|
Cotoneaster Apiculatus
''Cotoneaster apiculatus'', the cranberry cotoneaster, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae Rosaceae (), the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants that includes 4,828 known species in 91 genera. The name is derived from the type genus ''Rosa''. Among the most species-rich genera are ''Alchemilla'' (270), ''Sorbus .... It is native to central China, and it has been introduced to various locales in Europe and the United States. A rabbit-tolerant shrub reaching tall but spreading to , and hardy in USDA zones 4 through 7, it is recommended for covering large areas. It is good on streambanks and slopes where erosion control is desired, as its branches will grow roots where they touch soil. References apiculatus Endemic flora of China Flora of North-Central China Flora of South-Central China Plants described in 1912 {{Maleae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistence (botany)
Persistence is the retention of plant organs after their normal function has been completed, in contrast with the shedding of deciduous organs after their purpose has been fulfilled. Absence or presence of persistent plant organs can be a helpful clue in plant identification, and may be one of many types of anatomical details noted in the species descriptions or dichotomous keys of plant identification guides. Many species of woody plants with persistent fruit provide an important food source for birds and other wildlife in winter. Species with persistent parts There are numerous herbaceous and woody plant species that produce persistent parts, such as strobili (cones) or fruit. Note that the trait of persistence exhibited by a given species within a genus may not be exhibited by all species within the genus. For example, the ''Equisetum'' genus includes some species that have persistent strobili and others that have deciduous strobili. Persistent strobili The following a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Rehder
Alfred Rehder (4 September 1863 in Waldenburg, Saxony – 25 July 1949 in Jamaica Plain, Massachusetts) was a German-American botanical taxonomist and dendrologist who worked at the Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University. He is generally regarded as the foremost dendrologist of his generation. Life Georg Alfred Rehder was born in the castle of Waldenburg to Thekla née Schmidt (1839–1897) and Paul Julius Rehder (1833–1917), the superintendent of parks and gardens of the principality of Schönburg-Waldenburg. Through his father, Rehder was introduced to the gardening profession. On his mother's side of the family, Rehder was likely descended from Henry, Duke of Anhalt-Köthen (1778–1847). Rehder broke off his attendance at the gymnasium in Zwickau in 1881 and did not pursue university studies, instead working for three years as an apprentice under the tutelage of his father. His professional career began in 1884 at the Berlin Botanical Garden. Here he was able to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Henry Wilson
Ernest Henry "Chinese" Wilson (15 February 1876 – 15 October 1930), better known as E. H. Wilson, was a notable British plant collector and explorer who introduced a large range of about 2000 Asian plant species to the Western culture, West; some sixty bear his name. Career Wilson was born in Chipping Campden, Gloucestershire but the family soon moved to Shirley, Warwickshire, where they set up a floristry business. He left school early for employment at the local nursery of Messrs. Hewitt, Warwickshire, as apprentice gardener, and, aged 16, at the Birmingham Botanical Gardens (United Kingdom), Birmingham Botanical Gardens; there he also studied at Aston University, Birmingham Municipal Technical School in the evenings, receiving the Queen's Prize for botany. In 1897 he began work at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, where he won the Joseph Dalton Hooker, Hooker Prize for an essay on conifers. He then accepted a position as Chinese plant collector with the Veitch Nurseries, firm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosaceae
Rosaceae (), the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants that includes 4,828 known species in 91 genera. The name is derived from the type genus ''Rosa''. Among the most species-rich genera are ''Alchemilla'' (270), ''Sorbus'' (260), '' Crataegus'' (260), ''Cotoneaster'' (260), ''Rubus'' (250), and ''Prunus'' (200), which contains the plums, cherries, peaches, apricots, and almonds. However, all of these numbers should be seen as estimates—much taxonomic work remains. The family Rosaceae includes herbs, shrubs, and trees. Most species are deciduous, but some are evergreen. They have a worldwide range but are most diverse in the Northern Hemisphere. Many economically important products come from the Rosaceae, including various edible fruits, such as apples, pears, quinces, apricots, plums, cherries, peaches, raspberries, blackberries, loquats, strawberries, rose hips, hawthorns, and almonds. The family also includes popular ornamental trees and shrubs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
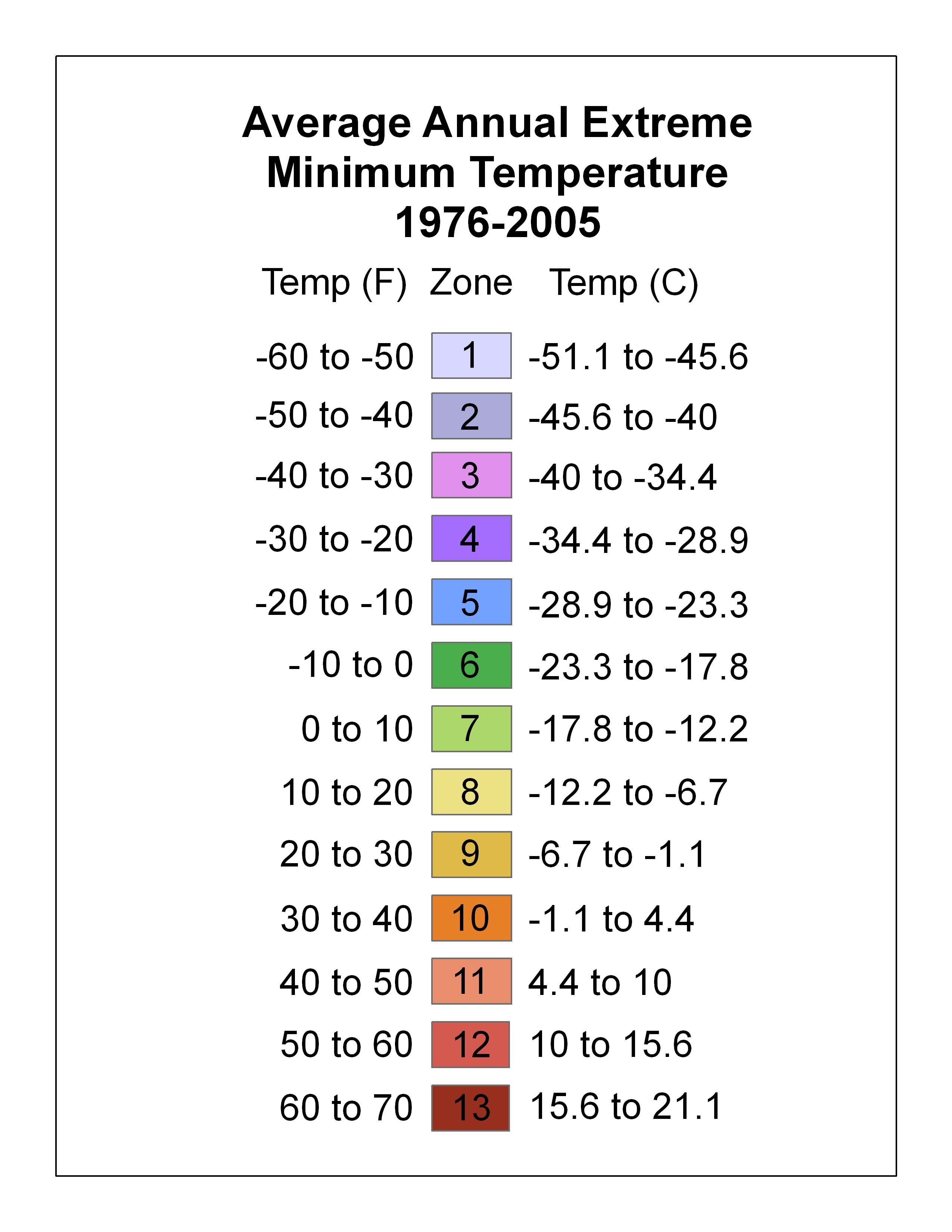
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotoneaster
''Cotoneaster'' is a genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, native to the Palaearctic region (temperate Asia, Europe, north Africa), with a strong concentration of diversity in the genus in the mountains of southwestern China and the Himalayas.Flora of China''Cotoneaster''(includes most of the world's ''Cotoneaster'' species) ''www.efloras.org'' They are related to hawthorns (''Crataegus''), firethorns (''Pyracantha''), photinias (''Photinia''), and rowans (''Sorbus''). Depending on the species definition used, between 70 and 300 different species of ''Cotoneaster'' are described, with many apomictic microspecies treated as species by some authors, but only as varieties by others.Bean, W. J. (1976). ''Trees and Shrubs Hardy in the British Isles'' 8th edition. John Murray . The majority of species are shrubs from tall, varying from ground-hugging prostrate plants to erect shrubs; a few, notably ''C. frigidus'', are small trees up to tall and trunk diameter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Flora Of China
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of North-Central China
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de Phyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of South-Central China
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms ''gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de Phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
