|
Timber Framing
Timber framing () and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy Beam (structure), timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and Woodworking joints, joined timbers with joints secured by large wooden pegs. If the Structural system, structural frame of Load-bearing wall, load-bearing timber is left exposed on the exterior of the building it may be referred to as half-timbered, and in many cases the infill between timbers will be used for decorative effect. The country most known for this kind of architecture is Germany, where timber-framed houses are spread all over the country. The method comes from working directly from logs and trees rather than pre-cut Lumber#Dimensional lumber, dimensional lumber. Artisans or framers would gradually assemble a building by hewing logs or trees with broadaxes, adzes, and draw knife, draw knives and by using woodworking tools, such as hand-powered Brace (tool), braces and Auger (dril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purlin
A purlin (or historically purline, purloyne, purling, perling) is a longitudinal, horizontal, structural member in a roof. In traditional timber framing there are three basic types of purlin: purlin plate, principal purlin, and common purlin. Purlins also appear in steel frame construction. Steel purlins may be painted or greased for protection from the environment. Etymology Information on the origin of the term "purlin" is scant. The Oxford Dictionary suggests a French origin, with the earliest quote using a variation of ''purlin'' in 1447, though the accuracy of this claim has been disputed. In wood construction Purlin plate A purlin plate in wood construction is also called an "arcade plate" in European English, "under purlin", and "principal purlin". The term plate means a major, horizontal, supporting timber. Purlin plates are beams which support the mid-span of rafter A rafter is one of a series of sloped structural members such as Beam (structure), steel beam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall Church
A hall church is a Church (building), church with a nave and aisles of approximately equal height. In England, Flanders and the Netherlands, it is covered by parallel roofs, typically, one for each vessel, whereas in Germany there is often one single immense roof. The term was invented in the mid-19th century by Wilhelm Lübke, a pioneering German art historian. In contrast to an Basilica (architecture), architectural basilica, where the nave is lit from above by the clerestory, a hall church is lit by the windows of the side walls typically spanning almost the full height of the interior. Terms In the English language, there are two problems of terminology with respect to hall churches: * The term ''hall church'' is ambiguous because the term ''hall'' is ambiguous. In some cases, the church of a manor house ("hall") is called a hall church. The term is also used for large Aisleless church, aisleless churches, an entirely different type. Aisleless churches with a rectangular pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Load
A structural load or structural action is a mechanical load (more generally a force) applied to Structural engineering#Structural elements, structural elements. A load causes stress (physics), stress, deformation (engineering), deformation, displacement (vector), displacement or acceleration in a structure. Structural analysis, a discipline in engineering, analyzes the effects of loads on structures and structural elements. Excess load may cause structural failure, so this should be considered and controlled during the design of a structure. Particular mechanical structures—such as aircraft, satellites, rockets, space stations, ships, and submarines—are subject to their own particular structural loads and actions. Engineers often evaluate structural loads based upon published regulations, contracts, or specifications. Accepted technical standards are used for acceptance testing and inspection. Types In civil engineering, specified loads are the best estimate of the actual l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
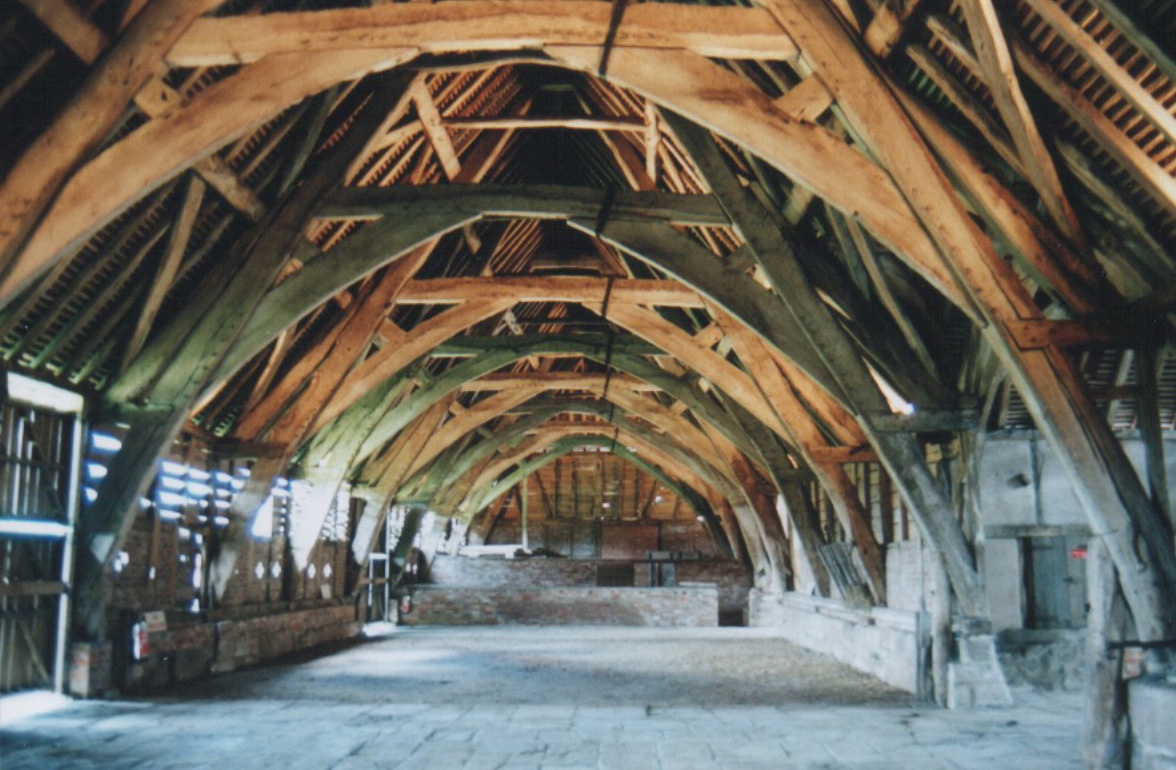
Interior Of Market Hall - Geograph
Interior may refer to: Arts and media * ''Interior'' (Degas) (also known as ''The Rape''), painting by Edgar Degas * ''Interior'' (play), 1895 play by Belgian playwright Maurice Maeterlinck * ''The Interior'' (novel), by Lisa See * Interior design, the trade of designing an architectural interior * ''The Interior'' (Presbyterian periodical), an American Presbyterian periodical * Interior architecture, process of designing building interiors or renovating existing home interiors Places * Interior, South Dakota * Interior, Washington * Interior Township, Michigan * British Columbia Interior, commonly known as "The Interior" Government agencies * Interior ministry, sometimes called the ministry of home affairs * United States Department of the Interior Other uses * Interior (topology), mathematical concept that includes, for example, the inside of a shape * Interior FC, a football team in Gambia See also * * * List of geographic interiors * Interiors (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metelen
Metelen is a municipality in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located on the river Vechte in the Steinfurt (district), district of Steinfurt. Metelen Land station is located on the Münster–Enschede railway and has an hourly train service to Münster Hauptbahnhof, Münster in one direction and to Enschede railway station, Enschede in the other direction. History The town history dates back to 889 AD, when it was first mentioned in an official document. Notable places Metelen is known for its aviary and, as the whole Münsterland region, as a great cycling area. People from Metelen * Arnold Kock (1822–1879), businessman * Anne Daubenspeck-Focke (born 1922), sculptor * Hermann Focke (born 1924), sculptor and painter * Hans Tietmeyer (1931–2016), economist * Klemens Tietmeyer (1937–1993), table tennis player * Elisabeth Tietmeyer (born 1960), ethnologin * Rolf Morrien (born 1972), author References External links * Towns in North Rhine-Westphalia Ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miltenberg
Miltenberg () is a town in the ''Regierungsbezirk'' of Lower Franconia (''Unterfranken'') in Bavaria, Germany. It is the seat of the Miltenberg (district), like-named district and has a population of over 9,000. Geography Location The old town lies on the Main (river), Main’s left bank on the "left knee" of the ''Mainviereck'' ("Main Square") between the Spessart and Odenwald ranges. Since the Main riverbed in the Miltenberg area is relatively near the foot of the Odenwald, only a narrow strip of usable land is left, little over 150 meters in width, which in past centuries was time and again flooded by the Main. The historic centre, which stands on this land, often sustained considerable damage in these floods. Only in the 21st century efficient flood control measures, most of all a wall, have significantly reduced the adverse effects of these floods. Since about the beginning of the 20th century, after buying land from the neighbouring community of Großheubach, Miltenbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backnang
Backnang (; ) is a town in Germany in the Bundesland (Germany), Bundesland of Baden-Württemberg, roughly northeast of Stuttgart. Its population has increased greatly over the past century, from 7,650 in 1900 to 37,957 in 2022. Backnang was ceded to Württemberg by the Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden (Zähringer family) in 1325. Backnang has been known as ''Gerberstadt'' due to several Tanning (leather), tanneries and leather factory, factories, and wool and Textile manufacturing, cloth mills that dominated Backnang's industries. Today, all of these have vanished, and instead, telecommunication companies such as Ericsson (formerly AEG (German company), AEG, Telefunken, ANT Nachrichtentechnik, Robert Bosch GmbH, Bosch and Marconi Company, Marconi) and Tesat-Spacecom dominate the town's industries. The ''Stiftskirche'', formerly the church of Backnang Abbey, dates back to the 12th century. Backnang hosts the annual ''Strassenfest'' during the last weekend in June where the monday is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
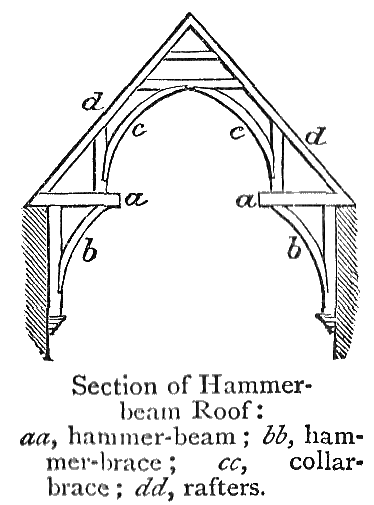
Hammerbeam Roof
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams projecting from the wall on which the rafters land, essentially a tie beam which has the middle cut out. These short beams are called hammer-beams and give this truss its name. A hammerbeam roof can have a single, double or false hammerbeam truss. Design A hammer-beam is a form of timber roof truss, allowing a hammerbeam roof to span greater than the length of any individual piece of timber. In place of a normal tie beam spanning the entire width of the roof, short beams – the hammer beams – are supported by curved braces from the wall, and hammer posts or arch-braces are built on top to support the rafters and typically a collar beam. The hammerbeam truss exerts considerable thrust on the walls or posts that support it. Hamme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eaves
The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural style, such as the Chinese dougong bracket systems. Etymology and usage According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', ''eaves'' is derived from the Old English (singular), meaning "edge", and consequently forms both the singular and plural of the word. This Old English word is itself of Germanic origin, related to the German dialect ''Obsen'', and also probably to ''over''. The Merriam-Webster dictionary lists the word as ''eave'' but notes that it is "usually used in plural". Function The primary function of the eaves is to keep rain water off the walls and to prevent the ingress of water at the junction where the roof meets the wall. The eaves may also protect a pathway around the building from the rain, prevent erosion of the footi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knee (construction)
In woodworking, a knee is a natural or cut curved piece of wood. Knees, sometimes called ship's knees, are a common form of bracing in boat building and occasionally in timber framing. A knee rafter in carpentry is a bent rafter used to gain head room in an attic. Strength characteristics Wood is a highly anisotropic material (its strength varies considerably with the direction of applied force, i.e., parallel, radial, or tangential to the grain). Because wood is strongest when loaded in tension or compression along the grain, the best knees are those in which the wood grain follows the bend. For a knee with relatively little bend, it may be possible to cut the knee out of a single straight-grained board and still achieve sufficient strength. However, with increasing bend this method becomes problematic since more and more of the knee is aligned across the grain and is therefore considerably weaker. A knee laid out this way might easily snap in two under hand pressure alone, even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruck
A cruck or crook frame is a curved timber, one of a pair, which support the roof of a building, historically used in England and Wales. This type of timber framing consists of long, generally naturally curved, timber members that lean inwards and form the ridge of the roof. These posts are then generally secured by a horizontal beam which then forms an "A" shape. Several of these "crooks" are constructed on the ground and then lifted into position. They are then joined together by either solid walls or cross beams which aid in preventing 'racking' (the action of each individual frame going out of square with the rest of the frame, and thus risking collapse). Etymology The term ''crook'' or ''cruck'' comes from Middle English ', from Old Norse ', meaning "hook". This is also the origin of the word "crooked", meaning bent, twisted or deformed, and also the crook used by shepherds and symbolically by bishops. Use Crucks were chiefly used in the medieval period for structures such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |