|
Macroscopic Scale
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic. Overview When applied to physical phenomena and bodies, the macroscopic scale describes things as a person can directly perceive them, without the aid of magnifying devices. This is in contrast to observations ( microscopy) or theories ( microphysics, statistical physics) of objects of geometric lengths smaller than perhaps some hundreds of micrometres. A macroscopic view of a ball is just that: a ball. A microscopic view could reveal a thick round skin seemingly composed entirely of puckered cracks and fissures (as viewed through a microscope) or, further down in scale, a collection of molecules in a roughly spherical shape (as viewed through an electron microscope). An example of a physical theory that takes a deliberately macroscopic viewpoint is thermodynamics. An exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Scale
In physics, length scale is a particular length or distance determined with the precision of at most a few orders of magnitude. The concept of length scale is particularly important because physical phenomena of different length scales cannot affect each other and are said to decouple. The decoupling of different length scales makes it possible to have a self-consistent theory that only describes the relevant length scales for a given problem. Scientific reductionism says that the physical laws on the shortest length scales can be used to derive the effective description at larger length scales. The idea that one can derive descriptions of physics at different length scales from one another can be quantified with the renormalization group. In quantum mechanics the length scale of a given phenomenon is related to its de Broglie wavelength , where ''ħ'' is the reduced Planck constant and ''p'' is the momentum that is being probed. In relativistic mechanics time and lengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics involved Scientific Revolution, substantial change in the methods and philosophy of physics. The qualifier ''classical'' distinguishes this type of mechanics from physics developed after the History of physics#20th century: birth of modern physics, revolutions in physics of the early 20th century, all of which revealed limitations in classical mechanics. The earliest formulation of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on the 17th century foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Leonhard Euler and others to describe the motion of Physical body, bodies under the influence of forces. Later, methods bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a Physical unit, unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth of a kilogram. Originally defined in 1795 as "the absolute Mass versus weight, weight of a volume of pure water equal to Cube (algebra), the cube of the hundredth part of a metre [1 Cubic centimetre, cm3], and at Melting point of water, the temperature of Melting point, melting ice", the defining temperature (0 °C) was later changed to the temperature of maximum density of water (approximately 4 °C). Subsequent redefinitions agree with this original definition to within 30 Parts-per notation, parts per million (0.003%), with the maximum density of water remaining very close to 1 g/cm3, as shown by modern measurements. By the late 19th century, there was an effort to make the Base unit (measurement), base unit the kilogram and the gram a derived unit. In 1960, the new International System of Units defined a '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass–energy Equivalence
In physics, mass–energy equivalence is the relationship between mass and energy in a system's rest frame. The two differ only by a multiplicative constant and the units of measurement. The principle is described by the physicist Albert Einstein's formula: E = mc^2. In a reference frame where the system is moving, its relativistic energy and relativistic mass (instead of rest mass) obey the same formula. The formula defines the energy () of a particle in its rest frame as the product of mass () with the speed of light squared (). Because the speed of light is a large number in everyday units (approximately ), the formula implies that a small amount of mass corresponds to an enormous amount of energy. Rest mass, also called invariant mass, is a fundamental physical property of matter, independent of velocity. Massless particles such as photons have zero invariant mass, but massless free particles have both momentum and energy. The equivalence principle implies that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quark, Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroscope (science Concept)
