|
Dynamics Of The Celestial Spheres
Ancient, medieval and Renaissance astronomers and philosophers developed many different theories about the dynamics of the celestial spheres. They explained the motions of the various nested spheres in terms of the materials of which they were made, external movers such as celestial intelligences, and internal movers such as motive souls or impressed forces. Most of these models were qualitative, although a few of them incorporated quantitative analyses that related speed, motive force and resistance. The celestial material and its natural motions In considering the physics of the celestial spheres, scholars followed two different views about the material composition of the celestial spheres. For Plato, the celestial regions were made "mostly out of fire" on account of fire's mobility. Later Platonists, such as Plotinus, maintained that although fire moves naturally upward in a straight line toward its natural place at the periphery of the universe, when it arrived there, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelic Movers
{{disambiguation ...
Angelic may refer to: * Angel, a supernatural being * Angelic (band), a British trance band * Angelic acid, an organic compound * Angelic de Grimoard, brother of Pope Urban V * ''Angelic Encounters'', an album by the Dutch band Thanatos * Angelic language (other) * ''Angelic Layer'', a 1999 Japanese comics * Angelic Organics, a community-supported agriculture farm in Caledonia, Illinois, US * Angelic Pretty, a Japanese fashion company * Angelic Society, a secret society * Angelic tongues, a term related to a Jewish theme * Angelic Upstarts, an English musical band * The Angelic Conversation (other) See also * Angelique (other) Angelique or Angélique may refer to: * Angélique (given name), a French feminine name Arts and entertainment Music * Angélique (instrument), a string instrument of the lute family * ''Angélique'', a 1927 opéra bouffe by Jacques Ibert * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
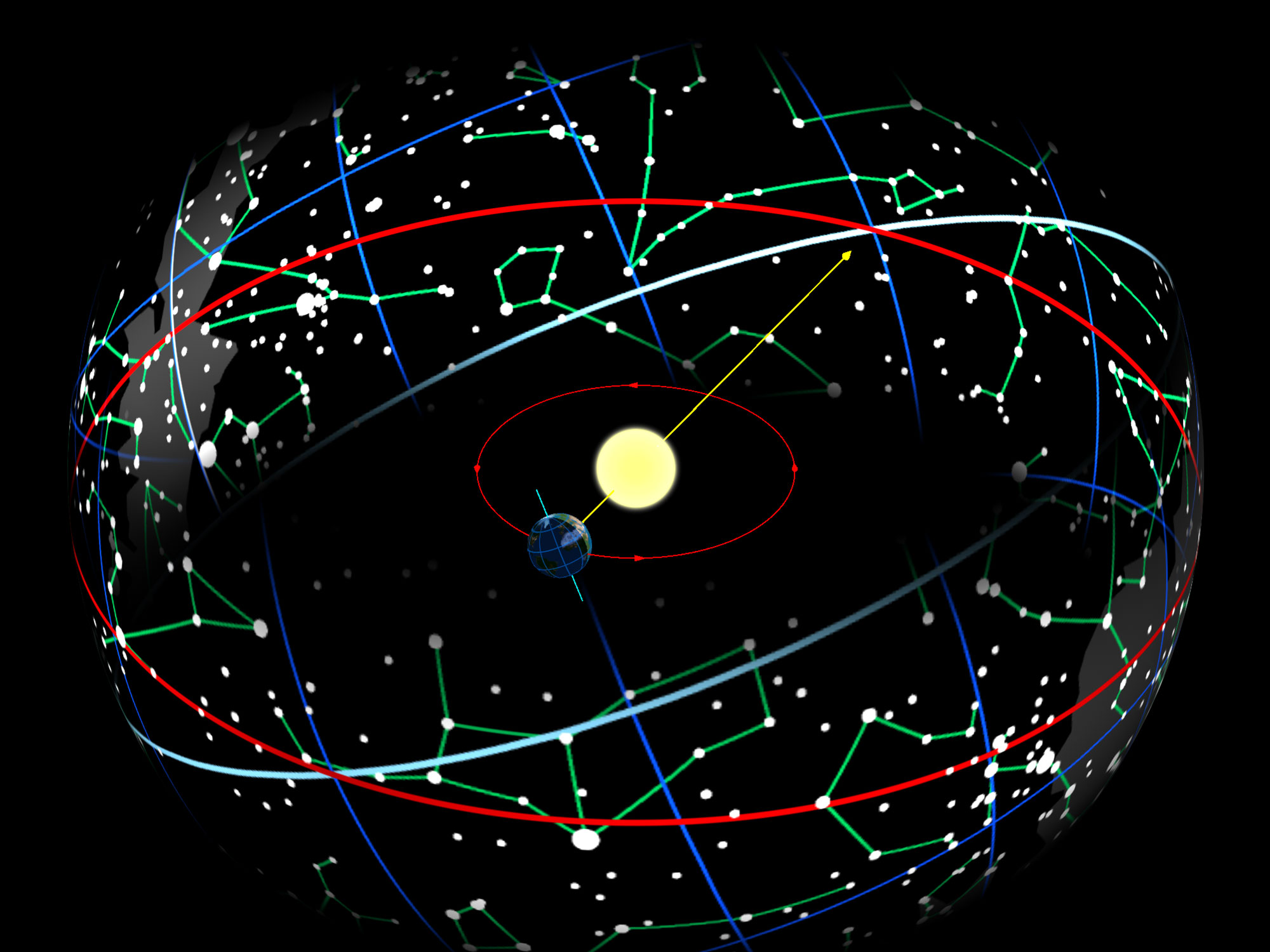
Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the Sun path, apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into astrological sign, twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries (astrology), Aries, Taurus (astrology), Taurus, Gemini (astrology), Gemini, Cancer (astrology), Cancer, Leo (astrology), Leo, Virgo (astrology), Virgo, Libra (astrology), Libra, Scorpio (astrology), Scorpio, Sagittarius (astrology), Sagittarius, Capricorn (astrology), Capricorn, Aquarius (astrology), Aquarius, and Pisces (astrology), Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic Golden Age, and the father of early modern medicine. Sajjad H. Rizvi has called Avicenna "arguably the most influential philosopher of the pre-modern era". He was a Muslim Peripatetic philosopher influenced by Greek Aristotelian philosophy. Of the 450 works he is believed to have written, around 240 have survived, including 150 on philosophy and 40 on medicine. His most famous works are ''The Book of Healing'', a philosophical and scientific encyclopedia, and ''The Canon of Medicine'', a medical encyclopedia which became a standard medical text at many medieval universities and remained in use as late as 1650. Besides philosophy and medicine, Avicenna's corpus includes writings on astronomy, alchemy, geography and geology, psychology, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Farabi
Abu Nasr Muhammad Al-Farabi ( fa, ابونصر محمد فارابی), ( ar, أبو نصر محمد الفارابي), known in the Western world, West as Alpharabius; (c. 872 – between 14 December, 950 and 12 January, 951)PDF version was a renowned Early Islamic philosophy, early Islamic philosopher and jurist who wrote in the fields of political philosophy, metaphysics, ethics and logic. He was also a Islamic science, scientist, Islamic astronomy, cosmologist, Mathematics in medieval Islam, mathematician and Islamic music, music theorist.Ludwig W. Adamec (2009), ''Historical Dictionary of Islam'', pp.95–96. Scarecrow Press. . In Islamic philosophy, Islamic philosophical tradition he was often called "the Second Teacher", following Aristotle who was known as "the First Teacher". He is credited with preserving the original Ancient Greek literature, Greek texts during the Middle Ages via his Commentary (philology), commentaries and treatises, and influencing many prominent philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Impetus
The theory of impetus was an auxiliary or secondary theory of Aristotelian dynamics, put forth initially to explain projectile motion against gravity. It was introduced by John Philoponus in the 6th century, and elaborated by Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji at the end of the 12th century. The theory was modified by Avicenna in the 11th century and Abu'l-Barakāt al-Baghdādī in the 12th century, before it was later established in Western scientific thought by Jean Buridan in the 14th century. It is the intellectual precursor to the concepts of inertia, momentum and acceleration in classical mechanics. Aristotelian theory Aristotelian physics is the form of Natural sciences, natural science described in the works of the Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 BC). In his work ''Physics (Aristotle), Physics'', Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies, both living and inanimate, celestial and terrestrial – includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Philoponus
John Philoponus (Greek: ; ; c. 490 – c. 570), also known as John the Grammarian or John of Alexandria, was a Byzantine Greek philologist, Aristotelian commentator, Christian theologian and an author of a considerable number of philosophical treatises and theological works. He was born in Alexandria. A rigorous, sometimes polemical writer and an original thinker who was controversial in his own time, John Philoponus broke from the Aristotelian–Neoplatonic tradition, questioning methodology and eventually leading to empiricism in the natural sciences. He was one of the first to propose a "theory of impetus" similar to the modern concept of inertia over Aristotelian dynamics. Later in life Philoponus turned to Christian apologetics, arguing against the eternity of the world, a theory which formed the basis of pagan attacks on the Christian doctrine of Creation. He also wrote on Christology and was posthumously condemned as a heretic by the Church in 680–81 because of what was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deferent
In the Hipparchian, Ptolemaic, and Copernican systems of astronomy, the epicycle (, meaning "circle moving on another circle") was a geometric model used to explain the variations in speed and direction of the apparent motion of the Moon, Sun, and planets. In particular it explained the apparent retrograde motion of the five planets known at the time. Secondarily, it also explained changes in the apparent distances of the planets from the Earth. It was first proposed by Apollonius of Perga at the end of the 3rd century BC. It was developed by Apollonius of Perga and Hipparchus of Rhodes, who used it extensively, during the 2nd century BC, then formalized and extensively used by Ptolemy in his 2nd century AD astronomical treatise the ''Almagest''. Epicyclical motion is used in the Antikythera mechanism, an ancient Greek astronomical device for compensating for the elliptical orbit of the Moon, moving faster at perigee and slower at apogee than circular orbits would, using fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicycle
In the Hipparchian, Ptolemaic, and Copernican systems of astronomy, the epicycle (, meaning "circle moving on another circle") was a geometric model used to explain the variations in speed and direction of the apparent motion of the Moon, Sun, and planets. In particular it explained the apparent retrograde motion of the five planets known at the time. Secondarily, it also explained changes in the apparent distances of the planets from the Earth. It was first proposed by Apollonius of Perga at the end of the 3rd century BC. It was developed by Apollonius of Perga and Hipparchus of Rhodes, who used it extensively, during the 2nd century BC, then formalized and extensively used by Ptolemy in his 2nd century AD astronomical treatise the '' Almagest''. Epicyclical motion is used in the Antikythera mechanism, an ancient Greek astronomical device for compensating for the elliptical orbit of the Moon, moving faster at perigee and slower at apogee than circular orbits would, using fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On The Heavens
''On the Heavens'' (Greek: ''Περὶ οὐρανοῦ''; Latin: ''De Caelo'' or ''De Caelo et Mundo'') is Aristotle's chief cosmological treatise: written in 350 BC, it contains his astronomical theory and his ideas on the concrete workings of the terrestrial world. It should not be confused with the spurious work ''On the Universe'' (''De mundo'', also known as ''On the Cosmos''). This work is significant as one of the defining pillars of the Aristotelian worldview, a school of philosophy that dominated intellectual thinking for almost two millennia. Similarly, this work and others by Aristotle were important seminal works from which much of scholasticism was derived. Argument According to Aristotle in ''De Caelo'', the heavenly bodies are the most perfect realities, (or "substances"), whose motions are ruled by principles other than those of bodies in the sublunary sphere. The latter are composed of one or all of the four classical elements (earth, water, air, fire) and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callippus
Callippus (; grc, Κάλλιππος; c. 370 BC – c. 300 BC) was a Greek astronomer and mathematician. Biography Callippus was born at Cyzicus, and studied under Eudoxus of Cnidus at the Academy of Plato. He also worked with Aristotle at the Lyceum, which means that he was active in Athens prior to Aristotle's death in 322 BC. He observed the movements of the planets and attempted to use Eudoxus' scheme of connected spheres to account for their movements. However, he found that 27 spheres was insufficient to account for the planetary movements, and so he added seven more for a total of 34. According to the description in Aristotle's ''Metaphysics'' (XII.8), he added two spheres for the Sun, two for the Moon, and one each for Mercury, Venus, and Mars. Callippus made careful measurements of the lengths of the seasons, finding them (starting with the spring equinox) to be 94 days, 92 days, 89 days, and 90 days. This variation in the seasons implies a variation in the speed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudoxus Of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus (; grc, Εὔδοξος ὁ Κνίδιος, ''Eúdoxos ho Knídios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer, mathematician, scholar, and student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original works are lost, though some fragments are preserved in Hipparchus' commentary on Aratus's poem on astronomy. ''Sphaerics'' by Theodosius of Bithynia may be based on a work by Eudoxus. Life Eudoxus was born and died in Cnidus (also spelled Knidos), which was a city on the southwest coast of Asia Minor. The years of Eudoxus' birth and death are not fully known but the range may have been , or . His name Eudoxus means "honored" or "of good repute" (, from ''eu'' "good" and ''doxa'' "opinion, belief, fame"). It is analogous to the Latin name Benedictus. Eudoxus's father, Aeschines of Cnidus, loved to watch stars at night. Eudoxus first traveled to Tarentum to study with Archytas, from whom he learned mathematics. While in Italy, Eudoxus visited Sicily, where he studied medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |