|
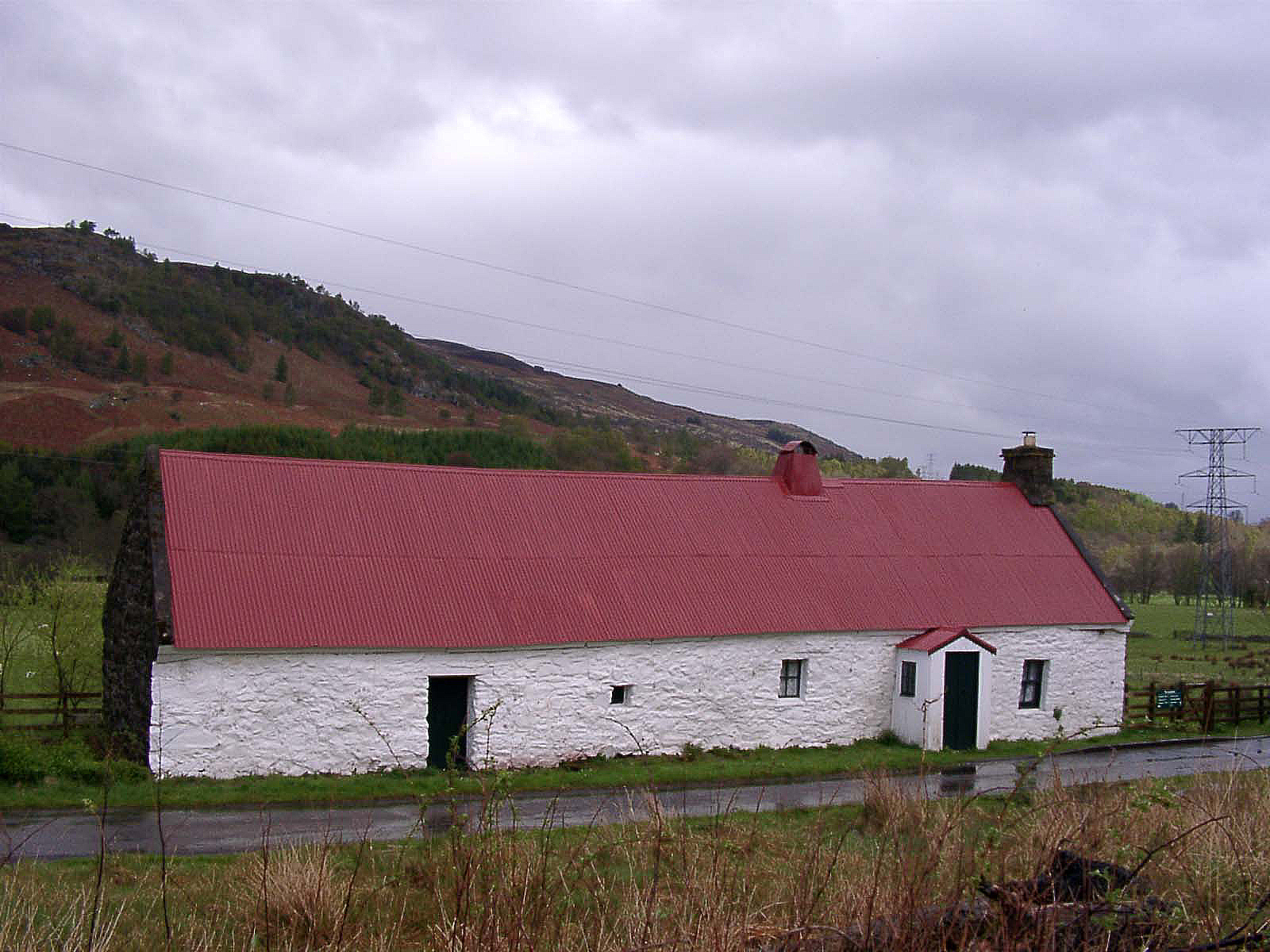
Cruck
A cruck or crook frame is a curved timber, one of a pair, which support the roof of a building, historically used in England and Wales. This type of timber framing consists of long, generally naturally curved, timber members that lean inwards and form the ridge of the roof. These posts are then generally secured by a horizontal beam which then forms an "A" shape. Several of these "crooks" are constructed on the ground and then lifted into position. They are then joined together by either solid walls or cross beams which aid in preventing 'racking' (the action of each individual frame going out of square with the rest of the frame, and thus risking collapse). Etymology The term ''crook'' or ''cruck'' comes from Middle English ', from Old Norse ', meaning "hook". This is also the origin of the word "crooked", meaning bent, twisted or deformed, and also the crook used by shepherds and symbolically by bishops. Use Crucks were chiefly used in the medieval period for structures such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruck Framing
A cruck or crook frame is a curved lumber, timber, one of a pair, which support the roof of a building, historically used in England and Wales. This type of timber framing consists of long, generally naturally curved, timber members that lean inwards and form the ridge of the roof. These posts are then generally secured by a horizontal beam which then forms an "A" shape. Several of these "crooks" are constructed on the ground and then lifted into position. They are then joined together by either solid walls or cross beams which aid in preventing 'racking' (the action of each individual frame going out of square with the rest of the frame, and thus risking collapse). Etymology The term ''crook'' or ''cruck'' comes from Middle English ', from Old Norse ', meaning "hook". This is also the origin of the word "crooked", meaning bent, twisted or deformed, and also the crook used by shepherds and crosier, symbolically by bishops. Use Crucks were chiefly used in the Middle Ages, medieva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruck Cottage In Wick - Geograph
A cruck or crook frame is a curved timber, one of a pair, which support the roof of a building, historically used in England and Wales. This type of timber framing consists of long, generally naturally curved, timber members that lean inwards and form the ridge of the roof. These posts are then generally secured by a horizontal beam which then forms an "A" shape. Several of these "crooks" are constructed on the ground and then lifted into position. They are then joined together by either solid walls or cross beams which aid in preventing 'racking' (the action of each individual frame going out of square with the rest of the frame, and thus risking collapse). Etymology The term ''crook'' or ''cruck'' comes from Middle English ', from Old Norse ', meaning "hook". This is also the origin of the word "crooked", meaning bent, twisted or deformed, and also the crook used by shepherds and symbolically by bishops. Use Crucks were chiefly used in the medieval period for structures such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber Framing
Timber framing () and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy Beam (structure), timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and Woodworking joints, joined timbers with joints secured by large wooden pegs. If the Structural system, structural frame of Load-bearing wall, load-bearing timber is left exposed on the exterior of the building it may be referred to as half-timbered, and in many cases the infill between timbers will be used for decorative effect. The country most known for this kind of architecture is Germany, where timber-framed houses are spread all over the country. The method comes from working directly from logs and trees rather than pre-cut Lumber#Dimensional lumber, dimensional lumber. Artisans or framers would gradually assemble a building by hewing logs or trees with broadaxes, adzes, and draw knife, draw knives and by using woodworking tools, such as hand-powered Brace (tool), braces and Auger (dril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernacular Architecture
Vernacular architecture (also folk architecture) is building done outside any academic tradition, and without professional guidance. It is not a particular architectural movement or style but rather a broad category, encompassing a wide range and variety of building types; with differing methods of construction from around the world, including historical and extant and classical and modern. Vernacular architecture constitutes 95% of the world's built environment, as estimated in 1995 by Amos Rapoport, as measured against the small percentage of new buildings every year designed by architects and built by engineers. Vernacular architecture usually serves immediate, local needs, is constrained by the materials available in its particular region, and reflects local traditions and cultural practices. The study of vernacular architecture does not examine formally schooled architects, but instead that of the design skills and tradition of local builders, who were rarely given any att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the :Human habitats, human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much architecture, artistic expression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands of England. It borders Greater Manchester, West Yorkshire, and South Yorkshire to the north, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south-east, Staffordshire to the south and west, and Cheshire to the west. Derby is the largest settlement, and Matlock is the county town. The county has an area of and a population of 1,053,316. The east of the county is more densely populated than the west, and contains the county's largest settlements: Derby (261,400), Chesterfield (88,483), and Swadlincote (45,000). For local government purposes Derbyshire comprises a non-metropolitan county, with eight districts, and the Derby unitary authority area. The East Midlands Combined County Authority includes Derbyshire County Council and Derby City Council. The north and centre of Derbyshire are hilly and contain the southern end of the Pennines, most of which are part of the Peak District National Park. They include Kinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodworking
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinetry, furniture making, wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning. History Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first materials worked by early humans. Microwear analysis of the Mousterian stone tools used by the Neanderthals show that many were used to work wood. The development of civilization was closely tied to the development of increasingly greater degrees of skill in working these materials. Among the earlliest finds of woodworking are shaped sticks displaying notches from Kalambo Falls in southen Africa, dating to around 476,000 years ago. The Clacton spearhead from Clacton-on-Sea, England, dating to around 400,000 years ago,Allington-Jones, L., (2015) ''Archaeological Journal'', 172 (2) 273–296 The Clacton Spear – The Last One Hundred Years the Schöningen spears, from Schöningen (Germany) dating around 300,000 years ago and the Lehringen spear from no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
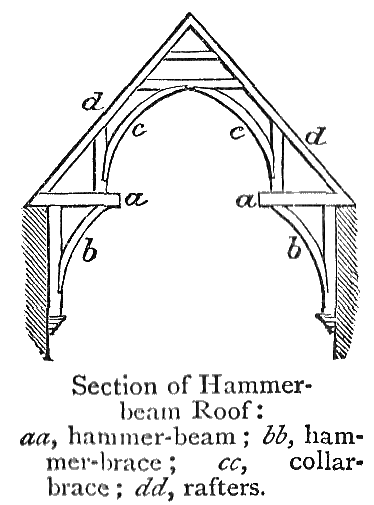
Hammerbeam Roof
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams projecting from the wall on which the rafters land, essentially a tie beam which has the middle cut out. These short beams are called hammer-beams and give this truss its name. A hammerbeam roof can have a single, double or false hammerbeam truss. Design A hammer-beam is a form of timber roof truss, allowing a hammerbeam roof to span greater than the length of any individual piece of timber. In place of a normal tie beam spanning the entire width of the roof, short beams – the hammer beams – are supported by curved braces from the wall, and hammer posts or arch-braces are built on top to support the rafters and typically a collar beam. The hammerbeam truss exerts considerable thrust on the walls or posts that support it. Hamme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glastonbury
Glastonbury ( , ) is a town and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated at a dry point on the low-lying Somerset Levels, south of Bristol. The town had a population of 8,932 in the 2011 census. Glastonbury is less than across the River Brue from Street, Somerset, Street, which is now larger than Glastonbury. Evidence from timber trackways such as the Sweet Track show that the town has been inhabited since Neolithic times. Glastonbury Lake Village was an Iron Age village, close to the old course of the River Brue and Sharpham, Sharpham Park approximately west of Glastonbury, that dates back to the Bronze Age. Centwine of Wessex, Centwine was the first Saxon patron of Glastonbury Abbey, which dominated the town for the next 700 years. One of the most important abbeys in England, it was the site of Edmund Ironside's coronation as King of England in 1016. Many of the oldest surviving buildings in the town, including the The Tribunal, Glastonbury, Tribunal, George Hotel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
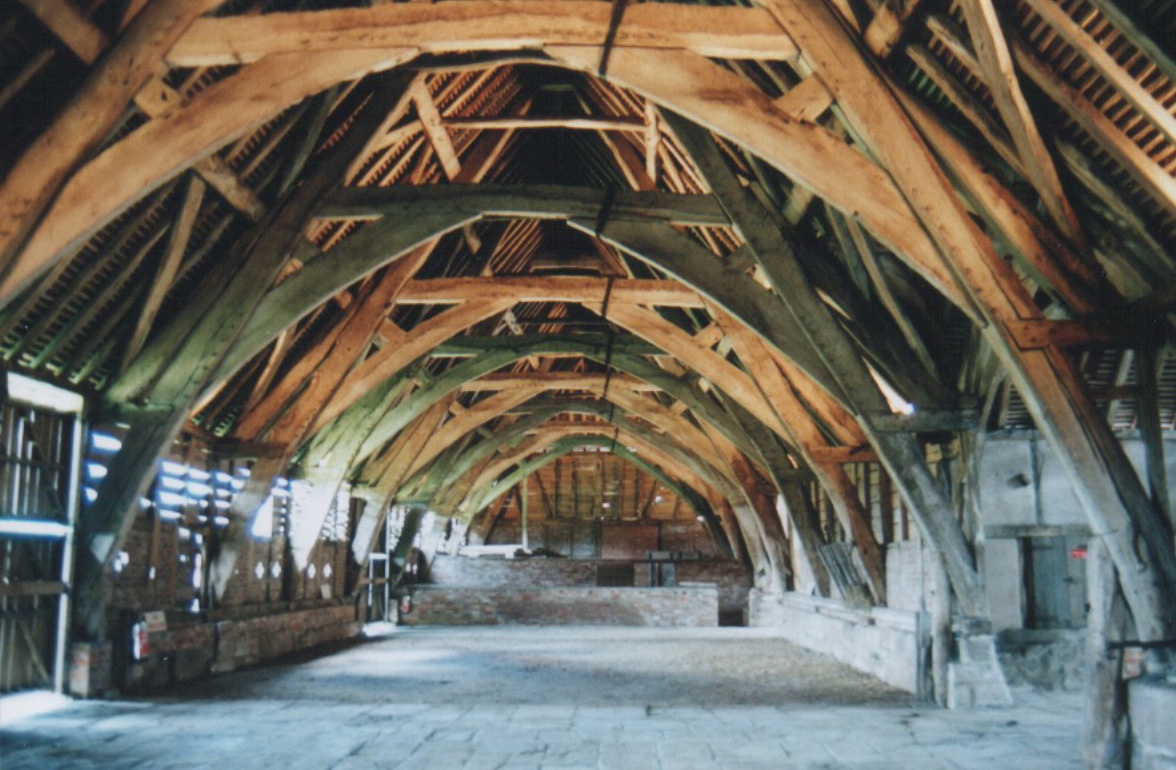
Tithe Barn, Pilton
The Tithe Barn at Cumhill Farm in Pilton, Somerset, England, was built in the 14th century as a tithe barn to hold produce for Glastonbury Abbey. It is a Grade I listed building and Scheduled Ancient Monument. The barn, of coursed and squared rubble, was originally built in the 14th and 15th centuries to hold the produce from farms in the area who paid one tenth (tithe) of their produce to Glastonbury Abbey as the landowner. It is one of four surviving monastic barns built by the Abbey, the others being the Tithe Barn, Manor Farm, Doulting, the West Pennard Court Barn and the Glastonbury tithe barn, now the Somerset Rural Life Museum. During the Second World War, farms in Pilton were used to train the Women's Land Army, including Cumhill Farm and the medieval barn. Despite being commonly referred to as the tithe barn, little evidence exists to suggest the barn actually stored tithes. It is possible that it was instead built to store produce farmed from land owned by Glastonbury ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrochronology
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of chronological dating, dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed in a tree. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and atmospheric conditions during different periods in history from the wood of old trees. Dendrochronology derives from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "tree", (), meaning "time", and (), "the study of". Dendrochronology is useful for determining the precise age of samples, especially those that are too recent for radiocarbon dating, which always produces a range rather than an exact date. However, for a precise date of the death of the tree a full sample to the edge is needed, which most trimmed timber will not provide. It also gives data on the timing of events and rates of change in the environment (most prominently climate) and also in wood found in archaeology or works of art and architecture, such as old pane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |