Mononegavirales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Mononegavirales'' is an order of
 A virus is a member of the order ''Mononegavirales'' if
* its genome is a linear, typically (but not always) nonsegmented, single-stranded, non-infectious
A virus is a member of the order ''Mononegavirales'' if
* its genome is a linear, typically (but not always) nonsegmented, single-stranded, non-infectious
 The mononegavirus
The mononegavirus
 The order has eleven families that include numerous genera, which consist of many different species:
* '' Artoviridae''
* ''
The order has eleven families that include numerous genera, which consist of many different species:
* '' Artoviridae''
* ''
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1753162 Animal viral diseases Viral plant pathogens and diseases Zoonoses Virus orders
negative-strand RNA virus
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is sy ...
es which have nonsegmented genomes. Some common members of the order are Ebola virus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and ot ...
, human respiratory syncytial virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a common, contagious virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. ...
, measles virus
''Measles morbillivirus'' (MeV), also called measles virus (MV), is a single-stranded, negative-sense, enveloped, non-segmented RNA virus of the genus ''Morbillivirus'' within the family ''Paramyxoviridae''. It is the cause of measles. Human ...
, mumps virus
The mumps virus (MuV) is the virus that causes mumps. MuV contains a single-stranded, negative-sense genome made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Its genome is about 15,000 nucleotides in length and contains seven genes that encode nine proteins. The g ...
, Nipah virus
Nipah virus, scientific name ''Nipah henipavirus'', is a bat-borne virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a high mortality rate. Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus have occurred in Sout ...
, and rabies virus
Rabies virus, scientific name ''Rabies lyssavirus'', is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in humans and animals. Rabies transmission can occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly through contact with human saliva. ''Rabies lyss ...
. All of these viruses cause significant disease in humans. Many other important pathogens of nonhuman animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s and plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s are also in the group. The order includes eleven virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
families: '' Artoviridae'', ''Bornaviridae
''Bornaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fata ...
'', ''Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known re ...
'', ''Lispiviridae'', ''Mymonaviridae
''Mymonaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales'', which infect fungi. Fungi serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of Ancient Greek ''my''co, which means fungus, and ''mo''noneg''a''virale ...
'', ''Nyamiviridae
''Nyamiviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Ecdysozoa and birds serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of ''Nya''manini Pan (place of isolation of type species Nyamanini virus in So ...
'', ''Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Ancient Greek, Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this ...
'', ''Pneumoviridae
''Pneumoviridae'' (from Greek pneumo-, lung, -viridae, virus from Latin, poison, slimy liquid) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Mononegavirales''. Humans, cattle, and rodents serve as natural hosts. Respiratory tract in ...
'', ''Rhabdoviridae
''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member viru ...
'', '' Sunviridae'', and ''Xinmoviridae''.
Use of term
The order ''Mononegavirales'' (pronounced: ) According to the rules for taxon naming established by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the name ''Mononegavirales'' is always to be capitalized, italicized, and never abbreviated. The names of the order's physical members ("mononegaviruses" or "mononegavirads") are to be written in lower case, are not italicized, and used without articles. is a virological taxon that was created in 1991 and amended in 1995, 1997, 2000, 2005, 2011, 2016, 2017, and 2018. The name ''Mononegavirales'' is derived from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
adjective ''μóνος'' ''monos'' (alluding to the monopartite and single-stranded genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
s of most mononegaviruses), the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
verb ''negare'' (alluding to the negative polarity In linguistics, a polarity item is a lexical item that is associated with affirmation or negation. An affirmation is a positive polarity item, abbreviated PPI or AFF. A negation is a negative polarity item, abbreviated NPI or NEG.
The linguistic ...
of these genomes), and the taxonomic
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry ...
''-virales'' (denoting a viral order).
Order inclusion criteria
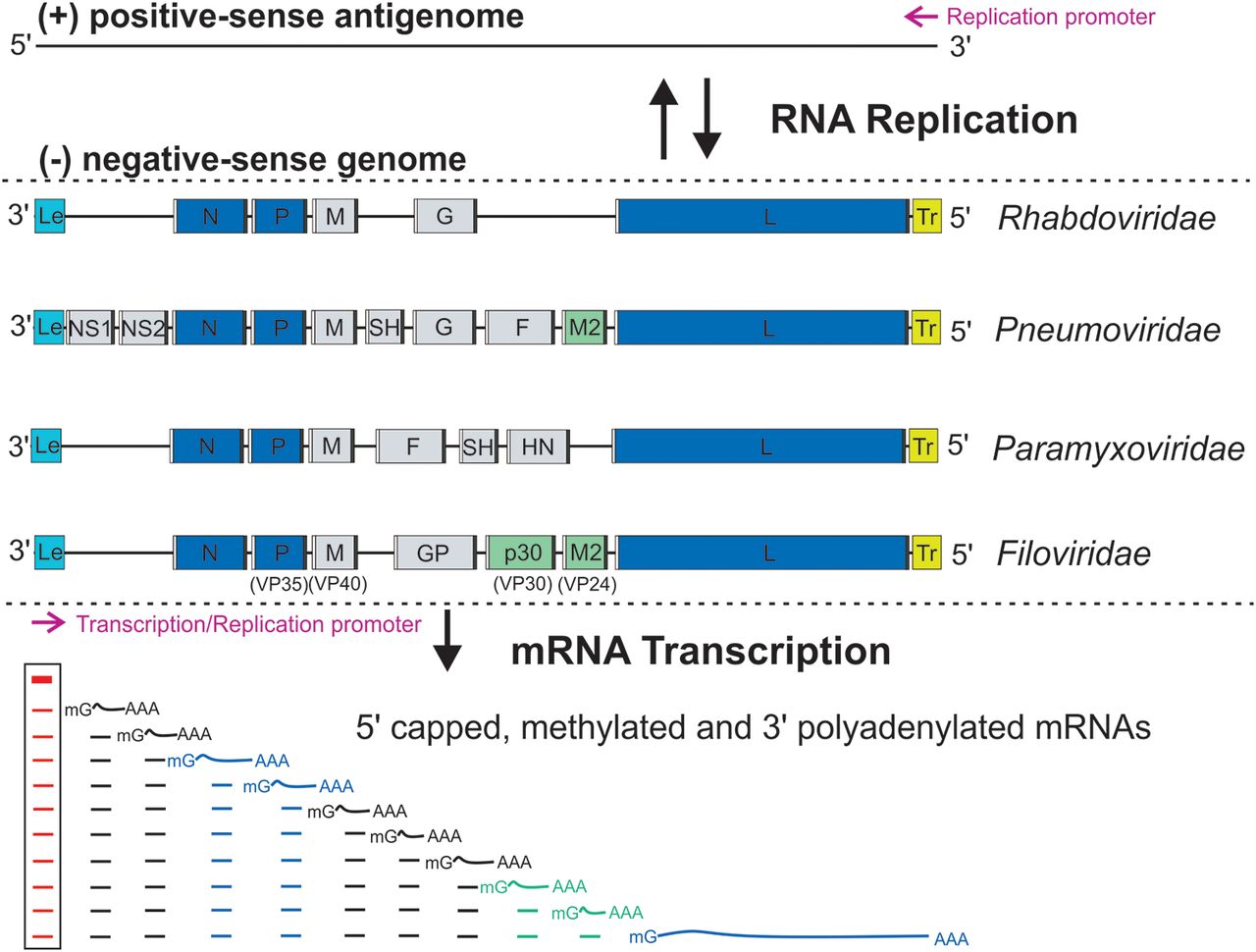
 A virus is a member of the order ''Mononegavirales'' if
* its genome is a linear, typically (but not always) nonsegmented, single-stranded, non-infectious
A virus is a member of the order ''Mononegavirales'' if
* its genome is a linear, typically (but not always) nonsegmented, single-stranded, non-infectious RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
of negative polarity; possesses inverse-complementary 3' and 5' termini; and is not covalently
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
linked to a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
;
* its genome has the characteristic gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
order 3'-UTR–core protein genes–envelope protein genes–RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene– 5'-UTR (3'-N-P-M-G-L-5') (there are, however, some exceptions);
* it produces 5–10 distinct mRNAs
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the p ...
from its genome via polar sequential transcription from a single promoter located at the 3' end of the genome; mRNAs are 5' capped and polyadenylated;
* it replicates by synthesizing complete antigenomes;
* it forms infectious helical
Helical may refer to:
* Helix, the mathematical concept for the shape
* Helical engine, a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive
* Helical spring, a coilspring
* Helical plc, a British property company, once a maker of steel bar stock
* Helicoil
A t ...
ribonucleocapsids as the templates for the synthesis of mRNAs, antigenomes, and genomes;
* it encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to t ...
(RdRp, L) that is highly homologous to those of other mononegaviruses; and/or
* it typically (but not always) produces enveloped virions with a molecular mass
The molecular mass (''m'') is the mass of a given molecule: it is measured in daltons (Da or u). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The related quanti ...
of 300–1,000; an S20W of 550–>1,045; and a buoyant density in CsCl CSCL can refer to:
* Caesium chloride (CsCl), a chemical compound.
* Computer Supported Collaborative Learning, a research topic on supporting collaborative learning with the assistance of computer artifacts.
* China Shipping Container Lines, a c ...
of 1.18–1.22 g/cm3.
Life cycle
 The mononegavirus
The mononegavirus life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
*Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
* Life-cycle hypothesis ...
begins with virion attachment to specific cell-surface receptors
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
, followed by fusion
Fusion, or synthesis, is the process of combining two or more distinct entities into a new whole.
Fusion may also refer to:
Science and technology Physics
*Nuclear fusion, multiple atomic nuclei combining to form one or more different atomic nucl ...
of the virion envelope with cellular membranes and the concomitant release of the virus nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
into the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
. The virus RdRp partially uncoats the nucleocapsid and transcribes the genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
into positive-stranded mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
s, which are then translated
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
into structural and nonstructural proteins.
Mononegavirus RdRps bind to a single promoter located at the 3' end of the genome. Transcription either terminates after a gene or continues to the next gene downstream. This means that genes close to the 3' end of the genome are transcribed in the greatest abundance, whereas those toward the 5' end are least likely to be transcribed. The gene order is therefore a simple but effective form of transcriptional regulation. The most abundant protein produced is the nucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating int ...
, whose concentration in the cell determines when the RdRp switches from gene transcription to genome replication.
Replication results in full-length, positive-stranded antigenomes that are in turn transcribed into negative-stranded virus progeny genome copies. Newly synthesized structural proteins and genomes self-assemble and accumulate near the inside of the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
. Virions bud
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be spec ...
off from the cell, gaining their envelopes from the cellular membrane they bud from. The mature progeny particles then infect other cells to repeat the cycle.
Paleovirology
Mononegaviruses have a history that dates back several tens of million of years. Mononegavirus "fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in ...
" have been discovered in the form of mononegavirus genes or gene fragments integrated into mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
ian genomes. For instance, bornavirus gene "fossils" have been detected in the genomes of bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
s, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, hyrax
Hyraxes (), also called dassies, are small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Typically, they measure between long and weigh between . They are superficially simil ...
es, marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a po ...
s, primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
s, rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are na ...
s, ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally ...
s, and elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae an ...
s. Filovirus gene "fossils" have been detected in the genomes of bats, rodents, shrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to different fa ...
s, tenrec
A tenrec is any species of mammal within the afrotherian family Tenrecidae endemic to Madagascar. Tenrecs are wildly diverse; as a result of convergent evolution some resemble hedgehogs, shrews, opossums, rats, and mice. They occupy aquatic, a ...
s, and marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a po ...
s. A Midway virus "fossil" was found in the genome of zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family ( Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often ...
. Finally, rhabdovirus "fossils" were found in the genomes of crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s, mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
es, tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s, and plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s.
Taxonomy
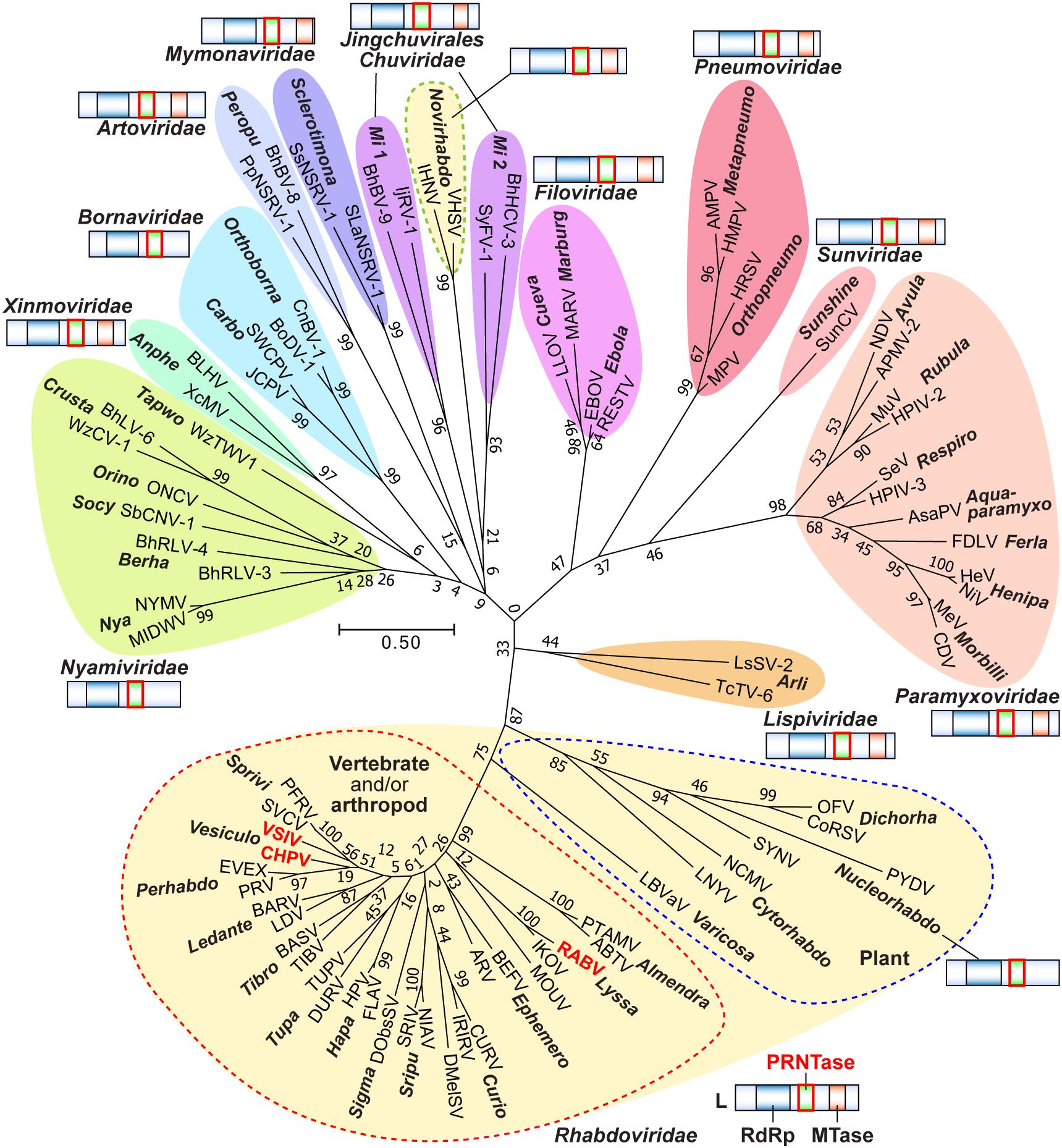
 The order has eleven families that include numerous genera, which consist of many different species:
* '' Artoviridae''
* ''
The order has eleven families that include numerous genera, which consist of many different species:
* '' Artoviridae''
* ''Bornaviridae
''Bornaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fata ...
''
* ''Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known re ...
''
* '' Lispiviridae''
* ''Mymonaviridae
''Mymonaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales'', which infect fungi. Fungi serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of Ancient Greek ''my''co, which means fungus, and ''mo''noneg''a''virale ...
''
* ''Nyamiviridae
''Nyamiviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Ecdysozoa and birds serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of ''Nya''manini Pan (place of isolation of type species Nyamanini virus in So ...
''
* ''Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Ancient Greek, Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this ...
''
* ''Pneumoviridae
''Pneumoviridae'' (from Greek pneumo-, lung, -viridae, virus from Latin, poison, slimy liquid) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Mononegavirales''. Humans, cattle, and rodents serve as natural hosts. Respiratory tract in ...
''
* ''Rhabdoviridae
''Rhabdoviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates (including mammals and humans), invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member viru ...
''
* '' Sunviridae''
* '' Xinmoviridae''
Table of the order showing all families, genera, species, and their viruses:
Table legend: "*" denotes type species.
Notes
References
External links
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1753162 Animal viral diseases Viral plant pathogens and diseases Zoonoses Virus orders