In science, the concept of a macroscope is the antithesis of the microscope, namely a method, technique or system appropriate to the study of very large objects or very complex processes, for example the Earth and its contents,de Rosnay, J. (1975). Le macroscope, vers une vision globale he macroscope, towards a global vision Editions du Seuil, Paris. English translation (as "The macroscope: a new world scientific system") available online at http://pespmc1.vub.ac.be/macroscope/default.html or conceptually, the Universe. Obviously, a single system or instrument does not presently exist that could fulfil this function, however its concept may be approached by some current or future combination of existing observational systems.Brown, J. H. (1995). ''Macroecology''. University of Chicago Press.http://www.research.ibm.comMacroscopes will help us understand Earth's complexity in infinite detail Accessed 8 June 2020 The term "macroscope" has also been applied to a method or compendium wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks "). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buffered saline). Preparation for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Pathology
Gross pathology refers to macroscopic manifestations of disease in organ (anatomy), organs, Tissue (biology), tissues, and body cavity, body cavities. The term is commonly used by anatomical pathology, anatomical pathologists to refer to diagnostically useful findings made during the gross examination portion of surgical specimen processing or an autopsy. In the intricate process of anatomical pathology, the grossing stage plays a pivotal role. It is vital to systematically explain the gross appearance of a pathological state, for example, a malignant tumor, noting the site, size, shape, consistency, presence of a capsule and appearance on cut section whether well circumscribed or diffusely infiltrating, homogeneous or variegated, cystic, necrotic, hemorrhagic areas, as well as papillary projections. Therefore, upon receipt of a specimen, pathologists meticulously document its characteristics. They note the specimen's dimensions, hue, texture, and any distinctive features that st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correspondence Principle
In physics, a correspondence principle is any one of several premises or assertions about the relationship between classical and quantum mechanics. The physicist Niels Bohr coined the term in 1920 during the early development of quantum theory; he used it to explain how quantized classical orbitals connect to quantum radiation. Modern sources often use the term for the idea that the behavior of systems described by quantum theory reproduces classical physics in the limit of large quantum numbers: for large orbits and for large energies, quantum calculations must agree with classical calculations. A "generalized" correspondence principle refers to the requirement for a broad set of connections between any old and new theory. History Max Planck was the first to introduce the idea of quanta of energy, while studying black-body radiation in 1900. In 1906, he was also the first to write that quantum theory should replicate classical mechanics at some limit, particularly if the Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Measurement Problem
In quantum mechanics, the measurement problem is the ''problem of definite outcomes:'' quantum systems have superpositions but quantum measurements only give one definite result. The wave function in quantum mechanics evolves deterministically according to the Schrödinger equation as a linear superposition of different states. However, actual measurements always find the physical system in a definite state. Any future evolution of the wave function is based on the state the system was discovered to be in when the measurement was made, meaning that the measurement "did something" to the system that is not obviously a consequence of Schrödinger evolution. The measurement problem is describing what that "something" is, how a superposition of many possible values becomes a single measured value. To express matters differently (paraphrasing Steven Weinberg), the Schrödinger equation determines the wave function at any later time. If observers and their measuring apparatus are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
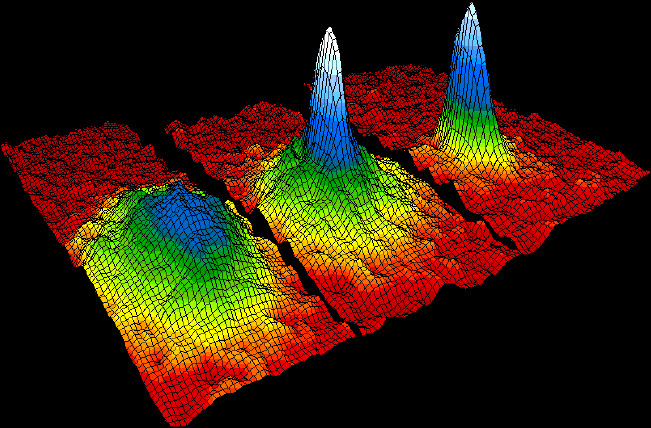
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low Density, densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero#Relation with Bose–Einstein condensate, absolute zero, i.e. . Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which microscopic Quantum mechanics, quantum-mechanical phenomena, particularly wave interference#Quantum interference, wavefunction interference, become apparent Macroscopic quantum phenomena, macroscopically. More generally, condensation refers to the appearance of macroscopic occupation of one or several states: for example, in BCS theory, a superconductor is a condensate of Cooper pairs. As such, condensation can be associated with phase transition, and the macroscopic occupation of the state is the order parameter. Bose–Einstein condensate was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein, credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |