|
Cuevavirus
The species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'' ( ) is the taxonomic home of a virus that forms filamentous virion, ''Lloviu virus'' (LLOV). The species is included in the genus '' Cuevavirus''. LLOV is a distant relative of the commonly known Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Use of term The species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'' is a virological taxon (i.e. a man-made concept) included in the genus '' Cuevavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Lloviu virus. Lloviu virus is the sole member of the species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'', which is included genus '' Cuevavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The name Lloviu virus is derived from ''Cueva del Lloviu'' (the name of a Spanish cave in which it was first discovered) and the taxonomic suffix ''virus'' (which denotes a virus species). In 2010, the species and the genus '' cuevavirus'' were proposed as independent species and genus. In July 2013, the species and the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuevavirus
The species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'' ( ) is the taxonomic home of a virus that forms filamentous virion, ''Lloviu virus'' (LLOV). The species is included in the genus '' Cuevavirus''. LLOV is a distant relative of the commonly known Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Use of term The species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'' is a virological taxon (i.e. a man-made concept) included in the genus '' Cuevavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Lloviu virus. Lloviu virus is the sole member of the species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'', which is included genus '' Cuevavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The name Lloviu virus is derived from ''Cueva del Lloviu'' (the name of a Spanish cave in which it was first discovered) and the taxonomic suffix ''virus'' (which denotes a virus species). In 2010, the species and the genus '' cuevavirus'' were proposed as independent species and genus. In July 2013, the species and the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuevavirus
The species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'' ( ) is the taxonomic home of a virus that forms filamentous virion, ''Lloviu virus'' (LLOV). The species is included in the genus '' Cuevavirus''. LLOV is a distant relative of the commonly known Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Use of term The species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'' is a virological taxon (i.e. a man-made concept) included in the genus '' Cuevavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Lloviu virus. Lloviu virus is the sole member of the species ''Lloviu cuevavirus'', which is included genus '' Cuevavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The name Lloviu virus is derived from ''Cueva del Lloviu'' (the name of a Spanish cave in which it was first discovered) and the taxonomic suffix ''virus'' (which denotes a virus species). In 2010, the species and the genus '' cuevavirus'' were proposed as independent species and genus. In July 2013, the species and the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
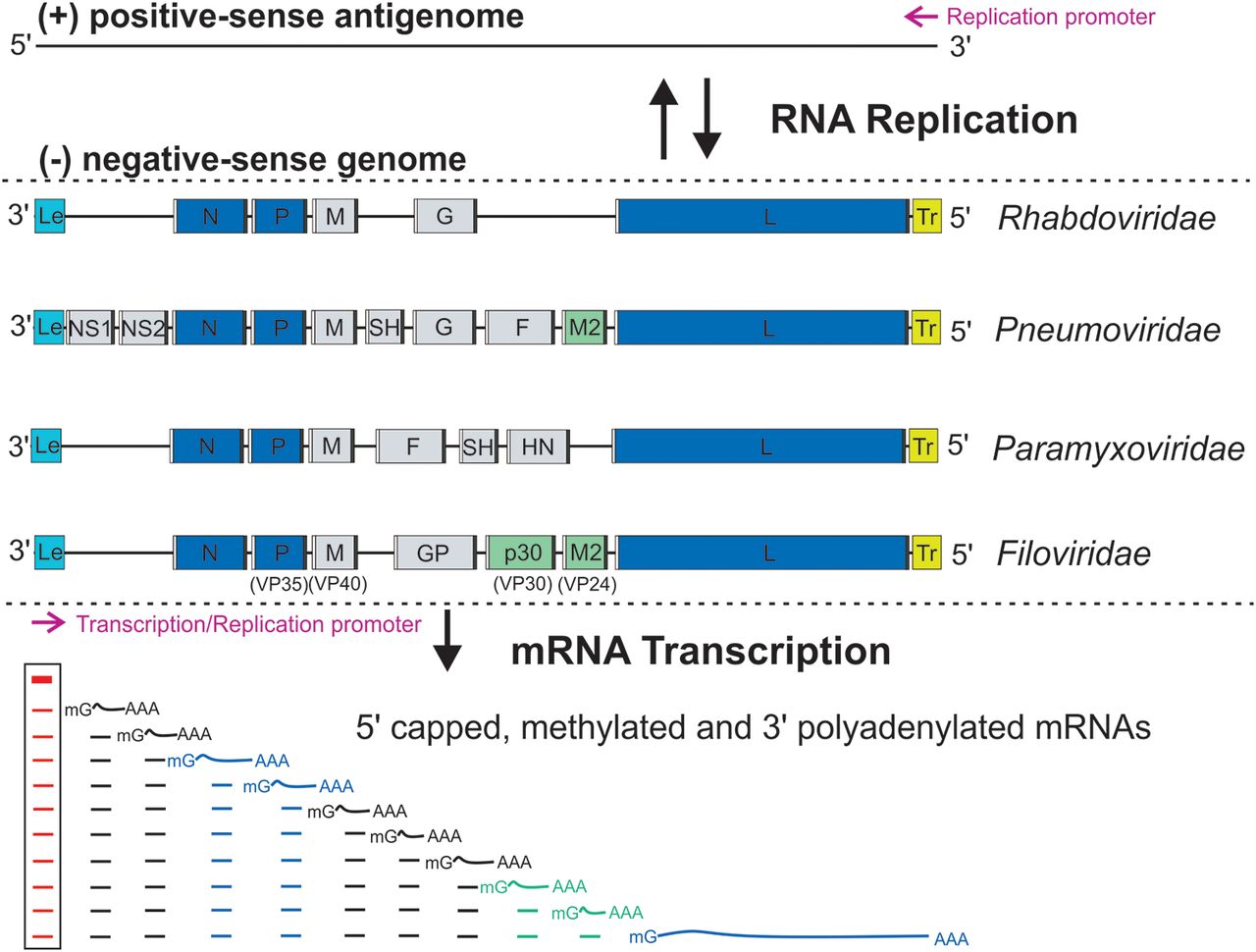
Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known relatives, cause severe disease in humans and nonhuman primates in the form of viral hemorrhagic fevers. All filoviruses are classified by the US as select agents, by the World Health Organization as Risk Group 4 Pathogens (requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment), by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases as Category A Priority Pathogens, and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as Category A Bioterrorism Agents, and are listed as Biological Agents for Export Control by the Australia Group. Use of term The family ''Filoviridae'' is a virological taxon that was defined in 1982 and emended in 1991, 1998, 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2011. The family currently includes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononegavirales
''Mononegavirales'' is an order of negative-strand RNA viruses which have nonsegmented genomes. Some common members of the order are Ebola virus, human respiratory syncytial virus, measles virus, mumps virus, Nipah virus, and rabies virus. All of these viruses cause significant disease in humans. Many other important pathogens of nonhuman animals and plants are also in the group. The order includes eleven virus families: '' Artoviridae'', ''Bornaviridae'', ''Filoviridae'', ''Lispiviridae'', ''Mymonaviridae'', ''Nyamiviridae'', ''Paramyxoviridae'', ''Pneumoviridae'', ''Rhabdoviridae'', '' Sunviridae'', and ''Xinmoviridae''. Use of term The order ''Mononegavirales'' (pronounced: ) According to the rules for taxon naming established by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the name ''Mononegavirales'' is always to be capitalized, italicized, and never abbreviated. The names of the order's physical members ("mononegaviruses" or "mononegavirads") are to be writte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. A computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems and to spread the virus. Viruses use complex anti-detection/stealth strategies to evade antivirus software. Motives for creating viruses can inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present for research or educational purposes. (The term "necropsy" is generally reserved for non-human animals). Autopsies are usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist. In most cases, a medical examiner or coroner can determine the cause of death. However, only a small portion of deaths require an autopsy to be performed, under certain circumstances. Purposes of performance Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. Autopsies can be performed when any of the following information is desired: * Determine if death was natural or unnatural * Injury source and extent on the corpse * Manner of death must be determined * Post mortem interval * Determining the deceas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, and its Iberian portion is bordered to the west and south by the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain, the sole country to have a land border with Portugal. Its two archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population. Portugal is the oldest continuously existing nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples who had contact with Phoenicians and Ancient Greek traders, it was ruled by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etiology
Etiology (pronounced ; alternatively: aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek (''aitiología'') "giving a reason for" (, ''aitía'', "cause"); and ('' -logía''). More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origins, or reasons behind the way that things are, or the way they function, or it can refer to the causes themselves. The word is commonly used in medicine (pertaining to causes of disease) and in philosophy, but also in physics, psychology, government, geography, spatial analysis, theology, and biology, in reference to the causes or origins of various phenomena. In the past, when many physical phenomena were not well understood or when histories were not recorded, myths often arose to provide etiologies. Thus, an etiological myth, or origin myth, is a myth that has arisen, been told over time or written to explain the origins of various social or natural phenomena. For example, Virgil's ''Aeneid'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopic Scale
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale between the macroscopic scale and the quantum scale. Microscopic units and measurements are used to classify and describe very small objects. One common microscopic length scale unit is the micrometre (also called a ''micron'') (symbol: μm), which is one millionth of a metre. History Whilst compound microscopes were first developed in the 1590s, the significance of the microscopic scale was only truly established in the 1600s when Marcello Malphigi and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek microscopically observed frog lungs and microorganisms. As microbiology was established, the significance of making scientific observations at a microscopic level increased. Published in 1665, Robert Hooke’s book Micrographia details his microscopic observations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroscopic Scale
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic. Overview When applied to physical phenomena and bodies, the macroscopic scale describes things as a person can directly perceive them, without the aid of magnifying devices. This is in contrast to observations (microscopy) or theories ( microphysics, statistical physics) of objects of geometric lengths smaller than perhaps some hundreds of micrometers. A macroscopic view of a ball is just that: a ball. A microscopic view could reveal a thick round skin seemingly composed entirely of puckered cracks and fissures (as viewed through a microscope) or, further down in scale, a collection of molecules in a roughly spherical shape (as viewed through an electron microscope). An example of a physical theory that takes a deliberately macroscopic viewpoint is thermodynamics. An example of a topi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)