Basement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
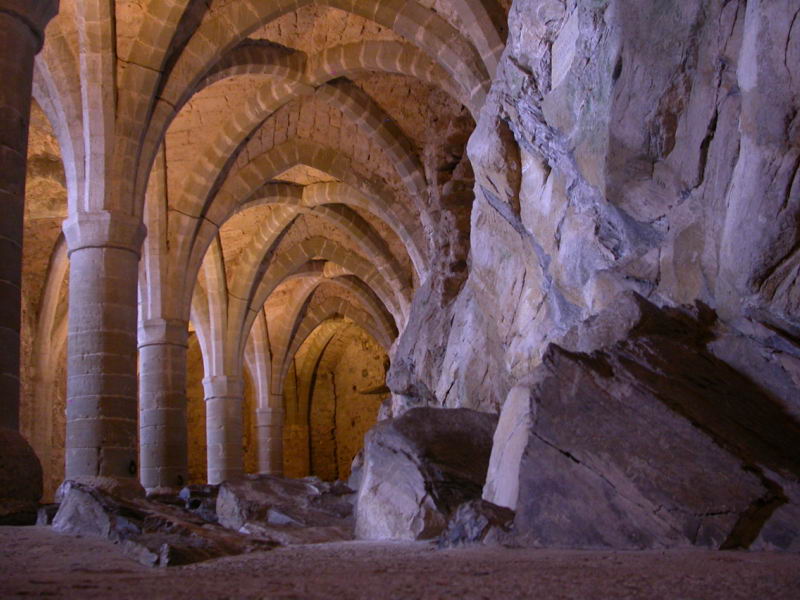



 A basement or cellar is one or more
A basement or cellar is one or more

 An
An
 According to the international ''
According to the international ''
 An underground crawl space (as the name implies) is a type of basement in which one cannot stand up—the height may be as little as one foot (30 cm), and the surface is often soil. Crawl spaces offer a convenient access to pipes, substructures and a variety of other areas that may be difficult or expensive to access otherwise. While a crawl space cannot be used as living space, it can be used as storage, often for infrequently used items. Care must be taken in doing so, however, as water from the damp ground, water vapour (entering from crawl space vents), and moisture seeping through porous concrete can create a perfect environment for mold/mildew to form on any surface in the crawl space, especially cardboard boxes, wood floors and surfaces, drywall and some types of insulation.
Health and safety issues must be considered when installing a crawl space. As air warms in a home, it rises and leaves through the upper regions of the house, much in the same way that air moves through a chimney. This phenomenon, called the "stack effect", causes the home to suck air up from the crawl space into the main area of the home. Mould spores, decomposition odours, and material from dust mites in the crawl space can come up with the air, aggravating asthma and other breathing problems, and creating a variety of health concerns.
It is usually desirable to finish a crawl space with a plastic vapour barrier that will not support mold growth or allow humidity from the earth into the crawl space. This helps insulate the crawl space and discourages the habitation of insects and vermin by breaking the ecological chain in which insects feed off the mould and vermin feed on the insects, as well as creating a physical inorganic barrier that deters entrance into the space. Vapour barriers can end at the wall or be run up the wall and fastened to provide even more protection against moisture infiltration. Some pest control agencies recommend against covering the walls, as it complicates their job of inspection and spraying. Almost unheard of as late as the 1990s, vapour barriers are becoming increasingly popular in recent years. In fact, the more general area of conditioned vs. unconditioned crawl spaces has seen much research over the last decade.
An underground crawl space (as the name implies) is a type of basement in which one cannot stand up—the height may be as little as one foot (30 cm), and the surface is often soil. Crawl spaces offer a convenient access to pipes, substructures and a variety of other areas that may be difficult or expensive to access otherwise. While a crawl space cannot be used as living space, it can be used as storage, often for infrequently used items. Care must be taken in doing so, however, as water from the damp ground, water vapour (entering from crawl space vents), and moisture seeping through porous concrete can create a perfect environment for mold/mildew to form on any surface in the crawl space, especially cardboard boxes, wood floors and surfaces, drywall and some types of insulation.
Health and safety issues must be considered when installing a crawl space. As air warms in a home, it rises and leaves through the upper regions of the house, much in the same way that air moves through a chimney. This phenomenon, called the "stack effect", causes the home to suck air up from the crawl space into the main area of the home. Mould spores, decomposition odours, and material from dust mites in the crawl space can come up with the air, aggravating asthma and other breathing problems, and creating a variety of health concerns.
It is usually desirable to finish a crawl space with a plastic vapour barrier that will not support mold growth or allow humidity from the earth into the crawl space. This helps insulate the crawl space and discourages the habitation of insects and vermin by breaking the ecological chain in which insects feed off the mould and vermin feed on the insects, as well as creating a physical inorganic barrier that deters entrance into the space. Vapour barriers can end at the wall or be run up the wall and fastened to provide even more protection against moisture infiltration. Some pest control agencies recommend against covering the walls, as it complicates their job of inspection and spraying. Almost unheard of as late as the 1990s, vapour barriers are becoming increasingly popular in recent years. In fact, the more general area of conditioned vs. unconditioned crawl spaces has seen much research over the last decade.
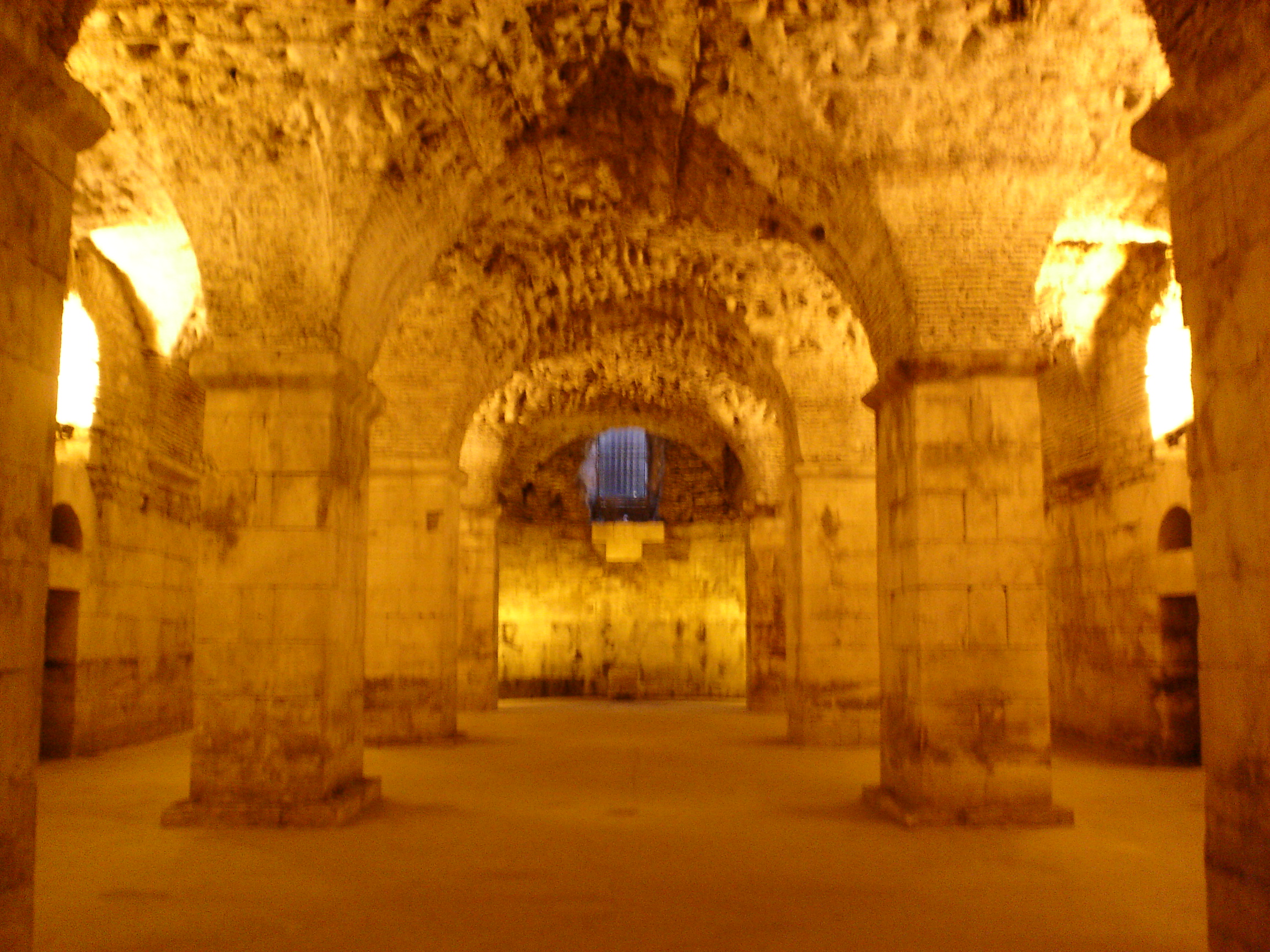



 Structurally, for houses, the basement walls typically form the foundation. In warmer climates, some houses do not have basements because they are not necessary (although many still prefer them). In colder climates, the foundation must be below the frost line. Unless constructed in very cold climates, the
Structurally, for houses, the basement walls typically form the foundation. In warmer climates, some houses do not have basements because they are not necessary (although many still prefer them). In colder climates, the foundation must be below the frost line. Unless constructed in very cold climates, the
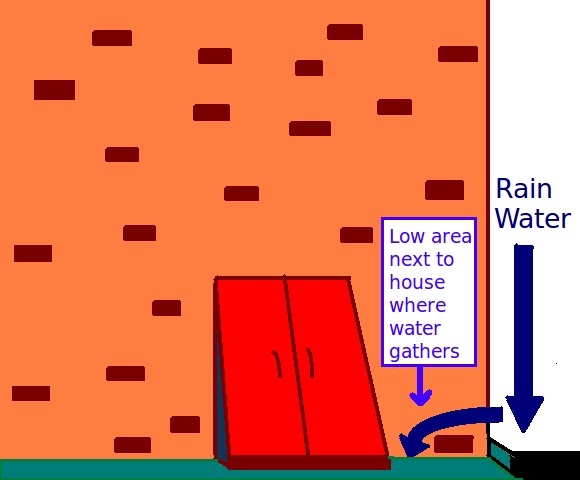 If the
If the
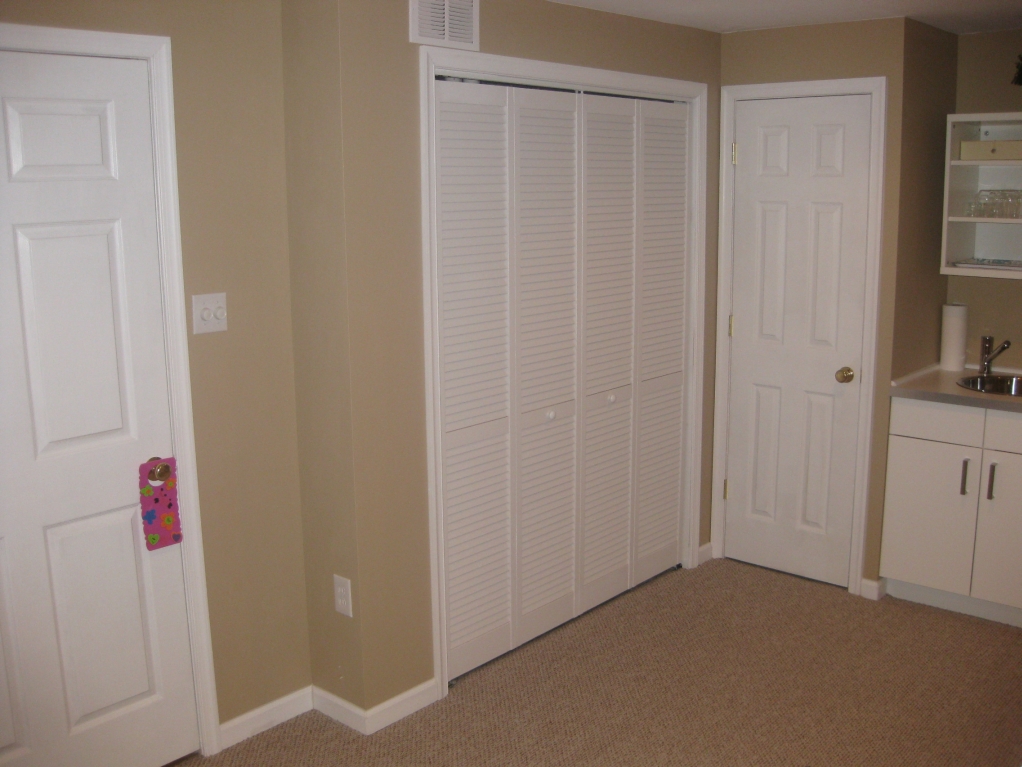 In this case the space has been designed, either during construction or at a later point by the owners, to function as a fully habitable addition to the house. Frequently most or all of the basement is used as a
In this case the space has been designed, either during construction or at a later point by the owners, to function as a fully habitable addition to the house. Frequently most or all of the basement is used as a
National Research Council (Canada) Basement subject search
Basement ideas
{{Authority control Rooms Building engineering Structural engineering Semi-subterranean structures Food storage



floors
A floor is the bottom surface of a room or vehicle. Floors vary from simple dirt in a cave to many layered surfaces made with modern technology. Floors may be stone, wood, bamboo, metal or any other material that can support the expected load ...
of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor
A storey (British English) or story (American English) is any level part of a building with a floor that could be used by people (for living, work, storage, recreation, etc.). Plurals for the word are ''storeys'' (UK) and ''stories'' (US).
T ...
. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace
A furnace is a structure in which heat is produced with the help of combustion.
Furnace may also refer to:
Appliances Buildings
* Furnace (central heating): a furnace , or a heater or boiler , used to generate heat for buildings
* Boiler, used t ...
, water heater
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated t ...
, breaker panel
A distribution board (also known as panelboard, breaker panel, electric panel, DB board or DB box) is a component of an electricity supply system that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits while providing a protective fus ...
or fuse box
A distribution board (also known as panelboard, breaker panel, electric panel, DB board or DB box) is a component of an electricity supply system that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits while providing a protective fus ...
, car park
A parking lot (American English) or car park (British English), also known as a car lot, is a cleared area intended for parking vehicles. The term usually refers to an area dedicated only for parking, with a durable or semi-durable surface ...
, and air-conditioning system
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HV ...
are located; so also are amenities such as the electrical system and cable television
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with broa ...
distribution point. In cities with high property prices, such as London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, basements are often fitted out to a high standard and used as living space.
In British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
, the word ''basement'' is usually used for underground floors of, for example, department stores. The word is usually used with houses when the space below the ground floor is habitable, with windows and (usually) its own access. The word ''cellar'' applies to the whole underground level or to any large underground room. A ''subcellar'' is a cellar that lies further underneath.
Purpose, geography, and history
A basement can be used in almost exactly the same manner as an additional above-ground floor of a house or other building. However, the use of basements depends largely on factors specific to a particular geographical area such as climate, soil, seismic activity, building technology, and real estate economics. Basements in small buildings such assingle-family detached
A stand-alone house (also called a single-detached dwelling, detached residence or detached house) is a free-standing residential building. It is sometimes referred to as a single-family home, as opposed to a multi-family residential dwelling ...
houses are rare in wet climates such as Great Britain and Ireland where flooding can be a problem, though they may be used in larger structures. However, basements are considered standard on all but the smallest new buildings in many places with temperate continental climates such as the American Midwest and the Canadian Prairies where a concrete foundation
Foundation may refer to:
* Foundation (nonprofit), a type of charitable organization
** Foundation (United States law), a type of charitable organization in the U.S.
** Private foundation, a charitable organization that, while serving a good cause ...
below the frost line
The frost line—also known as frost depth or freezing depth—is most commonly the depth to which the groundwater in soil is expected to freeze. The frost depth depends on the climatic conditions of an area, the heat transfer properties of the s ...
is needed in any case, to prevent a building from shifting during the freeze-thaw cycle
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), ...
. Basements are much easier to construct in areas with relatively soft soils and may be avoided in places where the soil is too compact for easy excavation. Their use may be restricted in earthquake zones, because of the possibility of the upper floors collapsing into the basement; on the other hand, they may be required in tornado-prone areas as a shelter against violent winds. Adding a basement can also reduce heating and cooling costs as it is a form of earth sheltering
An earth shelter, also called an earth house, earth bermed house, or underground house, is a structure (usually a house) with earth (soil) against the walls, on the roof, or that is entirely buried underground.
Earth acts as thermal mass, making ...
, and a way to reduce a building's surface area-to-volume ratio
The surface-area-to-volume ratio, also called the surface-to-volume ratio and variously denoted sa/vol or SA:V, is the amount of surface area per unit volume of an object or collection of objects.
SA:V is an important concept in science and engin ...
. The housing density of an area may also influence whether or not a basement is considered necessary.
Historically, basements have become much easier to build (in developed countries) since the industrialization of home building. Large powered excavation machines such as backhoes
A backhoe—also called rear actor or back actor—is a type of excavating equipment, or digger, consisting of a digging bucket on the end of a two-part articulated arm. It is typically mounted on the back of a tractor or front loader, the latt ...
and front-end loaders have dramatically reduced the time and manpower needed to dig a basement as compared to digging by hand with a spade
A spade is a tool primarily for digging consisting of a long handle and blade, typically with the blade narrower and flatter than the common shovel. Early spades were made of riven wood or of animal bones (often shoulder blades). After the a ...
, although this method may still be used in the developing world.
For most of its early history, the basement took one of two forms. It could be little more than a cellar, or it could be a section of a building containing rooms and spaces similar to those of the rest of the structure, as in the case of basement flats and basement offices.
However, beginning with the development of large, mid-priced suburban homes in the 1950s, the basement, as a space in its own right, gradually took hold. Initially, it was typically a large, concrete-floored space, accessed by indoor stairs, with exposed columns and beams along the walls and ceilings, or sometimes, walls of poured concrete or concrete cinder block.
Types
English basement
 An
An English basement
An English basement is an apartment (flat in UK English) on the lowest floor of a building, generally a townhouse or brownstone, which is partially below and partially above ground level and which has its own entrance separate from those of the r ...
, also known as a daylight basement or lower ground floor, is contained in a house where at least part of the floor goes above ground to provide reasonably-sized windows. Generally, the floor's ceiling should be enough above ground to provide nearly full-size windows. Some daylight basements are located on slopes, such that one portion of the floor is at-grade with the land. A walk-out basement almost always results from this.
Most daylight basements naturally result from raised bungalows and at-grade walk-out basements. However, there are instances where the terrain dips enough from one side to another to allow for 3/4 to full-size windows, with the actual floor remaining below grade.
In most parts of North America, it is legal to set up apartments and bedrooms in daylight basements, whether or not the entire basement is above grade.
Daylight basements can be used for several purposes—as a garage
A garage is a covered structure built for the purpose of parking, storing, protecting, maintaining, and/or repairing vehicles. Specific applications include:
*Garage (residential), a building or part of a building for storing one or more vehicle ...
, as maintenance rooms, or as living space. The buried portion is often used for storage, laundry room
A laundry room (also called a utility room) is a room where clothes are washed and dried. In a modern home, a laundry room would be equipped with an automatic washing machine and clothes dryer, and often a large basin, called a ''laundry tub ...
, hot water tanks, and HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HV ...
.
Daylight basement homes typically appraise higher than standard-basement homes, since they include more viable living spaces. In some parts of the US, however, the appraisal for daylight basement space is half that of ground and above ground level square footage. Designs accommodated include split-foyer and split-level home
A split-level home (also called a bi-level home or tri-level home) is a style of house in which the floor levels are staggered. There are typically two short sets of stairs, one running upward to a bedroom level, and one going downward toward a ...
s. Garages on both levels are sometimes possible. As with any multilevel home, there are savings on roofing and foundations.
Walk-out basement
A walk-out basement is any basement that is partially underground but nonetheless allows egress directly outdoors and has floating walls. This can either be through a stairwell leading above ground, or a door directly outside if a portion of the basement is completely at or above grade. Many walk-out basements are also daylight basements. The only exceptions are when the entire basement is nearly entirely underground, and a stairwell leads up nearly a floor's worth of vertical height to lead to the outdoors. Generally, basements with only an emergency exit well do not count as walk-out. Walk-out basements with at-grade doors on one side typically are more costly to construct since the foundation is still constructed to reach below the frost line. At-grade walk-out basements on the door-side are often used as livable space for the house, with the buried portion used for utilities and storage.Subbasement
A subbasement is a floor below the basement floor. In the homes where there is any type of basement mentioned above, such as a look-out basement, all of the volume of the subbasements from floor to ceiling are located well below ground. Therefore, subbasements have no windows nor an outside door. In the homes that have subbasements, all of the basement can be used as part of the main home where people relax and do recreational things, while all of the subbasement can be used for storage. Subbasements are much more common in larger structures, such as commercial buildings and larger apartment buildings, than they are in single family homes. It is common forskyscrapers
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ri ...
to have multiple subbasements.
Building a subbasement is more difficult, costly, and time-consuming than building a basement as the lowest floor. Subbasements are even more susceptible to flooding and water damage than basements and are therefore rare, except in dry climates and at higher elevations.
Some famous landmarks contain subbasements. The subbasement of the US Capitol Building
The United States Capitol, often called The Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the seat of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, which is formally known as the United States Congress. It is located on Capitol Hill ...
is used as storage and that in the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
is used to store guest items.
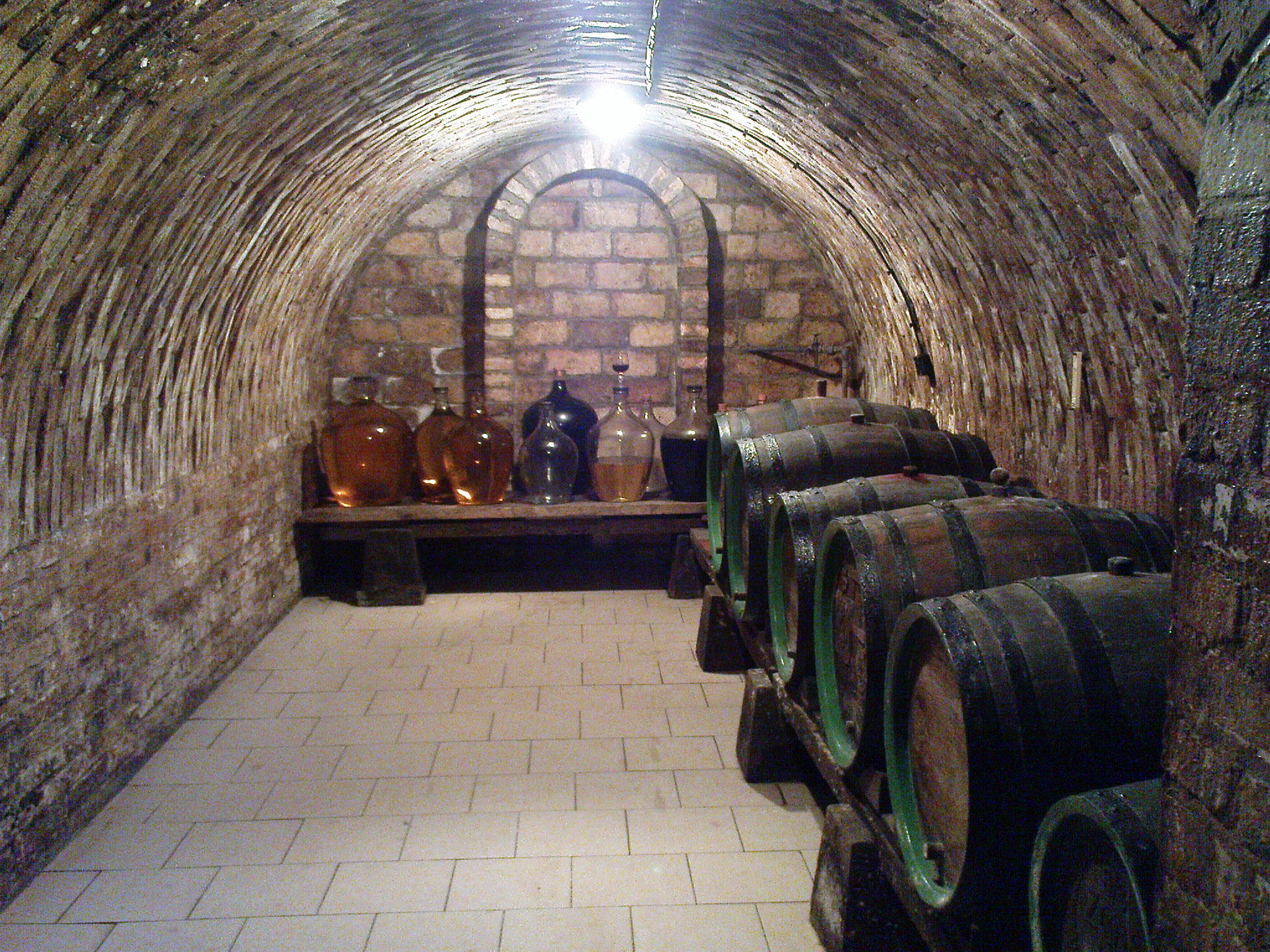
Finished fully underground cellar
Oxford Dictionary of English
The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' (''ODE'') is a single-volume English dictionary published by Oxford University Press, first published in 1998 as ''The New Oxford Dictionary of English'' (''NODE''). The word "new" was dropped from the titl ...
'', a finished fully underground cellar is a room below ground level in a house that is often used for the storage of wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
or coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
; it may also refer to the stock of wine itself. A cellar is intended to remain at a constant cool (not freezing) temperature all year round and usually has either a small window/opening or some form of air ventilation (air/draught bricks, etc.) in order to help eliminate damp or stale air. Cellars are more common in the United Kingdom in older houses, with most terraced housing built during late 19th and early 20th centuries having cellars. These were important shelters from air raids during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. In parts of North America that are prone to tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, altho ...
es (e.g. Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley is a loosely defined area of the central United States where tornadoes are most frequent. The term was first used in 1952 as the title of a research project to study severe weather in areas of Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Kansas, ...
), cellars still serve as shelter in the event of a direct hit on the house from a tornado or other storm damage caused by strong winds.
Except for Britain, Australia and New Zealand, cellars are popular in most western countries. In the United Kingdom, almost all new homes built since the 1960s have no cellar or basement due to the extra cost of digging down further into the sub-soil and a requirement for much deeper foundations and waterproof tanking. The reverse has recently become common, where the impact of smaller home-footprints has led to roof-space being utilised for further living space and now many new homes are built with third-floor living accommodation. For this reason, especially where lofts have been converted into living space, people tend to use garages for the storage of food freezers, tools, bicycles, garden and outdoor equipment. The majority of continental European houses have cellars, although a large proportion of people live in apartments or flats rather than houses. In North America, cellars usually are found in rural or older homes on the coasts and in the South. However, full basements are commonplace in new houses in the Canadian and American Midwest and other areas subject to tornado activity or requiring foundations below the frost line.
Underground crawl space
 An underground crawl space (as the name implies) is a type of basement in which one cannot stand up—the height may be as little as one foot (30 cm), and the surface is often soil. Crawl spaces offer a convenient access to pipes, substructures and a variety of other areas that may be difficult or expensive to access otherwise. While a crawl space cannot be used as living space, it can be used as storage, often for infrequently used items. Care must be taken in doing so, however, as water from the damp ground, water vapour (entering from crawl space vents), and moisture seeping through porous concrete can create a perfect environment for mold/mildew to form on any surface in the crawl space, especially cardboard boxes, wood floors and surfaces, drywall and some types of insulation.
Health and safety issues must be considered when installing a crawl space. As air warms in a home, it rises and leaves through the upper regions of the house, much in the same way that air moves through a chimney. This phenomenon, called the "stack effect", causes the home to suck air up from the crawl space into the main area of the home. Mould spores, decomposition odours, and material from dust mites in the crawl space can come up with the air, aggravating asthma and other breathing problems, and creating a variety of health concerns.
It is usually desirable to finish a crawl space with a plastic vapour barrier that will not support mold growth or allow humidity from the earth into the crawl space. This helps insulate the crawl space and discourages the habitation of insects and vermin by breaking the ecological chain in which insects feed off the mould and vermin feed on the insects, as well as creating a physical inorganic barrier that deters entrance into the space. Vapour barriers can end at the wall or be run up the wall and fastened to provide even more protection against moisture infiltration. Some pest control agencies recommend against covering the walls, as it complicates their job of inspection and spraying. Almost unheard of as late as the 1990s, vapour barriers are becoming increasingly popular in recent years. In fact, the more general area of conditioned vs. unconditioned crawl spaces has seen much research over the last decade.
An underground crawl space (as the name implies) is a type of basement in which one cannot stand up—the height may be as little as one foot (30 cm), and the surface is often soil. Crawl spaces offer a convenient access to pipes, substructures and a variety of other areas that may be difficult or expensive to access otherwise. While a crawl space cannot be used as living space, it can be used as storage, often for infrequently used items. Care must be taken in doing so, however, as water from the damp ground, water vapour (entering from crawl space vents), and moisture seeping through porous concrete can create a perfect environment for mold/mildew to form on any surface in the crawl space, especially cardboard boxes, wood floors and surfaces, drywall and some types of insulation.
Health and safety issues must be considered when installing a crawl space. As air warms in a home, it rises and leaves through the upper regions of the house, much in the same way that air moves through a chimney. This phenomenon, called the "stack effect", causes the home to suck air up from the crawl space into the main area of the home. Mould spores, decomposition odours, and material from dust mites in the crawl space can come up with the air, aggravating asthma and other breathing problems, and creating a variety of health concerns.
It is usually desirable to finish a crawl space with a plastic vapour barrier that will not support mold growth or allow humidity from the earth into the crawl space. This helps insulate the crawl space and discourages the habitation of insects and vermin by breaking the ecological chain in which insects feed off the mould and vermin feed on the insects, as well as creating a physical inorganic barrier that deters entrance into the space. Vapour barriers can end at the wall or be run up the wall and fastened to provide even more protection against moisture infiltration. Some pest control agencies recommend against covering the walls, as it complicates their job of inspection and spraying. Almost unheard of as late as the 1990s, vapour barriers are becoming increasingly popular in recent years. In fact, the more general area of conditioned vs. unconditioned crawl spaces has seen much research over the last decade.
Dry rot
Dry rot is wood decay caused by one of several species of fungi that digest parts of the wood which give the wood strength and stiffness. It was previously used to describe any decay of cured wood in ships and buildings by a fungus which resul ...
and other conditions detrimental to buildings (particularly wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
and timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
structures) can develop in enclosed spaces. Providing adequate ventilation
Ventilation may refer to:
* Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation
** Mechanical ventilation, in medicine, using artificial methods to assist breathing
*** Ventilator, a m ...
is thought to reduce the occurrence of these problems. Crawl space vents are openings in the wall which allow air movement. Such vents are usually fitted with metal grating
A grating is any regularly spaced collection of essentially identical, parallel, elongated elements. Gratings usually consist of a single set of elongated elements, but can consist of two sets, in which case the second set is usually perpendicul ...
, mesh
A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many attached or woven strands.
Types
* A plastic mesh may be extruded, oriented, ex ...
, or louvers which can block the movement of rodents and vermin
Vermin (colloquially varmint(s) or varmit(s)) are pests or nuisance animals that spread diseases or destroy crops or livestock. Since the term is defined in relation to human activities, which species are included vary by region and enterpr ...
but generally not insects such as termites and carpenter ants. One common rule is to provide vents in cross sectional area equal to 1/150 of the floor area served.
Modern crawl space thinking has reconsidered the usage of crawl space vents in the home. While crawl space vents do allow outside air to ventilate into the home, the ability of that air to dry out the crawl space is debatable. In areas with humid summers, during the summer months, the air vented into a crawl space will be humid, and as it enters the crawl space, which has been cooled naturally by the earth, the relative humidity of the air will rise. In those cases, crawl space vents can even increase the humidity level of a crawl space and lead to condensation on cool surfaces within, such as metal and wood. In the winter, crawl space vents should be shut off entirely, to keep out the cold winter air which can cool hot water pipes, furnaces, and water heaters stored within. During rainy weather, crawl space vents bring wet air into the crawl space, which will not dry the space effectively.
Design and structural considerations


 Structurally, for houses, the basement walls typically form the foundation. In warmer climates, some houses do not have basements because they are not necessary (although many still prefer them). In colder climates, the foundation must be below the frost line. Unless constructed in very cold climates, the
Structurally, for houses, the basement walls typically form the foundation. In warmer climates, some houses do not have basements because they are not necessary (although many still prefer them). In colder climates, the foundation must be below the frost line. Unless constructed in very cold climates, the frost line
The frost line—also known as frost depth or freezing depth—is most commonly the depth to which the groundwater in soil is expected to freeze. The frost depth depends on the climatic conditions of an area, the heat transfer properties of the s ...
is not so deep as to justify an entire level below the ground, although it is usually deep enough that a basement is the assumed standard. In places with oddly stratified soil substrata or high water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
s, such as most of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
, Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
, and areas within of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
, basements are usually not financially feasible unless the building is a large apartment or commercial structure.
Excavation using a backhoe or excavator
Excavators are heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels. They are a natural progression fro ...
is commonly used to dig a basement. If shelf rock
Shelf ( : shelves) may refer to:
* Shelf (storage), a flat horizontal surface used for display and storage
Geology
* Continental shelf, the extended perimeter of a continent, usually covered by shallow seas
* Ice shelf, a thick platform of ice ...
is discovered, the need for blasting may be cost prohibitive. Basement walls may need to have the surrounding earth backfilled around them to return the soil to grade. A water stop, some gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gravel is classifi ...
and a french drain may need to be used to prevent water from entering the basement at the bottom of the wall. Walls below grade may need to be sealed with an impervious coating (such as tar
Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat. "a dark brown or black bit ...
) to prevent water seepage. A polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bo ...
of about 6 mil ( visqueen) serves as a water barrier underneath the basement.
Some designs elect to simply leave a crawl space under the house, rather than a full basement due to structural challenges. Most other designs justify further excavations to create a full-height basement, sufficient for another level of living space. Even so, basements in Canada and the northern United States were typically only in height, rather than the standard full of the main floors. Older homes may have even lower basement heights as the basement walls were concrete block
A concrete masonry unit (CMU) is a standard-size rectangular block used in building construction. CMUs are some of the most versatile building products available because of the wide variety of appearances that can be achieved using them.
Tho ...
and thus, could be customized to any height. Modern builders offer higher basements as an option. The cost of the additional depth of excavation is usually quite expensive. Thus, houses almost certainly never have multi-storey basements though basements heights are a frequent choice among new home buyers. For large office or apartment buildings in prime locations, the cost of land may justify multi-storey basement parking garages.
The concrete floor in most basements is structurally not part of the foundation; only the basement walls are. If there are posts supporting a main floor beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
to form a post and beam system, these posts typically go right through the basement floor to a footing underneath the basement floor. It is the footing that supports the post and the footing is part of the house foundation. Load-bearing wood-stud walls rest directly on the concrete floor. Under the concrete floor is typically gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gravel is classifi ...
or crushed stone
Crushed stone or angular rock is a form of construction aggregate, typically produced by mining a suitable rock deposit and breaking the removed rock down to the desired size using crushers. It is distinct from naturally occurring gravel, which i ...
to facilitate draining. The floor is typically four inches (100 mm) thick and it rests on top of the foundation footings. The floor is typically sloped towards a drain point, in case of leak
A leak is a way (usually an opening) for fluid to escape a container or fluid-containing system, such as a tank or a ship's hull, through which the contents of the container can escape or outside matter can enter the container. Leaks are usually ...
s.
Modern construction for basement walls typically falls into one of two categories: they will be made of poured-in-place concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wi ...
using concrete forms with a concrete pump
A concrete pump is a machine used for transferring liquid concrete by pumping. There are different types of concrete pumps.
A common type of concrete pump for large scale construction projects is known as a boom concrete pump, because it uses ...
, or they will use concrete masonry unit
A concrete masonry unit (CMU) is a standard-size rectangular block used in building construction. CMUs are some of the most versatile building products available because of the wide variety of appearances that can be achieved using them.
Tho ...
s (block walls). Rock may also be used, but is less common. In monolithic architecture
Monolithic architecture describes buildings which are carved, cast or excavated from a single piece of material, historically from rock. The most basic form of monolithic architecture is a rock-cut building, such as the monolithic churches of Et ...
, large parts of the building are made of concrete; in insulating concrete form
Insulating concrete form or insulated concrete form (ICF) is a system of formwork for reinforced concrete usually made with a rigid thermal insulation that stays in place as a permanent interior and exterior substrate for walls, floors, and roofs. ...
construction, the concrete walls may be hidden with an exterior finish or siding. Inside the structure, a single Lally column
A Lally column is a round or square thin-walled structural steel column filled with concrete and oriented vertically to provide support to beams or timbers stretching over long spans.Lally columns are an engineered Component and as such mu ...
, steel basement jack, wooden column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
or support post may hold up the floor above in a small basement. A series of these supports may be necessary for large basements; many basements have the support columns exposed.
Since warm air rises, basements are typically cooler than the rest of the house. In summer, this makes basements damp, due to the higher relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
. Dehumidifiers
A dehumidifier is an air conditioning device which reduces and maintains the level of humidity in the air. This is done usually for health or thermal comfort reasons, or to eliminate musty odor and to prevent the growth of mildew by extracting wa ...
are recommended. In winter, additional heating, such as a fireplace or baseboard heaters may be required. A well-defined central heating
A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building from one main source of heat. It is a component of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (short: HVAC) systems, which can both cool and warm interior spaces.
...
system may minimize this requirement. Heating ducts typically run in the ceiling of the basement (since there is not an empty floor below to run the ducts). Ducts extending from the ceiling down to the floor help heat the cold floors of the basement. Older or cheaper systems may simply have the heating vent in the ceiling of the basement.
The finished floor is typically raised off the concrete basement floor. In countries such as Canada, laminate flooring is an exception: It is typically separated from the concrete by only a thin foam underlay. Radiant heating
Radiant heating and cooling is a category of HVAC technologies that exchange heat by both convection and radiation with the environments they are designed to heat or cool. There are many subcategories of radiant heating and cooling, including: ...
systems may be embedded within the concrete floor. Even if unfinished and unoccupied, basements are heated in order to ensure relative warmth of the floor above, and to prevent water supply pipes, drains, etc. from freezing and bursting in winter. It is recommended that the basement walls be insulated to the frost line. In Canada, the walls of a finished basement are typically insulated to the floor with vapor barriers to prevent moisture transmission. However, a finished basement should avoid wood or wood-laminate flooring, and metal framing and other moisture resistant products should be used. Finished basements can be costly to maintain due to deterioration of waterproofing materials or lateral earth movement etc. Below-ground structures will never be as dry as one above ground, and measures must be taken to circulate air and dehumidify the area.
Drainage considerations
Basementfloor drain
A floor drain is a plumbing fixture that is installed in the floor of a structure, mainly designed to remove any standing water near it. They are usually round, but can also be square or rectangular. They usually range from ; most are {{convert ...
s that connect to sanitary sewers need to be filled regularly to prevent the trap from drying out and sewer gas
Sewer gas is a complex, generally obnoxious smelling mixture of toxic and nontoxic gases produced and collected in sewage systems by the decomposition of organic household or industrial wastes, typical components of sewage.
Sewer gases may inc ...
from escaping into the basement. The drain trap can be topped up automatically by the condensation from air conditioners or high-efficiency furnace
A furnace is a structure in which heat is produced with the help of combustion.
Furnace may also refer to:
Appliances Buildings
* Furnace (central heating): a furnace , or a heater or boiler , used to generate heat for buildings
* Boiler, used t ...
s. A small tube from another downpipe is sometimes used to keep the trap from drying out. Health Canada advocates the use of special radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through ...
gas traps for floor drains that lead to soil or to a sealed sump pump. In areas where storm and sanitary sewer
A sanitary sewer is an underground pipe or tunnel system for transporting sewage from houses and commercial buildings (but not stormwater) to a sewage treatment plant or disposal. Sanitary sewers are a type of gravity sewer and are part of an o ...
s are combined, and there is the risk of flooding and sewage backing up, backwater valve
A backwater valve is a backflow prevention device used to prevent outbound water through a dwelling's drain pipes from re-entering -- " back flowing"—into a home. The valve contains a flap that allows water to exit the home, but closes to preven ...
s in all basement drains may be mandated by code and definitely are recommended even if not mandated.
The main water cut-off valve is usually in the basement. Basements often have "clean outs" for the sanitary and storm sewers, where these pipes can be accessed. The storm sewer access is only needed where the weeping tile
A weeping tile (also called a drain tile or perimeter tileGradwell, John B., and Malcolm Welch. ''Technology--shaping our world''. South Holland, Ill.: Goodheart-Willcox, 1991. 116. Print.) is a porous pipe used for underground water collection ...
s drain into the storm sewers.
Other than with walk-out or look-out basements, windows in basements require a well and are below grade. A clear window well cover may be required to keep the window wells from accumulating rain water. There should be drains in the window well, connected to the foundation drains.
 If the
If the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
outside the basement is above the height of the basement floor, then the foundation drains or the weeping tiles outside the footings may be insufficient to keep the basement dry. A sump pump may be required. It can be located anywhere and is simply in a well that is deeper than the basement floor.
Even with functioning sump pumps or low water tables, basements may become wet after rainfall, due to improper drainage. The ground next to the basement must be graded such that water flows away from the basement wall. Downspouts from roof gutters should drain freely into the storm sewer or directed away from the house. Downspouts should not be connected to the foundation draintiles. If the draintiles become clogged by leaves or debris from the rain gutters, the roof water would cause basement flooding through the draintile. Damp-proofing
Damp proofing in construction is a type of moisture control applied to building walls and floors to prevent Damp (structural), moisture from passing into the interior spaces. Dampness problems are among the most frequent problems encountered in r ...
or waterproofing
Waterproofing is the process of making an object or structure waterproof or water-resistant so that it remains relatively unaffected by water or resisting the ingress of water under specified conditions. Such items may be used in wet environme ...
materials are typically applied to outside of the basement wall. It is virtually impossible to make a concrete wall waterproof, over the long run, so drainage is the key. There are draining membranes that can be applied to the outside of the basement that create channels for water against the basement wall to flow to the foundation drains.
Where drainage is inadequate, waterproofing may be needed. There are numerous ways to waterproof a basement, but most systems fall into one of three categories:
*Tanking – Systems that bond to the basement structure and physically hold back groundwater.
*Cavity drainage – Dimpled plastic membranes are used to line the floors and walls of the basement, creating a "drained cavity." Any water entering this drained cavity is diverted to a sump pump and pumped away from the basement.
*Exterior foundation drain – Installing an exterior foundation drain that will drain away by gravity is the most effective means to waterproof a basement. An exterior system allows water to flow away from the basement without using pumps or electricity. An exterior drain also allows for the installation of a waterproof membrane to the foundation walls.
The waterproofing system can be applied to the inside or the outside walls of a basement. When waterproofing existing basements it is much cheaper to waterproof the basement on the inside. Waterproofing on the outside requires the expense of excavation, but does offer a number of advantages for a homeowner over the long term. Among them are:
* Gravity system
* No pumps or electrical wiring required
* Membrane applied to exterior walls to prevent dampness, mold, moisture, and soil gases from entering the home
* Permanent solution
Basement culture and finishings
Unfinished basement
The unfinished design, found principally in spaces larger than the traditional cellar, is common in residences throughout the U.S. and Canada. One usually finds within it a water heater, various pipes running along the ceiling and downwards to the floor, and sometimes a workbench, a freezer or refrigerator, or a washer/dryer set. Boxes of various materials, and objects unneeded in the rest of the house, are also often stored there; in this regard, the unfinished basement takes the place both of the cellar and of the attic. Home workshops are often located in the basement, since sawdust, metal chips, and other mess or noise are less of a nuisance there. The basement can contain all of these objects and still be considered to be "unfinished", as they are either mostly or entirely functional in purpose.Finished basement
recreation room
A recreation room (also known as a rec room, rumpus room, play room, playroom, games room, or ruckus room) is a room used for a variety of purposes, such as parties, games and other everyday or casual activities. The term ''recreation room'' is c ...
or living room, but it is not uncommon as well to find there (either instead of or alongside the living/recreation room) a guest bedroom or teenager's room, a bathroom, a home office, a home gym, a home theater, a basement bar, a sauna
A sauna (, ), or sudatory, is a small room or building designed as a place to experience dry or wet heat sessions, or an establishment with one or more of these facilities. The steam and high heat make the bathers perspire. A thermometer in a ...
, craft room, play room, kitchenette, and one or more closets. Occasionally a part of the basement is unfurnished and is used for storage, a workshop, and/or a laundry room; when this is the case the water heater and furnace will also often be located there, although in some cases the entire basement is finished, and the water heater and furnace are boxed off into a closet.
Partially finished basement
The main point of distinction between this type of basement and the two others lies in its being either entirely unmodified (unlike the finished basement) beyond the addition of furniture, recreational objects and appliances, and/or exercise equipment on the bare floor, or slightly modified through the installation (besides any or all of the aforementioned items) of loose carpet and perhaps simple light fixtures. In both cases, the objects found there—many of which could be found in a finished basement as well—might include the following: weight sets and otherexercise equipment
Exercise equipment is any apparatus or device used during physical activity to enhance the strength or conditioning effects of that exercise by providing either fixed or adjustable amounts of resistance, or to otherwise enhance the experience or ...
; the boom box
A boombox is a transistorized portable music player featuring one or two cassette tape recorder/players and AM/FM radio, generally with a carrying handle. Beginning in the mid 1980s, a CD player was often included. Sound is delivered through ...
es or entertainment systems used during exercise; musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
s (which are not in storage, as they would technically be in an unfinished basement; an assembled drum set would be the most easily identified of these); football tables, chairs, couches and entertainment appliances of lesser quality than those in the rest of the house; refrigerators, stand-alone freezers, and microwaves (the first and the second being also sometimes used as supplementary storage units in an unfinished basement); and sports pennants and/or other types of posters which are attached to the walls.
As the description suggests, this type of basement, which also might be called "half-finished", is likely used by teenagers and children. The entire family might utilize a work-out area. It is also common to have a secondary (or primary) home office in a partially finished basement, as well as a workbench and/or a space for laundry appliances.
Toilets and showers sometimes exist in this variety of basement, as many North American basements are designed to allow for their installation.
Fully finished basement – retro fit
InLondon
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
the construction of finished retrofit basements is big business with a large number of projects in the 100–200 square meter bracket. There are a smaller number of projects in the 200–500 square meter bracket under construction. It is also not unusual to see multi-level retrofit basements. These are considerable works of civil engineering and require some skill and intuitive understanding as well as good engineering. Some of the more grandiose of these basement projects have been widely reported in the national media, including the "Witanhurst
Witanhurst is a large Listed building#England and Wales, Grade II listed 1930s Georgian Revival mansion on in Highgate, North London. It has had several prominent owners since being rebuilt by soap magnate Sir Arthur Henry Crosfield, Arthur Cro ...
" project in the Highgate area of London. and the huge iceberg-like homes which are beginning to be constructed in prime London areas such as Kensington and Chelsea.
Use in hospitals
Hospitals often place their nuclear chemistry and radiation therapy and diagnostic resources in basements to utilize the shielding from the earth.Real estate floorspace measures
InCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, historically the basement area was excluded from advertised square footage of a house as it was not part of the living space. For example, a "2,000-square-foot bungalow" would, in reality, have of floor space. More recently, finished space has become increasingly acceptable as a measure which includes the developed basement areas of a home. Due to fire code requirements, most jurisdictions require an emergency egress (through either egress-style windows, or, in the case of a walk-out basement, a door) to include the basement square footage as living space.
See also
*Coal hole
A coal hole is a hatch in the pavement (sidewalk, in US usage) above an underground coal bunker. They are sometimes found outside houses that existed during the period when coal was widely used for domestic heating from the early 19th century t ...
* Loft conversions in the United Kingdom
A loft conversion or an attic conversion is the process of transforming an empty attic space or loft into a functional room, typically used as a bedroom, office space, a gym, or storage space. Loft conversions are one of the most popular fo ...
References
External links
*National Research Council (Canada) Basement subject search
Basement ideas
{{Authority control Rooms Building engineering Structural engineering Semi-subterranean structures Food storage