the capital and largest city of the state of Saarland, Germany. Saarbrücken is Saarland's administrative, commercial and cultural centre and is next to the French border. The modern city of Saarbrücken was created in 1909 by the merger of three towns, Saarbrücken, St. Johann, and Malstatt-Burbach. It was the industrial and transport centre of the Saar coal basin. Products included iron and steel, sugar, beer, pottery, optical instruments, machinery, and construction materials. Historic landmarks in the city include the stone bridge across the Saar (1546), the Gothic church of St. Arnual, the 18th-century Saarbrücken Castle, and the old part of the town, the ''Sankt Johanner Markt'' (Market of St. Johann). In the 20th century, Saarbrücken was twice separated from Germany: from 1920 to 1935 as capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's 21st-largest city, with a 2020 population of 309,119 inhabitants. The city is the cultural and economic centre of the Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region, Germany's seventh-largest metropolitan region with nearly 2.4 million inhabitants and over 900,000 employees. Mannheim is located at the confluence of the Rhine and the Neckar in the Kurpfalz (Electoral Palatinate) region of northwestern Baden-Württemberg. The city lies in the Upper Rhine Plain, Germany's warmest region. Together with Hamburg, Mannheim is the only city bordering two other federal states. It forms a continuous conurbation of around 480,000 inhabitants with Ludwigshafen am Rhein in the neighbouring state of Rhineland-Palatinate, on the other side of the Rhine. Some northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesautobahn 6
, also known as Via Carolina (between Nuremberg and the Czech border continuing to Prague - by czech motorway D5) is a 477 km (296.4 mi) long German autobahn. It starts at the French border near Saarbrücken in the west and ends at the Czech border near Waidhaus in the east. The first plans for the A 6 were laid out in 1935; construction on several parts began in 1938. In 1940, construction near Mannheim was stopped when the bridge across the Rhine collapsed, killing many workers. A new bridge, the Theodor Heuss Bridge (Frankenthal), was opened in 1953. Other parts of the A 6 were completed in 1941. A part near Kaiserslautern was used as an airstrip by the Luftwaffe during World War II. After the war, it was taken over by US forces and became the Ramstein Air Base, while the A 6 was re-built south of the air base. In the 1960s, construction was continued. One new section cut through the Hockenheimring, requiring a major redesign of the race track whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landesstraße
''Landesstraßen'' (singular: ''Landesstraße'') are roads in Germany and Austria that are, as a rule, the responsibility of the respective German or Austrian federal state. The term may therefore be translated as "state road". They are roads that cross the boundary of a rural or urban district (''Landkreis'' or ''Kreisfreie Stadt''). A ''Landesstraße'' is thus less important than a ''Bundesstraße'' or federal road, but more significant than a ''Kreisstraße'' or district road. The classification of a road as a ''Landesstraße'' is a legal matter (''Widmung''). In the free states of Bavaria and Saxony – but not, however, in the Free State of Thuringia – ''Landesstraßen'' are known as ''Staatsstraßen''. Designation The abbreviation for a ''Landesstraße'' consists of a prefixed capital letter ''L'' and a serial number (e. g. L 1, L 83, L 262 or L 3190). ''Staatsstraßen'' in Saxony are similarly abbreviated using a capital ''S'' (e. g. S 190) and the ''Staatsstraßen' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isenach
The Isenach is a left tributary of the Rhine in the northeastern Palatine region of Rhineland-Palatinate. It is nearly long. Course The Isenach rises in the northern Palatinate Forest, southwest of Carlsberg Hertlingshausen. Its source in the Diemerstein Forest on the southeast flank of a saddle between the peaks Krummes Eck, elevation , and Hohe Bühl, elevation , is marked with Ritterstein number 277, with the inscription "Isenach source". The first of the river flow in a southeasterly direction. After the Isenach passes the Isenachweiher reservoir, it flows east through a valley it shares with Bundesstraße 37, Kaiserslautern-Bad Dürkheim. In Bad Dürkheim, the Isenach breaks through the Haardt, the eastern edge of the Palatinate Forest, and enters the hills flanking the German Wine Road. It the flows northeast through the Upper Rhine Plain. Between Lambsheim and the Frankenthal district of Eppstein, the Isenach is joined by the Floßbach from the right. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



